Accounting
In accounting, reflect the increase in the size of the authorized capital as of the date of state registration of changes made to the organization’s charter. This is due to the fact that the amount of the authorized capital reflected in the accounting must correspond to its size recorded in the constituent documents of the organization (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 21, 2007 No. 07-05-12/03).
As of the date of the decision to place an additional issue of shares, no accounting entries need to be made.
To reflect the size of the organization’s authorized capital, use account 80 “Authorized capital”; to account for settlements with shareholders, use a special subaccount 75-1 “Settlements on contributions to the authorized (share) capital”.
The property that shareholders contribute in payment for additional shares should be taken into account at the cost determined by the board of directors (clause 3 of Article 34 of Law 208-FZ, clause 8 of PBU 5/01, clause 9 of PBU 6/01, clause 11 of PBU 14 /2007, paragraph 12 PBU 19/02).
When placing additional shares at the expense of shareholders, make the following entries in your accounting records:
Debit 51 (50, 08, 10) Credit 75-1
– funds (other property) were received from shareholders as payment for shares of an additional issue;
Debit 75-1 Credit 80
– the increase in the authorized capital at the expense of shareholders’ funds is reflected (as of the date of state registration of changes in the organization’s charter).
If the actual price of the issued shares exceeds their par value, the organization will generate share premium. To reflect the amount of the difference between the actual cost of placing shares and their nominal value, use special subaccount 83-1 “Share premium” (Instructions for the Chart of Accounts). Make an accounting entry for the difference:
Debit 75-1 Credit 83
– reflects the excess of the actual cost of placement of shares over their nominal value.
An example of increasing the authorized capital of an organization by additionally issuing shares at the expense of shareholders. Additional shares are paid for in cash at a price equal to their par value
The general meeting of shareholders of Alfa JSC decided to increase the authorized capital by additionally issuing shares at the expense of shareholders.
All shares are distributed by private subscription among shareholders at a price equal to their par value.
The company places 1000 ordinary shares, the par value of which is 200 rubles. per share. Shares are placed at a price of 200 rubles.
Shareholders pay for additional shares in cash.
The organization paid state duty in the following amounts:
– 400 rub. ((1000 pieces × 200 rubles) × 0.2%) - for registration of an additional issue of shares placed by subscription and a report on the results of the issue; – 800 rub. – for registration of changes in the charter.
Alpha's accountant made the following entries in the accounting.
On the date of receipt of money from shareholders:
Debit 51 Credit 75-1 – 200,000 rubles. (1000 pieces × 200 rubles) – funds were received from shareholders in payment for shares of an additional issue.
On the date of payment of the state duty for registration of an additional issue of shares and a report on the results of the issue:
Debit 68 subaccount “State duty” Credit 51 – 400 rub. – state duty has been paid to the budget.
As of the date of receipt of the notification of state registration of the additional issue of shares and the report on the results of the issue:
Debit 91-2 Credit 68 subaccount “State duty” - 400 rubles. – the cost of state duty is included in other expenses.
As of the date of payment of the state fee for registration of changes in the charter:
Debit 68 subaccount “State duty” Credit 51 – 800 rub. – state duty has been paid to the budget.
As of the date of receipt of the certificate of state registration of changes in the charter:
Debit 91-2 Credit 68 subaccount “State duty” - 800 rubles. – the cost of state duty is included in other expenses;
Debit 75-1 Credit 80 – 200,000 rub. – reflects the increase in the authorized capital of the organization.
An example of increasing the authorized capital of an organization by additionally issuing shares at the expense of shareholders. Additional shares are paid for in cash at a price exceeding their par value
Public joint-stock company "Proizvodstvennaya" decided to increase the authorized capital in the amount of 500,000 rubles. through an additional issue of 250 ordinary shares with a par value of RUB 2,000. per share.
The price for placing shares by open subscription is RUB 2,100. per share.
