We are accustomed to calling advance payment of wages an advance payment of wages. As a rule, employers, when paying an advance, do not think much about the correctness of setting its size, compliance with the deadline and procedure for payment. And some do not pay it at all, limiting themselves to one salary payment per month. Meanwhile, the advance is the same salary, only for half of the month worked. According to the Labor Code, it is mandatory to pay it. At the same time, it is also necessary to correctly establish its size, term and conditions of payment. We will talk about the rules for paying an advance on wages, the procedure for reflecting it in accounting, as well as the need to calculate personal income tax on its amount in this article.
Mandatory advance payment
The obligation to pay an advance on wages is indicated by Art.
136 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. According to its provisions, wages must be paid at least every half month. Thus, paying wages once a month is a violation of labor laws. Administrative liability is provided for violation of labor legislation.
It should be borne in mind that the employee’s statement of consent to receive wages once a month does not relieve the employer from liability. Rostrud specialists draw attention to this in Letter No. 472-6-0 dated 03/01/2007.
Provisions of Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation are imperative, that is, mandatory for execution. Labor legislation does not provide for any exceptions to the established rule. It does not matter where a person works: at his main place or part-time. Thus, in relation to part-time workers, the employer is also obliged to pay wages in two parts: advance and payment (Letter of Rostrud dated November 30, 2009 No. 3528-6-1).
Advances to newly hired employees - what and where do we prescribe?
Include the deadlines for advance payments to newly hired employees in the PVTR (or other local act) in one section describing the salary deadlines common to the entire team.
The following example can be used as a sample.
Example
At Tekhnostroyprom LLC, all salary nuances are reflected in the Regulations on Remuneration. Based on the modern wording of labor legislation, the company decided not to use the term “advance” and determined that salaries would be paid twice a month.
At the same time, for newcomers in the first month of work, special terms for payment of wages are provided, allowing:
- comply with the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation to pay wages at least every half month (more often is possible, less often is not possible);
- gradually (without prejudice to newcomers and the employer) transfer newcomers to the regular payment schedule provided by the company, without violating the requirements of labor legislation.
Excerpt from the Regulations on remuneration of Tekhnostroyprom LLC:
3.1. Salaries at Tekhnostroyprom LLC are paid:
- 20th day of the current month - for the 1st half of the billing month;
- 5th day of the next month - for the 2nd half of the billing month.
3.2. Deadlines for issuing salaries in the first month of work for newly hired employees:
| Calendar dates for employment | Deadline for first salary payment |
| From 1st to 14th | 15th - exclusively for newly hired employees |
| From the 15th to the 19th | 20th - at the same time as all employees |
| From the 20th to the end of the month | 5th - on the general deadline for salary payments |
3.3. Subsequent wage payments are made within the deadlines established by Tekhnostroyprom LLC, specified in clause 3.1.”
You can see the full text of the Regulations on remuneration of Tekhnostroyprom LLC at the link below:
Find out about local acts that help in your work from the following materials:
- «Regulations on business trips - sample»;
- “Regulations on the occupational safety and health management system - sample”;
- “Regulations for working with accounts receivable - sample”.
In addition to the deadlines, the local act may also contain an indication of the algorithm for calculating the amount of each salary payment, including the advance payment for the first month of work.
Deadlines for payment of wages
According to the new[1] version of Art.
136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in force since October 3, 2016, the specific date for the payment of wages is established by internal labor regulations, a collective or labor agreement no later than 15 calendar days from the end of the period for which it was accrued. If the payment day coincides with a day off or a non-working holiday, wages are paid on the eve of this day (Part 8 of Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
For example, an advance for the first half of August cannot be paid later than August 30, and wages for the second half (calculation) cannot be paid later than September 15.
Thus, the Labor Code contains a requirement for the maximum permissible period of time between payments of parts of the salary while regulating specific terms for its payment at the employer level.
For incorrectly setting the deadline for paying the advance, as well as violating it, the employer will have to pay a fine.
Setting the advance amount
Often the amount of the advance is set at a certain integer, constant value.
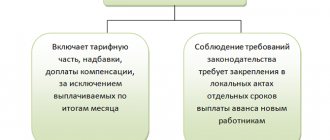
Moreover, for some, this value is approximately 40% of the total salary for the month, for others - 30%, etc. According to the author, since the advance is the same salary, only for the first half of the month, it is impossible to formally approach the establishment its size.
