Common mistakes
If we talk about typical mistakes when abbreviating, these include:
- absence (non-delivery) of notice of reduction;
- dismissal of an employee before the two-month notice period;
- failure to notify employment authorities and the trade union (if any) within the established time limits;
- failure to offer vacancies when available.
When it comes to reducing the number of employees, a fairly common mistake is failure to conduct or incorrect assessment of the preemptive right (Article 179 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). For example, employers often have no criteria for assessing labor productivity and qualifications at all, or these criteria are recognized by the courts as subjective.
Notification
This is a mandatory condition: each employee dismissed on this basis must be personally warned against signature at least two months before the actual date of dismissal.
Sample notice of reduction in the number of employees
Only if the employee agrees to terminate the employment relationship before the expiration of the two-month period at the employer’s proposal, the contract can be terminated earlier. It should be taken into account that the employee retains the right to all guarantees and payments due to him, and he is also paid additional compensation in proportion to the time remaining before the expiration of the specified period of notice of dismissal.
The employer is also obliged to notify the employment service body in writing about the release of specialists, indicating the positions, profession, specialty, qualification requirements and payment terms. The organization does this two months before the start of implementation of the solution, the individual entrepreneur - two weeks, and in the case of a mass release (parameters) - three.
Who can't be laid off?
Art. 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes categories of persons who are not subject to reduction. These include:
- pregnant woman;
- a woman with a child under 3 years of age;
- a single mother raising a disabled child under the age of 18;
- a single mother raising a child under 14 years of age;
- another person raising the above children without a mother;
- a parent (other legal representative of the child) who is the sole breadwinner of a disabled child under the age of 18 or the sole breadwinner of a child under 3 years of age in a family raising three or more young children, unless the other parent (other legal representative of the child) is in an employment relationship.
For more information about the categories of persons who cannot be laid off, read the article “6 situations when laying off an employee can result in a lawsuit.”
What are preemptive rights and who has them?
Given equal levels of qualifications and labor productivity of employees, preference is given to those who have advantages in the reduction of staff. According to Art. 179 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the following categories of workers can apply for job retention:
- family people who have two or more dependents (minor children, other disabled family members who are fully supported by the employee or regularly receive assistance from him, representing their permanent and main source of livelihood);
- the only “breadwinners” in the family are employees whose families do not have other people with a regular income;
- employees with injuries and occupational diseases received while working in this organization;
- employees who are currently improving their qualifications in the direction of the employer.
If you were illegally fired due to layoffs, you need to contact several authorities. First, send a written application to the organization's trade union. The union must consider the complaint within a week. This case may also be considered by the Federal Labor Inspectorate and the prosecutor's office. If the trade union and the labor inspectorate do not reveal any violations, then a lawsuit must be filed.
In addition to the categories of employees listed in the Labor Code, certain other persons also have benefits during layoffs in accordance with federal laws:
- military spouses;
- military personnel transferred to the reserve;
- authors of inventions;
- disabled people of the Second World War and combat operations;
- persons affected by radiation;
- and some others.
Preferential rights to remain at work may also be provided for by internal collective agreements in the company.
About dismissal due to staff reduction and the required payments here.
How and why to prove the fact of reduction
The burden of proving the fact of layoff lies with the employer. The launch of the reduction procedure begins with a decision by the authorized person of the company to carry out the reduction.
Such a decision must be made in writing. This could be, for example, an order from the general director or a protocol of the board of directors. Based on this decision, an order is issued to change the staffing table and the staffing table is directly changed. It is these documents that will serve as proof of the reduction.
In addition, since labor disputes most often arise after dismissal due to a reduction in the number or staff of employees, the court also examines whether a new employee was hired for the same position after the dismissal. In this case, the reduction may be considered illegal (“imaginary”). From this we can conclude that the fact of a reduction can be proven by the absence of a position in the staffing table in effect at the time of consideration of the dispute.
Stage 9. Apply for a personal card
An employee’s personal card is an internal document of the enterprise, filled out in form T-2 (established by Resolution No. 1). Item XI of the form is intended for entering information about the dismissal of an employee. It states:
- the reason why the employee will no longer work for the organization;
- date of dismissal due to staff reduction;
- details of the dismissal order;
- information about the personnel officer who made the entry in the personal card.
