Net profit indicator: who, where and why calculates it
Net profit and commercial activity are inextricably linked concepts.
For the sake of profit, new production facilities are created, material and labor resources are intensively used, and effective ways are sought to increase the profitability of commercial activities. Net profit is one of the important final performance indicators of any company. Not only the management and owners of companies are interested in obtaining net profit. Good net profit indicators attract new investors, contribute to making positive decisions on issuing loans to the company, as well as strengthening the company’s authority in market conditions.
It is net profit that allows firms to develop their material base, invest in expanding production, improving technology and mastering advanced techniques and methods of work. All this leads to the company entering new markets, expanding sales volumes and, as a result, an increase in net profit.
Find out how to analyze net profit from the article “Procedure for analyzing net profit of an enterprise.”
Many financial indicators take part in calculating net profit, and the formula for calculating it is not as simple as it seems at first glance. In the accounting records of any company, net profit is reflected in line 2400 of the financial results statement (OFR), and all indicators in column 2 of this report are involved in determining net profit .
Learn about the structure and purpose of the ODF from this publication.
A detailed algorithm for calculating net profit is given in the next section.
What do they think?
Since EBITDA is not subject to generally accepted accounting standards, the indicator is not included in standard reporting forms. To calculate it, you need to know individual indicators excluding VAT. For example:
- operating profit size;
- labor costs;
- taxes on transport, land, property and similar fees.
EBITDA can be adjusted for other expenses and income. The calculation may take into account exchange rate differences, sales of capital assets, etc.
EBITDA reflects the planned or received profit, therefore part of the necessary information is taken from the “Statement of Financial Results” or from the “Budget of Income and Expenses”.
The difficulty of using classical accounting reporting is that depreciation is shown as part of other cost items. Therefore, financial statements are not enough to calculate EBITDA.
Depreciation data is indicated in the explanatory note or in the transcripts to the balance sheet. But the necessary information may not be there. For this reason, it is advisable to approve a specially developed form of profit and loss statement in management reporting, which will allow EBITDA to be calculated without other documentation.
As for the calculation method, different formulas are used for this. The most popular calculation formula is:
EBITDA = revenue – (direct costs + indirect costs) – (labor costs + social taxes, contributions and fees) – operating taxes (excluding VAT and profit tax) + other income – other expenses
Companies can independently choose which expenses and income to include in the calculation. If the calculation methodology changes, the EBITDA value may change significantly. For example, ignoring exchange rate differences on foreign exchange earnings and corresponding losses will overestimate the value of the final indicator.
One of the simplest ways to manipulate EBITDA is to sell products to conditionally controlled entities. Since the calculation does not take into account cash flows, it is not necessary to receive payment from customers.
Subsequently, the debt can be repaid using non-monetary methods. This method is simple because there is no need to withdraw monetary assets from circulation. At the same time, transparency of operating activities is maintained.
Since EBITDA is not a standardized indicator, it is recommended to always clarify what exactly was included in the calculation.
Composition of EBITDA in the financial statements of PJSC Gazprom
EBITDA can also be calculated by reverse calculation from net profit:
EBITDA = net profit + accrued income tax + interest payable + depreciation - income tax recoverable - interest receivable
Let's calculate EBITDA from net profit. The main part of the data can be obtained from the “Income Statement”. Depreciation data is in the “Explanation to the Balance Sheet”. The net profit of the conditional Fortuna LLC for 2022 amounted to 5 million rubles. Income tax payable is 1 million rubles. Accrued depreciation amounted to 500 thousand rubles. Interest on loans and credits received - 800 thousand rubles. There is no interest earned. There were no deviations between accounting and tax accounting and, therefore, no income tax was generated for reimbursement.
Calculation:
5,000,000 + 1,000,000 + 800,000 + 500,000 = 7,300,000 rubles
It follows from the calculation that the organization is able to bear an annual credit burden of up to 7.3 million rubles.
When comparing companies in the same industry, modernized EBITDA is often used. This is how the EBITDAR indicator is used for retail. The value is adjusted to the amount of payment for rented space. A similar indicator is used in the aviation industry, adjusting the result by the volume of payments for aircraft purchased on lease:
EBITDAR = EBITDA + (rental expenses / operating leases)
This approach smoothes out differences in costs for different companies.
