The buyer returned a shipment of goods, the documents arrived late, they made a mistake in the declaration, is there a task to balance the amount of tax? How to reflect expenses of past tax periods?
What determines the choice of the period for reflecting expenses, what documents are used to confirm expenses of previous years? You will find answers to these and other questions on this topic in our article.
Let's start the article with a resonant story. Limited Liability Company "SBSV-Klyuchavto Mineralnye Vody" included more than 7.5 million rubles in non-operating expenses, designating these expenses as losses of previous tax periods identified in the reporting period. The expenses were VAT amounts that must be taken into account in the cost of goods, services, and work, in accordance with Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. However, the Federal Tax Service assessed the company additionally over 1.5 million rubles in income tax based on the results of an on-site tax audit.
The company did not agree with the decision of the tax authorities and went to court, and its confidence in its rightness was so great that, despite the refusal in three courts, it reached the Supreme Court. The courts of first instance supported the position of the Federal Tax Service that the identified costs should be reflected in the periods when the costs were incurred, that is, in income tax returns for previous periods that were known. However, the Judicial Collegium for Economic Disputes of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation took a different position: reflecting corrected information in the current tax return is acceptable, since an error (distortion) in determining the tax base and the amount of tax led to excessive payment of tax in previous periods. The overpayment did not have any negative consequences for the state budget. The court recognized in this case the filing of a tax return for previous tax periods as optional, provided that the three-year period provided by law for the return or offset of the overpayment has not expired.
This decision of the Supreme Court, rendered in 2022, is a kind of landmark, because judicial practice in resolving similar issues in Russia is ambiguous. This court decision was “adopted” by the tax authorities, it was included in the review of the Federal Tax Service (according to letter No. SA-4-7/7164 dated April 16, 2019), where they described the situation in detail in the fifth paragraph of the letter.
General rule for accounting expenses
According to current legislation, an organization's expenses are recognized in the reporting (tax) period in which they arose based on the terms of the transaction. This is the so-called general principle of cost recognition for income tax purposes. In other words, the taxpayer does not have the right to choose the tax period at his own discretion to reflect expenses; it is tied to the moment of signing the primary documents.
Based on the above principle, if it is necessary to reflect expenses of previous years, the taxpayer must adjust the taxable base for the income tax of the previous period by the amount of expenses incurred, as a result, adjust the amount of tax payable and submit an updated declaration to the inspectorate.
Correction of the amount of purchased services for the fourth quarter during the error detection period (in the second quarter)
If the financial statements are not signed or the tax base is underestimated, then to adjust the “closed” previous period, first open it.
Postings
By default, when correcting an error in primary documents, the program classifies the error as not significant. Posting date:
- Accounting – 04/22/2020 (date of error detection): financial statements are always signed, regardless of the entered data;
- NU – 10.31.2019 (date of error): the base is underestimated: increasing the tax base by reducing expenses – Dt 76.K Kt 90.01.1;
But in this case, the updated income tax return for the fourth quarter will have to be generated manually!
Despite the fact that the posting date refers to the previous period, the sequence boundary in closing the month is not violated.
Read more Is the sequence boundary violated during receipt and sales adjustments?
To automatically generate an updated declaration:
- check the Manual adjustment ;
- on the Accounting and tax accounting : change account 90.01.1 in posting Dt 76.K Kt 90.01.1 to the cost accounting account, in our case, indicate Dt 90.08.1 Kt 76.K and indicate the amount with a “-” sign.
For VAT accounting purposes, corrections are made automatically:
- by register VAT Purchases: an entry canceling the primary SF in the additional sheet of the purchase book during the period of its registration (IV quarter), for the entire amount of VAT accepted for deduction.
- motion type recording Comingto the new (correct) amount of input VAT presented by the supplier.
Deduction of VAT on a corrective invoice in 1C is possible only through the document Generating purchase ledger entries .
When are past expenses incurred?
Let's look at the most typical situations when a taxpayer needs to take into account expenses from previous years.
- The emergence of new circumstances relating to transactions of the previous period.
