The patent tax system differs from other regimes in that a separate patent must be obtained for each type of activity. The recommended list of business areas for PSN is given in Article 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, but in the regions it can be reduced or supplemented.
Now the constituent entities of the Russian Federation have the right to establish almost any amount of potential income on the PSN, from which the tax is calculated at a rate of 6%. This has led to the fact that in some municipalities the cost of a patent has increased several times.
Therefore, before applying for an individual entrepreneur patent, we recommend that you find out its cost using the Federal Tax Service calculator. Please also keep in mind that in 2022, the PSN tax can be reduced by the amount of contributions paid for the entrepreneur and his employees.
If you find out the cost of the patent and this amount suits you, you need to submit an application in Form 26.5-1. Please note that in 2022, the form approved by the order of the Federal Tax Service dated December 9, 2020 No. KCh-7-3/ [email protected]
When filling out the second page of the application for a patent for an individual entrepreneur, you must indicate the identification code of the type of business activity. What is it and where can I get it? Let's tell you in more detail.
Free tax consultation
Regulation of the use of codes
The patent taxation system (PTS) was introduced in the Russian Federation on January 1, 2013.
A little earlier, on December 14, 2012, anticipating the introduction of a new taxation system, the Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation was issued and approved under the number MMV-7-3 / [email protected] on the introduction of the Classifier (KVPDP), which includes a complete list of types of activities Russian entrepreneurs to whom the patent system is applicable.
At the same time, changes and additions were made to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, namely Art. 25.5 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, regulating the rules for the application of PSN. In accordance with this article, the right to use PSN is strictly limited by the status of the entrepreneur and the level of profitability of his activities. Thus, only individual entrepreneurs whose income from business activities does not exceed 60,000,000 rubles per year and whose type of activity is included in the list provided by the Classifier have the right to apply the patent system.
Also, the patent tax system has some territorial restrictions, namely:
- the use of a patent for an activity included in the Classifier is permissible only in the municipality that issued the patent;
- work under a patent outside the territorial entity is permitted only to individual entrepreneurs whose business activities are related to the provision of transportation and outbound trade services.
Decoding UTII codes
You can select the code from the list.
Self-regulation of entrepreneurial activity - what is it?
Domestic services. Must be provided to citizens on a paid basis. Listed on lists approved at the federal level and local authorities. The form of payment for services is not taken into account.
Veterinary services. These include the types of activities provided for by OKPD2:
- providing medical care to animals;
- conducting laboratory research and providing technical services;
- consultations regarding animal feed (including dietetics).
Work not related to the treatment and health of animals does not fall under veterinary services.
Activities of service stations (repairs) and car washes, with the exception of:
- work with transport within the framework of warranty service;
- gas station;
- paid and fine parking.
Paid parking lots. Provides types of services:
- storage of vehicles (except impound lots);
- provision of parking spaces for rent.
Remember ! The entrepreneur is obliged to conclude an agreement in a simple form by issuing a parking ticket. Services are provided to owners of legally registered vehicles
Freight transportation. Passenger transportation. A necessary condition is that the vehicle must be designed for driving on public roads. Other conditions (for example, licensing, agency agreement) must be observed as required by law.
Retail trade in the premises of retail chains with trading floors. Retail trade in the premises of retail chains without trading floors or at non-stationary retail outlets up to 5 sq.m.
Retail sales in kiosks or pavilions. The following sales are not included in the list:
- listed excisable products (list in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- drinks and food products;
- homemade products (in whole or in part);
- gas;
- items left at the pawnshop;
- trucks and buses of all brands;
- goods outside of stationary retail chains.
Catering services with premises for accommodating consumers up to 150 sq.m. Catering services without premises for customer service.
The condition for choosing a special mode is the ability for consumers to consume the products directly at the point of sale. Sales through vending machines are retail trade and are not included in catering services.
Application of a patent
Placement of outdoor advertising on special structures. Must be carried out by the owner of the advertising object for the purpose of making a profit (for a fee).
Placement of outdoor advertising on vehicles. If there is a contract for the provision of services with the owner of the vehicle.
