For the state, a second child in a complete family means maintaining the demographic situation at the same level. Therefore, financial incentive programs are being developed at the federal level. And in many regions, in addition to federal benefits, additional so-called gubernatorial payments are provided for the second child.
Read about gubernatorial payments for your first child here, and for your third child here.
Payments in regions
Not all republics, regions and territories provide financial assistance for new parents, unlike federal benefits.
Most often, it is provided where there is a decline in the birth rate. The assistance itself can vary in size, payment method, frequency of payments, intended purpose, requirements for recipients, etc.
Types of material support:
- regional lump sum payment at the birth of a second child;
- one-time assistance for the birth of twins;
- monthly payments until the child reaches a certain age (most often up to 3 years, sometimes up to 1.5 years or up to 16 years or until adulthood);
- regional certificate for 2 children (local maternity capital), in most cases the capital is targeted at improving living conditions, for education, for medical expenses, for the purchase of a family car.
There are also individual benefits, benefits, compensation for utility bills, parental fees in kindergartens, travel on public transport, and priority placement in preschool institutions.
These types of assistance can be combined with each other.
Features of receiving funds
Governor's assistance to families in which a third child is born is considered a significant type of support, enabling citizens to use a large amount of funds for various purposes. The rules for making such a payment include:
- it is important to first study all the requirements for recipients of funds;
- the amount of payment may vary significantly in different regions, but is usually within 100 thousand rubles;
- the benefit is issued only as a lump sum;
- You can find out the exact rules for its registration directly from social security workers.
Funds can be directed by parents for any purpose.
Who should
Governor's payments for 2 children are provided to legal parents. In many cases, also to adoptive parents (when adopting a child).
The applicant for benefits can be either the mother or the father of their choice. However, only the mother can claim her right to certain subsidies.
Regional benefits for a second child are definitely not available:
- citizens deprived of parental rights;
- if the child was stillborn;
- when the applicant is not registered and does not live in the region where he is applying for payment;
- if the other parent has already received a specific benefit.
There are other situations as well.
Guardians and adoptive parents cannot always count on financial assistance on the same basis as full-fledged mothers and fathers.
For foreigners and stateless persons in some regions, a governor's allowance for 2 children is available, just like for citizens of the Russian Federation. The main thing is that these persons are registered in the given region/region/republic.
Parents' employment status has nothing to do with receiving financial support. But the financial situation of the family often plays a decisive role. Quite often, the right to assistance arises if the average per capita income for each family member does not exceed the subsistence minimum, and sometimes 1.5 or 2 times the regional minimum.
Results
The state fully supports parents in their desire to give birth or adopt a second child. The expectant mother of the baby is paid a benefit for registering in the early stages of pregnancy, as well as maternity benefits. After the birth of a child, parents are entitled to one-time and regular payments (maternity capital, governor's benefits, monthly child care allowance, etc.).
To find out what payments are given for a second child in 2022 by regional authorities, you should contact the social security authorities at your place of residence or the local administration.
Sources:
- Federal Law of December 28, 2017 N 418-FZ “On monthly payments to families with children”
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of January 24, 2019 N 32
- Federal Law of December 29, 2006 N 255-FZ “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity”
- Federal Law of May 19, 1995 N 81-FZ “On state benefits for citizens with children”
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
When?
A parent can ask for support from the moment the child is born. The restrictive period for benefits varies (3 months, six months, one and a half years, 3 years, etc.).
If this deadline is missed, the applicant loses the right to assistance. The term can be restored in court. It is necessary to prove that it was not possible to apply in a timely manner for valid reasons (illness, forced departure from the Russian Federation, etc.).
Transfers are also made at different times. Governor's payments at the birth of a child can be made from the moment of application for:
- 10 days;
- 30 days;
- at other times, for example, no later than the 25th day of the next month after submitting an application for a subsidy.
In any case, when submitting documents, the social protection specialist/MFC notifies you of the date of transfer of funds.
Payment of one-time benefit
The established one-time benefit for a mother in connection with the birth of a second child is 18,886 rubles 32 kopecks .
The payment is made at the parent’s place of work, provided that he has submitted an application for social assistance, attaching a package of documents necessary for this. The appointment and payment are made no less than ten days from the date of submission of the set of documents, but no more than six months after the child was born.
Benefits are also paid for caring for a child up to one and a half years old. In this case, the amount is about 40% of the established average income over the past period of time, two years. In fact, benefits can be received by other relatives if it is proven that they are caring for the child.
