What is account 60 used for in accounting?
The current Chart of Accounts establishes that settlements with suppliers and contractors must be carried out using account 60.
Here, transactions involving the receipt of goods, works, services from counterparties, and the amount of allocated VAT are recorded, if these companies work with VAT.
The use of account 60 involves reflecting on it advances for the next receipt of goods, as well as making payments for material assets already received or services rendered, work performed.
Attention! Thus, the information reflected on account 60 allows you to find out the status of mutual settlements with each supplier, and the balance on the account reflects either the amount of debt that the company must transfer to these companies, or the cost of goods, works and services expected to be received.
The same account reflects material assets that came to the company without documents being issued for them from suppliers, that is, uninvoiced supplies.
In what situation is the posting Debit 60 Credit 62 applicable?
Posting Debit 60 Credit 62 reflects the repayment of mutual claims to counterparties - the supplier and the buyer.
Example 2
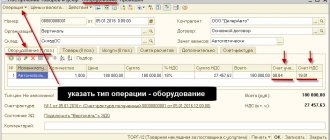
LLC "Mag" signed a contract for the purchase of goods from LLC "Optovik" in the amount of 156,000 rubles. (including VAT RUB 23,796.61). On March 14, 2022, “Mag” paid the cost of the goods (RUB 156,000) and on March 17, 2022, registered the goods for the specified amount. On March 30, 2018, “Mag” returned the goods in full due to the lack of demand for them.
Mag LLC made the following accounting entries:
Dt 60 Kt 51 -
prepayment for goods of 156,000 rubles
is reflected Dt 41 Kt 60 -
the cost of the goods is taken into account 132,203.39 rubles.
Dt 19 Kt 60 - reflected input VAT of RUB 23,796.61.
Dt 68 Kt 19 - VAT is accepted for deduction in the amount of RUB 23,796.61.
Dt 62 Kt 90 - return of goods 156,000 rubles.
Dt 90 Kt 68 - VAT charged RUB 23,796.61.
Dt 90 Kt 41 - the cost of goods is written off
132,203.39 rubles.
Dt 51 Kt 62 - advance payment of 156,000 rubles was returned.
In practice, a situation of offsetting mutual claims is also possible if the parties did not make monetary payments. In this case, in our example, instead of postings Dt 60 Kt 51 and Dt 51 Kt 62, the following entry will appear:
Dt 60 Kt 62 - offset of obligations in the amount of 156,000 rubles was carried out.
IMPORTANT! Tax officials consider the return of a quality product as a reverse sale (letter from the Ministry of Finance dated February 18, 2013 No. 03-03-06/1/4213).
Characteristics of account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”
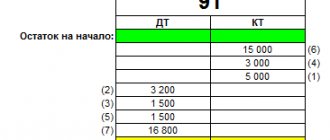
Legislative norms determine that account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” is an active-passive account, which can have two balances - on the debit and credit of the account.
That is, both receivables and payables are indicated here:
- A credit balance on account 60 means that the company has unfulfilled obligations to transfer funds for previously received goods, works, and services.
- A debit balance on account 60 means that organizations that are suppliers of work, services, and material assets in relation to the company where accounting is kept have not fulfilled their obligations.
The credit of account 60 shows the receipt of material assets from supplier companies, the cost of work performed by contractors as provided for in contracts, and the cost of services provided. At the same time, the cost of goods, works, and services received under contracts may include amounts of input VAT that must be paid to suppliers.
The debit of account 60 reflects the payment under contracts within the deadlines established therein. This can be either an advance payment, which is reflected in advances paid, or payment for goods supplied. Payment can also be made using bills of exchange.
Determining the account balance depends on what the balance was at the beginning:
- If it is debit, then you need to add the debit turnover to it and subtract the credit turnover. The final balance must be reflected in debit if it is at the beginning in debit plus the debit turnover is greater than the turnover in the credit account. Otherwise, the balance must be reflected on the credit of the account.
- If the initial balance is a credit balance, then the credit turnover of the account is added to it and the debit turnover is subtracted. The same rule applies here: if the excess goes to debit, then the final balance will be debit, otherwise it is the balance on the credit of the account.
Attention! Account 60 balances are shown in different sections of the balance sheet. The debit balance must be taken into account as part of accounts receivable in the assets of the balance sheet, and the credit balance in the liabilities of the balance sheet must be included in accounts payable.
