The essence of balance sheet profit and its calculation
Balance sheet profit can be briefly described as profit from all activities before taxes. A certain period is taken into account, usually a year or a quarter.
How is the balance sheet profit indicator ?
From the above, we can determine the general formula for balance sheet profit (loss):
PB = Pr + Pim + Pvnro, where:
- PB – balance sheet profit (loss);
- Pr – part of the profit received from the sale of products (goods, works, services);
- Pim - part of the profit received from the sale of property;
- Pvnro – part of the profit formed by non-operating operations.
If one of the component indicators is determined to be unprofitable, it is taken with a minus, not a plus.
How is retained earnings (uncovered loss) ?
In the financial statements (“Income Statement”), balance sheet profit is reflected on line 2300. To calculate it, you must:
- sum lines 2200, 2310, 2320, 2340;
- Subtract lines 2330, 2350 from the result obtained.
The financial result from sales, income from participation in other organizations, interest to be received, and other income are summed up. Interest payable and other expenses are deducted. If the result is negative (loss), it is indicated in parentheses.
Reflection of balance sheet profit in statutory reporting
If the term “balance sheet profit” itself is present, there is no line in the balance sheet with this name, which has its own justification and logic.
The organization's balance sheet presents aggregated indicators of the organization's assets and liabilities as of a specific reporting date according to the accounting registers. An organization's balance sheet profit is an indicator that accumulates on an accrual basis throughout the year, but is completely exhausted at the reporting date, being, according to accounting rules, allocated to accounts for taxes payable and accounts for net (retained) profit.
Consequently, on the reporting date in the balance sheet of the enterprise in an expanded sense (if we present it as a list of all accounts indicating the balances on them), the balance sheet profit will already be distributed and equal to zero, as will be the zero line with the same name in the balance sheet as a reporting form, if that was used.
The indicator “balance sheet profit” can be calculated using the formula from both the interim and final balance sheet data, and from accounting data using the formula:
What does the indicator consist of?
The profit formula shows three possible sources of its receipt. Let's look at them in more detail:
- Profit from sales of products (Pr). It is formed from revenue for goods, works, services, reduced by costs. These include production and sales costs, as well as tax deductions (VAT, excise taxes, export tariff payments, and other similar payments). In essence, this is the company’s net income, which can vary significantly and which can be effectively influenced by management decisions. The other two elements of the formula represent, as a rule, previously created income and their movement.
- Profit from the sale of property (Pim). As a rule, we are talking about the sale of fixed assets and property. Sales proceeds are reduced by sales expenses (transportation, payments to intermediaries, etc.) and by the residual value. In addition to fixed assets, the property sold may include any tangible assets belonging to the company, intangible assets (patents, trademarks). Profit from sales here will be determined by the difference between the selling price and the book value, adjusted for selling expenses.
- Non-operating income and expenses form the third component of balance sheet profit (Pvnro). This takes into account, summing or subtracting accordingly, income from financial investments in the capital of other companies, from bonds, income from rental premises; as well as expenses for fines, penalties, penalties for counterparties, losses, legal costs, etc.
Components of balance sheet profit
The main items of balance sheet profit are profits or losses from:
- Sales of manufactured products.
- Actions aimed at generating profit other than the main activity.
- Secondary implementation actions.
Of the listed items, the main one is the sale of manufactured products, since this item accounts for from 65% to 88% of the organization’s main profit.
It is formed throughout the entire period of activity. In an example it looks like this:
- The company is a manufacturer of a certain category of goods, their sale is considered gross (main) income. The final balance calculation amount will be the difference between the selling price (cost) and the purchase price (store price).
- Secondary actions for the sale and receipt of profit are considered to be actions for the sale of tangible property owned by the enterprise. These actions also include the sale of parts of the leading fund, various materials, fuel and raw materials. Sales of products, as mentioned above, are the main type of income. In addition to it and the secondary one, there is a 3rd type that forms balance sheet profit.
- Non-realization actions or actions different from the main ones. Their profit comes from incoming income from renting out their own premises, investments in other enterprises, and foreign exchange differences. In case of legal proceedings, fines, penalties, and penalties are also considered non-sales income.
Why are calculations needed?
Accounting records serve as a reliable basis for calculating the indicator and assessing the performance of the company for the period. Both the managers of the company itself and its investors, current and potential, are interested in obtaining data characterizing balance sheet profit.