Which documents
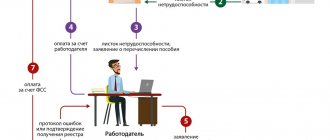
The social security/MFC specialist accepting the application will tell you exactly what documents are needed to apply for gubernatorial benefits. But in order not to waste time on unnecessary visits to institutions, you should know what is included in the basic package.
- Application for payment. Now such an application is filled out by the specialist himself. He will only need individual information from the parent and his signature;
- A copy of the birth certificate (or adoption certificate) for the second and first baby;
- A copy of the parents' marriage certificate;
- A copy of certificate form No. 25 from the registry office (for a single mother);
- Certificate of family composition or certificate of registration of parents and children;
- A certificate from social security stating that the other parent did not receive gubernatorial benefits for the birth of a second child;
- Parents’ passports, they are only presented, and copies remain with the specialist;
- Copy of the applicant's SNILS.
In some cases, additional documents will be required:
- 2NDFL certificate, which can be obtained from the employer or the tax service. Through the Federal Tax Service website, a 2NDFL certificate is provided for all income received. True, information about income for the past year is formed only in the middle of the current year. You also need to be registered in your personal account on the Federal Tax Service website and the certificate is valid only in electronic form (on a flash drive or when sent via the Internet). In any case, the citizen can choose what is more convenient for him in the employer’s accounting department or on the Federal Tax Service website;
- a copy of the work book or an extract from it;
- a certificate from the bank about the balance of the loan, a copy of the loan agreement and a payment schedule;
- And so on.
In certain social security departments and MFCs, the provision of some documents is not required, since specialists can obtain the necessary information independently from their databases.
How to receive gubernatorial payments for your second child
Governor's assistance is awarded when submitting an application to the local authorities of the Department of Social Protection of the Population or any multifunctional center. Government agencies are given a 10-day period to make a decision. In case of a positive verdict, the family can either apply for a certificate for further intended use, or wait for the transfer of cash using the provided details.
Documentation
The list of documents required to apply for payment from the governor includes:
- application of the established form;
- copies of the applicant’s passport and child’s birth certificate (upon presentation of the originals).
It is also necessary to open an account in advance in the name of the applicant or child and indicate the correct details in the application.
The place of registration according to the applicant's passport must correspond to the region in which documents are submitted and, in some areas, the established minimum period of residence there.
Sequencing
If the commission makes a negative decision on the governor's payment, the applicant is given a conclusion clearly indicating the reasons for the refusal. If these reasons are possibly eliminated, you can resubmit your application.
If the decision is positive, the young family can apply for a certificate immediately after the birth of their second baby. If parents choose to receive funds in cash, then the transfer is possible when the child turns 3 years old.
Deadlines for payment of benefits
After a 10-day wait for a verdict from the social security authorities, in the case of a positive decision, it takes about a month to accrue funds.
This period is approximate and may last less or longer depending on the queue of those wishing to receive the payment. Thus, regional support for families who decide to have a second child consists of various benefits and payments, including one-time gubernatorial ones. The registration of such benefits depends only on the parents, who, if they submit the application correctly and on time, can count on receiving a sum of money to improve the living conditions of all family members.