The organization paid state duty in the following amounts:
– 1000 rub. ((250 pieces × 2000 rubles) × 0.2%) – for registration of an additional issue of shares placed by subscription and a report on the results of the issue; – 800 rub. – for registration of changes in the charter.
The Master's accountant made the following entries in the accounting.
On the date of receipt of money from shareholders:
Debit 51 Credit 75-1 – 525,000 rub. (250 pcs. × 2100 rubles) – funds were received from shareholders to pay for additional shares.
On the date of payment of the state duty for registration of an additional issue of shares and a report on the results of the issue:
Debit 68 subaccount “State duty” Credit 51 – 1000 rub. – state duty has been paid to the budget.
As of the date of receipt of the notification of state registration of the additional issue of shares and the report on the results of the issue:
Debit 91-2 Credit 68 subaccount “State duty” - 1000 rubles. – the cost of state duty is included in other expenses.
As of the date of payment of the state fee for registration of changes in the charter:
Debit 68 subaccount “State duty” Credit 51 – 800 rub. – state duty has been paid to the budget.
As of the date of receipt of the certificate of state registration of changes in the charter:
Debit 91-2 Credit 68 subaccount “State duty” - 800 rubles. – the cost of state duty is included in other expenses;
Debit 75-1 Credit 80 – 500,000 rub. (250 pcs. × 2000 rub.) – reflects the increase in the authorized capital;
Debit 75-1 Credit 83 – 25,000 rub. (RUB 525,000 – RUB 500,000) – reflects the excess of the actual cost of placement of shares over their nominal value.
Reflect the increase in the authorized capital at the expense of the organization’s own property with the following entries:
Debit 83 Credit 80 – reflects the increase in the authorized capital due to the additional capital of the organization;
Debit 84 Credit 80 – reflects the increase in the authorized capital due to retained earnings of previous years.
An example of increasing the authorized capital by additionally issuing shares at the expense of the organization’s own property (retained earnings from previous years)
The general meeting of shareholders of Alfa JSC decided to increase the authorized capital by additionally issuing shares at the expense of the organization’s own property - retained earnings from previous years.
All additional shares are distributed among shareholders in proportion to the number of shares owned by each of them.
The company places 2,000 ordinary shares, the par value of which is 100 rubles. per share.
The organization paid state duty in the following amounts:
– 20,000 rub. – for registration of an additional issue of shares and a report on the results of the issue; – 800 rub. – for registration of changes in the charter.
Alpha's accountant made the following entries in the accounting.
On the date of payment of the state duty for registration of an additional issue of shares and a report on the results of the issue:
Debit 68 subaccount “State duty” Credit 51 – 20,000 rub. – state duty has been paid to the budget.
As of the date of receipt of the notification of state registration of the additional issue of shares and the report on the results of the issue:
Debit 91-2 Credit 68 subaccount “State duty” - 20,000 rubles. – the cost of state duty is included in other expenses.
As of the date of payment of the state fee for registration of changes in the charter:
Debit 68 subaccount “State duty” Credit 51 – 800 rub. – state duty has been paid to the budget.
As of the date of receipt of the certificate of state registration of changes in the charter:
Debit 91-2 Credit 68 subaccount “State duty” - 800 rubles. – the cost of state duty is included in other expenses;
Debit 84 Credit 80 – 200,000 rub. (2000 units × 100 rubles) – reflects the increase in the authorized capital due to retained earnings of previous years.
Include the state duty for registration of changes in the charter, additional issue of shares and report on the results of the issue as part of other expenses (clause 11 of PBU 10/99). For the amount of state duty paid, make the following entries in your accounting:
Debit 68 subaccount “State duty” Credit 51 – state duty was transferred to the budget;
Debit 91-2 Credit 68 subaccount “State duty” - the cost of the state duty is charged to other expenses.
The procedure for accounting for an increase in the authorized capital due to additional placement of shares when calculating taxes depends on what taxation system the organization uses.
