In the process of reflecting the facts of economic activity and preparing primary documents, each accountant needs to create accounting registers (Part 5, Article 10 of Law No. 402-FZ). Let's take a closer look at creating and setting up accounting register data in the 1C: Accounting 8 program, ed. 3.0.
- Mandatory details of accounting registers
- Accounting registers in 1C
- Setting up accounting registers
- Signing and saving accounting registers in electronic form
Accounting registers in accounting
All facts of the economic life of the institution are confirmed by relevant primary documents.
It is unacceptable to enter business transactions and entries into accounting without a primary account. In fact, accounting registers are internal documents that the accountant creates independently to confirm the operations of the financial and economic activities of the organization. The information contained in the primary documentation is subject to special registration, generalization and accumulation in special journals, statements, books and accounting cards. In practice, accounting registers in accounting are used to reflect accounting entries and register primary documents. Information is systematized for further reflection on accounting accounts. Internal accounting documents are the basis for the formation of reliable accounting statements and separate reporting forms for management activities.
It is permissible to maintain accounting registers not only in paper form, but also in electronic form. For example, using specialized programs or websites. Electronic accounting documents are certified with the electronic signature of the responsible person (manager and chief accountant).
Use free access to ConsultantPlus to download current forms and find instructions on how to fill them out.
to read.
Accounting registers. Concepts and sections
Registers are a special register that contains information about the primary documents of the accounting department, accounts in safe deposit boxes, as well as the necessary reporting papers. They are filled out by the chief accountant or his assistant. They are available in every accounting department, but they have different forms and sections:
- Registers vary in their purpose. So, they can be of three types:
- With chronology display. Such documents are filled out upon completion of the transaction and are grouped only by date.
- In compliance with the system. Such registers are scattered among the corresponding accounts. As a result, their search is carried out by the name of the operation.
- Mixed. In them, papers can be kept both by keeping the date and by scattering them across accounts. In this case, they will be searched by document title.
- From primary accounting to reporting.
- From reporting to initial inspection papers.
Depending on what type of registers is used in a given organization, the entire work of the accounting department is structured.
Types of accounting registers
Accounting documentation and accounting registers are used to accumulate and systematize information contained in primary forms accepted for accounting in an organization. This is a fairly general concept.
Here is an example: to generate financial statements, in particular the annual balance sheet, an accountant prepares balance sheets for accounting accounts. The indicators contained in the SALT are entered into the reporting form in accordance with established requirements. In this example, OSV is an accounting register.
When classified by purpose, accounting registers are divided into:
- chronological - these are forms in which the registration of accounting data is carried out exclusively in chronological order, without any additional detail, as an example - a cash book;
- systematic - in such documents information is entered in the context of accounting accounts, this is the general ledger, the chess sheet;
- synchronistic - a separate type of documents that combine the principles of reflecting accounting data of systematic and chronological RBU, that is, information is entered into such documents in the context of accounts in chronological order. An example is any order journals.
According to the volume of accounting information contained:
- analytical - RBU, for which detail is provided in the context of one account according to analytical indicators: in the context of fixed assets and MH objects, by financially responsible persons, items, storage locations, and so on;
- synthetic - RBU, in which information is grouped according to accounting accounts, that is, transactions of the same type in monetary terms are reflected in a generalized form (general ledger);
- complex - RBU, which combines synthetic and analytical principles of compilation, an example is a journal order.
Accounting also provides for other RBU classifications. For example, according to the forms of construction they distinguish:
- one-sided;
- double sided;
- chess sheets.
By filling method:
- filled in by hand;
- using printing machines or a computer;
- mixed method.
Let's give an example of what accounting registers are based on the form or appearance of the document:
- statement;
- book;
- magazine;
- card.
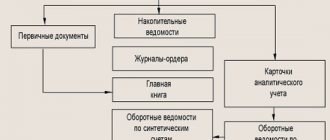
The entire list of accounting registers for accounting policies in the form of a block diagram:
Responsible person
Registers are part of accounting; all organizations, except individual entrepreneurs and branches of foreign companies, are required to compile them. The chief accountant must provide the head of the company with a list of all necessary information. Based on the approved list, an Order on the use of registers is issued; the information must be reflected in the accounting policies of the enterprise. The order approves the forms for each account:
- turnover balance sheet;
- account card;
- account analysis.
A person responsible for maintaining documents is appointed. According to Instruction No. 33n, all accounting registers are formed within the reporting period. If a company does not meet deadlines, this may indicate poor record keeping and weak management control.
Budget accounting
In fact, the content of accounting registers is individual for each economic entity: organizations independently develop and approve accounting registers that will be used in accounting. This rule is defined in Law No. 402-FZ. But there are exceptions. For state and municipal institutions, forms are developed and recommended by higher ministries and departments. For example, the Ministry of Finance of Russia or executive authorities.
