May 17, 2022 #Accounting
OKTMO, UIN, KPP, RSV - you won’t surprise a good accountant with this. But for a person far from this sphere, such a set of letters is sometimes even difficult to pronounce. They may seem awkward or funny, but each has its own special role in this huge mechanism. Today we will tell you about KBK - three mysterious letters, without which not a single payment order to the state budget can be completed.
The budget classification code (BCC) is the link between the taxpayer and the state. It is with its help that money ends up in the right “cell” of the state budget, eliminating confusion from the process.
It is difficult to underestimate the importance of the KBK: one mistake, and the money will end up in the wrong budget, or will not reach it at all. In the second case, the payment will be classified as unclear, and it will simply “hang” without reaching its intended destination. In both options, the supervisory authority will consider that payment has not been made and will begin to accrue penalties on a daily basis.
To prevent this from happening, it is important to understand why the code is needed, where it is used and how to fill it out correctly. An error in the KBK is not only a waste of money. Additional headaches, stress, loss of time and energy are inevitable. And if the situation gets worse, the current account may be blocked.
Analysis of BCC for individual entrepreneurs, legal entities and individuals
In terms of structure, the KBK is a large nesting doll.
It has 3 main codes, which are divided into different groups and subgroups. The number of numbers, their order and meaning are determined by orders of the Ministry of Finance, so there should be no lyrics or amateur performances.
Let us explain its structure in 2 times shorter than in the orders, avoiding unnecessary bureaucracy:
• 1-3 — Code of the chief administrator of budget revenues; • 4-13 — Code of the type of budget income; • 14-20 — Code of budget income subtype.
Refusal from the tax office based on clarification from the KBK
There are many cases when the tax office refuses to accept an application for clarification of payment. Employers have to prove in court that the Tax Inspectorate’s decision was not legitimate.
We advise you to read: How to return money sent by mistake?
And the judges take the side of the employers, explaining that if the BCC is incorrectly indicated in the payment order, it does not entail the transfer of taxes to the state budget, but only for the correct distribution of funds between budgets. This means that an erroneous BCC does not constitute non-payment of tax.
If the payment order contains only one error according to the KBK, then the tax amount is in the Treasury current account and there is no need to transfer funds a second time.
According to letter dated June 17, 2008 N 03-02-07/1-288, penalties are also not charged if the tax payment was transferred on time. A clarified statement is enough and the funds will go to the correct CBC. An example is the FAS Resolution of May 14, 2013, case No. A33-8935/2012.
Another thing is if the accountant makes a mistake in the current account number or the name of the bank, the bank assigns such payments to unclear payments or returns them back to clarify the details.
Code of the chief budget revenue administrator
The most harmless of all: it consists of only three digits, and the list of administrators and the codes assigned to them are clearly stated in Appendix 6 to Federal Law No. 459-FZ of November 29, 2018.
Who is the chief administrator?
These are ministries and federal services that form the state budget and actively participate in it. Administrators include, for example, the Ministry of Health (code 056), the Federal Customs Service (153), the Central Bank (999) - in total there are more than 80 of them. 182 in our example is the Federal Tax Service.
Budget income type code
It is the most voluminous in terms of content and variability, as it includes groups, subgroups, articles and subarticles.
The groups and subgroups in the order are not divided and are stated in a single number: 100 - tax and non-tax revenues; 200 - gratuitous receipts.
Of course, everything cannot be that simple, so there is a list for groups:
• 101 - taxes on profits, income; • 102 — insurance contributions for compulsory social insurance; • 108 — state duty; • 201 – gratuitous receipts from non-residents.
Articles and sub-articles are not presented in the order itself, unlike groups. The text contains only a subtle reference to the Appendix, where all types of budget income and codes for them are spelled out. Their task is to indicate the most specific purpose of payment.
For example, codes for insurance premiums are divided into payment of insurance pensions and funded pensions, insurance against accidents at work and in case of temporary disability due to maternity. There are many options, some sub-items even have a breakdown by year.
