How to create a tax accounting register
To use tax accounting registers, you will have to spend time developing their form, and then consolidate them in the annex to the accounting policy by issuing the appropriate order (paragraph 7 of article 314 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Read about the nuances of developing a tax accounting policy in the article “How to draw up an organization’s tax policy?” .
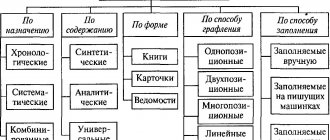
The legislator does not limit taxpayers in choosing the type and form of these documents, so tax accounting registers may look different. The volume of information contained in them should give an idea of the basis on which documents and how the tax base is formed. The placement of data in the register can be any (in tabular or text form) - these features are provided for when developing tax accounting register forms.
The only thing you cannot be proactive about when preparing tax registers is the required details. Their composition must comply with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For example, when calculating income tax, tax accounting registers containing the following information are used (paragraph 10, article 313 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- register name;
- date of compilation;
- natural (if possible) and monetary measures of the operation;
- name of accounting objects or business transactions;
- signature of the person responsible for compiling the register and its decoding.
Such registers can be maintained in any way convenient for the taxpayer: on paper or electronically.
What tax registers exist for VAT? See the answer to this question in the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. If you don't have access to the system, get a free trial online.
Income tax registers
Proceeds from the sale of property (work, services) are reflected in the register for recording disposal operations of property, work, services, and rights. In some cases, the amount of revenue is also indicated in additional tax accounting registers. The list of these registers depends on the type of property sold. The table shows the registers for accounting for revenue recommended by tax authorities.
| Type of income | Registers |
| Revenue from sales of finished products | Register of accounting for disposal operations of property, works, services, rights |
| Revenue from sales of works and services | Register of accounting for disposal operations of property, works, services, rights |
| Proceeds from the sale of other property (materials) | Register of accounting for disposal operations of property, works, services, rights |
| Proceeds from the sale of goods purchased for resale | Register of accounting for disposal operations of property, works, services, rights |
| Proceeds from the sale of fixed assets | — Register of accounting for disposal operations of property, works, services, rights; — Register-calculation “Financial result from the sale of depreciable property” |
| Proceeds from the sale of intangible assets | — Register of accounting for disposal operations of property, works, services, rights; — Register-calculation “Financial result from the sale of depreciable property” |
| Proceeds from the sale of securities | Register of accounting for disposal operations of property, works, services, rights |
If the revenue received relates to future reporting (tax) periods or your company determines income using the cash method, after receiving money from customers, a cash receipt register is drawn up.
The Federal Tax Service has provided tax registers only for recording fines accrued for violations by counterparties of the terms of business contracts and written off accounts payable.
There are no other registers for accounting for non-operating income in the Tax Officials' Recommendations. Therefore, the organization will have to develop the appropriate register independently. For tax accounting of non-operating income, you can use:
| Type of non-operating income | Registers |
| From renting out property | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Fines and penalties accrued for violation by partners of the terms of business contracts | — Register of accounting for settlements of penalties; — register-calculation of the amounts of accrued penalties for the reporting period; — register of accounting for non-operating income of the reporting period |
| The value of property and money received free of charge | — Register of accounting for non-operating income of the reporting period; — register “Formation of the cost of an accounting object” |
| Income of previous years identified in the reporting (tax) period | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Positive exchange rate difference resulting from revaluation of currency and foreign currency debt | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Positive amount difference | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Cost of valuables received upon liquidation of fixed assets | — Register of accounting for non-operating income of the reporting period; — register “Formation of the cost of an accounting object” |
| A positive difference arising from the sale or purchase of foreign currency at a rate that deviates from the official rate of the Bank of Russia | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Surplus valuables identified as a result of inventory | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Written off accounts payable | — Register of accounting of transactions on the movement of accounts payable; — act of inventory of accounts payable as of the reporting date; — register of accounting for non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Total amount of reserves recovered, including: | — Register of accounting for non-operating income of the reporting period; — registers for accounting reserves |
| - for doubtful debts | — Calculation of the reserve for doubtful debts of the current reporting (tax) period; — Register of movement of reserve for doubtful debts |
| — for warranty repairs and maintenance | — Register-calculation of reserve costs for warranty repairs; — register-calculation of the coefficient for recalculating the reserve for warranty repairs |
| - repair of fixed assets | Register of reserves for repairs of fixed assets |
| - for the payment of vacation pay, long-service benefits | Register for accounting for reserves for vacation pay (remunerations for long service) |
| Dividends received from equity participation in the authorized capital of other companies | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Interest on loan agreements, securities, bank account and bank deposit agreements | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Income from participation in a simple partnership (joint activity) | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Other non-operating income | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
Proceeds from the sale of property (work, services) are reflected in the register for recording disposal operations of property, work, services, and rights. In some cases, the amount of revenue is also indicated in additional tax accounting registers. The list of these registers depends on the type of property sold. The table shows the registers for accounting for revenue recommended by tax authorities.
