Subordinate to the “Materials” account (10).
Account type: Active.
Account type:
- Quantitative
- Tax
Analytics for the account “10.08”:
| Subconto | RPM only | Total accounting | Accounting in currency |
| Nomenclature | No | Yes | No |
| Parties | No | Yes | No |
| Warehouses | No | Yes | No |
Material reserves: concept and classification
When defining the concept of inventory, accountants are guided by PBU 5/01 - a document that defines the rules for their accounting.
Question: How to reflect in an organization’s accounting the write-off of inventories (inventory) (goods) disposed of as a result of their destruction due to a fire in a warehouse in the absence of perpetrators? The actual cost of goods in accounting coincides with the cost of goods in tax accounting and amounts to 380,000 rubles. VAT presented upon the purchase of goods was accepted for deduction. The facts of the fire and the absence of the perpetrators are confirmed by the relevant documents of the authorized bodies, the destruction of the goods is confirmed by the act of writing off the goods, drawn up by the technical service of the organization. The organization uses the accrual method of accounting for income and expenses for profit tax purposes. View answer
The following assets are recognized as material reserves:
- used as raw materials for the production of products that will subsequently be sold;
- which themselves can be realized;
- which are used for management purposes.
How to create a commission for writing off inventory ?
Inventory, therefore, can be represented by finished products, goods, and actual materials and raw materials. The nature of inventories can be different, and for effective accounting and subsequent internal and external audits, it is necessary to correctly classify them, first of all, by their role in the production process. Usually distinguished:
- raw materials and materials;
- spare parts;
- fuel;
- semi-finished products purchased externally (purchased);
- auxiliary materials, etc.
This classification underlies analytical accounting data. The classification takes into account the specifics of production and types of activities. For example, if an organization is conducting its own construction, the category “building materials” is distinguished, and if we are talking about agricultural production, the category “seeds”, “feed” is distinguished.
Question: Are VAT amounts that cannot be offset due to lack of documents included in the cost of inventories for income tax purposes (clause 2 of Article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)? View answer
Auxiliary materials include materials that improve the production process and make it easier: cleaning rags, paints and varnishes and others like them.
Analytical data can take into account the order of use of the MPZ:
- in production (raw materials, supplies);
- for sale (products, goods);
- as means of labor (equipment, household supplies).
If a company has inventories that do not belong to it, for example, those given to it for storage under an agreement, they are separated into a separate category in accounting, while others are classified as the property of this legal entity. Here there is a classification according to the nature of ownership.
By the way! The concepts of inventory items (inventory) and inventories mean the same thing.
The provisions of PBU 5/01 do not allow work in progress to be classified as inventories.
Question: What should be taken into account when filling out Form N INV-19 “Comparison sheet of inventory results of inventory items”? View answer
Inventory: start
Let's figure out how household and construction materials appear in companies in general.
Property tends to wear out. To identify structural and other defects, objects must be inspected periodically. If there is a need for repairs or improvement, you need to purchase the appropriate materials and justify the costs. All this is preceded by the preparation of a defective statement. Next, the commission for the receipt and disposal of assets records the fact of the presence of faults that need to be eliminated.
To allocate funds to eliminate defects, the financially responsible person submits a memo to management. The document reflects a preliminary calculation of the cost of the necessary materials. Management gives the go-ahead and allocates funds.
So, the materials have been purchased, what next? They must be capitalized and reflected in accounting. And this is where the fun begins. An accountant faces a difficult task. Materials must be sorted by type according to KOSGU codes.
Accounting
Industrial inventories include assets whose service life does not exceed one year. PBU 6/01, regarding fixed assets, determines that inventories cannot have a value exceeding 40 thousand rubles. – this is the limit on inventories in accounting.
PBU 5/01 provides the right to independently determine in which units the accounting of inventories will be organized: by item numbers, batches, groups and in any other way that the company deems necessary for the reliability of the information.
materials and other materials in tax accounting ?
This asset is reflected in the accounting system at its actual cost, which includes the seller’s price, consulting services of third-party companies, transport and any other costs directly related to the acquisition of the asset (clause 6 of PBU 5/01).