Important! Transport must be classified according to code 310.00.00.00.000 in the All-Russian Classifier of Fixed Assets.
Provision of hotel services (temporary accommodation).
Provision for temporary paid use (up to 5 sq. m):
- food outlets in the absence of a hall for visitors;
- places for trading in the premises of stationary networks without trading floors;
- places of non-stationary trade.
Provision for temporary paid use (more than 5 sq. m):
- food outlets in the absence of a hall for visitors;
- places for trading in the premises of stationary networks without trading floors;
- places of non-stationary trade.
Providing lease of land (up to 10 sq.m.) plots (clean from buildings) for the installation of retail or catering facilities on them.
Selling goods using vending machines. Used in situations not covered by code 08.
Tax return
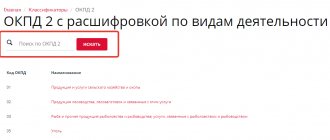
Working with the Classifier
The patent system is a very convenient way of taxation, since it does not involve complex accounting calculations and the individual entrepreneur is exempt from:
- from taxes on personal income within 60 million rubles of potential income;
- from taxes on property of individuals on that part of the property of an individual entrepreneur that is used by him to conduct business activities under a patent.
- From VAT. An exception is the obligation to pay VAT: if, in addition to the patent type of activity, the individual entrepreneur conducts another type of activity that does not fall under the PSN, as well as in cases provided for in Art. 174.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The amount of the tax and the timing of its payment are established simultaneously with the issuance of the patent, that is, the tax is not related to the income of the entrepreneur, which means, in fact, the tax on the patent is an advance tax.
Thus, when choosing between PSN and other types of taxation, an individual entrepreneur should weigh both the pros and cons of PSN. We talked about the advantages above. As for the disadvantages, they include:
- the advance nature of the tax, since the individual entrepreneur at the time of the transition to the PSN does not yet know what income he will have and whether he will have any at all;
- impossibility of deducting insurance payments.
If the pros were able to outweigh the cons, then the next step would be to study the Classifier to identify in it the type of activity that the individual entrepreneur is engaged in or plans to engage in.
Despite its scary name, the Classifier of types of business activities for which the use of PSN is permissible is, in fact, a very logical and easy-to-use document.
It simply lists:
- types of business activities that an individual entrepreneur can engage in under a patent;
- codes of types of activities and links to the relevant norm of law that regulates this type of activity.
In order to switch to PSN, an individual entrepreneur must indicate in the application a six-digit digital code XX YY ZZ, in which:
- the first group of characters XX is the activity code;
- the second group of characters YY is the code of the subject of the Federation;
- the third group of characters ZZ is the serial number of the type of activity.
Groups of signs are distributed in accordance with subparagraphs of clause 2 of Article 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. So:
- the type of activity code (XX) consists of two digits from 01 to 99. The number 99 refers only to household services to the population (according to the OKUN classifier No. 163 of June 28, 1993) and is not included in Article 346.43, paragraph 2. The full list of codes is included in section 5 of the Classifier;
- codes of the subjects of the Federation (YY) are included in the Classifier in accordance with the Directory BG -3-13/149 of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated March 25, 2002;
- the serial number of the type of activity (ZZ) is determined by the list of types of activity at the level of the subject of the Federation and represents differentiation from the numbers XX from 01 to 99. Do not be afraid of the word “differentiation”. We'll talk about it separately.
Main activity according to OKVED
But here you need to be careful. The fact is that the calculation of contributions for workers for insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases occurs according to the tariffs for the main type of activity. The more risky (traumatic or provoking occupational diseases) the activity is, the higher the insurance premium rate.
Before April 15 of the year following the reporting year, employers must submit to the Social Insurance Fund documents confirming the main type of activity, in the manner prescribed by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 55 of January 31, 2006. Organizations submit such confirmation annually, and individual entrepreneurs - employers only if they have changed their main type of activity. The main type of activity is considered to be the type of activity from which the income received is higher in comparison with the income from other activities for the previous year.
If confirmation is not submitted, then the FSS sets the highest tariffs of all types of activities specified by the policyholder, and this is where excessively specified OKVED codes can turn out to be very inappropriate.