The information in the personal card is certified by the signature of the employee himself and the personnel officer responsible for maintaining it. The absence of an employee’s personal card entails the possibility of bringing the employer to administrative liability under Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
Why is a redundancy commission needed?
Legislatively, the employer has no obligation to create a redundancy commission, but from a practical point of view, its necessity is beyond doubt.
First of all, it is needed to determine the categories of employees who are not subject to layoffs. In addition, the work of this commission is useful in assessing the preemptive right. The staff reduction commission reviews the information provided for each candidate for dismissal. The decision made regarding employees who are not subject to layoffs and have a preferential right to remain at work is documented in writing - a protocol, a decision, etc.
The commission is created by order of an authorized person. The commission, as a rule, includes personnel specialists, one or two employees who are members of a trade union (if the company has one), and lawyers.
Normative base
Don’t know how to correctly formalize a reduction in staff according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, but want to fire without consequences? We recommend that you start by studying the regulatory documents that will be needed in the process of preparing for the dismissal of subordinates. The list of required standards is small and is presented in the table:
| Legislative norm | What features and nuances are spelled out in it? |
| Resolution of the Council of Ministers No. 99 of 02/05/1993 | Mass dismissal criteria |
| Article 179 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation | Preferential right to remain at work |
| Article 373 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation | The need to take into account the opinion of the trade union |
| Law of April 19, 1991 No. 1032-1 | The need to notify the employment service |
| Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation | Grounds for dismissal |
| Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation | List of employees who cannot be fired |
| Article 139 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation | Payments upon dismissal |
| Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation | Responsibility for violation of order |
Seasonal workers and conscripts
The legislation provides for specifics in the procedure for laying off seasonal workers and workers who have entered into a fixed-term employment contract of up to 2 months. Please note that for other employees with whom a fixed-term employment contract has been concluded for other reasons, the reduction procedure is similar to that provided for employees with whom an employment contract has been concluded for an indefinite period.
The specifics of laying off seasonal workers and workers with whom a fixed-term employment contract of up to 2 months has been concluded relate to the timing of delivery of notice and payment of benefits.
Thus, an employee engaged in seasonal work must be notified of his upcoming dismissal due to a reduction in the number or staff of the organization’s employees at least 7 calendar days in advance.
Accounting and tax accounting, employee settlements, reporting to the Federal Tax Service, Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, Social Insurance Fund and Rosstat, currency accounting - all in one service.
To learn more
For employees who have entered into an employment contract for a period of up to 2 months, the period is even shorter - they must be notified of the upcoming layoff at least 3 calendar days in advance.
As for the payment of severance pay to these categories of employees upon dismissal under clause 2, part 1, art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, then for seasonal workers the amount of benefits is equal to the amount of two-week average earnings. And employees who have entered into an employment contract for a period of up to two months are not paid severance pay upon dismissal as a general rule, unless otherwise established by federal laws, a collective agreement or an employment contract.
Reduction of headcount (staff): dealing with complex issues
The topic of downsizing or staffing is not new. However, personnel workers encounter difficulties when carrying out reductions, and the specialists of the “Consultation Line” service of the Regional Information Center in the city of Khabarovsk continue to receive questions related to this procedure. We publish an overview of the most difficult issues and remind you of the purpose of the “Consultation Line” service.
“Consultation Line” - legal advice solely based on the materials of the ConsultantPlus System in the field of tax legislation, accounting, civil and labor law. Specialists of the “Consultation Line”, having studied the written request, select from the array of information of the ATP “ConsultantPlus” the materials that are most suitable for the situation presented in the request.
Let's move on to analyzing the issues that arise when implementing a reduction.
1. At what point does the two-month notice period for layoffs begin if the employer has decided to cut some positions and all laid-off employees have been given appropriate notices?
The two-month notice period for layoffs must be calculated from the day following the date of notification of employees about the upcoming layoff. However, there is judicial practice according to which the two-month period begins from the day the employee was notified of the layoff.