Accounting for shares when selling: postings
The owner of shares can dispose of them at his own discretion: (click to expand)
- Sell;
- Invest in management companies of other companies;
- Pay for goods;
- Transfer free of charge.
The sale of shares in accounting is shown as a disposal of financial investments (clause 25 of PBU 19/02):
Dt 76 Kt 91.1 - securities sold;
Dt 91.2 Kt 58.1, 76 - the cost of securities and selling expenses are written off.
Write-off for property expenses
At the same time, the cost of property contributed to pay for additional shares can be written off as expenses. To do this, it needs to be assessed. The organization must use the property in commercial activities.
The procedure for determining the value of contributed property depends on who contributed it: a citizen, a Russian organization or a foreign organization.
If the property was contributed by a citizen or a foreign organization, the following rules must be followed. The value of the property contributed to pay for the shares is equal to the amount of documented expenses for its acquisition. Documents that confirm the expenses of the founder (shareholder) can be receipts for cash receipts, sales receipts, cash receipts, etc. In addition, an independent specialist must give his assessment of the property. When calculating income tax, an organization will be able to include the lesser of these amounts in expenses. If the value of the contributed property is not documented, then in tax accounting it will have to be recognized as zero.
Property contributed as payment for shares by a Russian organization is assessed according to the following rules. Its value in tax accounting will be equal to the residual value of the object in the tax accounting of the transferring party. The residual value of the property can be confirmed by extracts (copies) from tax registers. If the transferring party cannot confirm the residual value of the transferred property, then in tax accounting accept such property with zero initial cost.
The transferor's expenses associated with the transfer of property increase the initial cost of the fixed asset only if they are indicated as a contribution towards payment for shares in the constituent documents.
This follows from the rules provided for in subparagraph 2 of paragraph 1 of Article 277 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Procedure and methods of placement of shares
Shares can be placed in the following ways:
- All papers are distributed among the founders on the day of registration of the JSC. If the company has only one founder, then the full package of shares goes to him.
- If additional shares are issued, the distribution occurs between shareholders when increasing the company's authorized capital without attracting funds from the acquirers.
- Through open or closed subscription. This method is also aimed at increasing the volume of authorized capital, but is based on attracting money from potential purchasers of securities.
- Conversion, during which one paper is exchanged for another under predetermined conditions.
Conversion is carried out in the following cases:
- The face value of the paper changes.
- The range of shareholder rights is changing.
- In a situation where the size of the authorized capital and the number of shareholders remain the same, consolidation or splitting of shares is carried out. In consolidation, two or more securities are merged into one. A split involves dividing one share into two or more new shares.
In accounting, account 80 reflects information about the indicators of the authorized capital and cash flow. Posting KT 80 DT 75-1 indicates the amount of debt of the founders. Cash received in payment for corporate rights is reflected under loan 75-1.
Sub-accounts that allow you to reflect capital movements:
- 80-1 – used to indicate the nominal value of paper intended for sale;
- 80-2 – used to account for shares with subscription;
- 80-2-1 – the entry reflects the rights under the securities of the first founder;
- 80-2-n - rights of the nth founder;
- 80-3 – determines the cost of redeemed shares.
Important! During the initial placement, the company must prepare a special document - a prospectus. It reflects essential information about the issuer, its financial position, and shares issued. The share prospectus must be approved by the Board of Directors.
Accounting for fixed assets and intangible assets
The procedure for accounting for fixed assets and intangible assets received from the founders (third parties) depends on whether they are recognized as depreciable property or not.
Fixed assets or intangible assets received from the founders (third parties), the value of which is greater than that specified in paragraph 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, must be depreciated (Clause 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the cost of fixed assets does not exceed the cost criterion established by clause 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, include it in material expenses as they are put into operation (subclause 3 of clause 1 of Article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For more information about accounting for fixed assets contributed to the authorized capital of an organization, see How to formalize and reflect in accounting and taxation the receipt of fixed assets as a contribution to the authorized capital.