6-APK
To record the operation on account 60, journal order No. 6-APK is used. Records are generated for each document (account, TTN, RN). Accounting is carried out by suppliers.
The journal consists of two sections: the general ledger and analytical data. The last page provides a summary of the settlement status at the end of the period. Data can also be displayed on separate journal forms. Reviews from accountants confirm that, in particular, it is easier for agricultural organizations to separately account for transactions for the purchase of valuables that are intended for capital construction.
The left side of the journal reflects transactions from KT60 to DT accounts for inventory, costs, and investments in non-current assets. VAT amounts are recorded on a separate line. The right side displays amounts from DT60, i.e. payments to suppliers. If the maturity date of the liability is extended, this is reflected as a separate entry at the end of the journal. The results of the left side of the journal are transferred to the general ledger, and the right side is used to reconcile turnover. Entries in the Book are made according to settlement documents. Excess inventory items are displayed as a separate line in the journal.
Payment data is entered into the journal based on bank statements, cash orders, and other monetary documents. Write-offs of debt amounts are reflected in accounting statements.
What subaccounts are used?
According to the standard working plan of accounts, sub-accounts can be opened for the account:
- Advances issued - information on settlements is shown here when the company makes preliminary transfers under concluded contracts.
- Urgent—shows settlements with suppliers whose shipment of goods and materials is not yet due for payment.
- Settlements on bills issued - used if payment for goods supplied is carried out using bills of exchange.
- Calculations for uninvoiced deliveries - shows the receipt of goods from the supplier without documents issued for delivery.
- Settlements on documents for which payment is overdue - it is very important to keep records of overdue accounts payable. Within a subaccount, subaccounts can be formed with designated periods (up to 45 days, 45-90 days, over 90 days).
You might be interested in:
Account 03 in accounting “Profitable investments in material assets”, what is taken into account, correspondence of accounts, postings
If settlements with counterparties are carried out not only in Russian rubles, but also in foreign currency, it is advisable to open separate sub-accounts for these operations:
- Settlements with suppliers and contractors in foreign currency;
- Settlements on advances issued in foreign currency.
Each company, taking into account the specifics of its activities, can open other sub-accounts to account 60 (commercial loan, etc.)
Attention! Within these subaccounts, analytical accounting can be maintained for each supplier separately. Sub-accounts can also be opened based on contracts concluded with the supplier.
Accounting for settlements on advances issued
Separately, I would like to say about the features of accounting for 60 advances issued on the account. If an organization transfers an advance payment to a supplier for the future supply of assets, for work or services, that is, it issues an advance, then a separate sub-account 60. 2 “Advance issued” is opened to account for them. In this case, subaccount 60.1 will take into account settlements with suppliers in the general case.
When transferring the advance, posting D60 is performed. 2 K51 (50, 52). In this case, a receivable from the supplier to the organization is formed.
When the supplier offsets the advance received and delivers assets (work, services), posting D60 is performed. 1 K60. 2.
Postings for accounting of advances issued:
Very often the question arises: is 60 count active or passive? As you can see, a debit can take into account the organization’s receivables, and a credit can take into account accounts payable, that is, accounting account 60 can simultaneously take into account assets and liabilities, which means it is active-passive. This was discussed in detail here.
Is a visa regime necessary between Russia and Ukraine?
No Yes
Accounting for bills
An organization can issue a bill of exchange to the supplier for the assets received, under which the organization undertakes to pay for the delivery within a specified period. That is, a bill represents a debt obligation of an organization (accounts payable). To account for bills issued, a separate subaccount 60. 3 “Bills issued” is opened. The issued bill is reflected by posting D60. 1 K60. 3.
After the debt on the bill is repaid, posting D60 is performed. 3 K51.
Example:
The organization received goods worth RUB 29,500 from the supplier. , including VAT 4500 rub. The supplier was issued a bill of exchange in the amount of 29,500 rubles. After the period specified in the contract, the organization fully repaid the bill.
What postings should the organization make?
Which accounts does it correspond with?
The current instructions establish that account 60 can correspond with the following accounts:
By debit:
- With account 50 — Payment in cash.
- With account 51 — Payments are made by non-cash payment.
- With account 52 — When payments are made through a foreign currency account.
