Well-established partnerships are important for any company. They will not become like this on their own; working on them is an important part of the enterprise’s management strategy. During the negotiations, meetings of representatives, meetings, and receptions take place. The costs of these activities constitute a serious expense item.
Tax authorities are very attentive to checking this type of expense, so it is worth carefully monitoring their accounting and documenting it correctly.
Let's figure out which expenses can be attributed to this type of expense and which cannot be written off to this account, what documents can serve as confirmation and how to correctly reflect this item in accounting and tax accounting. Let’s also consider current legislative changes regarding hospitality expenses and trends for the near future.
Entertainment expenses: what the law says
Representation expenses (PR) is a term from the Tax Code. Their standards are given in paragraphs. 22 clause 1 and clause 2 art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The definition of entertainment expenses is given based on these standards. Representative expenses will be considered expenses for official reception, support and services for authorized persons of other companies, as well as those who intend to attend a meeting of the board of directors, board or other governing bodies.
Are entertainment expenses considered expenses related to production and sales ?
Factors not relevant for determining OL
- Location. It does not matter where exactly the reception is organized: on the premises of the company or in a bar or restaurant. Exceptions are entertainment establishments of other formats - PR does not apply to them.
- Time spending. Whether business hours, evenings, or a weekend are chosen for the date of the event, the expenses still remain representative.
- Participants status. Counterparty participants include both individuals and officials; they can be not only representatives of the management of other companies, but also clients.
- Result of the meeting. The outcome of the entertainment event does not matter either. Whether a positive decision on cooperation was made, contracts were concluded, or the participants left with nothing, the funds for the event were spent and can be recognized.
- The number of participants also does not determine hospitality expenses. This factor can only affect the amount of spending, but if it does not exceed the established norm, this indicator does not matter.
Expenses that can and cannot be considered representative
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation identifies special categories of expenses that, from a taxation point of view, can be legitimately considered representative expenses. These include the following expenses:
- Payment for organizing an official event to receive guests from other companies. Such an event could be:
- breakfast;
- dinner;
- off-site meeting.
- Buffet service accompanying said reception event.
- Transfer of participants to the reception site and back.
- Remuneration for the work of a freelance translator, if he was invited to attend the event.
NOTE! Food and alcohol costs are also included in this cost group.
ATTENTION! If the organization has its own translator, the tax authorities may not consider the costs of an invited specialist to be representative. A company can try to prove its case in court by convincing it that the qualifications or specifications of in-house translators do not meet the objectives of the entertainment event.
According to the Federal Tax Service, the list of entertainment expenses is closed and cannot be expanded.
It is unlawful to count as entertainment expenses:
- provision of rest and food in sanatoriums, boarding houses, and other entertainment establishments (except for restaurants and bars);
- funds for an entertainment program for participants;
- cost of excursions;
- money for flowers for guests, memorable souvenirs, etc.;
- finances for decorating the hall for the event;
- medical expenses, if required;
- travel and accommodation of guests;
- payment for visa services for participants;
- spending on corporate events (New Year, March 8, anniversaries, etc.);
- any financial interaction with the management of structural divisions and branches of your own company (representation expenses - by default only for “outsiders”).
Criteria for classifying expenses as entertainment expenses
The concept of “official reception and service”, through which the Tax Code defines entertainment expenses, in turn, does not have an unambiguous interpretation in legislative documents. Therefore, they can be interpreted with an expansive meaning. Because of this, situations often arise when, formally and in fact, expenses may turn out to be representative expenses, but in the legislative sense, the tax authorities think otherwise.
To avoid disputes with tax authorities, which can only be resolved in arbitration court, it is recommended when determining expenses to use the criteria outlined in the Tax Code and regulations of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation (in particular, Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 15, 2000 No. 26n):
- Reception and service must be arranged for the purpose of establishing or maintaining cooperation for the mutual benefit of the parties.
- Events must be strictly official (for example, a banquet in a restaurant, even if it is held with partners, will not be considered official, unlike a business breakfast or lunch). The formality of the event can be confirmed by the program of issues to be discussed during the event.
- Costs must be justified, that is, justified from an economic point of view.
- Each expense item must have documentary evidence.
In controversial cases, you should turn to arbitration practice. In court, expenses that meet one of two conditions will be considered representative:
- directly named as such in the relevant paragraph of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- they are allowed to be included in representative ones by separate regulations of the tax service or the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
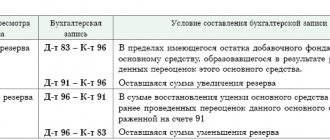
About the composition of entertainment expenses
Entertainment expenses (PR) are taken into account separately from other types of expenses according to the rules of Art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Paragraph 2 of this article states what applies to such costs.