The income element completes the chain. It is similar to the chief administrator code, but it specifies exactly the budget level to which the payment will go.
The range of codes here is from 01 to 14: 01 - federal budget, 06 - Pension Fund budget, 07 - Social Insurance Fund budget.
First thing
The Tax Code does not establish an algorithm for the actions of companies and entrepreneurs in the event of an incorrect indication of the KBK in the “payment”.
In this case, I advise you to be guided by the provisions of paragraph 2 of paragraph 7 of Article 45 of the Tax Code. The norm states what needs to be done “after discovering an error in the execution of an order to transfer a tax, which did not result in the non-transfer of this tax to the budget system to the appropriate account of the Federal Treasury.” That is, we are talking about those cases when the money, although not in the right place, nevertheless arrived. So, the first thing you need to do is submit an application to the inspectorate at the place of your registration, in which you report the inaccuracy. The payment order itself must be attached to this paper. The document also needs to make a request to clarify the BCC.
In addition, you can invite tax authorities to conduct a joint reconciliation of the fees paid. By the way, the inspectorate itself can initiate such an audit.
Based on the application and the joint reconciliation report (if one was carried out), the auditors make a decision to clarify the payment. At the same time, they will have to recalculate the amount of penalties. We are talking about interest that was accrued on the amount of tax for the period from the date of its actual payment until the moment the inspectors made a decision to clarify the payment.
However, in practice, everything does not always go so smoothly. As a result, numerous disputes between companies and inspectorates arise.
Budget income subtype code
The final element in the KBK structure is also divided into groups, but only into two: the income subtype group and the analytical group.
The subtype group determines the status of the payment obligation: arrears, penalties or fines. Codes range from 1000 to 7000. Code 0000 is set only if code 116 is in digits 4-6.
The analytical group has two main code options: 100 - income; 400 - disposal of non-financial assets. In our example, 160 are insurance contributions for compulsory social insurance.
Common mistakes when paying insurance premiums
| Common errors | Outcome and options for correcting mistakes made |
| December insurance premiums for 2016 were credited in January 2017 to the Pension Fund (the details of the fund are indicated, not the tax service, the BCC is inaccurate) | The obligation to pay contributions has not been fulfilled. To rectify the situation, the obligated person has the right to write an application to the fund for the return of the erroneously transferred money. The appeal indicates the details of the organization (tax office) where the money should be returned |
| Contributions were credited correctly to the required tax service account, but the wrong BCC is indicated (a code is needed for the period from 01/1/2017, but instead the code used before 01/1/2017 is written down) | There is no need to re-pay contributions; no penalties will be charged. The payer must request clarification of the BCC to the tax authorities |
| Excess amount for insurance payments transferred | The payer has the right to use one of the options: · return the overpayment; · offset the excess against future payments. To do this, he must submit an appropriate application (for a credit or refund of the excess amount) to the tax authorities |
What features does KBK have?
KBK is a very fickle thing. Laws and orders, which contain up-to-date information, change annually, and sometimes more often. The Internet is full of stale data, so when working with codes you need to select sources with special care. At Button we always monitor such changes, so if you are not ready to scroll through endless pages of orders, or are afraid of making mistakes, you can entrust sending reports and preparing payment orders with filling out the KBK to us.
Remember that when you change the BCC, the old ones become invalid. This is especially important if you plan to pay taxes for the past period when other codes were in effect. You need to indicate those that are relevant now.
The budget classification code is the same throughout Russia and does not change depending on the region. And thanks for that
From 2022 to 2022, they did not undergo major changes, their list was only expanded: new BCCs were introduced for administrative fines and those specified in the first part of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Personal income tax was sent to the wrong KBK. How to fix the error?
02.09.2021
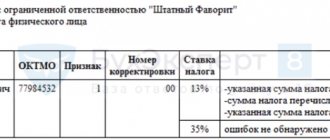
In the second quarter of 2022, payments in excess of RUB 5 million were made to employees. Personal income tax was withheld and transferred in full, but the payment order erroneously indicated the BCC, which refers to the tax rate of 13%. How to offset from this KBK to KBK, which reflects tax at a rate of 15%, if the calculation in form 6-NDFL for 6 months of 2022 has not yet been submitted?