On accounting for intangible assets with a value less than the limit established by paragraph 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, see What property is considered depreciable in tax accounting.
Advantages and disadvantages of issuing shares by a company
The issue procedure will have both a positive and negative impact on the enterprise itself. Advantages of the issue:
- The company raises additional funds to develop its activities, while there are no obligations to repurchase securities.
- The issuer has no strict obligation to pay dividends to holders of common shares. If the financial position of the company is unstable, then dividends are not accrued.
- JSC participation in tenders allows us to obtain an adequate assessment of the company’s value. Without participation in exchange trading, difficulties arise when selling a business or its share.
- The issue is associated with increasing the prestige of the company. After entering the stock market, the company becomes recognizable and popular.
Disadvantages of emissions:
- Outsiders gain access to the management of the company's assets.
- The issuing company cannot influence shareholders and force them to sell their securities.
- The company is obliged to pay dividends on the preferred line of shares regardless of the state of the financial affairs of the enterprise.
- The procedure requires significant expenses aimed at issuing and registering securities, attracting an underwriter, etc.
Thus, the issue allows the company to attract investor funds on favorable terms. Incorporation allows the company to establish itself as a financially stable enterprise with the prospect of further successful development. Like any process, the issue has its advantages and weaknesses, which must be taken into account by the company's management before making a decision to issue securities.
How to make money without leaving home. Ways to earn money for pensioners, mothers on maternity leave and schoolchildren. A profitable business for men. Useful skills for making money without access to the Internet.
Procedure for taxation of income on bonds in 2022. Features of calculating tax on coupon interest and profit upon redemption. Tax benefits on bonds.
Stock trading tax: how it is calculated and by whom it is withheld. Filling out and submitting a declaration in form 3-NDFL. Benefits and tax deductions
Information exchange between the Central Bank of Russia and financial market participants registered in the Russian Federation. A new version of the Central Bank’s personal account and its capabilities. Advantages and disadvantages of the new version. Step-by-step algorithm for creating an account
Conditions for using maternity capital to build a house with your own hands or by contractors. Receiving compensation if the house is built. Required documents.
How can you cash out maternity capital without waiting for your child to turn 3 years old? Is it possible to get matkapital in cash? Punishment for illegal use of money.
One way to legally use maternity capital funds is to make a down payment on a mortgage. The contract must indicate that the client takes money to purchase real estate - this is a mandatory condition. This way, families can get a home loan without having the cash for a down payment. Let's take a closer look at how this process is organized and which banks
Ways to receive money in VK on a page, group or public. Tips for making money for beginners. How to withdraw money to a card or transfer it to another user using VK Pay.
Accounting for state duty
The amount of state duty paid for registration of an additional issue of shares, a report on the results of the issue and amendments to the charter can be attributed to:
- for other expenses (subclause 1, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated June 26, 2006 No. 20-12/56686);
- for non-operating expenses - as costs associated with the issue of shares (subclause 3, clause 1, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The organization has the right to independently decide which expenses include the amount of state duty (clause 4 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When using the accrual method, take into account the amount of the state duty at the time of its accrual (subclause 1, clause 7, article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). With the cash method - as it is paid to the budget (subclause 3, clause 3, article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Situation: is it possible to take into account the costs of consulting services related to the registration of a decision on an additional issue of shares when calculating income tax? A joint stock company increases its authorized capital by revaluing fixed assets.
Yes, you can.
When calculating income tax, an organization has the right to take into account any economically justified expenses that are documented and related to activities aimed at generating income. This follows from the provisions of paragraph 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The connection between the costs of registering an additional issue of shares and activities aimed at generating income can be justified as follows.
The economic justification of expenses that reduce taxable profit must be assessed taking into account the circumstances indicating the organization’s intentions to obtain an economic effect. It is this intention, and not the actually achieved result, that is the main condition for recognizing expenses as economically justified. This conclusion is contained in the ruling of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated June 4, 2007 No. 320-O-P and the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated October 12, 2006 No. 53.