You can learn more about this in our article “Which expenses for taxation are representative expenses.”
Expenses for the purchase of alcoholic beverages can also be attributed to the PR, taking into account the position of the Ministry of Finance, published in letter dated January 22, 2019 No. 03-03-06/1/3120. As the department explains, the list of products is not fixed , therefore expenses for alcohol purchased as part of a business event can be included in the PR.
But, for example, treats and drinks that are on tables in the hall where participants are waiting for a meeting or receiving documents cannot be taken into account as part of the PR. This position was reflected in the letter of the Ministry of Finance dated March 25, 2010 No. 03-03-06/1/176.
Documents to confirm hospitality expenses
IMPORTANT! A sample estimate of entertainment expenses from ConsultantPlus is available here
Despite the legal requirement for documentary evidence of entertainment expenses, no single standard or list of such documents has been developed. We can say that the presence of official papers is mandatory, but their form is not unified. This issue is resolved by the accounting policies of the organization itself.
Such acts may include:
- the director's order to hold a representation event - be sure to indicate the purpose, date, time and place of organizing the reception, list the counterparties taking part, and also provide the names of responsible and controlling persons;
- the program of the future event will not be valid without an order; in it, the main stages of the representative meeting must be tied to specific dates and times;
- estimate of the event - a list of expenses for specific items (transport, catering, etc.), it is better to create it for each stage separately, be sure to approve it with management;
- report on the event - compiled by the responsible person specified in the order, it reflects all the same positions as in the order, plus the specific result achieved at each stage (especially if during the event any official agreements were concluded or documents were signed);
- an act for writing off this type of expense - contains information about the exact amount for all types of entertainment expenses (this document must be certified not only by the manager, but also by the chief accountant);
- payment documents that confirm expenses : checks, invoices, certificates of work performed, etc.
FOR INFORMATION! In the event of a dispute being considered in an arbitration court, priority will be given to organizations that have taken care of both preliminary supporting documents (order, estimate, program) and final ones (report, act).
Results
Entertainment expenses in accounting are accepted in full and are reflected as part of current expenses in the debit of general or commercial expenses, depending on the type of activity of the company.
According to the requirements of the Ministry of Finance, all expenses must be economically justified and documented not only by the primary document, but also by the order of the manager, cost estimates and a report on the event.
Sources:
Tax Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Rationing of entertainment expenses
The law does not allow spending uncontrolled amounts for entertainment purposes, then writing them off, thereby reducing the income tax base. A strict limit has been established for this type of expense. It is prohibited to spend more than 4% of the wage fund for a given reporting period as representative funds (clause 2 of Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
As labor costs increase over time, the ceiling on hospitality expenses also increases. If, for example, in the 1st quarter there were no entertainment events or the money spent on them was less than normal, then in the remaining quarters it will be possible to “freeze” and take into account more funds for this item. Naturally, we are talking only about the results of the current year.
How to prepare an advance report for entertainment expenses ?
You can calculate the required amount of restrictions on entertainment expenses in one of 3 ways.
Method 1 – quarterly. When filling out an income tax return at the end of each quarter, entertainment expenses are taken into account, taking into account the wage fund for that quarter. This method is more convenient for companies with a cash method of determining income and expenses. If entertainment expenses exceed a quarter, a deferred tax liability is formed, which can be reversed at the end of the year.
Method 2 – annual. Firms' annual budgets are usually not very different. This allows you, when planning the next year, to immediately allocate approximately 4% of last year’s wage fund to entertainment expenses, and then divide this amount into quarters. There will be no non-standard costs with this method, but you will have to constantly adjust the planned and actual indicators.
Method 3 – official. The company establishes which officials can be responsible for entertainment events and what maximum amounts they can spend on this. It is important that expenses are made exclusively for the stated purposes. A check will be required to ensure compliance with the 4% limit.
How to report to the Federal Tax Service?
