Regulatory framework
The legal basis on which organizations must sell and then record goods is PBU 9/99 (Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 32n dated 05/06/1999). In it, the accountant will be able to find the answer to all questions regarding the sale of manufactured products or services provided. Organizations divide income into:
- ordinary - from the main activities;
- others - not related to the main activity, not always regular, insignificant in the total volume of profitability from the sale of products.
Ordinary income also includes profitability from trade in goods, works and services (clause 5 of PBU 9/99). The amount of income is calculated without value added tax and VAT (clause 3 of PBU 9/99). Personal income tax is also not taken into account in this case. Each institution chooses the procedure for dividing income independently, based on the specifics of the type of activity and legal form. The chosen method must be fixed in the accounting policy (clause 4 of PBU 9/99).
Clause 12 of PBU 9/99 states that revenue from trade is recognized in accounting only if the following characteristics are simultaneously determined:
- the enterprise has the right to receive it;
- it is calculated in a certain amount;
- the income is beneficial for its recipient;
- upon sale, a transfer of ownership was carried out;
- the value of sales costs is also known.
For organizations operating under a simplified accounting scheme, it is possible to recognize profitability at the time of receipt of payment for goods and services. In cases of a long production cycle, revenue can also be recognized in stages - after completing a certain stage or manufacturing a specific part (clause 13 of PBU 9/99).
Which accounts should be used to record sales?
Accounting for transactions for the sale of goods and services of an organization is reflected in account 90 “Sales” of the chart of accounts (Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 94n dated October 31, 2000). Account 90 records transactions for the sale of inventory and materials and expenses directly related to the sale of goods and materials, as well as VAT accrued on these transactions. On the account 90 you can maintain both synthetic and analytical accounting. Analytics is carried out according to such parameters as the types of industrial and technical works being sold and the structural divisions of the organization.
Account 90 has a number of sub-accounts that the organization opens based on the industry and production specifics of its scope of operation:
- revenue - 90.1;
- cost - 90.2;
- VAT - 90.3;
- excise taxes - 90.4;
- expenses - 90.5;
- profit and loss - 90.9.
Indicators and movements in subaccounts are taken into account throughout the month on an accrual basis. At the end of the reporting period - month - loan turnover (subaccount 90.1) is compared with the total debit turnover for subaccounts such as 90.2, 3, etc. The result is posted in the “Profit and Loss” subaccount with the following entry: Dt 90.9 Kt 99.
Where in accounting is information about net profit collected during the year?
To reflect the financial results of the enterprise's activities during the year, an account is used. 99 "Profits and losses." It is to this account that the financial results from sales and other activities are written off. In addition, on the account. 99 hit:
- accrual of conditional income tax;
What is a conditional expense and income tax income and how to correctly display it in accounting, find out in ConsultantPlus. Study the material by getting trial access to the K+ system for free.
- accrual of a single tax under the simplified tax system;
- accrual of a single tax for UTII;
ATTENTION! Starting from 2022, UTII will no longer be valid. Read more here.
- tax sanctions;
- losses associated with extraordinary circumstances;
- income received as a result of emergency circumstances;
- write-off of deferred tax assets and liabilities;
- other income or expense items.
As a result of analyzing the account turnover for the year, you can understand whether the enterprise’s activities were profitable or not. If the debit turnover exceeds the credit turnover of the account. 99, then the organization worked at a loss, and if vice versa, then the year ended with a profit. The balance sheet reformation ends with a record reflecting the financial results of all the organization’s activities for the year:
- Dt 99 Kt 84 - profit accrued;
- Dt 84 Kt 99 - the entry means that the activity for the year was unprofitable.
To better understand the process of generating profit or loss, read about which accounts are active.
How to account for sales of goods
The accounting record of sold inventory items is made at the time of shipment of goods. Accounting procedures for the sale of goods are as follows:
| Debit | Credit | Description |
| 62 | 90.1 | Revenue received from product sales |
| 90.2 | 41 | Write-off of the cost of goods sold |
| 90.5 | 44 | Write-off of costs associated with the sale |
| 51 | 62 | Receiving payment from the customer |
If, under the terms of the agreement, the transfer of ownership of sold goods and materials from the seller to the buyer is carried out at the time of payment, then, on the basis of clause 12 of PBU 9/99 (subclause “d”), revenue is not recognized at the time of delivery of the goods. When reflecting shipment and sale transactions, invoices are used. 45. Accounting entries for the sale of goods and services will be as follows:
| Posts | Transaction data |
| Dt 45 Kt 41 | Shipment of goods and materials to the customer |
| Dt 76 Kt 68 | VAT calculation |
| Dt 51 Kt 62 | Receipt of payment to the seller |
| Dt 62 Kt 90.1 | Revenue recognition |
| Dt 90.2 Kt 45 | Write-off of cost of goods and materials |
| Dt 90.3 Kt 76 | VAT credit accrued upon shipment |
| Dt 90.5 Kt 44 | Write-off of sales costs |
Accounting for goods under a supply contract with transfer of ownership at the time of payment. Accounting entries
- home
- Postings
- Postings reflecting the sale of goods under a supply agreement
- Postings reflecting the purchase of goods under a supply agreement
Postings reflecting the sale of goods under a supply agreement. The delivery agreement determines the transfer of ownership at the time of payment for the goods
The accounting entries of this business transaction reflect the situation when the transfer of ownership of goods from the supplier to the buyer occurs at the time of payment (determined by the terms of the contract). This type of supply agreement is used very rarely in practice.