Despite the fact that the Labor Code does not regulate the specific amounts of the advance, specialists from Rostrud and the Ministry of Labor note: when determining the amount of wage payment for half a month, the time actually worked by the employee (the work actually performed by him) should be taken into account (letters dated 02/03/2016 No. 14-1/ 10/B-660, dated 09/08/2006 No. 1557-6).
Thus, with the advance method of calculating wages for each half of the month, wages should be accrued in approximately equal amounts (Letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated February 25, 2009 No. 22-2-709).
Based on the above, the advance payment should be set in the amount of wages accrued for the days worked in the first half of the month based on the submitted time sheet. Since the amount of wages varies from month to month, the amount of the advance cannot be a constant, round amount.
We fix “salary” deadlines
Determine the dates of the first and second salary payments yourself. For example, you can set the numbers 30 (31) and 15 (16) respectively - officials consider this option optimal (letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated February 25, 2009 No. 22-2-709).
Download the salary slip form here.
Don’t forget about newcomers - it is also important for them to set the deadline for their first salary, and it may not coincide with the dates established by the company.
Make a description of salary aspects in a local intra-company act - this could be PVTR (internal labor regulations), regulations on remuneration, collective agreement, etc.
The following publications will introduce you to internal local acts that include “salary” aspects:
- “Internal labor regulations - sample 2022”;
- “Regulations on incentive payments with performance criteria.”
See below for specific wording on how to set wages.
Other conditions for advance payment
Otherwise, the same conditions apply to the payment of the advance as for the payment of monthly wages.
Let us remind you that according to Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, wages are paid to the employee, as a rule, at the place where he performs the work or is transferred to the credit institution specified in the employee’s application, under the conditions determined by the collective or labor agreement. The employee has the right to change the credit institution to which the salary should be transferred by notifying the employer in writing about the change in the details for transferring the salary no later than five working days before the day of its issue.
The amount of the advance paid (as a component of wages) is indicated in the payslip, the form of which is approved by the employer, taking into account the opinion of the representative body of employees.
Preliminary steps before charging an advance
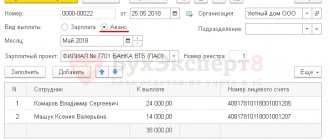
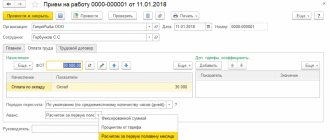
The accrual for the first half of the month is traditionally called an “advance”. This is an operation by the time it is calculated, all personnel changes that occurred during the first half of the month (hires, transfers and dismissals of employees), changes in salaries and other planned accruals must already be entered into the program, all one-time accruals must be reflected and all employee absences for the first half of the month must be recorded. .
In this article we will not consider in detail how to reflect all the events that occurred during the first half of the month in the information base 1C 8.3 ZUP 3.1; if necessary, you can find this information in the articles listed below, posted in the public domain, as well as in the materials of the ZUP portal rubricator BukhExpert8 for commercial subscribers. We will imagine that all these steps have already been completed, and now we need to accrue and pay an advance to employees.
How to correctly register personnel events, one-time accruals and employee absences - see the publications:
- Hiring in ZUP 3.1 - step-by-step instructions
- Changing the work schedule in ZUP 3.1 - step-by-step instructions
- Change of salary in ZUP 3.1. - step-by-step instruction
- Dismissal of an employee in ZUP 3.1 - step-by-step instructions
- Calculation of vacation pay in ZUP 3.1 - step-by-step instructions
- Sick leave in ZUP 3.1 - step-by-step instructions
- Parental leave in ZUP 3.1. - step-by-step instruction
- One-time charges in ZUP 3.1
- Financial assistance in ZUP 3.1
And in order for you to always follow the correct procedure when calculating the advance in ZUP 3.1, we have prepared for you a Memo on calculating the advance in 1C:ZUP 3.
Responsibility for violating the terms of advance payment
Violation of the deadline for paying advance wages, establishing its amount, as well as other payment conditions provided for by labor legislation, entails the imposition of an administrative fine under Art.
5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. It is worth noting that from October 3, 2016, Federal Law No. 272-FZ dated 07/03/2016 introduces a separate fine for violating the terms of payment of wages (including advance payments) in the amount (clause 6 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation):
– from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles. in relation to officials;
– from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles. in relation to legal entities.