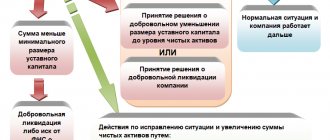
The authorized capital of an organization determines the minimum amount of property that guarantees the interests of its creditors (paragraph 3, paragraph 1, article 25 of the Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ). Therefore, its increase is one of the signs of increasing financial stability and investment attractiveness of the organization for counterparties.
Thus, an additional issue of shares indicates the organization’s intentions to strengthen its position in the market, expand the composition of potential clients and, ultimately, increase its profitability. Consequently, the costs associated with registering an additional issue of shares can be considered economically justified.
If, when preparing documents for registering an additional issue of shares, an organization uses consulting services, their cost can be included in non-operating expenses as costs associated with the issue of its own securities. The basis for this is an open list of such expenses given in subparagraph 3 of paragraph 1 of Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If an organization calculates income tax using the accrual method, non-operating expenses are recognized in the reporting (tax) period in which they were actually incurred (subclause 3, clause 7, article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Under the cash method, expenses are recognized only after they have been paid (clause 3 of Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Similar clarifications are contained in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 6, 2009 No. 03-03-06/1/40 and dated January 21, 2009 No. 03-03-06/2/7. In arbitration practice there are examples of decisions in which judges take the same position (see, for example, decisions of the FAS North Caucasus District dated January 22, 2009 No. A53-7057/2008-C5-37, Volga-Vyatka District dated December 10 2007 No. A29-8106/2006a).
However, it should be noted that if the organization had the opportunity not to incur costs for consulting services (for example, the organization has qualified specialists in this field on its staff), then the question of the economic justification of these costs may be questioned by the inspectors.
Issue procedure, state registration and its cost
The issue includes a number of actions:
- The company decides to release.
- The decision is approved by the company's management team.
- The issue is registered with a government agency, and the securities are assigned an identification number.
- Placement of issue papers.
- Providing a report on the results of the issue of shares.
When issuing, many companies enlist the support of a professional participant in the stock market - an underwriter. The issue procedure may require special knowledge and skills, so seeking help from an underwriter is justified. The underwriter receives a fee for his services.
Prices for registering a securities issue vary; on average, the cost of the procedure ranges from 10 to 100 thousand rubles. The final value may vary depending on additional services provided by the legal entity.
simplified tax system
Organizations applying the simplification do not include the cost of additionally received shares and share premium from their placement in taxable income (subclause 1, clause 1.1, article 346.15, subclause 3, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Organizations that pay a single tax on the difference between income and expenses cannot include the cost of property contributed as payment for shares as expenses. For more information about this, see How to take into account the receipt of fixed assets and intangible assets using the simplified tax system, How to write off material expenses using the simplified tax system.
The amount of state duty paid for registering an additional issue of shares, a report on the results of the issue and making changes to the charter, organizations that pay a single tax on the difference between income and expenses, have the right to take into account in expenses (subclause 22, clause 1, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) . Include the amount of the state duty in expenses at the time of its payment to the budget (clause 2 of Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Example
The three founders decided to found a joint stock company. Capital in the amount of 800 thousand rubles. divided into 800 shares. Nominal value of the Central Bank: 800,000: 800 = 1000 rubles. Shares are distributed among the founders in the following proportions: 40%, 35% and 25%. When placing, 50% of the securities were paid. The remaining amount should arrive in three months.