We are talking about unforeseen circumstances. For example, the most common circumstance is a return under warranty or a return due to inadequate quality. Revenue from the goods (batch of goods) was received in the previous reporting period, and the return was issued in the current reporting period. As a result, the company incurs new expenses in the amount of the returned payment.
- Detection of errors (distortions) related to transactions of the previous period.
We are talking about errors in calculating corporate income tax. An error (distortion) means an incorrect reflection of the facts of economic activity when calculating income tax. The most common mistake of this kind is recording expenses in one reporting period, while receiving primary documents for these expenses in another reporting period. The contractor received payment, but delayed the delivery and signing of the acceptance certificate, invoices or certificates took too long to arrive - quite common situations...
How are last year's expenses identified in the reporting year reflected in accounting?
The accounting rules do not provide for any corrections in accounting and reporting for past periods. Distortions and expenses not reflected on time that were made in previous years are always reflected in accounting exclusively in the period in which they were found, and making any changes to accounting after approval of the annual reporting is strictly prohibited.
Therefore, unlike tax accounting, in accounting, correction of distortions in expenses of past periods is carried out using a different algorithm. PBU 10/99 recognizes losses from previous years discovered in the reporting period as other costs. If the errors are insignificant, then they are reflected in the current year’s accounting in the debit of account 91, corresponding with the accounts of materials, calculations, depreciation, etc.
Significant distortions (for example, those that can affect the price of shares or financial results, i.e., user decisions depend on the distortion (clause 3 of PBU 22/2010) are reflected in the retained earnings account (84), recording the write-off of losses from previous years at the expense of profit. Note that the company sets its own materiality criteria, securing and approving them in its accounting policies.
How to reflect expenses from previous years
If circumstances are discovered in the current tax period leading to an adjustment of the tax base relating to previous tax (reporting) periods, the tax base and tax amount are recalculated for the period in which these errors were made. However, there are a number of exceptions that allow companies to take into account past expenses in the current period.
According to Article 54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, there are two circumstances that allow you to take into account expenses of past periods in the current period.
- If it is impossible to determine the period of errors (distortions), the tax base and tax amount are recalculated for the tax (reporting) period in which the errors (distortions) were identified.
- If errors (distortions) made in the previous tax period led to excessive payment of tax, the taxpayer has the right to recalculate the tax base and the amount of tax in the period in which the errors (distortions) were identified.
It was based on the latter circumstance that the decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation was made in the case of SBSV-Klyuchavto Mineralnye Vody LLC, which we described at the beginning of the article. Previously, judicial practice was based on the fact that expenses of previous tax periods could be declared by a taxpayer in the current tax period only on the basis that the period in which the expenses arose was unknown. However, starting from 01/01/2009, in the third paragraph of clause 1 of Art. 54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation enshrines the taxpayer’s right to recalculate the tax base and tax amount during the tax (reporting) period when errors (distortions) were identified, if the errors (distortions) led to excessive payment of tax.
Unaccounted expenses of previous periods in income tax
In addition to errors discovered during inventory, an accountant can also find his own shortcomings. The Ministry of Finance of Russia, in letter No. 03-03-06/1/23851 dated March 26, 2020, clarified the issue of when an organization can, when calculating income tax for the current period, take into account the identified amounts of unaccounted expenses that relate to previous periods.
Unaccounted expenses appear, for example, when expenses were incurred in the previous tax period, and their documentary evidence appeared later.
Rules for reflecting unaccounted expenses
If an organization has identified the presence of expenses classified as unaccounted for, operations must be carried out to recognize these expenses in accounting and tax accounting. Such errors are allowed to be corrected in accordance with Art. 54 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Thus, paragraph 1 of Article 54 of the Tax Code establishes that if errors (distortions) are detected in the calculation of the tax base relating to previous tax (reporting) periods, in the current period the tax base and tax amount are recalculated for the period in which these errors were committed.
What does it mean?
An error discovered in the current period (the amount of unaccounted expenses) that was made in past periods can only be corrected by filing an updated income tax return.