| Type of income | Registers |
| Revenue from sales of finished products | Register of accounting for disposal operations of property, works, services, rights |
| Revenue from sales of works and services | Register of accounting for disposal operations of property, works, services, rights |
| Proceeds from the sale of other property (materials) | Register of accounting for disposal operations of property, works, services, rights |
| Proceeds from the sale of goods purchased for resale | Register of accounting for disposal operations of property, works, services, rights |
| Proceeds from the sale of fixed assets | — Register of accounting for disposal operations of property, works, services, rights; — Register-calculation “Financial result from the sale of depreciable property” |
| Proceeds from the sale of intangible assets | — Register of accounting for disposal operations of property, works, services, rights; — Register-calculation “Financial result from the sale of depreciable property” |
| Proceeds from the sale of securities | Register of accounting for disposal operations of property, works, services, rights |
If the revenue received relates to future reporting (tax) periods or your company determines income using the cash method, after receiving money from customers, a cash receipt register is drawn up.
The Federal Tax Service has provided tax registers only for recording fines accrued for violations by counterparties of the terms of business contracts and written off accounts payable.
There are no other registers for accounting for non-operating income in the Tax Officials' Recommendations. Therefore, the organization will have to develop the appropriate register independently. For tax accounting of non-operating income, you can use:
| Type of non-operating income | Registers |
| From renting out property | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Fines and penalties accrued for violation by partners of the terms of business contracts | — Register of accounting for settlements of penalties; — register-calculation of the amounts of accrued penalties for the reporting period; — register of accounting for non-operating income of the reporting period |
| The value of property and money received free of charge | — Register of accounting for non-operating income of the reporting period; — register “Formation of the cost of an accounting object” |
| Income of previous years identified in the reporting (tax) period | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Positive exchange rate difference resulting from revaluation of currency and foreign currency debt | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Positive amount difference | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Cost of valuables received upon liquidation of fixed assets | — Register of accounting for non-operating income of the reporting period; — register “Formation of the cost of an accounting object” |
| A positive difference arising from the sale or purchase of foreign currency at a rate that deviates from the official rate of the Bank of Russia | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Surplus valuables identified as a result of inventory | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Written off accounts payable | — Register of accounting of transactions on the movement of accounts payable; — act of inventory of accounts payable as of the reporting date; — register of accounting for non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Total amount of reserves recovered, including: | — Register of accounting for non-operating income of the reporting period; — registers for accounting reserves |
| - for doubtful debts | — Calculation of the reserve for doubtful debts of the current reporting (tax) period; — Register of movement of reserve for doubtful debts |
| — for warranty repairs and maintenance | — Register-calculation of reserve costs for warranty repairs; — register-calculation of the coefficient for recalculating the reserve for warranty repairs |
| - repair of fixed assets | Register of reserves for repairs of fixed assets |
| - for the payment of vacation pay, long-service benefits | Register for accounting for reserves for vacation pay (remunerations for long service) |
| Dividends received from equity participation in the authorized capital of other companies | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Interest on loan agreements, securities, bank account and bank deposit agreements | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Income from participation in a simple partnership (joint activity) | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
| Other non-operating income | Register of accounting of non-operating income of the reporting period |
Requirements for tax registers
From Art. 314 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation it follows that tax accounting registers (TA) are filled out on the basis of primary accounting documents continuously in chronological order. This means that random or unfounded entry of data into the register, as well as omissions or any deletions are not allowed.
IMPORTANT! There is no decoding of the phrase “primary accounting document” in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, therefore the primary accounting document can serve as confirmation of the entries in the NU (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 17, 2014 No. 03-03-06/1/1156).
We should not forget that the generated tax registers must be protected from unauthorized correction. Any errors in tax accounting registers are corrected only with appropriate justification, and the responsible executor certifies all adjustments made with his signature and indicates the date.