2. The employee has a child aged 13 years. Her position is being made redundant. The employer knows that this employee, although not in a registered marriage, has a so-called. common-law spouse (unregistered marriage). Is it possible to lay off such an employee?
A woman who is a single mother raising a child under the age of 14 cannot be fired due to a reduction in the number and/or staff of employees. There is no official definition of the concept of a single mother either in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or in other federal laws. At the same time, under previous regulation in the field of social protection of motherhood and childhood, the concept of a single mother was generally accepted if there is no entry about his father in the child’s birth certificate or this entry was made in the prescribed manner at the direction of the mother. If the employee is not a single mother, taking into account the above interpretation of this concept, there is no prohibition on her dismissal due to reduction.
3. When being laid off, will an employee have a preferential right to remain at work if there are no other self-employed workers in his family, but there are people receiving unemployment benefits?
In Part 2 of Art. 179 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states, in particular, that preference in remaining at work is given to persons in whose family there are no other workers with independent earnings. Unemployment benefits do not indicate that a person has independent earnings. With equal labor productivity and qualifications, a priority right will be given to the employee whose family does not have other workers with independent earnings, but there are persons receiving unemployment benefits (Appeal ruling of the Court of the Jewish Autonomous Region dated 09/05/2014 in case No. 33-473/2014 ).
4. Due to the difficult financial situation in the company, a decision was made to reduce staff. A month later, the company received a large order. Can a manager cancel an order to reduce the number of employees, provided that the reduction procedure has already begun?
The procedure for canceling reductions is not regulated by law. In practice, you can cancel a layoff at any time, since you have the right to make any personnel decisions yourself. To cancel a layoff, issue an order to this effect and revoke the notice of layoff from employees. If at the time of cancellation of the layoff you had already dismissed the employee early on this basis, then in order to avoid risks, we recommend that you offer him “reinstatement.”
5. What liability does an employer have for violating the procedure for dismissing an employee when reducing staff without notifying the employment center about this upcoming dismissal?
The employer is obliged to notify the employment service authority in writing about the upcoming dismissal of employees due to a reduction in staff or numbers (clause 2 of article 25 of the Law of the Russian Federation of April 19, 1991 N 1032-1). For failure to submit or untimely submission to the employment service authority of the information specified in paragraph. 1 item 2 art. 25 of the Law of the Russian Federation of April 19, 1991 N 1032-1, or the presentation of such information in incomplete volume or in a distorted form may be subject to liability under Art. 19.7 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. In Art. 19.7 states that it is possible to warn or impose an administrative fine on citizens in the amount of one hundred to three hundred rubles; for officials - from three hundred to five hundred rubles; for legal entities - from three thousand to five thousand rubles.
6. An employee who switched to an electronic work book is dismissed due to staff reduction. On the basis of what document will the employer pay the average salary for the second month after dismissal?
If more than one month has passed since the employee was dismissed, pay him the average monthly salary for the second month or part thereof, proportional to the period of employment that occurred in the second month of job search (that is, if the employee found a job in the second month from the date of dismissal). The basis for such payment is a passport, a written application submitted within the due period (15 days) of the dismissed employee and the following documents depending on the period of employment:
- if the period is equal to a full month - the work book (if it is maintained) and (or) the STD-PFR form, in which the last entry is the dismissal record;
- if the period is equal to part of a month - a duly certified copy of the work record book (if it is kept) or the STD-PFR form, which contains a record of employment with a new employer.
As for the first case, a dismissed employee can receive information about work activity in the STD-PFR form, in particular, from the Pension Fund of Russia, through the Unified Portal of Public Services or from the MFC.
But there is a nuance that is worth paying attention to - the STD-PFR form must be up-to-date, although the deadlines are not provided for by law, it is better to verbally discuss adequate deadlines upon dismissal, because the employee may have already gotten a job, but not inform you about it and provide STD-PFR form received before employment. 7. Is there a special reduction procedure for people of pre-retirement age?
There is no special procedure for dismissal of employees of pre-retirement age due to reduction in number (staff). When dismissing employees of pre-retirement age, you can inform them about the conditions for granting early retirement. Please note that for the unjustified dismissal of such employees, criminal liability is provided under Art. 144.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. It occurs only in cases where the employer was guided by a discriminatory motive related to the employee reaching pre-retirement age (clause 16 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated December 25, 2018 N 46).