For NU purposes, income in the form of property received as a contribution to the capital of an organization is not taken into account when determining the basis for calculating the NPP (Article 1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Let's display the issue of shares in accounting. The postings are presented in the table below.
| Operations | DT | CT | Amount (thousand rubles) |
| Registration of JSC | |||
| The management company is reflected in accordance with the charter | 75-1 | 80-1 | 800 |
| Payment of 50% of shares from the share of each participant | |||
| first (800 x 40%) second (800 x 35%) third (800 x 25%) | 50 | 75-1 | 160 140 100 |
| The report on the issue of the Central Bank was approved | |||
| The value of the shares is reflected: first founder second founder third founder | 80-1 | 80-2-1 | 320 280 200 |
| The cost of securities paid is reflected: by the first participant second participant third party | 80-2-1 | 80-3-1 | 160 140 100 |
| Accounting records for the payment completion date | |||
| Funds were received on account of the remaining portion of the Central Bank: first founder (320 -160) second founder (280 – 140) third founder (200-100) | 50, 51 | 75-1 | 160 140 100 |
| The cost of paid securities is reflected (for each shareholder) | 80-2-1 | 80-3-1 | 160 140 100 |
The accounting entries reflecting the issue of uncertificated shares are no different from those presented above. Confirmation of a contribution to the company is a certificate or an extract from the register of owners of securities.
Combination of OSNO and UTII
An organization can use the property received from the founders (shareholders) as payment for additional shares, simultaneously in activities subject to UTII and in activities for which the organization pays taxes under the general taxation system. In this case, when writing off as expenses, the value of the property (the amount of depreciation on fixed assets and intangible assets) and the amount of state duty must be distributed. Payment of the state duty for registration of changes in the charter and additional issue of shares is simultaneously related to the organization’s activities on the general taxation system and to activities subject to UTII. Therefore, the collection amount also needs to be distributed. Income tax expenses include only the cost of property and the amount of state duties related to the organization’s activities on the general taxation system. This follows from the provisions of paragraph 9 of Article 274 and paragraph 7 of Article 346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
For more information on how to distribute expenses related to both tax regimes, see How to take into account expenses for income tax when combining OSNO with UTII.
Owners and nominee holders of securities
The owner of shares is one of the owners of the joint-stock company and has the right to part of the property of the enterprise and its profits. Shareholders receive dividends - part of the company's annual income.
A nominee holder does not have ownership of the securities, but holds them in his own name. The holder represents the interests of the shareholder and protects him from possible errors when accounting for rights to securities. The broker or depository becomes the nominee holder. It must be registered in the securities holder registry system.
Primary issue involves the sale of securities among an unlimited number of investment market participants. The volume of the issue directly depends on the size of the company's authorized capital. Each shareholder has a determined share of rights to the property and income of the company. With an additional issue, an additional block of shares is issued, and the share of a specific shareholder is diluted. Additional securities may be distributed among former shareholders and new investors.
Read more: about the types and characteristics of shares, as well as the rights of the owner of a blocking stake.
Issue of additional shares.
The issue of additional shares is carried out in accordance with the Standards for the issue of shares when establishing joint stock companies, additional shares, bonds and their prospectuses, approved by Resolution of the Federal Commission for the Securities Market of Russia dated September 17, 1996 No. 19 (hereinafter referred to as the Standards).
The procedure for paying for additional shares is established by Article 34 of the Federal Law “On Joint-Stock Companies”, according to which additional shares of a joint-stock company must be paid for within the period specified in the decision on their placement, but no later than one year from the date of their acquisition.
The issue of additional shares can be carried out by:
- subscriptions,
- distribution among shareholders of the joint stock company and
- by conversion.
How to record the acquisition of shares (shares) of other organizations in accounting
You just need to enter one number. < ... Home → Accounting consultations → Accounting Current as of: December 5, 2016 We talked in a separate consultation about synthetic and analytical accounting of financial investments. In this material we will dwell in more detail on securities accounting. What applies to securities Securities include, in particular (clause 2 of article 142
Civil Code of the Russian Federation):
- promotion;
- bill of exchange;
- mortgage;
- investment unit of a mutual investment fund;
- bill of lading;
- bond;
- check.
The essence and definition of securities can be found in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Federal Law of April 22, 1996 No. 39-FZ “On the Securities Market”. Securities accounting Securities accounting is maintained on account 58 “Financial investments” (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n) in accordance with PBU 19/02.