Differentiation
Art. 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for the subjects of the Federation the right to set their own amount of the maximum income of an individual entrepreneur, giving him the right to work on a patent. At the Federation level, this maximum amount, as we have already said, is 60 million rubles. Since the cost of a patent is, in fact, the amount of tax, the right of subjects to set an income limit is just a local tax adjustment depending on the type of activity under the patent.
For the purpose of this regulation, the subjects of the Federation received the right to differentiate types of entrepreneurial activities (that same incomprehensible definition in the Classifier). Thus, all types of activities named in paragraph 2 of Art. 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (digits XX) can receive their values (digits ZZ) at the regional level.
Of course, differentiation is not carried out according to the personal desire of the head of the Federal Tax Service of a particular region. Differentiation must be justified by the provisions of one of the existing classifiers in the Russian Federation:
- services to the population - OKUN (Resolution of the State Standard of the Russian Federation No. 163 of June 28, 1993);
- types of economic activity - OKVED (Resolution 454-st of the State Standard of the Russian Federation of November 6, 2011).
Differentiation is also carried out based on the amount of expected income, which, in turn, can be calculated based on:
- average number of individual entrepreneurs' staff;
- area of real estate for rent;
- number of retail outlets with an area of more than 50 m2;
- number of non-stationary retail outlets, etc.
Actually, the methods and grounds for differentiation are not so important when using the Classifier. It is enough to know that differentiation is just an adaptation of activities established on a nationwide scale to the scale of a specific subject of the Federation.
In a purely applied sense, this means that when filling out an application in the fields reserved for the ZZ numbers, you indicate the regional number of the type of activity.
For greater clarity, let’s give a small example and take a type of activity such as services for leasing residential real estate in the city of Khimki, Moscow region.
In the code classifier, this type of rental activity and we see that rental is divided into two types - rental of residential premises has a digital designation according to scheme 195001, of which:
- 19 is XX, that is, the all-Russian activity code;
- 50 is YY, that is, the digital designation of the Moscow region;
- 02 is ZZ, that is, the number of the type of activity for the Moscow region.
Physical parameters of a business according to UTII
If an entrepreneur has chosen one or more types of activities for his business, he needs to check whether he can count on UTII. For this purpose, the presence of this area in the relevant list of Tax Codes is not enough. It is necessary that it correspond to certain physical parameters of the business, which are taken into account in the same document:
- application in specific areas of business provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- the number of hired employees, including the entrepreneur himself - the owner of the business;
- restrictions on the area of territory or premises;
- the number of units involved (vehicles, etc.).
FOR EXAMPLE! If an individual entrepreneur decides to open a cafe, then the tax he must pay will depend on the area of the hall where visitors are served, and the imputed income will be calculated from the amount of 1000 rubles. per month. The UTII code for this type of activity is 11. If a service hall is not planned, as, for example, in cheburechnayas, then UTII will depend on the number of hired personnel, and the income rate will increase to 4,500 rubles. per month. The code for such activities is already different - 12, although both of them are related to the organization of public catering.
All physical parameters specified in the legislative act are mandatory and must be indicated in tax reporting.
Do not confuse with OKVED!
The General Classifier of Types of Economic Activities (OKVED) lists all possible forms of small and medium-sized businesses. Some of them may or may not fall within the parameters of UTII. These are different types of accounting, the basis of which lies in various legislative acts and provides for mention in different documentation.
Territoriality and extraterritoriality of a patent
Conducting business activities in the territories of various constituent entities of the Russian Federation within the framework of a single type of activity involves the acquisition of a patent in each of the constituent entities.
For example, a patent for the repair of household appliances, obtained, say, in the Yaroslavl region, does not give the right to repair household appliances in a neighboring region, although the individual entrepreneur, in fact, will carry out in the neighboring region the same work for which he acquired the patent.
That is, if you assume a traveling nature of your work, then remember that you will have to purchase a patent in each of the subjects of the Federation in which you intend to work.
Work under a single patent in the territories of several subjects of the Federation is possible only for individual entrepreneurs whose activities are in one way or another related to the provision of transportation and outbound trade services.