There are exceptions to this rule when taxpayers can take into account “old” unaccounted expenses in the current period. To do this, you must meet the following conditions:
- it is impossible to determine the period of errors (distortions);
- errors led to excessive payment of tax in previous periods;
- there is profit subject to taxation in the current reporting period;
- Three years have not passed since the date of payment of the tax on the return with an error.
Thus, there can be two options for action when unaccounted costs are detected:
- correction of the situation during the current period;
- making changes during the period in which the inaccuracy arose.
Please note: if an error results in an overpayment, the company has the right to correct it, i.e. declare expenses not only in the period to which they relate, but also when the distortion is identified. The main thing is that the three-year period provided for resolving the issue of overpayment does not expire.
If there is a loss in the current period
If a loss is incurred in the reporting period, then in this period the tax base is recognized as equal to zero (clause 8 of Article 274 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this regard, recalculation of the tax base of the current reporting period is impossible. Accordingly, errors cannot be taken into account.
Therefore, if a loss is incurred at the end of the reporting period, it is necessary to recalculate the tax base for the period in which the error occurred, that is, to submit an updated income tax return.
About the period during which the tax base can be adjusted
The Russian Ministry of Finance draws attention to a three-year period during which the tax base can be adjusted.
Norms clause 1 art. 54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is used in close connection with the provisions of paragraph 7 of Art. 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation on the offset (refund) of overpaid tax amounts. And an application for a credit or refund of the amount of overpaid tax, including due to a recalculation of the tax base that resulted in an excessive payment of tax, can be submitted within three years from the date of payment of the specified amount.
This opinion is also expressed in the Ruling of the RF Armed Forces dated January 21, 2019 No. 308-KG18-14911.
Thus, according to the position of the official bodies, it will be problematic to take into account expenses with a limitation period of more than three years.
Accounting
The procedure for correcting errors in accounting is regulated by PBU 22/2010 “Correcting errors in accounting” (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 28, 2010 No. 62n).
In accordance with clause 9 and clause 14 of PBU 22/2010, a minor error identified after the signing of the financial statements and a significant error identified after its approval are corrected in the current reporting period.
Thus, an error made in 2022 is subject to correction in the period of its detection, that is, in 2022. Moreover, if an error recognized as insignificant is corrected, the income or expenses that arise as a result of the adjustments should be reflected using account 91 “Other income and expenses.” When correcting a significant error, account 84 “Retained earnings” is used.
Example. When to correct an error made when calculating the tax base
The accountant of Alpha LLC made a mistake when calculating the income tax base in December 2022. The same error led to an understatement of income taxes and distorted the company's accounting data.
The bug was discovered in December 2022. The Liability accountant must reflect the corrections as follows:
- in accounting – in reporting for 2022;
- in tax accounting - in the income tax return for 2018. The error cannot be taken into account in the current period, since the error led to an understatement of income tax.
The Federal Tax Service has been waiting for three years
According to paragraph 7, article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, “an application for offset or refund of the amount of overpaid tax can be filed within three years from the date of payment of the specified amount, unless otherwise provided by the legislation of the Russian Federation on taxes and fees or based on the results of a mutual agreement procedure in accordance with the international treaty of the Russian Federation on taxation issues.”
For example, if an organization discovers in 2022 that certain expenses were not taken into account when calculating income tax in 2015, then, as they say, “the train has left.” There is no point in filing an updated return for 2015 - overpayment of income tax is no longer refundable.