Inventories can be reflected in the reporting at the contract price, with further clarification of the data to actual ones in two cases (clause 26 of PBU 5/01):
- purchased goods are on the way;
- MPZs are pledged to the buyer
The actual price is not affected by VAT. This tax is allocated as a separate posting.
General, or synthetic accounting, assets are reflected in accounts 10, 43, 41, affecting, respectively, materials, finished products, goods. Subaccounts detail this information taking into account the classification of inventory items. For example, information on account 10 can be detailed by subaccounts: 10/1 “Raw materials and materials”, 10/3 “Fuel”, 10/4 “Container”, 10/5 “Spare parts”, 10/9 “Inventory and household supplies” and etc.
The most important element of analytical accounting is properly organized warehouse accounting of inventories - receipts and releases into production, for household needs, for sale.
Capitalization and release are carried out according to primary documents, for example:
- consignment note TORG-12, consignment note for the transfer of products to the warehouse MX-18;
- receipt order M-4 (or act M-7, if there is a deviation in the actual volume and invoice data); TORG-1 act upon acceptance of finished products;
- invoice for internal movement M-11, limit-fence card, invoice, consignment note, consignment note;
- other forms adopted in the accounting policies and legislation of the Russian Federation.
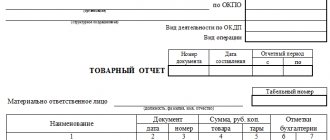
All movements of inventory items are recorded in the warehouse record card (book), the goods and finished goods log book.
Control in the accounting department is carried out based on reports from materially responsible persons on the movement of inventory items, commodity reports, and inventory records. As a rule, unified forms of documents are used, but legislation does not prohibit the development and use of a company’s own forms.
Analytical data is collected in accordance with accepted accounting units.
Receipt of materials in 1C 8.3
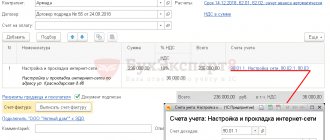
Receipt of materials is reflected in the standard document “Receipts (acts, invoices)”. The document is available in the “Purchase” section. When receiving materials, as well as when goods arrive at an enterprise, you should select the document type “Goods (invoice)” or “Goods, services, commission” (in the latter case, materials are entered on the “Goods” tab).
The accounting account is set automatically if the “Materials” type was specified for the item, or they are selected manually:
The document makes accounting entries in Dt account 10, and also, for an organization that is a VAT payer, in Dt 19.03 (“VAT on purchased inventories”). Printing of a receipt warehouse order (M-4) is available.
Examples of accounting entries
Due to the extreme diversity of types of inventories, accounting policy options for them, and specific accounting situations, accounting schemes can also be different. Here are the most common options.
Admission:
- D10 K60;
- D19 K60;
- D68 K19 – materials were purchased from the supplier, VAT was allocated and submitted for deduction.
Postings for goods are made in the same way; instead of account 10, account 41 is used. For trading organizations, the markup is taken into account by posting D41 K42. Finished products account for D43 K20, 23, 29, etc. - by type of production.
This actual cost method is used most often. If a decision is made to use additional accounts for materials and finished products, the accounting price (cost) method is used; for materials, the receipt will be reflected as follows:
- D15 K60 – purchase price of goods and materials – excluding VAT;
- D10 K15 – cost of receipt;
- D15(16) K16(15) deviations of fact and accounting value;
- D20, 23, etc. K 16 (or reversal if deviations are minus).
A similar scheme will take place for finished products:
- D43 K40 – accounting value of GP;
- D40 K20, etc. – actual cost;
- D90/2 K40 - discrepancies between the fact and the accounting cost (or reversal, see balance on account 40).
Retirement:
- D20, 23, 29, 25, 26 K10 – materials for production, for experimental work, industrial maintenance, for the production of containers;
- D90 K41, 43 – shipment of goods and products to buyers.
- D94 K10,41,43 – shortages, damage to goods and materials.