In which regions are
Regional benefits for the birth of a child
| Region of the Russian Federation | a one-time sum paid at the birth of a second child | Additional support measures |
| Bryansk region and Bryansk | 1000 rub. | none |
| Vladimir region and the city of Vladimir | RUB 3,913 | RUB 13,039 at the birth of twins |
| Vologda region and Vologda | 2000 rub. for low-income families | none |
| Irkutsk region and Irkutsk | none | 70,000 rub. at the birth of twins in families where the average per capita income is less than 2 times the subsistence level in the Irkutsk region |
| Kaluga region and Kaluga city | RUB 15,600 | none |
| Kirov region and Kirov city | none | 5000 rub. monthly child care allowance for families with income below the regional subsistence level |
| Kostroma region and Kostroma city | 4500 rub. if the average per capita income of family members is below the subsistence level in the region | none |
| Kurgan region and Kurgan city | none | 40,000 rub. at the birth of twins |
| Kursk region and Kursk | none | 2000 rub. monthly |
| Leningrad region and St. Petersburg | RUB 39,788 (Saint Petersburg) | 4285 rub. monthly for a low-income family until the child is 1.5 years old (St. Petersburg) |
| Magadan region and Magadan city | 15,000 rub. for women from the indigenous population of the North. | 30,000 rub. at the birth of twins |
| Moscow region and Moscow | 20,000 rub. for a low-income family; 14,500 rub. (in Moscow); RUB 113,120 parents under 30 years of age (in Moscow) | 70,000 rub. at the birth of twins in a family with an income of less than the monthly minimum in the Moscow region for each member |
| Murmansk region and Murmansk | none | RUB 26,772 at the birth of twins |
| Nizhny Novgorod region and Nizhny Novgorod | 8000 rub. families who are financially insecure | 25,000 rub. regional maternity capital |
| Novgorod region and Veliky Novgorod | none | 200,000 rub. for twins to improve living conditions |
| Novosibirsk region and Novosibirsk | 12,000 rub. if parents are not older than 30 years old | 5000 rub. at the birth of twins |
| Omsk region and Omsk | none | 20,000 for the birth of twins |
| Orenburg region and Orenburg city | none | 50,000 rub. at the birth of twins |
| Oryol region and Orel | none | RUB 693.08 monthly payment for the second child of a single mother |
| Penza region and Penza city | none | RUB 22,680 at the birth of twins |
| Ryazan region and Ryazan | none | 10,000 rub. low-income families at the birth of twins |
| Samara region and Samara city | none | 50,000 rub. at the birth of twins |
| Sakhalin region and Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk | none | RUB 229,754 regional material capital. |
| Sverdlovsk region and Yekaterinburg | none | 10,000 rub. at the birth of twins |
| Tula region and Tula city | RUB 11,826.19 | 21,866.82 for the birth of twins |
| Ulyanovsk region and Ulyanovsk | 2000 rub. | 50,000 rub. regional capital 10,000 rub. at the birth of twins. |
| Chelyabinsk region and Chelyabinsk | 3000 rub. | none |
| Yaroslavl region and Yaroslavl | RUB 5,677 | RUB 42,720 at the birth of twins |
Republican benefits
| Adygea and Maykop | 1,600 rub. | |
| Bashkortostan and Ufa | none | 1000 rub. monthly for twins born until the children are 3 years old, paid to a family with an income for each family member less than the republican minimum monthly wage. |
| Dagestan and Makhachkala | none | 20,000 rub. at the birth of twins |
| Karelia and Petrozavodsk | 3000 rub. | none |
| Crimea, Simferopol and Sevastopol | RUB 27,466.9 (Sevastopol) | none |
| Tatarstan and Kazan | none | 200,000 rub. (but not more than the balance of the mortgage loan debt) Republican maternity and mortgage capital |
| Udmurtia and Izhevsk | none | 15,000 rub. at the birth of twins |
*The table shows only special benefits specifically for the second child. General purpose support, which is provided for both the second and other children, is not indicated.
As you can see, many regions do not provide subsidies for children (Amur, Arkhangelsk, Astrakhan, Belgorod, Volgograd, Voronezh, Ivanovo, Kaliningrad, Lipetsk, Rostov, Saratov, Smolensk, Tambov, Tver, Tomsk, Tyumen regions, as well as Altai, Buryat, Ingush , Kabardino-Balkarian, Karachay-Cherkess, Kalmyk, Komi, Mari El, Sakha, Mordovian, North Ossetian, Tyva, Khakassia, Chechen, Chuvash republics).
Monthly payments after the birth of the 3rd child
In addition to the lump sum, after the birth of the third child, many regions assign the family a monthly allowance. In some areas it is prescribed regardless of the financial situation and age of the spouses, in others its size depends on one or both factors.
This benefit can be paid only for the last child or for all other children (poor) until they reach one and a half, three or seven years of age.
The specific amount depends on the region. For example, any large family in Kaliningrad is paid 9,321 rubles. Low-income families in Murmansk receive 16,130 rubles, and parents of triplets in Yaroslavl receive 28,248 rubles. In all cases, payments stop after 3 years.
How to challenge a refusal
If money does not arrive in the parent’s bank account for a long time, then the benefit was either refused or the payment did not go through due to technical reasons.
To find out how to receive gubernatorial payments, you should first call the specialist who accepted the documents and find out who the executor is on your application. And find out the true reason for the lack of funds from the relevant official.
If the reason is a technical/organizational problem, then ask that your issue be put under control.
If it was a refusal, request a written decision on the refusal. This refusal must be carefully studied. If the decision is unlawful, it should be appealed in court.