In the mining industry, a different adjusted indicator is used - EBITDAX. The cost of development is taken into account here:
EBITDAX = EBITDA + exploration costs
In this case, the difference in cost accounting is ignored. The procedure for recognizing exploration costs differs in the accounting policies of mining companies.
The impact of the company's main performance indicators on net profit
Net profit is a multi-component indicator - this can be seen from the composition of its calculation formula. Moreover, each parameter involved in the calculation is also complex. For example, a company's revenue may be divided into different lines of business or geographic segments, but its entire volume must be reflected in the formula for calculating net profit.
For information on how revenue and gross income of a company are related, see the article “How to correctly calculate gross income?” .
An indicator such as cost may have a different structure in certain companies and have a different impact on net profit. Thus, you should not expect a large net profit if amounts equal to or exceeding the amount of revenue received are spent on the products manufactured by the company (this is possible in case of material-intensive or labor-intensive production or the use of outdated technologies).
The impact on net profit of selling and administrative expenses is obvious: they reduce it. The magnitude of such a reduction directly depends on the ability of the company’s management to rationally approach the structure and volume of this type of costs.
However, even with zero or negative sales profit, which is influenced by the indicators listed above, it is possible to obtain a net profit . This is due to the fact that, in addition to profits from its core activities, the company can earn additional income. This will be discussed in the next section.
The role of other income and expenses in the formation of net profit
Often, the company's core activities do not bring it the desired net profit. This happens especially often at the initial stage of a company’s formation. In this case, the additional income received by the company can be of great help.
For example, you can make a profit from participating in other companies or successfully invest free funds in securities. The income received will help increase net profit. Even a regular agreement with a bank on using the balance of money in the company’s current accounts for a certain percentage will allow the company to receive additional income, which will certainly affect its net profit.
But if a company uses borrowed funds in its work, the interest accrued for using the loan can significantly reduce the net profit - one should not forget about the impact of the fact of borrowing on net profit. The amount of interest on borrowed obligations (even calculated at the market rate) can seriously reduce net income, and in certain cases lead to losses and bankruptcy.
Whether the company's debts can be collected from the chief accountant in the event of bankruptcy, find out by following the link.
A variety of income and expenses not related to the company's core activities have a significant impact on net profit. For example, renting out unused space or equipment can bring good additional income and have a positive impact on your net profit. Net profit will increase if the company's assets that are not used in its activities are sold.
At the same time, we should not forget about the need for constant monitoring of the composition and amount of other expenses - as they increase, net profit decreases. For example, net income may decrease as a result of excessive spending on charity and other similar situations.
We will tell you in this material how to reflect charity expenses in accounting.
How to calculate profit?
Profit is a positive difference between the income and expenses of an enterprise; a negative difference is called a loss. There are different forms of profit: gross, financial, operating, net - they describe different formulas for calculating profit. To analyze business performance, several forms of profit are important, which are calculated sequentially and follow from one another.
To find out the amount of net profit that remains in the hands of the entrepreneur and interests him most, we will carry out a series of calculations.
First of all, we need to know the amount of total revenue for the goods or services of the enterprise, as well as the amount of VAT, excise taxes and other mandatory payments that may be included in the amount of total revenue. This is how we find out the amount of net revenue:
Net revenue = total sales revenue - mandatory payments
Now let's calculate the gross profit, i.e. the difference between net revenue from the main activity and the cost of products or services sold. In manufacturing, trade and services, cost can be calculated differently. A manufacturer may include depreciation on machines, electricity, and employee wages in its cost if their earnings depend on the units produced. Services that sell hourly services may also include wages in the cost of the service. For an entrepreneur, for his own management analysis, it is important to follow the correct and understandable procedure for calculations and decide what indicators he includes in the cost and how he details them in his management analysis:
Gross profit = net revenue - cost
Gross profit is an important indicator. This is the amount of money that must finance the entire business: all taxes, operating costs, staff salaries, utility costs, rent - all the constant payments that the company has from month to month. If we see that the gross profit is enough to provide these regular payments, then the company has passed the break-even point. If the gross profit is not enough for this, then the break-even point has not yet been passed.