- With account 55 – special invoices are used for payment.
- From accounts 60, 62, 76 - under mutual settlement agreements.
- From account 66 - when payment is made using borrowed funds.
- With account 79 - when the parent company pays for organizing the account.
- With account 91 - overdue accounts payable are written off.
- With account 99 - debt write-off in emergency circumstances
By loan:
- With account 07 - purchase of equipment that requires installation.
- With account 08 — acquisition of fixed assets.
- With account 10 - purchase of materials.
- With account 15 - when the receipt of materials is recorded using this account.
- With account 19 - when allocating incoming VAT.
- With account 20,23,25,26, 29, 44 - when the acquisition of works and services is carried out.
- With account 41 - upon receipt of goods that will be resold in the future.
- With account 50,51,51, 55 - upon return of overpaid amounts.
- With account 60, 76, 79 - for mutual settlements.
- With account 91 - when writing off overdue accounts receivable
- With account 94 - when a shortage of supplies from suppliers is identified.
- With account 97 - when recording expenses that are subject to distribution over a certain period (for example, rent, compulsory motor liability insurance, etc.)
Results
Account 60 is present in almost every transaction of a business entity, forming transactions for purchased goods, works or services. Posting Dt 60 Kt 60 allows you to reflect a business transaction that is quite common in practice - repayment of debt for goods using an advance payment transferred to the supplier.
When preparing for a test or exam in accounting, you need to know that teachers often like to ask about different accounts and entries in accounting. For dummies, it will be useful to know what counting 60 means. We’ll talk about this in our article today.
Any enterprise is engaged in accounting for payments to contractors and suppliers. This includes not only the supply of goods, but also various types of work and provision of services.
Balance sheet for account 60
Account 60 is active-passive, that is, it can simultaneously contain both debit and credit balances. In order to track their formation, it is advisable to keep records for each supplier.
Modern software products for accounting allow you to build registers to review calculations for the general account, for subaccounts, and also allow you to create a balance sheet for each individual supplier.
The balance sheet for account 60 is an accounting register. The law does not define a special form for this type of document, but it establishes a list of mandatory details:
- Company name, register name;
- Start and end date of the register, period of compilation;
- The value of monetary measurement;
- Signatures and names of responsible persons.
When creating a statement for account No. 60, you must adhere to the following rules:
- When generating debit turnover, all operations to repay the debt to the supplier, or prepayment for work or services are indicated there. It is also necessary to indicate here information about all payment documents - orders or cash settlement orders on the basis of which the payment was made. Also in this turnover it is necessary to show the operations of offset of claims, as well as the return of goods to the supplier.
- When forming credit turnover, all operations for the acquisition of inventory and materials from the supplier are indicated here - goods, works, non-current assets, etc. Also here you need to show all the primary documents on the basis of which the goods or services are posted - delivery notes, invoices, etc. etc. Also in this turnover you need to enter returns from prepayment suppliers for unfulfilled deliveries.
Decor
Almost all primary accounting documents have a unified form. Delivery registration is accompanied by TORG-12. The work acceptance certificate is not unified. But it is necessary to include the following details:
- number, date of compilation;
- names of the parties to the transaction;
- if an agreement was previously concluded, then the act must contain a reference to it;
- bank details of the parties.
Having received the primary documents, they must be immediately reflected in accounting. Let's look at the basic accounting entries for account 60.
The procedure for writing off receivables and payables on account 60
According to accounting requirements, only true facts must be reflected in accounting data and reporting. If the documents show accounts payable with an expired collection period, then this rule is violated.
You might be interested in:
Account 01 - Fixed assets in accounting: correspondence of accounts, postings
Thus, the company is obliged to write off accounts payable if the collection period established by law has passed.
In addition, a debt that can no longer be repaid is subject to removal if the counterparty has been deregistered and no longer exists as a legal entity.
The law establishes that the period during which the creditor has the right to demand its coverage is set at 3 years. In this case, it is necessary to correctly determine the beginning of this period.
When concluding a supply or service agreement, this document usually indicates the date for repayment of obligations. From the day following it, you need to start counting the statute of limitations.
However, the law provides for the deadline to be reset and counted from the beginning. This happens if the debtor acknowledges the existing debt in writing, makes partial payment, signs a reconciliation report, etc. In this situation, the limitation period must be counted first from this moment.