IMPORTANT! Information reflected in tax registers is a tax secret. For its disclosure (including by tax authorities), administrative and criminal liability is provided (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 12, 2011 No. 03-02-08/41).
Read more about the requirements for tax accounting and tax registers here.
Tax accounting registers for income tax
To fill out a “profitable” declaration, you will need at least 2 NU registers: one for accounting for income, the other for expenses. Information about income received and expenses incurred, generated according to NU norms, will make it possible to determine profit - an object of taxation, without which the calculation of the income tax itself is impossible.
Read about what the tax base for different types of taxes may be in the article “Basic elements of taxation and their characteristics .
Additional registers will have to be drawn up in the case where the taxpayer has many types of activities, and also, in addition to standard business transactions, operations are carried out with special conditions for the transfer of ownership or for which a special procedure for forming the tax base is provided.
IMPORTANT! If the taxpayer cannot or does not want to develop tax accounting registers, but does not want to be punished under Art. 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for their absence, he has the right to use ready-made ones. Their forms can be found in the recommendations of the Ministry of Taxes of Russia “Tax accounting system recommended by the Ministry of Taxes of Russia for calculating profits in accordance with the norms of Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation” dated December 19, 2001.
Example
Specialists of Ritm LLC reflect the information necessary for calculating income tax for the year in the following tax accounting registers (RNU):
- RNU "Income from sales" LLC "Rhythm";
- RNU "Expenses that reduce sales income" LLC "Rhythm";
- RNU "Non-operating income" LLC "Rhythm";
- RNU "Non-operating expenses" LLC "Rhythm".
Taking into account that during the specified period, Ritm LLC had no non-operating income and expenses, let us dwell in more detail on the preparation of tax registers for income received and expenses incurred for core activities.
ConsultantPlus experts spoke about the nuances of organizing tax accounting for income tax. Get trial access to the K+ system and move on to the Ready-made solution for free.
What are tax registers
There is no single form of registers, so each company must develop them independently and approve them as an annex to the order on accounting policies for tax purposes.
Each register must contain mandatory details. Here they are:
- Name;
- period (date) of compilation;
- transaction meters in physical (if possible) and monetary terms;
- name of business transactions;
- signature (decryption of the signature) of the person responsible for compiling the register.
When developing tax accounting registers, you can use the recommendations of the Ministry of Taxes of Russia (now the Federal Tax Service of Russia) “Tax accounting system recommended by the Ministry of Taxes of Russia for calculating profits in accordance with the norms of Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.”
Here is a complete list of these registers:
| Register-calculation “Formation of the cost of an accounting object” | Register of accounting of settlements with the budget |
| Register-calculation of depreciation of intangible assets | Register of movement of reserve for doubtful debts |
| Register-calculation of the cost of written-off raw materials using the FIFO method | Register of expenses for warranty repairs |
| Register-calculation of the cost of written-off goods using the FIFO method | Register of accounting for settlements of penalties |
| Register-calculation of the cost of raw materials/materials written off in the reporting period | Register of accounting transactions for the acquisition of property, works, services, rights |
| Register of doubtful and bad receivables based on inventory results as of the reporting date | Register of accounting for disposal operations of property, works, services, rights |
| Register of doubtful and bad debts based on inventory results as of the reporting date | Cash receipts register |
| Calculation of the reserve for doubtful debts of the current reporting (tax) period | Cash expense register |
| Accounts payable inventory report as of the reporting date | Register-calculation of the amounts of accrued penalties for the reporting period |
| Register of contracts for voluntary insurance of employees | Register of labor costs accounting |
| Register of expenses for voluntary insurance of employees | Register of accrual of taxes and fees included in expenses |
| Register-calculation of accounting expenses for employee insurance of the current period | Register-calculation of depreciation of fixed assets |
| Register-calculation of expenses for repairs of the current reporting period (maintained by organizations that are not organizations listed in paragraph 1 of paragraph 1 of Article 260) | Register for recording the cost of goods written off in the reporting period |
| Register-calculation of repair costs taken into account in the current and future periods (maintained by organizations that are not organizations listed in clause 1, clause 1, article 260) | Register of accounting for other expenses of the current period |
| Register for accounting of non-operating expenses for transactions of assignment of rights of claim relating to future periods | Register-calculation “Financial result from the sale of depreciable property” |
| Register-calculation of reserve costs for warranty repairs | Register for recording the cost of sold other property |
| Register-calculation of the coefficient for recalculating the reserve for warranty repairs | Register-calculation of the balance of transportation costs |
| Register of information about a fixed asset object | Register of accounting for non-operating expenses of the current period |
| Register of information about the object of intangible assets | Register-calculation of the financial result from the sale of rights that were previously acquired as part of an operation to provide financial services |
| Register of information on purchased consignments of goods accounted for using the FIFO method | Register-calculation of the financial result from the assignment of rights of claim (expenses for the sale of rights, except for situations of sale of previously acquired rights) |
| Register of information on purchased batches of raw materials/materials accounted for using the FIFO method | Current period income register |
| Register of information on the movement of purchased goods accounted for using the average cost method | Register of losses of service industries and farms |
| Register of information on the movement of purchased raw materials/materials accounted for using the average cost method | Register-calculation “Financial result from the activities of service industries and farms” |
| Register of deferred expenses | Register of receipts of target funds |
| Register of accounting transactions for the movement of receivables | Register of accounting for the use of target revenues |
| Register of accounting transactions for the movement of accounts payable | Register of accounting of earmarked funds used for purposes other than their intended purpose |
It is quite possible that this list may not contain some registers that are necessary specifically for your company. In this case, you can develop them yourself or supplement existing ones.
