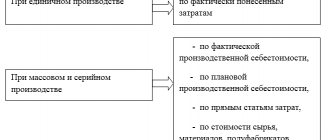
Conditions: mandatory and initiative
The rules of conduct are determined by the business entity itself, except in cases where such an inspection is mandatory. Cases of mandatory inspection are given, for example, in paragraph 27 of Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 34n. Thus, it is imperative to check the composition and value of the company’s assets and debts:
- before starting the preparation of annual financial statements;
- in cases of theft or damage to property, suspicion of abuse;
- when changing the materially responsible person (hereinafter referred to as the MOL);
- during reorganization or liquidation of the organization;
- in case of natural disasters (fire, flood and other cases of force majeure), etc.
To confirm the safety of property, as well as to verify the actual availability with the data reflected in the records, the management of the organization can at any time initiate monitoring in the interests of the owner. This is especially true for manufacturing and trading companies, where cases of theft are, unfortunately, not uncommon.
Inventory of fixed assets in the budget: drawing up an act on internal assessment of surplus
Fixed assets (FPE) of budgetary organizations are subject to inventory. When it is carried out, the actual presence of fixed assets in the organization is compared with accounting data <*>.
Surplus fixed assets identified during inventory are taken into account at their original cost. It is determined on the date of inventory on the basis of <*>:
— conclusions on their assessment carried out by persons carrying out assessment activities;
— documents confirming the value of similar assets.
In the latter case, when determining the value of an unaccounted fixed asset, an organization can use data on prices for similar assets received in writing from manufacturing organizations, from the media and other information sources. Also in this case, one should take into account the percentage of depreciation of the asset, which is established according to its actual technical condition with the registration of data on assessment and depreciation in the relevant acts <*>.
If a budget organization decides to determine the initial cost of surplus fixed assets without involving appraisers, then in this case we recommend that it draw up an act on the assessment and depreciation of surplus assets identified during the inventory (hereinafter referred to as the assessment act). The specific form of such an act has not been established. The organization develops it independently.
Let's look at the procedure for drawing up an assessment report using an example.
Example
As of 10/19/2018, an inventory was carried out at the State Educational Institution “Secondary School”, during which surplus OS was identified - a used metal archival cabinet. According to the price list of a trade organization, the cost of a new cabinet of a similar model is 350 rubles. Taking into account depreciation, determined at 10%, the organization’s commission decided to value this object at 315 rubles.
When developing the form of an assessment report, you can use the following sample:
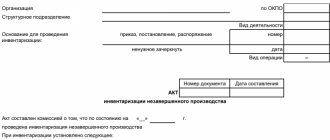
| State Educational Institution "Secondary School" I APPROVED (name of organization) Director Samsonov Samsonov V.V. (position) (signature) (last name, initials) October 19, 2022 ACT on the assessment and depreciation of surplus assets identified during inventory, dated October 19, 2022 A commission consisting of: chairman - Bessonova A.S., commission members: Schetova V.P., Yablokov A.V., assessed and determined the depreciation of the following assets identified during the inventory as of 10/19/2018:
Chairman of the commission: Deputy Director Bessonova Bessonova A.S. (position) (signature) (last name, initials) Members of the commission: accountant V.P. Schetova. (position) (signature) (last name, initials) electronics engineer Yablokov Yablokov A.V. (position) (signature) (last name, initials) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Note The form of the assessment report is given as an example. You can use it as a basis when developing your own form.
Objects to be checked
When comparing data, the presence of completely different assets and liabilities of the company can be analyzed. Here are the most common objects (liabilities):
- fixed assets (buildings, structures, equipment, transport, inventory, etc.);
- intangible assets (exclusive rights to software products, trademarks, etc.);
- goods;
- components and materials;
- products;
- funds (cash, in accounts with credit institutions);
- the amount and terms of debts and obligations.
MOLs are responsible for the safety of material objects: storekeepers in warehouses, cashiers, and other responsible persons. When hired, such employees sign an agreement on full financial responsibility for the property entrusted to them.
Obtaining printed forms for the inventory report
If you need to print an inventory report, this can be done through the Export / Import
on the top toolbar.
Printable forms are available in the following formats:
- Inventory results.
- Inventory form.
- Collation statement.
Files are uploaded in xls format. For printing and editing, you must use Microsoft Excel or any other editor that supports this format.
Order of conduct
The decision to conduct data comparison in any case is made by the management of the organization. This decision is formalized by an order, which indicates information about the inspection being carried out:
- objects;
- deadlines;
- site (dislocation);
- members of the inventory commission;
- chairman
The order form can be downloaded below.
Before the start of the inspection, the MOL submits a receipt to the accounting department stating that all documents confirming the receipt and expenditure of the property entrusted to them have been transferred in full (clause 2.4 of Order No. 49 of the Ministry of Finance). During the process, inventory records are compiled, which are then transferred to the accounting department to reconcile actual data with accounting data. If discrepancies are detected between actual and accounting data, the reasons for the discrepancies are identified. These may include:
- re-grading of goods;
- defect not written off in a timely manner;
- deviations from technological write-off standards (with the standard accounting method);
- errors in acceptance and deregistration;
- theft, incl. theft.