8. An employee was given a notice of reduction of his position, but he refuses to receive it, what should the employer do in such a situation?
If the employee refuses to read the notice, then this document must be read out loud to him in the presence of witnesses and a report must be drawn up stating that the notice was presented to the employee, read out loud, but he refused to read it under his signature. A report drawn up in the presence of at least two witnesses will confirm that the employee has been informed of his dismissal.
9. The organization has a separate division in another region, which was planned to be liquidated. Notices were issued to workers and the employment center was notified. Then the management decided not to liquidate the OP, but to reduce staff. A letter was sent to the employment center to withdraw the notice of liquidation and to carry out the layoff procedure. Is it necessary to notify employees again about layoffs?
If the employer for some reason changes his mind about carrying out organizational and staffing measures, all decisions made by him are canceled - in this case, the liquidation of the organization is cancelled. If the employer again wants to carry out measures to reduce staff, he will have to start the entire procedure associated with reducing the number or staff of employees again.
The dismissal of an employee due to the liquidation of an organization (branch) and the dismissal of an employee due to staff reduction are regulated by different parts of Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The procedure for these two types of dismissal differs. When liquidating an organization (or an OP in another location), the employer has the right to dismiss all employees without exception. When reducing staff, there are categories of employees who are prohibited by law from dismissal.
If you would like to receive additional information on the topic of workforce reduction or have questions on other topics of legislation, please contact the materials of the ConsultantPlus System and the specialists of the Consultation Line service. You can access the “Consultation Line” service from the “ConsultantPlus” System shell, using the “Ask a question to an expert” button, on the Regional Information Center website, by filling out the order form in the “Consultation Line” tab, and by email to the Regional Information Center.
The information was prepared by Consultation Line specialists based on materials posted in the ConsultantPlus legal reference system
Dismissal of an employee upon change of ownership
First of all, it is worth noting that a change of owner does not automatically terminate the employment contract with existing employees.
The categories of employees with whom the employment contract can be terminated and the periods during which dismissal can be effected are limited. To employees with whom employment relations can be terminated on the basis provided for in clause 4, part 1, art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (change of owner of the organization’s property), includes the head of the organization, his deputies and the chief accountant.
The period during which the new owner has the right to terminate the employment contract with the above-mentioned persons in connection with a change in the owner of the organization’s property must be no later than 3 months from the date his ownership rights arise.
A change in the owner of the organization’s property is not grounds for terminating employment contracts with other employees of the organization.
If the new owner decides to carry out a reduction, then starting this procedure is allowed only after state registration of the transfer of ownership.
When staffing is downsized
In business, various unforeseen situations often occur. If they are associated with additional difficulties, including financial ones, it is necessary to cut costs, reduce costs, and reduce the number of personnel. To do this, employers choose one of two ways or combine them:
- trying to make do with fewer employees – reducing the number of staff;
- removing certain positions or staffing units for them - staff reduction.
REFERENCE! If positions that are currently vacant are removed from the staffing table, this does not constitute a reduction.
Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates in detail all the provisions for the dismissal of an employee from a position as a result of reduction.
Guarantees and compensation
When an employment contract is terminated due to a reduction in the number or staff of the organization's employees, the dismissed employee is paid a severance pay in the amount of average monthly earnings. He also retains his average monthly salary for the period of employment, but not more than 2 months from the date of dismissal (including severance pay).
In exceptional cases, the average monthly salary will be retained by the employee for the third month from the date of dismissal by decision of the employment service body, provided that within two weeks after dismissal the employee applied to this body and was not employed by it.
It is worth noting that Art. 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes minimum guarantees. Thus, an employment contract or collective agreement may establish an increased amount of severance pay, with the exception of cases expressly provided for by law.
One cannot fail to say something about the “northern” workers. They retain their average monthly earnings for the period of employment, but not more than 3 months from the date of dismissal, including severance pay.
In exceptional cases, the average monthly salary is retained for the specified employees during the 4th, 5th and 6th months from the date of dismissal by decision of the employment service body, provided that within a month after dismissal the employee applied to this body and was not they are employed.