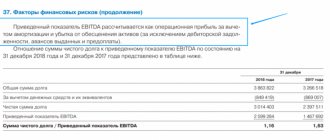
Consideration of the indicator in dynamics helps to determine how much the efficiency of the business entity has increased or decreased. By analyzing the components of profit, one can see promising directions for its receipt, factors that prevent an increase in volume, which contributes to making effective economic decisions.
For example, a decrease in profit from sales of core products may indicate:
- about the ineffective work of sales managers;
- about the fall in market prices for products;
- about a drop in demand for certain goods, works, and services.
Note! Based on accounting profit, another important indicator is calculated - net profit, the commercial efficiency of an economic entity. Net profit = book profit – income tax payable.
Taxation
Before taxes, the calculated profit includes all the costs that the company incurred during a certain period. It also includes other profits with deducted expenses for their implementation. After summing up, interest is calculated on this profit according to the tax burden.
In addition, it is worth understanding that the balance sheet profit already includes expenses for insurance premiums and deductions of wages to employees. Before taxation, income taxes and other duties, fees and taxes are assessed. In isolated situations, the company includes in its balance sheet profits the costs incurred associated with the payment of these contributions for previous periods.
Income before taxation reflects the entire financial result of the company for the specified period. It includes all items of expenses and income for all types of activities, including non-operating ones. The need for such a calculation is that there is no tax burden on it, since it is an informative tool for further development of a development strategy.
Profit is a necessary financial resource and at the same time a tool for the productive development of any industry in business. Correctly calculated balance sheet profit will help an owner of any level from individual entrepreneurs and above to understand and correct any deviations in the income component, assess the profitability of their business and stay afloat in conditions of high competition and external economic factors in the market of goods and services.
>Formula for balance sheet profit
Balance sheet profit and specifics of activity
It is obvious that the sources of balance sheet profit will primarily depend on the nature and type of core activity, on the goods, works and services sold and the proceeds for them. For example, trading revenue is nothing more than the gross income from the sale of goods.
Gross income is defined as the difference between the purchase and sale prices of goods sold and represents a markup or discount on the goods.
An enterprise providing services, for example, a repair company, will consider revenue as payment for its services according to tariffs, and a manufacturing company will reflect the money received for its products from customers as revenue.
The specifics of expenses also have an impact. Example: the costs incurred in construction will differ from the costs of an agricultural enterprise or an audit firm.
Briefly
- Balance sheet profit (accounting profit, profit before tax) is calculated using a formula that includes profit from sales of products, profit from the sale of property and other non-operating profits.
- The result obtained with a minus sign means a loss.
- Balance sheet profit is reflected in the financial statements in the income statement on line 2300.
- The composition and amount of balance sheet profit are directly related to the company's core activities.
- Balance sheet profit is one of the most important indicators of financial analysis of a company. It is analyzed both in composition and in dynamics.
- This information is used both within the company itself to make balanced management decisions, and by external users - investors, counterparties.
Distribution and increase
The distribution and increase in balance sheet profit characterizes its profitability. The entire analysis of studying the positive economic growth of an organization is aimed at determining financial efficiency. Profitability calculation determines whether a company is using its resources effectively depending on its field of activity.
Profitability assessment is an effective tool in calculating the profitability of products, industries and various assets.
For each type of income there is a profitability formula. The data obtained on the basis of these formulas is needed to draw up the direction of the company’s development, its effectiveness or identify weaknesses in the production and sale of products.
Such calculations are divided into types that are based on spending policies, volumes of resources and specializations of profit. All data is taken on the basis of accounting reports, pricing policies and product costs, gross income and various financial expenses associated with the activities of the enterprise.
Calculation of the profitability of the main activity is responsible for the cost part and actions responsible for the sale of manufactured goods. Calculations are carried out to assess the liquidity of one ruble spent for the sale of goods. Also, the difference between the income from the sale and the total amount of its cost, which includes items of commercial expense, services sold and costs for administrative needs, is determined.
The resulting result from the calculations allows the company to autonomously cover the costs of the income component.
Calculating the profitability of a current asset determines the income received from all assets contributed to them, and determines whether they are being used effectively.
Both the components of net profit and its balance after tax plus asset turnover are determined. The results of calculations using this formula show the company’s ability to provide the required amount of profit in relation to the working capital used.
