What accounting requirements must be met so that high-quality financial statements can be generated on its basis?
When preparing financial statements, companies must proceed from the fact that such statements must give a reliable picture of its financial position as of the reporting date, financial results and cash flows for the reporting period, which are necessary for users of these statements to make economic decisions (Article 13 of the Federal Law dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”).
The preparation of financial statements begins with checking the correctness of the generated turnovers and balances in the accounting accounts.
And in order for financial statements to be reliable, it is necessary to comply with accounting requirements. After all, if the turnover is formed in accordance with the current accounting standards and accounting policies of the company, and the accounting program provides the necessary detail (analytics) of the accounts, then the preparation of financial statements is, in fact, a technical work.
Important! In many 1C software products there is an express check of accounting and analysis of the state of accounting. One of the purposes of such checks is to analyze accounting results, the presence of account balances that must be distributed, etc.
However, in a number of non-standard, complex business transactions, it would be useful for an accountant to trace the movement in the accounts of synthetic and analytical accounting and evaluate the correctness of the formation of the corresponding line of accounting statements.
How to do accounting?
Companies keep accounting records of property, liabilities and business transactions (facts of economic life) by double entry on interconnected accounting accounts.
Accounting registers are used to systematize and accumulate information contained in primary accounting documents accepted for accounting, for reflection in accounting accounts and in accounting (financial) statements.
The procedure for reflecting individual facts of economic life in accounting is established by federal and industry accounting standards, as well as by company methodological documents.
All transactions carried out in the company are documented by supporting documents drawn up in accordance with the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation on accounting. These documents serve as primary accounting documents on the basis of which accounting is maintained and the company's accounting (financial) statements are compiled.
Data contained in primary accounting documents (accounting objects) are subject to timely registration and accumulation in accounting registers.
Omissions or withdrawals are not allowed when registering accounting objects in accounting registers, as well as registration of imaginary and feigned accounting objects in accounting registers. An imaginary accounting object is understood as a non-existent object reflected in accounting only for appearance (including unrealized expenses, non-existent obligations, facts of economic life that did not take place). A sham accounting object is understood as an object reflected in accounting instead of another object in order to cover it up (including sham transactions recognized as such in accordance with clause 2 of Article 170 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Reserves, estimated liabilities, funds provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation, and the costs of their creation are not imaginary objects of accounting.
Such requirements for accounting are established in Part 3 of Art. 6, parts 2 and 3 art. 10, part 2 art. 12 of Law No. 402-FZ.
Important! Micro-enterprises and non-profit organizations have the right to conduct accounting using a simple system (that is, without using double entry), having prescribed such a procedure in the accounting policy (clause 6.1 of PBU 1/2008, part 4 of article 6 of Law No. 402-FZ).
Starting from 2013, the forms of primary accounting documents used (with the exception of government organizations) are determined by the head of the economic entity (clause 4 of article 9 of Law No. 402-FZ). These can be unified forms or your own, developed in compliance with the mandatory details of the primary documents. Before this date, when using unified forms, it was impossible to delete the existing details of such documents; it was only possible to supplement the form with new lines or columns.
At the same time, as practice shows, few economic entities have abandoned the use of the usual unified forms for which most accounting software products are designed.
And only for registration of business transactions for which unified forms of primary accounting documents are not provided, companies independently develop the necessary forms of documents, which are approved by separate administrative documents for the company (usually an appendix to the company’s accounting policy).
For example, to account for production costs, a route sheet is used, which is generated in the software product “1C: Enterprise 8.3” and contains the following information:
- Order number;
- division carrying out order fulfillment;
- basis of order (specification number).
Primary accounting documents can be compiled electronically using an electronic signature in the prescribed manner. A primary accounting document drawn up in electronic form can be accepted for accounting only if it is signed with the electronic signature of the responsible persons in compliance with the requirements and conditions of Art. 6 of the Federal Law “On Electronic Signature” dated April 6, 2011 No. 63-FZ.
A primary accounting document signed with a non-qualified electronic signature can be accepted for accounting if the use of such a signature is provided for by agreement of the parties (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated November 24, 2011 No. ED-4-3 / [email protected] ).
Which documents list accounting requirements?
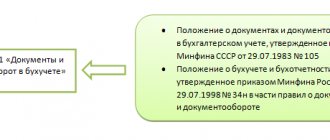
Accounting requirements are established by the law dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”, as well as by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n “On approval of the Regulations on Accounting...”.
At the same time, the provisions of these regulations, although they overlap in meaning in terms of establishing accounting requirements, still have some nuances. Thus, Law 402-FZ, Chapter 2, entitled “General Accounting Requirements”, establishes:
- list of accounting objects;
- a list of persons who are required to maintain accounting, are exempt from it, or have the opportunity to maintain accounting in a simplified version;
- principles of organizing accounting (who can be entrusted with accounting responsibilities, what qualifications should the person responsible for accounting have);
- general requirements for accounting policies;
- rules for drawing up primary documentation;
- the procedure for compiling and maintaining accounting registers;
- general requirements for inventory;
- rules for monetary measurement of accounting objects;
- general requirements for accounting;
- clarification of the concepts “reporting date”, “reporting period”;
- features of preparing accounting reports during the reorganization and liquidation of legal entities;
- rules for submitting legal deposit statements;
- obligation to maintain internal control by a business entity.
Read about what accounting studies in the publication “What is the subject of accounting?”
In turn, order No. 34n includes among the accounting requirements:
- the need to use double entry using accounting accounts;
- rules for approving the working chart of accounts;
- the procedure for monetary valuation of accounting objects;
- requirements for the language used to document facts of economic activity in the Russian Federation;
- brief requirements for accounting policies;
- the need for separate accounting of current and capital costs.