When issuing a payment order for the payment of tax in relation to personal income tax withheld from the amount of earnings not exceeding 5 million rubles. and relating to part of the income in excess of 5 million rubles, different BCCs are applied.
Subclause 1, clause 3, art. 45 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
it is established that the obligation to pay tax is considered fulfilled by the taxpayer from the moment of presentation to the bank of an order to transfer funds to the budget system of the Russian Federation to the appropriate account of the Federal Treasury from the taxpayer’s account (from the account of another person if he pays tax for the taxpayer) in the bank if there is there is sufficient cash balance on the payment date.
The obligation to pay tax is not considered fulfilled in the cases listed in clause 4
of this norm. At the same time, incorrect indication of the BCC in the payment order is not a basis for recognizing the obligation to pay tax as unfulfilled. The budget classification code (BCC) refers to a group of details that allow you to determine the ownership of the payment.
In accordance with paragraph 7 of Art. 45 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
If a taxpayer (another person who has submitted an order to the bank to transfer funds to the budget to pay a tax on behalf of a taxpayer) discovers an error in the execution of an order to transfer a tax, which does not result in the non-transfer of the corresponding funds to the budget, the taxpayer has the right to do so within three years from the date of transfer of such funds to the budget, submit to the tax authority at the place of registration an application for clarification of the payment in connection with an error, attaching documents confirming the payment of the relevant tax and its transfer to the budget system, with a request to clarify the basis, type and affiliation of the payment, the tax period, payer status or Federal Treasury account.
An application for clarification of payment can be submitted on paper or in electronic form with an enhanced qualified electronic signature via telecommunication channels or through the “Taxpayer’s Personal Account”.
Since there is no approved application form, it is drawn up in any form. We recommend that you indicate in your application:
– information about the organization, contact details; – information about the inspection to which the application will be sent; – the circumstances of the payment transfer (number and date of the payment order, name of the tax, period for which the tax is transferred, payment amount); – an error made when filling out a payment order, as well as the correct details; – the position and contact telephone number of an employee (for example, an accountant), whom the tax inspector can contact if necessary.
Along with the application, you must submit a copy of the payment order and a copy of the bank statement (the statement will confirm that there were sufficient funds in the account to pay the tax on the date of payment).
The application is signed by the head of the organization or an authorized representative.
When a tax authority receives an application from a taxpayer to clarify the type and attribute of a payment, the tax authority will make a decision to clarify the payment within 10 working days from the date of receipt of the application (see Procedure for tax authorities to deal with uncleared payments
, approved
by Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated July 25, 2017 No. ММВ-7-22/
[email protected] ). The decision to clarify the payment is made on the day of actual payment of the tax to the budget.
Thus, if an erroneously specified BCC is detected in a payment order for the transfer of personal income tax, the organization has the right to contact the tax authority with an application to clarify the identity of the payment (see Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 19, 2017 No. 03-02-07/1/2145
).
By the way, the controllers indicated that it is possible to clarify the BCC only within the limits of the same tax. In the case under consideration, this is possible, since the organization transferred personal income tax for employees to the wrong BCC, but also intended for this tax.
For your information:
The Federal Tax Service informed that from August 2, 2021, if an error is detected in the execution of a payment order, taxpayers can submit an application to clarify the payment at any tax authority, that is, regardless of the place of registration.
Search and clarification of payment are carried out in the tax machine mode. The taxpayer will be informed in writing about the results of processing the application. The new functionality will significantly reduce the labor costs of citizens for interaction with tax authorities, reduce the costs of tax authorities for processing citizens’ applications and clarifying payments, and ensure a high-quality level of tax services. Users of the “Taxpayer’s Personal Account” can also submit an application for payment clarification.
In conclusion, we note that in order to correct the error, it is necessary to submit an application to the tax authority to clarify the identity of the payment.
Manokhova S. V., expert of the information and reference system "Ayudar Info"
Send to a friend