If this value increases, it means that working capital is used in a positive direction.
Return on sales is calculated using a coefficient that denotes net profit. The result of the calculation shows the financial result of the activity in general, which may depend on 2 lines of the income profitability indicator: profitability of sales of gross output and operating profitability in terms of the amount in net profit.
Calculation of cost profitability determines whether the funds spent on the production of goods are recouped. The result shows an assessment of the effectiveness of invested funds on costs.
Which accounting entry reflects profit from the sale of products?
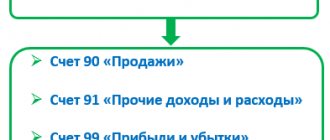
To account for income and form the cost of goods sold, work or services, account 90 “Sales” is used. Depending on the type of activity and the specifics of the organization’s work, the entries to reflect the receipt of revenue and write-off of expenses may differ. But the reflection of profit or loss from sales will be the same regardless of what activity the company conducts.
To properly understand how profit from sales is formed, it is best to analyze which turnovers fall into the 90th account:
- Revenue is reflected by posting Dt 62 Kt 90.1. But in retail trade, the wiring will look like Dt 50 Kt 90.1 or Dt 57 Kt 90.1.
- The cost of services and work is written off with such entries as Dt 90.2 Kt 20 (23, 26, 25, etc.). In wholesale trade, the cost of goods will be written off using the operation Dt 90.2 Kt 41, and sales expenses - Dt 90.2 Kt 44. In retail, you additionally need to take into account the markup Dt 90.2 Kt 42. And in production, the cost of finished products will be written off using the entry Dt 90.2 Kt 43.
- VAT for any type of activity will be charged by posting Dt 90.3 Kt 68.
- Profit from sales will be reflected in the accounting record Dt 90.9 Kt 99.
- The loss from sales will be reflected by the posting Dt 99 Kt 90.9.
IMPORTANT! In some accounting programs, subaccount numbers may differ from the Chart of Accounts approved by the Ministry of Finance. In addition, the organization can change, delete or introduce additional sub-accounts independently if required by the specifics of its activities.
The amount of the posting in correspondence with account 99 will be equal to the profit or loss received from the sale. That is, the amount of revenue minus cost, VAT and excise taxes, if any. If the calculation is correct, the collapsed (without analytics) balance of account 90 should become zero at the end of the period. The presence of a balance will mean that the formation of the entry for writing off profit (loss) was made with an error.
When reforming the balance, it is necessary to close the 90th account. This event involves writing off the balance of all subaccounts to account 90 to account 90.9. These can be operations such as (if there is turnover during the year):
- Dt 90.1 Kt 90.9 - for writing off revenue turnover during the year;
- Dt 90.9 Kt 90.2 - for writing off turnover at cost;
- Dt 90.9 Kt 90.3 (90.4) - for writing off turnover based on accrued VAT or excise taxes.
The balance on account 90.9 (as well as on account 90 as a whole) should become zero automatically after the above operations. If this does not happen, you should look for an error in the wiring.
Read more about balance sheet reformation in the material “How and when to carry out balance sheet reformation.”
New definition of current income tax
Current income tax is the amount that is actually payable to the budget.
It is determined based on the income tax base. The income tax base is determined as the difference between income and expenses. Until 2022, the current income tax was calculated from profit according to accounting data, adjusted by the amount of PNA (PNA) and the amount of change in IT (ONA). In 2022, the current income tax is the amount of tax calculated in accordance with the Tax Code.
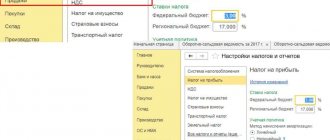
Now only the norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are taken as a basis. To calculate income tax, the tax base is multiplied by the tax rate.
The basic tax rate is 20%: 3% to the federal budget, 17% to the regional budget.
The main thing is to correctly determine the tax base.
Let us remind you that income tax income is determined on the basis of Articles 249, 250, 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, expenses - 253, 265, 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
They contain lists of income and expenses from sales, non-operating income and expenses that are included in the tax base. It also lists costs and revenues that are not taken into account when calculating the tax base.
Read in the berator “Practical Encyclopedia of an Accountant”
Income not subject to income tax
What expenses are not taken into account?