For a similar repeated offense, liability will be increased. The official faces a fine of 20,000 to 30,000 rubles. or disqualification for a period of one to three years, for a legal entity - a fine of 50,000 to 100,000 rubles. (clause 7 of article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
For other violations of labor legislation (including violations of the conditions for payment of advance payments) the following is provided (clauses 1, 2 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation):
a) in the case of a primary violation:
– fine from 1,000 to 5,000 rubles. (for officials);
– fine from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles. (for legal entities);
b) in case of repeated violation:
– fine from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles. or disqualification for a period of one to three years (for officials);
– fine from 50,000 to 70,000 rubles. (for legal entities).
conclusions
The timing of payment of advances and wages in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is established in such a way that payments to employees are made at least once every 2 weeks. The procedure for calculating the advance payment is not directly defined by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Government authorities recommend issuing an advance based on the actual time worked in the first half of the month. When setting the advance as a percentage, according to officials, the advance and payment at the end of the month should be comparable in amount. Personal income tax is not withheld when an advance is issued, but if the advance is issued on the last day of the month, disputes may arise with the tax authorities.
Accounting (budget) accounting of advance payment transactions
Not so long ago, account 0 206 11 000 “Calculations for advances on wages and accruals for wage payments” was introduced into the charts of accounts of accounting (budget) accounting of state (municipal) institutions, as well as instructions for their use, in particular:
– to the Unified Chart of Accounts and Instruction No. 157n[2] – by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 01.03.2016 No. 16n;
– in the Chart of Accounts of Budget Accounting and Instruction No. 162n[3] – by orders of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 08/17/2015 No. 127n and dated 11/30/2015 No. 184n;
– in the Chart of Accounts for accounting of budgetary institutions and Instruction No. 174n [4] – by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 31, 2015 No. 227n;
– in the Chart of Accounts of Autonomous Institutions and Instruction No. 183n [5] – by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 31, 2015 No. 228n.
This account has been in use since 2016.
By virtue of clause 202 of Instruction No. 157n, account 0 206 00 000 takes into account settlements for advance payments provided by the institution in accordance with the terms of concluded agreements (contracts), agreements (except for advances issued to accountable persons). At the same time, it is not specified which agreements we are talking about. Thus, the provisions of this paragraph can be fully extended not only to civil contracts concluded with suppliers (contractors, performers), but also to employment contracts concluded with employees of an institution, which stipulate the conditions for the payment of advance wages.
With the introduction of account 0 206 11 000 in instructions No. 162n, 174n and 183n, only one accounting entry was added for its use - an entry to reflect the employee’s wage arrears arising from the recalculation of wages previously paid to him (Account debit 0 302 11 000 / Credit accounts 0 206 11 000). This accounting entry is prepared using the “red reversal” method.
The question arises: is it necessary to use this account for the generally accepted (monthly) payment of advance wages, since there are still no such entries in the specified instructions?
According to the author, in order to put into practice the additionally introduced accounting entries for accounting in account 0 206 11 000 of the amounts of excess wages accrued, institutions must initially reflect the payment of advances on wages in this account. Based on this, operations for the calculation and payment of wages must be accompanied by the following accounting entries:
| Contents of operation | State and budgetary institutions | Autonomous institutions | ||
| Debit | Credit | Debit | Credit | |
| Advance payment of wages for the first half of the month was paid | 0 206 11 560 | 0 201 34 610 0 201 11 610 (only for budgetary institutions) 0 304 05 211 (only for government institutions) 0 201 21 610 | 0 206 11 000 | 0 201 11 000 0 201 21 000 |
| Monthly salary accrued for actual hours worked | 0 109 00 211 0 401 20 211 | 0 302 11 730 | 0 109 00 211 0 401 20 211 | 0 302 11 000 |
| The advance has been offset | 0 302 11 830 | 0 206 11 660 | 0 302 11 000 | 0 206 11 000 |
| An overpayment of wages was identified as a result of recalculation (in terms of amounts subject to deduction from future wage accruals with the consent of employees). The posting is reflected using the “red reversal” method | 0 302 11 830 | 0 206 11 660 | 0 302 11 000 | 0 206 11 000 |
Taking into account the current ambiguous situation with the reflection in accounting (budget) accounting of transactions for the payment of salary advances, we recommend that the use of account 0 206 11 000 for these purposes be agreed upon with the founder and fixed in the accounting policy.