This business transaction can be reflected in accounting in two ways, depending on the moment the buyer pays for the goods. In addition, it is worth paying attention to the procedure for calculating VAT. According to Art. 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the moment of determining the tax base for calculating VAT is the earliest of the following dates:
- day of shipment (transfer) of goods;
- day of payment, partial payment on account of upcoming deliveries of goods.
Also in paragraph 3 of Art. 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states: “In cases where the goods are not shipped or transported, but the transfer of ownership of this product occurs, such transfer of ownership ... is equivalent to its shipment.”
Based on the above, we will generate accounting entries.
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | Transaction amount | A document base |
| 1. Sale of goods with payment after shipment (transfer) | ||||
| 45 | 41 | The shipment of goods is reflected. The amount depends on the methodology for estimating the value of goods upon disposal (at the cost of each unit, at the average cost, using the FIFO method) | Cost of goods | Consignment note according to form No. TORG-12 |
| 68.2 | 76 | VAT is charged on shipped goods in accordance with Art. 167 Tax Code of the Russian Federation | VAT amount | InvoicePurchase bookSales book |
| 51 | 62.01 | The fact of payment by the buyer for shipped goods is reflected. Moment of transfer of ownership | Sales value of goods | Bank statementPayment order |
| 62.01 | 90.1 | Revenue is reflected in the sales price of goods shipped and paid for, including VAT. | Sales value of goods (amount including VAT) | Consignment note (form No. TORG-12) Invoice |
| 90.2 | 45 | The disposal of goods from the supplier’s balance sheet is reflected | Cost of goods | Consignment note (form No. TORG-12) |
| 90.3 | 76 | The amount of revenue is reduced by the amount of VAT accrued on goods sold | VAT amount | Consignment note (form No. TORG-12) Invoice |
| 2. Sale of goods (shipment) with prepayment | ||||
| 51 | 62.01 | The buyer's prepayment for goods is reflected | Advance payment amount | Bank statementPayment order |
| 62.01 | 90.1 | Revenue is reflected in the sales price of goods including VAT. | Sales value of goods (amount including VAT) | Consignment note (form No. TORG-12) Invoice |
| 90.2 | 41 | The disposal of goods is reflected. The amount depends on the methodology for estimating the value of goods upon disposal (at the cost of each unit, at the average cost, using the FIFO method) | Cost of goods | Consignment note (form No. TORG-12) |
| 90.3 | 68.2 | VAT is charged on goods sold | VAT amount | Consignment note (form No. TORG-12) Invoice |
| 002 | Goods that have become the property of the buyer are reflected on the off-balance sheet account | Sales value of goods | Consignment note (form No. TORG-12) | |
| 002 | The shipment of goods to the buyer is reflected | Sales value of goods | Consignment note (form No. TORG-12) | |
Postings reflecting the purchase of goods under a supply agreement. The delivery agreement determines the transfer of ownership at the time of payment for the goods
This type of supply agreement is used very rarely in practice.
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | Transaction amount | A document base |
| 1. Postings for accounting for the purchase of goods with payment to the supplier after receipt of the goods | ||||
| 002 | Reflection of goods received but unpaid from the supplier | Purchase price of goods | Consignment note (form No. TORG-12) | |
| 60.01 | 51 | Payment of goods to the supplier is reflected | Purchase price of goods | Bank statementPayment order |
| 41 | 60.01 | Reflects the transfer of ownership of goods received from the supplier | Cost of goods without VAT | Consignment note (form No. TORG-12) |
| 19.3 | 60.01 | The amount of VAT related to the goods received is reflected. | VAT amount | Consignment note (form No. TORG-12) |
| 68.2 | 19.3 | The VAT amount applies to reimbursement from the budget. Posting is done if there is a supplier invoice | VAT amount | Invoice Purchase book Consignment note (form No. TORG-12) |
| 002 | Goods that become the property of the buyer after payment are debited from the off-balance account | Purchase price of goods | Consignment note (form No. TORG-12) | |
| 2. Postings for accounting for the purchase of goods on prepayment | ||||
| 60.01 | 51 | Payment to the supplier for goods is reflected | Payment amount to supplier | Bank statementPayment order |
| 15 | 60.01 | Reflects the transfer of ownership of goods | Cost of goods without VAT | Payment order |
| 19.3 | 60.01 | The amount of VAT related to purchased goods is reflected | VAT amount | Payment order |
| 41 | 15 | Receipt of goods from the supplier is reflected | Cost of goods without VAT | Consignment note (form No. TORG-12) |
| 68.2 | 19.3 | The VAT amount applies to reimbursement from the budget. Posting is done if there is a supplier invoice | VAT amount | Invoice Purchase book Consignment note (form No. TORG-12) |
List of accounts involved in accounting entries:
|
|
How to account for services