Order No. 34n also provides rules (which it does not directly call accounting requirements, unlike Law No. 402-FZ):
- documenting business operations;
- compiling and maintaining accounting registers;
- valuation and inventory of assets and liabilities;
- preparation and submission of accounting reports.
ConsultantPlus experts explained in detail who has the right to conduct simplified accounting and how to do it correctly. Get trial access to the K+ system and upgrade to the Ready Solution for free.
Thus, in general, the considered regulations constitute a complete picture of modern accounting requirements. Let's take a closer look at them.
Who is completely exempt from accounting?
Completely exempt from accounting:
- an individual entrepreneur (if he keeps records of income or income and expenses and (or) other objects of taxation or physical indicators in the manner established by Russian tax legislation);
- A branch, representative office or other structural unit of a company located on the territory of Russia, created in accordance with the legislation of a foreign state (if they keep records of income, expenses and (or) other objects of taxation in the manner established by tax legislation).
Such rules are established by clauses 1 and 2 of Article 6 of Law No. 402-FZ.
Who can do accounting in a simplified way?
“Kids” (small businesses) can do accounting in a simplified way.
However, the situation changes if the “kids” are subject to mandatory audit. In this case, the company is faced with the need to ensure the maintenance of accounting records in full, including the formation of differences between accounting and tax accounting in the accounting accounts (i.e., apply PBU 18/02, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 19, 2002. No. 114n), create a reserve for vacation pay (i.e. apply PBU 8/2010, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 13, 2010 No. 167), etc.
The simplified method can be used by organizations that have received the status of participants in the Skolkovo project and non-profit organizations (clause 4 and clause 5 of Article 6 of Law No. 402-FZ).
1.2. Accounting policies in credit institutions
Each credit institution independently develops and approves its own accounting policies
, based on Regulation No. 579-P and other regulatory documents of the Bank of Russia. The accounting policy is formed directly by the chief accountant of the credit institution and his deputies. The following elements of the accounting policy are subject to mandatory approval by the head of the credit institution:
- working Chart of Accounts of an accounting credit organization, which is based on the Chart of Accounts approved by Regulation No. 579-P. In its Chart of Accounts, a credit institution will include only those accounts that will be used by it in its activities;
- unified forms of all primary accounting documents that employees of the credit institution will use when carrying out their activities, except for the standard forms established by the regulatory documents of the Bank of Russia;
- the procedure for document flow, technology for processing all accounting information, including the transfer of information and all types of settlements with separate structural divisions of a credit institution - branches, additional offices, etc.;
- the procedure for reflecting certain types of banking operations in accounting, if this does not contradict the current legislation and regulations of the Bank of Russia;
- the procedure for assessing all types of property and liabilities, as well as the procedure for conducting an inventory of all assets and liabilities of the credit institution;
- the chosen method of calculating depreciation (amortization) of fixed assets, intangible assets, limits on the acceptance of objects for accounting as part of fixed assets and intangible assets, the procedure for writing off low-value and rapidly wearing items. The procedure for changing the value of fixed assets as a result of revaluation, repair, construction and reconstruction;
- if for individual accounting transactions there are different accounting methods permitted by law (federal standard), then you must choose one of them yourself and reflect it in the accounting policy of the credit institution;
- the procedure for organizing and implementing intrabank control;
- the procedure for conducting an internal audit in a credit institution;
- all other activities that are necessary to organize accounting in a credit institution.
When forming accounting policies
credit institution, it must be assumed that:
- the assets and liabilities of the credit organization exist and are accounted for separately from any other assets and liabilities, namely the owners of the credit organization or other organizations;
- the credit institution will operate continuously in the future, taking into account the fulfillment of all its long-term obligations;
- Previously adopted accounting policies must be implemented consistently, ensuring comparability of one accounting period with another. Major changes in accounting policies can only be caused by changes in the legislation of the Russian Federation;
- facts of banking transactions, as well as any movement of property and liabilities of a credit institution, must be reflected in the reporting period in which they took place, regardless of the actual receipt of funds.
In the form of a diagram, the accounting policy of a credit organization can be presented as follows:
The accounting policy of a credit institution must ensure:
- completeness and timeliness of reflection in accounting and reporting of all banking operations performed by a credit institution, as well as all movements of its property and all liabilities;
- priority of content over form, that is, operations and facts of economic activity of a credit organization are reflected in accounting in accordance with their economic essence, and not their legal form;
- data (balances) on analytical accounting accounts must correspond to data (balances) on synthetic accounting accounts;
- the requirement of rationality for accounting, that is, to ensure a minimum cost of ensuring the accounting process, based on the size and volume of transactions performed by the credit institution.
The accounting policy of a credit organization formed and approved by the manager is subject to formalization by its administrative documents - instructions, orders and standards. The main provisions of the accounting policy, as well as the procedure for recording individual transactions, are communicated to the accounting and other employees of the credit institution, and are also subject to reflection in their job descriptions. The adopted accounting policy comes into force in the credit institution, as well as in all its separate divisions (branches, additional offices) from January 1 of the calendar year. A credit organization is obliged to disclose the main provisions of its accounting policies, as well as the accounting methods used, which allow interested users to reliably assess its financial position.
Entrust your accounting to professionals - specialists!
Errors and inattentive attitude of company management to accounting issues can lead to penalties. It is extremely important to either provide the staff with a sufficient number of specialists with the necessary experience, or, which is more reliable, simpler and more profitable for the manager, to transfer the solution of these tasks to a third party.
Important! offers accounting services and solutions to other issues related to the work of accounting, with a guarantee of quality. Choose a modern offer for your business!