The procedure for calculating average earnings is established by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 24, 2007 No. 922.
Payments
The amount of benefits upon dismissal due to staff reduction is calculated in the manner established by Article 139 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. As an additional compensation for dismissal due to reduction, there may be a payment that is due to the employee if he or she has written consent to terminate the employment contract before the expiration of the warning period about the upcoming dismissal.
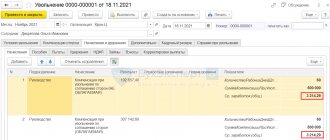
Example of calculating monetary compensation
To calculate the amount of compensation for dismissal due to staff reduction, all types of cash payments provided for in the remuneration system and used in the organization are taken into account.
On the day of dismissal (regardless of the reason for dismissal), the employer is obliged to transfer to the employee all funds due to him, including compensation for unused days of annual paid leave.
The size of the amount in a particular case does not matter; let’s call it X.
The amount of payment X is included in the calculation of the employee’s average monthly earnings, on the basis of which the employee will receive compensation in connection with the reduction, let’s call it Y.
On the last day of his work, the employee receives a cash payment equal to X + Y.
Next month, the employee will receive another payment equal to Y if he does not find a new job (the employer requires the original work book to be presented before making the accrual).
Further, if a person is registered with the employment agency within two weeks from the date of dismissal, but is still not employed, the employment agency has the right to decide on the need to accrue a third compensation. In this case, the former employee will receive another payment in the amount of Y.
If the employment relationship is terminated before the expiration of the two-month warning period about the upcoming dismissal at the initiative of the organization and the person is dismissed with his written consent, the employer compensates him for unworked time with a cash payment in the amount of average earnings (calculation is carried out according to Article 139 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In fact, this makes it possible to start looking for a new job as early as possible without losing financially.
Schematic step-by-step instructions for laying off employees in 2020 look like this:
Advantages and disadvantages
Of course, layoffs are not a pleasant thing for an employee, especially during a crisis in the labor market. But still, a reduction, in contrast to voluntary dismissal, has a plus - it is severance pay, paid in the amount of average monthly earnings and retained by the employee for at least two months.
For the employer, the advantages are obvious - his initiative, that is, the employee cannot refuse, further optimization of expenses and reduction of the fund for wages. However, such a procedure will only further reduce the fund, since the reduction procedure itself is expensive.
List of persons who cannot be dismissed due to reduction
The list of those who cannot be laid off by law includes the following categories of workers:
- temporarily disabled persons;
- employees on leave (including student leave and unpaid leave);
- mothers of small children under 3 years of age;
- women and men raising alone a child under 14 years of age or a minor child with a disability;
- members of the trade union organization.
Those who cannot be laid off from work also include pregnant employees and women on maternity leave. If an employee from the “untouchable” category is nevertheless fired due to staff reduction, he will be reinstated at work automatically by court decision.
We are ready to answer any questions you may have - ask them in the comments
Mass layoff
In order for an employer to understand whether he has a mass layoff, he should refer to industry and (or) territorial agreements. Part 1 of Art. speaks about this. 82 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
So, for example, in Moscow, according to the Moscow tripartite agreement for 2016-2018 between the Moscow Government, Moscow trade union associations and Moscow employers' associations, the criteria for mass dismissal are considered to be the indicators of the number of dismissed employees of organizations registered in the city of Moscow, with a workforce of 15 or more people for a certain period of time:
- dismissal within 30 calendar days of more than 25% of the total number of employees;
- dismissal of employees in connection with the liquidation of an organization of any organizational and legal form;
- reduction in the number or staff of the organization's employees in the amount of:
- 0 or more people within 30 calendar days;
- 200 or more people within 60 calendar days;
- 500 or more people within 90 calendar days.
What happens if you don't sign the notice?
In case of refusal to sign a notice of staff reduction, it is necessary to draw up a corresponding act and attach it to the employee’s personal file. A refusal issued in this manner will indicate that the employer has completed the entire procedure for dismissing the employee in full.
Likewise, if an employee refuses to receive a redundancy letter from a postal worker and it is returned to the sender, it must be attached to the file.