Based on the results of the inspection, a decision is made to take into account the identified shortages and surpluses. Identified surpluses are taken into account, and shortages are either recovered from the guilty parties, or, if it is impossible to write off from the guilty parties, written off as losses.
Passage mechanism
It all starts with the manager’s order (INV-22 form) to begin this procedure. A commission is selected. It can consist of both the heads of the institution and external auditors or ordinary company employees, specialists in measuring something, etc.
Each financially responsible person first draws up a receipt stating that the material assets under his control are classified and then written off or capitalized (and transferred for inventory). Employees do this in accordance with clause 2.4 of Order of the Ministry of Finance dated June 13, 1995 No. 49.
The commission begins the process on the appointed day. All persons listed in the order must be present, otherwise the entire event may be declared invalid with all the ensuing consequences.
Documentation of inspection results
In the process of checking the actual existence of objects (obligations), control documents are drawn up, which differ depending on the object. The organization has the right to independently develop forms of control documents or use standardized forms approved by Resolution 88 of the State Statistics Committee.
The results are presented:
- inventory records, which reflect the actual availability and quantity;
- matching statements, where discrepancies between fact and accounting data are indicated.
Control of inventory, fixed assets and cash
You can download a sample act of inventory of shipped inventory items and a sample act of inventory of fixed assets (unfinished repairs) at the end of the article.
It is recommended to inventory cash more often in case of significant movement of funds. To do this, use the form for checking funds at the cash desk.
- The cash register inventory report can be found in the appendix to the article. There is also a sample of filling out a cash inventory report.
Debt control
Verification of obligations is carried out to determine current, overdue debt, debt that is unrealistic for collection, among:
- buyers and suppliers;
- creditors (debtors) and other persons.
The results are documented in writing - see Sample of an inventory report of receivables and payables.
More information about the unrealistic debt of liquidated counterparties, as well as debt for which the statute of limitations has expired, can be read in the response of the Ministry of Finance.
Control of intangible assets
Occurs with the registration of INV 1-a form. If discrepancies are identified based on the results of the audit, a comparison sheet INV-18 is drawn up.
Completion
To record the results of control checks on the correctness of monitoring, a report on the results is drawn up. To find out the rules for filling it out, see Sample of filling out an act on inventory results.
Inventory order
Inventory report of shipped inventory items
Inventory report of fixed assets (unfinished repairs)
Cash inventory report (form)
Cash inventory report (filling sample)
Inventory report of receivables and payables
Form INV 1-a
Form INV-18
Statement of results (form)
When the act of inventory results is applied f. 0504835
The document is used in various commercial organizations, private and government institutions. The form is suitable for inventorying non-financial and financial assets.
Conventionally, the inventory process can be divided into several stages:
- First, the head of the company issues an order in which he appoints and approves members of the inspection team.
- Accounting balances and primary documents that will be needed for verification are drawn up. Other similar work related to preparation for inventory is being carried out.
- Financially responsible employees properly draw up a receipt. Thus, they confirm the actual existence of the property for which they are responsible.
- A direct inspection is carried out, in which each member of the commission must take part.
- Entering the results obtained into the relevant act.
If a mistake was made when drawing up the act, it is easier to start filling out a new document. Although the law allows corrections to be made in this case. But they need to be done correctly. So, incorrect information needs to be crossed out with one line. The information above is correct. After this, all members of the review team must sign their autographs next to the correction. The financially responsible employee must also confirm with his signature that the correction took place in his presence. You should not leave empty columns. If for some reason there is nothing to write in them, it is necessary to put dashes.
( Video : “Procedure for carrying out inventory, accounting for surpluses and shortages”)
Condition for taking inventory
The commission must include a representative of the management team. It is also allowed to involve third-party specialists. Before starting the inspection, the employee who is financially responsible must give a receipt. This way he confirms that the property under his responsibility is in perfect order.
Important conditions for conducting an inventory include the presence of all members of the inspection team. In the absence of anyone, the act is considered invalid; accordingly, the results of the inspection cannot be called correct. All information is entered into the act, which must have at least two copies. In some cases, the number of copies may be increased.
The Methodological Recommendations describe methods that can be used during verification. Commission members have the right to independently choose suitable options that will allow them to obtain complete information about the property being inspected.
As a rule, the basis for filling out the act is an inventory of property, which is drawn up for individual areas and responsible persons. You can often encounter a situation where actual property differs from accounting information. In this case, the act is still drawn up. However, as a supplement to it, a special statement is drawn up, which is intended to display the existing discrepancies. Together with the corresponding inventory, these documents officially record the discrepancies found. Here you can clearly see for which position shortages or surpluses have been identified. There can be quite a few reasons, from basic mistakes to theft.
Often inventory is carried out for quite a long time with breaks for lunch. In such situations, during the absence of a commission, the property should be stored in a safe or room to which unauthorized persons do not have access. It is customary to seal such rooms at night.
( Video : “How to reflect inventory results in 1C?”)