If the Tax Service is interested in documents confirming the intended use of money as entertainment expenses, the organization is obliged to provide them. Unfortunately, the Federal Tax Service has not yet prepared any unified form for such a document, so taxpayers have to use their imagination and draw up the necessary papers themselves. However, in addition to engaging in creative activities, taxpayers will also need to provide original source documents, such as checks and receipts. This can also include certificates of completed work, contracts, invoices and other “goods”. And yet, if you don’t go far from creativity, it would not be amiss to remind you that it is necessary to bring it to life within the framework of the requirements reflected in Article 9 of Federal Law No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”, otherwise this document will not be of any value for tax authorities. As for its content, using the example of a trip to a restaurant with business partners, you must indicate the following:
- Date, time and place of the business lunch;
- Who, in fact, “ate lobster” on the part of the company itself and their future clients;
- How much did this whole event cost (exact amount based on checks);
- Where did the dialogue stop (the contract was signed, the goals and methods of further cooperation were determined, etc.).
To some this may seem overly ephemeral, but rules are rules and in order not to pay for everything out of your own pocket, you will have to deal with this “writing”. Well, it's up to you to choose what you like best.
The role of entertainment expenses in the income tax base
Entertainment expenses are deducted from the amounts that make up the net profit of the enterprise, thereby reducing the tax base. In this case, input VAT is also deducted. If in subsequent reporting periods expenses fall within the 4 percent limit, VAT on them can also be deducted.
It is for this reason that “spears are broken” regarding the recognition or non-recognition of various expenses as entertainment expenses. Even if the organization of the event actually required costs that are not included in entertainment expenses by the Tax Code, they cannot be included in these costs to reduce the tax base.
Is it possible to take into account for income tax purposes the costs of purchasing alcoholic beverages for organizing an official reception? View answer
FOR EXAMPLE. Kassandra LLC organized a meeting with representatives of other organizations to discuss the terms of cooperation. 140 thousand rubles were spent on this event. Of these funds, 70 thousand rubles were spent on the reception and lunch, 25 thousand rubles on buffet service, 20 thousand rubles on transportation of participants to the lunch place and back to the company, 10 thousand rubles on attending a performance in the theater. . rub., for a tour of memorable places of the city - 15 thousand rubles, for flowers and souvenirs for participants - 45 thousand rubles.
In this case, only 115 thousand rubles can be written off for hospitality expenses, that is, the amount of expenses for reception, catering and transport. The remaining funds are in the amount of 25 thousand rubles. must be paid from net profit after calculating the tax amount.
NOTE! Entertainment expenses are deductible only for taxpayers using the general taxation system. In Art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides a list of expenses by which a payer working under the simplified tax system can reduce the base - entertainment expenses are not included in this list. Entrepreneurs who rely on preferential tax systems can use only funds from net profit (the difference between income and expenses) for entertainment expenses.
Advertising expenses
In paragraph 4 of Art. 264 states that advertising expenses can reduce the tax base only within 1% of sales revenue, determined in accordance with Article 249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. But this does not apply to all types of advertising costs. The following expenses are not standardized for tax purposes:
- for advertising events through the media (including advertisements in print, radio and television) and telecommunication networks;
- illuminated and other outdoor advertising, including the production of advertising stands and billboards;
- participation in exhibitions, fairs, expositions; design of shop windows, sales exhibitions, sample rooms and showrooms; production of advertising brochures and catalogs containing information about goods sold (works, services), trademarks and service marks or about the organization itself; discounting of goods that have completely or partially lost their quality during exhibition.
If advertising expenses have arisen and the amount of revenue is not yet known, then such expenses cannot be written off. Only after the reporting period for income tax has ended can the accountant take them into account. In this case, actual expenses are compared with those that are subject to rationing. Costs within normal limits are included in the tax base.
How to deal with expenses that are incurred in excess of the norm? The tax period for income tax according to paragraph 1 of Article 285 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is a calendar year. The tax base is calculated on an accrual basis from the beginning of the year. Therefore, before the end of the tax period, expenses not taken into account in one reporting period can be recognized in the next reporting period.
What are daily expenses for a business trip?
Daily expenses are a type of travel expenses intended to reimburse expenses outside the place of residence due to business needs.
Important! If the traveler has the opportunity to return every day during the business trip to his place of residence, then the daily allowance is not paid.
Paid for every day, as well as on holidays and weekends, including days on the road. At the same time, daily allowances are paid even in the case of documented sick leave during a business trip.
Daily allowance amounts are prescribed in local regulatory documents, with foreign business trips and business trips within the Russian Federation taken into account separately.
Daily allowances are not paid for one-day business trips within the Russian Federation and are paid at half the cost when traveling abroad.
Limits on daily expenses when calculating personal income tax (amounts less than the limit are not taxed):
- For business trips within the Russian Federation – 700 rubles;
- For foreign business trips – 2,500 rubles.