Tax accounting registers can be maintained either manually on paper or electronically on a computer. Each register must be signed by the person responsible for its preparation. They can be either a company accountant or a specialist directly involved in tax accounting.
Stay up to date with the latest changes in accounting and taxation! Subscribe to Our news in Yandex Zen!
Subscribe
“Profitable” register of NU
Continuation of the example
The income of Ritm LLC in the reporting period consisted of the following components:
- revenue from sales of self-made products (RUB 50,367,000);
- revenue from sales of purchased products (RUB 30,590,000)
- proceeds from the sale of other property (RUB 300,000);
IMPORTANT! It is necessary to take into account in the “income” part the entire amount of products sold during the reporting period, with the exception of the income listed in Art. 251 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
About what income is reflected in Art. 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, read the material “Art. 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: questions and answers" .
IMPORTANT! When drawing up the RNU “Income from sales”, one should not forget that revenue in the register and tax return must be indicated without taking into account VAT and excise taxes (clause 1 of Article 248 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Information for filling out the “income” RNU is taken from accounting data (according to accounts 90 “Sales” and 91 “Other income and expenses”).
On our website you can download completed tax accounting registers, a sample of which relating to income is drawn up according to the data in the example discussed.
How to fill out the “expenditure” tax register
Taxpayers may experience certain difficulties filling out expense registers. This is due to the fact that the recognition of expenses in tax accounting does not always coincide with the reflection of similar expenses in accounting. So it is not always possible to use accounting registers without making additional adjustments to them.
For example, certain types of expenses are reflected in full in the accounting system, but are normalized in the accounting system (advertising, representative expenses, etc.). And tax legislation generally prohibits recognizing some types of expenses as expenses that form the taxable base for income tax.
Read about the nuances of recognizing other expenses associated with production and sales here.
Continuation of the example
A specialist from Ritm LLC formed a RNU “Expenses that reduce sales revenue”, which reflected the following types of expenses: costs for basic raw materials and supplies, wages along with accrued insurance premiums, depreciation of property of Ritm LLC, expenses for heat, water, electricity, etc.
The accountant took the information to fill out the register from accounting data (for accounts 20, 26, 44, 91, etc.). During the reporting period, the company did not incur expenses, the recognition of which in the financial accounting does not coincide with the accounting rules, so there was no need to adjust the accounting data.
You can also download a sample of a completed tax accounting register “Expenses that reduce sales revenue” on our website.