Even an unreceived message will also serve as evidence of compliance with the law by the employer.
But if the employer did not bother to obtain the employee’s signature on the notice or did not draw up an act of refusal to sign it, in the future the subordinate can easily challenge his actions by contacting the labor inspectorate or court.
Who is the first to be laid off when staffing is reduced?
The reduction of employees must be carried out in compliance with the standards established by the legislation of the Russian Federation. To do this, the employer should adhere to the following algorithm:
- Based on the order to reduce staff, a new staffing table is drawn up (you can find out what the management of the enterprise needs to know about the procedure for reducing a position in the staffing table here).
- A special commission is being formed to identify employees who have preferential rights. Based on the results of her work, a protocol is drawn up, which contains a list of employees who have more rights to remain at work.
- Based on the protocol of the commission, the manager makes a decision and draws up a list of employees who are subject to dismissal.
- Employees who are to be laid off are given 2 months' notice.
When making a decision, the manager pays attention to several factors:
- Skill level. Highly qualified employees have an advantage over other employees. Such specialists are considered to be those who have a higher specialized education and periodically attend advanced training courses or other skills. The manager can also take into account the theoretical knowledge or practical skills of an individual employee. The speed and quality of completing assigned tasks, the absence of disciplinary sanctions, and the amount of work that the employee can do compared to other colleagues are compared.
- Age. Quite often, older workers are candidates for layoffs. Despite the fact that legislation determines the main factor for keeping an employee at work is his level of qualifications, managers try to fire first of all working pensioners or citizens of pre-retirement age. However, such an employee may have a higher level of qualifications. If an employer fires an employee of pre-retirement age without reason, he may be subject to criminal liability in the form of a fine or compulsory labor (Article 144.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). Pre-retirees are people who have less than 5 years left until retirement.
- Family circumstances. If it is not possible to choose between employees with the same qualifications and work performance, the personal circumstances of the employee may be taken into account.
If a position is reduced or all staff positions in one position are abolished, the preemptive right does not apply.
The following categories of workers who do not have benefits usually fall under layoff:
- informal workers;
- recently hired employees with little experience in the company;
- workers with low labor productivity;
- not highly qualified;
- single and childless citizens;
- having disciplinary sanctions;
- working pensioners.
Pensioners working at the enterprise
Quite often, employers believe that it is easier to lay off working pensioners, since they already have a stable additional income - a pension. However, the employer does not have the right to lay off a pensioner only due to his age, since this is regarded by law as discrimination.
If the position of an older employee is subject to reduction, then dismissal is permissible, because he is the same employee as his colleagues. Qualifications and labor productivity, family and social status are taken into account.
Rights and benefits of pensioners:
- retirement age is not a reason for layoffs;
- high qualifications and extensive experience can be an advantage when considering candidates by the commission;
- in case of layoff, the pensioner has the right to receive an offer with another vacancy, severance pay, like other employees (we talked about the procedure for offering vacancies to an employee before layoff here, and from this article you will learn what payments and compensations are paid upon dismissal due to staff reduction) .
Newly hired employees
This category of workers is first in line for layoffs, since they generate the least income for the company. In this case, the qualifications of the employee are taken into account. If a newly hired employee is a highly qualified specialist, then most likely he will be retained in the company. Employees are being laid off:
- without work experience or education;
- conflict;
- uninitiative;
- neglecting official duties.
How to challenge an unfair decision?
If a citizen believes that he was fired illegally, then he can complain to the judicial authorities (Article 391 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). To do this, you should contact the district court at the location of the organization or at the place of residence of the citizen himself with a statement of claim within 30 days from the date of dismissal (Article 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Citizens who apply to court for illegal dismissal do not have to pay a state fee. If the decision is positive, the employee must be reinstated to his previous position immediately.
When choosing employees to be laid off, attention is paid to the qualifications and labor productivity of the citizen. There are no selection criteria established by law; the decision is made by the head of the organization.
At the same time, he must take into account the existence of a preferential right to remain at work for some employees. If a dismissed citizen does not agree with the management’s decision, he can file a complaint with the labor inspectorate or court.