Services are considered transferred immediately at the time of their provision. Use the following accounting records for the sale of services:
| Accounting in accounting | Content |
| Dt 62 Kt 90.1 | Reflection of revenue |
| Dt 90.2 Kt 20, 23, 29, etc. | Write-off of cost |
| Dt 90.3 Kt 68 | VAT accrual on the price of the service provided |
| Dt 90.5 Kt 44 | Write off costs |
| Dt 51 Kt 62 | Receiving payment from the customer |
Sales of goods and services in 1C 8.3 - examples with postings
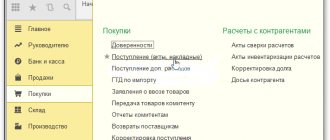
Write-off of sold goods from the organization’s warehouse occurs according to the “Sales” document. Let's take a step-by-step look at how this is done in 1C Accounting 8 edition 3.0. In the menu on the left we find “Sales” and select the journal “Sales (acts, invoices)”. In the window that opens, press the “Implementation” button. From the drop-down list, select “Products (invoices)”:
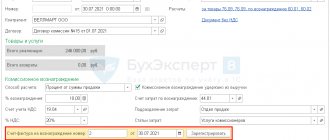
A form opens to fill out:
The following fields are required:
- Counterparty is the organization for which the sales document needs to be made.
- Contract for the counterparty.
- An invoice for payment is filled out if an invoice was previously issued to this counterparty and it was paid.
- Payments – here the number of the current account for making an advance payment to which the payment has been received is displayed.
- The price type is entered automatically based on the contract data filled in the counterparty card.
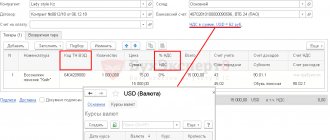
- Field with a list of goods. It can be filled in using the “Select” button.
Let's consider creating a “Sales” document for a previously issued invoice. Go to the “Customer Accounts” journal and select the required document. Let's open it. At the top we find the “Create on the basis” button and from the drop-down list select “Implementation (act, invoice)”:
The window for selecting the document form appears again:
Select “Goods (invoice)”. And the program itself creates a fully completed “Sales based on the selected account” document. All that remains is to issue an invoice. To do this, at the bottom of the screen we find the inscription “Invoice” and press the “Write an invoice” button. The document is generated automatically and the invoice number and date will appear in this place:
You can view this document by clicking on the same link or in the “Sales” section of the “Invoices issued” journal. Everything is filled out and all that remains is to submit the document.
Now let's see what transactions have been created in the system. To do this, click the small button in the top panel “Show transactions and other document movements”:
A window with generated transactions opens:
- Dt 90.02.1 - Kt 41 (43) - reflection of the cost of goods (or finished products);
- Dt 62.02 - Kt 62.01 - offset of the advance payment (if there was one);
- Dt 62.01 - Kt 90.01.1 - reflection of revenue;
- Dt 90.03 – Kt 68.02 – VAT accounting.
You can make changes to transactions manually. To do this, check the “Manual adjustment” box. It is not recommended to do this, as the program itself distributes everything based on previously filled in data.
To print documents on the created implementation, you need to click the “Print” button in the top panel. As a rule, a set of documents consists of a consignment note (Trading 12) and an invoice. Select them one by one from the drop-down menu and print. Or you can print everything at once; to do this, select “Set of documents”. After clicking, a selection window appears:
Here we put a checkmark next to the name of the required document and indicate the number of copies.
If you check the “Directly to printer” checkbox, the entire set will be immediately sent for printing without preview.
If there is a need to print a delivery note or a delivery note (T-1), then they can be printed from the above drop-down window:
To enter additional delivery details, at the bottom of the “Implementation” document itself, there is a “Delivery” link. The consignee and consignor are indicated here - if they differ from those stated, the delivery address, which transport company is delivering the goods - if the cargo is not transported by the selling organization, the car number, driver details, name of the cargo and a list of accompanying documents:
After filling out, click OK and send for printing.
How the implementation is adjusted
If the terms of the contract for the supply of industrial and industrial components have been changed or the accounting department has discovered a previously made error, then the accounting of sales operations can be changed in accordance with the legally established regulations. The parties can send the accompanying documentation necessary for the adjustment by e-mail (mail), and then hand over the original documents in person.
Postings for adjusting the implementation downward:
- reversal Dt 62 Kt 90.1 - decrease in revenue;
- reversal Dt 90.3 Kt 68 - deduction for the amount of the required difference;
- reversal Dt 20 Kt 60 - reduction of the buyer’s debt;
- reversal Dt 19 Kt 60 - VAT on the amount of the difference;
- Dt 19 Kt 68 - restoration of value added tax.