Attention! However, this cannot be done indefinitely. When a period of 10 years has been reached from the date of its formation, the debt must be written off unconditionally.
The debt write-off process is carried out in the following order:
- Carrying out an inventory of all payments. This procedure must be performed annually in order to compare the accounting data with the actual amounts of debt. During the inventory, it is also checked on what date the last movement on this debt occurred.
- Registration of an inventory report. There is a recommended form of the INV-17 form, but currently the company has the right to use its own forms. It is necessary to include in the act all the debts the company has, and not just the identified overdue ones. The document is drawn up in two copies, one is transferred to the accounting department, and the second remains with the commission.
- Preparation of accounting certificates. The accountant must analyze the executed act and draw up a certificate based on it. It reflects the counterparty for which there is a debt, the reason for the occurrence, the amount of the debt, as well as the day when the statute of limitations expired. Certificates of all expired debts, together with the act, are transferred to the manager for consideration and decision-making.
- Making an order. If the manager decides to write off, then he gives instructions to draw up an order to write off the debt. This document provides instructions to write off debt in accounting and tax accounting, and also appoints responsible persons. Based on the order, the accountant prepares accounting entries.
Recommended tasks for the discipline
Task No. 2482 (reflection of inventory results in accounting)
During the inventory of fixed assets, it was established that the organization unlawfully credited to its balance sheet a machine worth 200,000 rubles.
Task No. 723 (audit of cash transactions)
During an audit of the cash transactions of Progress OJSC, carried out in January after the reporting year, documents were found in the cash book that were not
Task No. 712 (accounting for the sale of fixed assets)
In April 2011, LLC A makes a decision and sells a fixed asset due to the impossibility of its production use.
Problem No. 5109 (calculation of insurance premiums)
Problem from the workshop “PM 03. Carrying out settlements with the budget and extra-budgetary funds (Tambov) The employee’s salary is 50,000 rubles per month. WITH.
Task No. 4024 (preparing accounting entries)
Prepare accounting entries for the following transactions: 1. Sold parts to customers, including VAT. 2. The cost of manufactured parts is written off. 3. Reflected.
1. Parts sold to customers, including VAT:
- 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”
- 90 "Sales"
2. The cost of manufactured parts is written off:
3. VAT payable is reflected:
- 90 "Sales"
- 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”
4. The costs of delivering sold goods to the buyer are reflected:
- 90 "Sales"
- 44 “Sales expenses”
5. The information costs of the intermediary organization associated with the implementation are reflected:
- 90 "Sales"
- 44 “Sales expenses”
6. The financial result from the sale of parts is reflected:
7. Received funds from the sale to the current account:
- 51 “Current accounts”
- 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”
8. Aktiv LLC accrued rental payments for February 20___:
- 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”
- 91 “Other income and expenses”
9. Aktiv LLC paid the rent of warehouse premises for February 20__:
- 51 “Current accounts”
- 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”
10. The organization reflected accrued interest on the issued long-term loan as part of other income:
- 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”
- 91 “Other income and expenses”
Learning to make accounting entries
Active accounts represent the organization's economic assets (account 01 - fixed assets, account 10 - materials, account 50 - cash on hand and other accounts). Looking ahead, I will say that active accounts always have a debit balance, or in other words, a balance with a plus sign. An increase in business assets on active accounts is reflected in the Debit, and a decrease - in the Credit of the account.
Active-passive accounts are accounts with a variable balance (the balance denotes the balance), i.e., for such accounts the balance can be either a credit or a debit. Active-passive accounts include settlement accounts, for example, settlements with suppliers (account 60), settlements with customers (account 62), etc. I will give examples when the balance on account 60 can be debit, and when it can be credit. Passive accounts include accounts that record the sources of formation of these economic assets. For example, such sources are profit (account 84), authorized capital (account 80), reserve capital (account 82) and others.
Passive accounts always have a credit balance. Unlike active accounts, an increase in funds in a passive account is reflected as a Credit, and a decrease as a Debit. A chart of accounts is a list of accounting accounts . In order for economic entities to maintain accounting records and submit financial statements according to uniform requirements, a chart of accounts is also required.
The chart of accounts of a commercial organization and the Instructions for its application were approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 94-n dated October 31, 2000.