IMPORTANT! If tax expenses exceed tax revenues and there is no taxable base for profit in any of the periods (tax or reporting), a declaration must still be submitted to the tax authorities (clause 1 of Article 289 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Tax accounting register “Non-operating income”
Tax accounting register “Non-operating income”
Reporting period ____________________________
Date of compilation ___________________________
————————————————————————— ¦ Code ¦ Name ¦ Transfer ¦ Again ¦ Total ¦ ¦ lines¦ non-operating income¦ data from ¦ generated¦ amount, rub . ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ other ¦ registers according to ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ tax ¦ data ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ registers ¦ accounting ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+ ————-+ ¦ 1 ¦ 2 ¦ 3 ¦ 4 ¦ 5 ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦From equity participation in ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ other organizations, including: ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+ ————-+ ¦ ¦foreign organizations ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦Russian organizations ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦Positive ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦(negative) difference, ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦resulting from ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦sales (purchases) ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ of foreign currency, ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ including: ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+————————— +————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦from the sale of currency ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+ ————-+ ¦ ¦from the purchase of currency ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦Fines, penalties and (or) other ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ sanctions, including: ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————- + ¦ ¦for violation of contractual ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ obligations ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦в in the form of amounts of compensation ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦loss or damage ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦From provision in ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ use of rights to ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ results ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ intellectual ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ activities and ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ equivalent to them ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ “means of individualization” ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦Interest received under ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦agreements, including : ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦loan ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+———— —————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦bank deposit ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+— ———+————-+ ¦ ¦bank account ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦ The amounts of restored ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ reserves, the costs of ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ the formation of which were ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ accepted as part of expenses ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ in the manner and on the conditions ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ installed ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦st. Art. 266 and 324 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, including: ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦for doubtful debts ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦upcoming expenses for ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ repair of fixed assets ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦formation costs ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦which were accepted ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦previously as part of expenses ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦for depreciation of valuable ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦papers ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦Received free of charge ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦property (work, ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦services) or ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦property rights ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+ ————-+ ¦ ¦Income distributed in ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ for the benefit of the taxpayer ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ with his participation in a simple ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ partnership ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+———— —————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦Income of previous years, ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ identified in the reporting ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ (tax) period ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦Positive ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦exchange rate difference ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+ —————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦Amount difference ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ arising from ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ the taxpayer, including ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦number: ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦by advance payment ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦other amount differences ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+——————— ——+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦Cost of received ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ materials or other ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ during dismantling ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ or disassembling during ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦elimination of the main ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ funds withdrawn from ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+——— —+————-+ ¦ ¦Used for purposes other than their intended purpose ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ property (including ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ money), ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ work, services that were received within the framework of charitable activities, targeted proceeds, targeted funding, ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦with the exception of budget ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ funds ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦Amounts for which in the reporting (tax) period there was a decrease in the authorized capital of the enterprise ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦Refund amounts from ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ non-profit ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ organization previously ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ paid contributions ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ (contributions) in the event that ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ such contributions (contributions) ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ were previously taken into account in ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ composition of expenses during the formation of the tax base ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ -+ ¦ ¦Amounts of accounts payable ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦debt written off due to the expiration of the statute of limitations or for other reasons — —+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦The cost of surplus inventory and ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦other property that¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ identified as a result of ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦inventory ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦Interest on valuables ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ papers at 15%, including ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ including: ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+—— ——-+ ¦ ¦difference between the amount of ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦accumulated coupon ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦income received and ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦paid ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+———————— —+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦difference between nominal ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦cost and price ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦initial placement ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—— ———————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦Income on bills, including: ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—— ———————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦interest-bearing bills ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+———— +————+————-+ ¦ ¦discount bills ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦Income from operations with ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦packaging ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦Other income (difference ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ depreciation accrued ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ on leased ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ fixed assets) ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+— ———+————+————-+ ¦ ¦Write-off (disposal) ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦special ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦equipment, special ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦devices ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +— —+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦Write-off (disposal) ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦special clothing and ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦other waste ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——+—————————+————+————+————-+ ¦ ¦Total income (line 010 + line 020 + ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ line 030 + sum of lines from 050 to 060 + line 070 + sum of lines from 080 to 120 + line 130 + sum of lines 140 to 190 + line 200 + line 210 + line 220 + line 230 + line 240) ¦ ¦ ——-+—————————————————-+—————
Responsible executor: _________________________________
Note.
Column 1 indicates the line code of the tax return under the current order.
Column 3 indicates the data of the accompanying tax accounting register.
Source - “Economic and Legal Bulletin”, 2009, No. 11
Results
Tax accounting registers are developed by the taxpayer himself, and their form is approved as an annex to the tax accounting policy. They can be compiled electronically or on paper - it doesn't matter. The main thing is that they contain the mandatory details established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. There is a basic requirement for information reflected in registers: all entries must be justified and reliable, and from the contents of the register it must be clear how the tax base is formed.
If tax accounting registers are not maintained by the taxpayer, penalties may be imposed by tax authorities under Art. 120 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Tax registers, samples of which you can download on our website, allow you to group available information about the company’s income and expenses and correctly calculate income tax.
Sources: Tax Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.