State employees work according to unified documentation. The forms are enshrined in Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 52n. Current list:
| OKUD form | Title of the document |
| F. 0504071 | Account journal “Cash desk” |
| Journal of transactions with non-cash funds | |
| Journal of settlements with accountable persons | |
| Journal of settlements with suppliers and contractors | |
| Journal of settlements with debtors by income | |
| Journal of settlement transactions for wages, salaries and scholarships | |
| Journal of transactions on disposal and transfer of non-financial assets | |
| Journal for other transactions | |
| F. 0504072 | main book |
| Not provided | Other forms of documents provided for by instruction No. 157n |
Unified transaction log form for public sector institutions
State employees have the right to use additional accounting documents necessary to systematize information about the facts of economic activity, values received, and completed documentation. Accounting registers are maintained both in a special program and on paper in the prescribed form. When developing additional forms and forms, you should take into account the mandatory requirements for the details of accounting documentation. The list of mandatory details is enshrined in Part 4 of Art. 10 of Law No. 402-FZ, clause 11 of Instruction No. 157n.
Accounting in a non-profit organization
The accounting documents of NPOs, like those of commercial sector organizations, do not have standardized formats. Each economic entity independently develops the structure of accounting documentation, and the correct reflection of business transactions in registers is ensured by those persons who compiled and signed them.
Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 94n provides a list of accounting registers for the organization:
| Journal order number | Accounting account | Contents of operations |
| № 1 | 50 | Cash flow in the organization's cash register for the reporting period |
| № 2 | 51 | Non-cash transactions, cash flows through current accounts |
| № 3 | 55 | Transactions on special bank accounts of the company |
| № 4 | 66, 67 | Loans and credits classified by maturity (short-term and long-term) |
| No. 5 and No. 5a | 20-99 | Analytics of enterprise expenses transactions |
| № 6 | 60 | Settlements with suppliers and contractors |
| № 7 | 71 | Settlements with accountants |
| № 8 | 60, 62, 68, 72 | Settlements with customers, budget, debtors, creditors |
| № 9 | 79 | Reflection of transactions for intra-economic settlements |
| № 10 | 20, 21, 23, 25, 26, 29, 69, 70, 94, 96, 97 | Journal of expenses for the main production with a credit to the corresponding accounts (operations for experimental work, operational maintenance, personnel wages, insurance premiums and tax deductions, auxiliary production, and so on) |
| № 11 | 40, 41, 43, 45, 46, 62, 90 | Reflection of information on finished products, sales, direct sales |
| № 12 | 86 | Information about target financing |
| № 13 | 01, 02, 08 | Operations with fixed assets, depreciation, contributions to the authorized capital |
| № 14 | 14 | Information about agricultural operations |
| № 15 | 84, 98, 99 | Results of operations (profit, losses, retained earnings, losses) |
| № 16 | 07, 08 | Investments in non-current assets. Equipment intended for installation and assembly |
Download current samples of accounting document forms for 2022 in the article “We draw up a journal of business transactions”; see examples of filling out forms in the special material “How to correctly fill out a journal order”.
How is the document stored?
No matter how trivial it may be, it is necessary to note some important nuances of storing registers. All accounting is located in rooms/containers/boxes that protect documents from moisture, direct light and other destructive phenomena. Typically, such places are safes, special cells, cabinets, etc.
How long the designated documents should be stored is prescribed by Article 29 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011, No. 402 - “On Accounting”. In addition, this moment is regulated by paragraph 8 of Article 23 of Part One of the Tax Code of Russia. In the first case, the period is 5 years
from the end of the reporting period.
In the second – at least 4 years
after the start of the tax period.
Such close attention to the time frame of storage is explained by the sometimes arising need to retrieve archives. A common reason is litigation. Moreover, there does not have to be a direct connection with the organization itself: some kind of litigation involving one of the employees is possible.
Note 3.
Sometimes registers last longer. For example, payroll records are kept for 75 years from the date of their creation and registration.
How to approve registers for work
Let's figure out how to approve the selected forms. The procedure depends on what forms of documentation you decide to use in your work.
Option No. 1. We work according to unified forms.
It is permissible for public sector institutions to state in their accounting policies that for work they will use forms and unified forms approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 52n. It is not necessary to attach samples; it is only permissible to list the names of the journals used for work, indicating their OKUD codes.
Option number 2. We use our own forms.
If an organization uses independently developed accounting registers, then such documents must be listed in the text of the accounting policy, in the appropriate section. Then draw up each of the documents used as an appendix to the accounting policy. It also states which accounting registers must be printed.
IMPORTANT!
Even if the registers are compiled electronically and signed with digital signatures, it is necessary to approve the samples. During the inspection, controllers will request an order or instruction on approval of accounting registers (accounting policies and appendices thereto).