Accounts for correcting errors of previous years identified through control activities
| Year in which the error was made | Accounting accounts used to correct errors from previous years | ||
| Correcting an error does not affect the financial result | Income adjustment required | Cost adjustments required | |
| Last year | 0 304 66 000 “Other calculations of the year preceding the reporting year, identified through control activities” | 0 401 16 000 “Income of the financial year preceding the reporting year, identified through control measures” | 0 401 26 000 “Expenses of the financial year preceding the reporting year, identified through control activities” |
| Other past years | 0 304 76 000 “Other calculations of previous years identified through control measures” | 0 401 17 000 “Income of previous financial years identified through control measures” | 0 401 27 000 “Expenses of previous financial years identified through control measures” |
More on the topic: OKOF 2022 - apply without errors
Example. In the reporting period in March 2022, in the accounting of a budgetary institution, the internal financial control authorities discovered an error made in September 2022: expenses for routine repairs of the building in the amount of 1,200,000 rubles. erroneously attributed to an increase in the original (book value) of the building. Expenses for the current repairs of the building in 2022 were made using subsidies for the implementation of the state (municipal) task. In the current year, the date of discovery of the error in the institution’s accounting reflects the corrective entries:
Debit 4,401 26,271 Credit 4,104 12,411 – reflects the adjustment to the amount of depreciation from September to December 2022;
Debit 4,401 20,271 Credit 4,104 12,411 – reflects the adjustment to the amount of depreciation from January to February 2022;
Debit 4,106 11,310 Credit 4,304 66,732 – the “Red reversal” method reflects the increase in capital investments in 2022;
Debit 4,101 12,310 Credit 4,304 66,732,
Debit 4,304 66,832 Credit 4,106 11,310 – the “Red reversal” method reflects the increase in the value of the building by the amount of current repairs in 2022;
Debit 4,401 26,225 Credit 4,304 66,732 – expenses for current repairs are included in the financial result for 2022.
Condition two: timely recording of expenses would not have led to losses in the previous period
Let's explain with numbers. Let’s say the taxable base in 2022 was 100,000 rubles. In 2022, expenses related to last year were identified in the amount of RUB 150,000. If the company had shown these costs in a timely manner, then in 2022 there would have been a loss of 50,000 rubles (100,000 - 150,000).
There is an opinion that given this state of affairs, it is impossible to take into account “forgotten” costs in 2022. After all, there is a mechanism that regulates the transfer of losses from the past period to the future. According to it, in the period from 2022 to 2022, when writing off last year’s losses, the current base is allowed to be reduced by no more than 50% (clause 2.1 of Article 283 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In the case when the base for 2022 is small, for example, 20,000 rubles, the organization has the right to take into account losses for 2019 only in the amount of 10,000 rubles (20,000 rubles x 50%). And reflecting the full amount of last year’s expenses in 2022 leads to a decrease in the base by 150,000 rubles. Thus, the damage to the budget in our example is equal to 140,000 rubles (150,000 - 10,000).
Maintain accounting and tax records for free in the web service
Condition one: the tax return for 2022 must include tax “payable”
The explanation here is simple. As we have already mentioned, to correct an error in the current period, it is necessary that the error lead to excessive payment of tax (Clause 1 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And “excessive payment” is possible only if there is a tax “to be paid.” If last year’s declaration indicated a loss, then there is no need to talk about any payment, especially “excessive” one.
Please note that the amount of income tax in the 2022 return is not important. It can be at least 1 ruble, as long as it is the amount “to be paid”.
You can find out how much taxes the counterparty paid and check its financial condition in the “Kontur.Focus” service. Connect to the service
Accounting in 1C
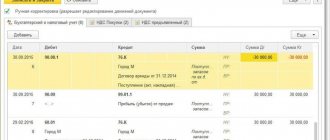
July 01 The Organization discovered that it had not recorded paid rental expenses for December last year. The organization decided to reflect expenses in the previous tax period and submit an updated declaration. Last year's financial statements have been approved.
Document the receipt of services with the document Receipt (act, invoice) transaction type Services (act) in the section Purchases – Purchases – Receipt (acts, invoices) – button Receipt – Services (act).
Please indicate:
- Act No. _ dated _ - date and number of the primary document;
- from - date of acceptance of the document for accounting;
- Accounting accounts : Cost account - 91.02 “Other expenses”.
- Other income and expenses - Profit (loss) of previous years . Selected from the directory Other income and expenses, Type of article - Profit (loss) of previous years ;
- Expenses (NU) - Not accepted .