Next we take into account operating expenses. These are the costs of maintaining the HR and legal departments, maintenance of non-production premises, business travel and communications, costs of storing products and advertising, interest on loans - all expenses that are not included in the cost of goods or services. This may include the costs of finding partners, concluding deals, expenses for employee training, and force majeure expenses. This is how we find the amount of profit from sales:
Sales profit = gross profit - operating expenses
Now we must take into account other income and expenses that are not related to the subject of the organization’s activities. These are side and even “accidental” funds: from the sale or rental of company assets, profit from joint activities with another organization, interest received for the use of company funds, fines, penalties, penalties. Knowing all these amounts for a period of time, we calculate the balance - that is, the difference in indirect income and expenses. It can be positive or negative. And now we can calculate book profit - that is, profit before tax:
Balance sheet profit = profit from sales + balance of other income and expenses
Finally, we need to figure out how taxes affect profits. We add tax assets and subtract tax liabilities, we get net profit:
Net profit = book profit - taxes
Net profit is the final and most important indicator; it demonstrates the final result of the company’s activities and shows how profitable running this business is. The scale of our plans and the breadth of our actions depend on our net profit. An enterprise can use it to form various funds and reserves, reinvest in production and increase working capital. If the company is a joint stock company, then dividends to shareholders are calculated based on the amount of net profit.
The net profit of an enterprise is an indicator calculated in different ways
Net profit, the calculation formula for which was described in the previous sections, can be determined in another way. For example:
Page 2400 = page 2300 – page 2410
Net profit, the calculation formula for which is given above , is equal to profit before tax minus income tax.
This algorithm for calculating net profit is simplified and can be used, for example, by small enterprises that have the right not to apply PBU 18/02 “Accounting for income tax calculations.”
IMPORTANT! The criteria for small enterprises are given in Federal Law No. 209-FZ dated July 24, 2007 “On the development of small and medium-sized enterprises in the Russian Federation.”
For more information on the criteria for small businesses, see this article.
Information about deferred tax assets and liabilities is generated in accounting and is required to reflect differences arising between tax and accounting accounting.
Results
Net profit is a complex indicator that includes all types of income received by the company, taking into account expenses incurred. If the company's costs exceed the total of sales revenue and additional other income, then we can talk about the absence of net profit and the company's activities are unprofitable.
Net profit allows merchants to expand their business, master new technologies and markets, which, in turn, has a positive effect on the increase in net profit.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Profit from sales of products: posting
The absolute value of the enterprise's profit or loss is formed on account 90. Its subaccounts accumulate the amounts of revenue and the amount of the actual cost. At the end of the reporting interval, sub-accounts are closed, and the final amount of profit from product sales is displayed.
Example
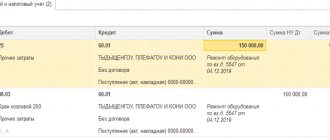
At the end of April 2022, Mak LLC received revenue from customers by bank transfer in the amount of 722,037 rubles, in cash - 38,700 rubles. The total cost of sales for the month amounted to RUB 598,050. Profit from the sale of finished products is reflected through the following set of accounting entries:
- D51 – K62 – payment received for goods to the current account in the amount of RUB 722,037.
- D50 – K62 – the buyer paid for the products in the amount of 38,700 rubles to the cash register.
- D62 – K90.1 – 760,737 rub. (722,037 + 38,700) – revenue from transactions on the sale of finished products is reflected.
- At the next stage, before determining the profit from the sale of products, an entry is made to recognize the cost in the amount of 598,050 rubles. – D90.2 – K41.
- How is profit from sales of products determined - by closing subaccounts in account 90. To do this, income in the form of revenue D90.1 - K90.9 is written off in the amount of 760,737 rubles. and costs included in the cost of D90.9 - K90.2 in the amount of 598,050 rubles.
- If profit is received from the sale of finished products, the posting to close subaccounts will form a credit balance on account 90.9. In the example, the profit amount is 162,687 rubles. (760 737 – 598 050).
- The profit from the sale of products is written off - the entry for profit from ordinary activities is made between accounts 90.9 and 99: D90.9 - K99 in the amount of 162,687.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.