The reflection of accounting data in the accounts could be, for example, like this. Let's assume that 1 thousand items of goods and materials have been purchased. in the amount of 120,000 rubles, incl. VAT 20%:
- D60 K51 120,000 rub. payment to the supplier for materials;
- D10 K60 100,000 rub. capitalization of inventory items;
- D19 K60 20,000 rub. VAT reflected;
- D19 K19 20,000 rub. to deduct VAT.
Briefly
- Reflection of inventories in accounting is associated with the peculiarities of the functioning of the organization, its size, and the nature of the production of goods, works, and services. Synthetic inventory accounting is maintained on accounts 10, 41, 43, corresponding to their types (materials, goods, finished products).
- Sub-accounts are opened, as a rule, on the basis of the accepted classification of inventories according to their role in the production process.
- Analytical accounting is carried out individually, by batch, by group - as is customary in the company’s accounting policy. The accountant monitors the movement of inventory on the basis of primary documents and reports of financially responsible persons.
Accounting
In accounting, income and expenses associated with the sale of materials are classified as other income and expenses (paragraph 6, paragraph 7, PBU 9/99, paragraph 5, paragraph 11, PBU 10/99). Record the sale using the following entries:
Debit 91-2 Credit 10
– the cost of materials sold is written off;
Debit 91-2 Credit 23 (20, 60...)
– expenses related to the sale of materials are written off (for example, transportation costs);
Debit 91-2 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
– VAT is charged on sales (if the transaction is subject to this tax);
Debit 62 (76, 73...) Credit 91-1
– sales of materials are reflected (as of the date of transfer of ownership).
Methods for assessing materials
To determine the price of materials being written off (i.e., the amount that is written off from account 10), use one of the methods for valuing them:
- at the cost of each unit of inventory;
- FIFO;
- at average cost.
The choice of method for estimating the cost of written-off materials is fixed in the accounting policy for accounting purposes.
Such rules are established by paragraph 73 of the Methodological Instructions, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 28, 2001 No. 119n.
fair value
To value inventories for which cost cannot be determined, you use fair value instead of market value from 2022 onwards.
Inventories received free of charge or paid for in kind are assessed at fair value (clause 15 of FSBU 5/2019).
Calculating fair value according to all the rules is labor-intensive and not always possible. Therefore, you can use the book value. The new FSBU provides such an opportunity.
Deviations from book value
If an organization accounts for materials using accounts 15 “Procurement and acquisition of material assets” and 16 “Deviation in the cost of material assets,” when they are sold, the amount of deviations from the accounting value of materials must be written off. This must be done at the end of the month, when the cost of materials received for the month and the amount of deviations from it will be known. To do this, it is necessary to determine the average percentage of deviations related to written-off materials using the formula:
| Average percentage of deviations related to write-off materials | = | The balance of deviations in cost at the beginning of the month + The amount of deviations for materials received during the month ______________________________________________________________________ | × | 100% |
| Cost of the balance of materials at the beginning of the month (in accounting prices) + Cost of materials received during the month (in accounting prices) |
After calculating the average percentage, determine the amount of cost variances that is written off to the cost of materials sold. To do this, use the formula:
| The amount of variances written off to the cost of materials sold | = | Average percentage of deviations related to write-off materials | × | Accounting value of materials written off |
In accounting, document this transaction by posting:
Debit 91-2 (45) Credit 16
– part of the deviations in the cost of materials is written off (at the end of the month) if the organization uses accounting prices.
This procedure is provided for in paragraph 87 of the Methodological Instructions, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 28, 2001 No. 119n.
The procedure for paying taxes when selling materials depends on the taxation system that the organization uses.
Inventory received during OS dismantling
Previously, inventories remaining from the disposal of fixed assets or other property were valued at market value.
From 2022, you evaluate reserves obtained as a result of dismantling or repair by the lower of two values (clause 16 of FSBU 5/2019):
- cost of similar inventories;
- the sum of the carrying amount of the assets being written off and the costs incurred during dismantling.
Read in the berator “Practical Encyclopedia of an Accountant”
Inventories received upon dismantling of a fixed asset
The result is that the value of the company's assets on the balance sheet is not overstated.