What is a currency transaction type code?
KVBO is a five-number value indicating the type of transaction. The code is selected depending on the purpose of the payment and the content of the documents accompanying the transaction. If the payment order and code do not match, the payment is rejected. The list of QVBOs is contained in Central Bank Instruction No. 181-I dated August 16, 2022.
How to make a foreign currency payment and what documents to submit to the bank ?
Where should I put the code? If this is an order for a transaction in rubles, you need to put it before the text about the purpose of payment. In other banking documents, KVVO is indicated in a line specially designated for this. The code is both alphabetic and numeric values. There is no need to put spaces or other symbols between letters and numbers.
KVVO consists of two parts. The first indicates the class of the transaction, the second – its essence. Let's look at an example. Operation code – 10100. Its components:
- 10 – indicates the export of products from the territory of Russia.
- 100 – indicates that the buyer made an advance payment.
the bank's commission for currency control in accounting and tax accounting ?
The very presence of this code means that this is a transaction with a foreign counterparty.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! Sometimes an accountant encounters problems when choosing a KVBO. There are a lot of codes in the Central Bank instructions. It is not always easy to decide which one is suitable for a particular operation. If an accountant is afraid of making a mistake, he can ask a representative of the servicing bank for advice.
Examples of currency transaction codes indicated in the payment order:
- 01010 – sale by a resident of foreign currency for rubles;
- 02010 – purchase of Russian currency for foreign currency by a non-resident;
- 10100 – a non-resident makes an advance payment to a resident for goods exported from the territory of the Russian Federation;
- 11100 – a resident transfers to a non-resident an advance payment for goods that are imported into the territory of the Russian Federation;
- 12060 – a resident transfers payment to a non-resident for goods sold outside the Russian Federation;
- 21300 – a resident transfers funds to a non-resident under a property lease agreement.
When a resident employer transfers funds to a non-resident employee, the following codes are most often used:
- 70060 – wages and other types of remuneration;
- 70040 – benefits and other social payments;
- 70125 – payments related to the execution of decisions of judicial authorities.
A complete list of encodings can be found in Appendix No. 1 to Bank of Russia Instruction No. 181-I.
Code groups
The KVVO group is the first 2 digits that reveal the class of the operation. Let's look at these groups and their meaning:
- 01 and 02 – non-cash conversion payments.
- 10 and 11 – payment for export or import of products.
- 12 and 13 – payment for products without import and export.
- 20 and 21 – payment for services, work, rights to intellectual activity.
- 22 and 23 – payment under mixed type agreements.
- 30 – payments for real estate.
- 32 – payment under an agreement for assignment of claims.
- 35 – other payments.
- 40 and 41 – issuance of loans.
- 42 and 43 – payment of loans and interest on them.
- 57 – payment under trust agreements.
- 58 – payment under brokerage service agreements.
- 70 – transactions not related to trade (for example, transfer of salary or pension).
- 90 – other operations.
The next three numbers reveal the contents of the operation. Example: code 70 affects a non-trading transaction. The last numbers indicate which transfer was made. For example, this could be the payment of travel allowances.
What is KVVO?
The currency transaction code is a five-digit number that reflects the nature of the transaction. The selected set of characters must correspond to the purpose of the payment and the content of the documents submitted to the bank's currency controller. In case of discrepancies, payment will be refused.
A complete list of currency transaction codes is given in the instruction of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation 138-I, in force since 2012. KVBO is the following combination of characters:
If an accountant prepares a ruble payment order, the specified set of characters precedes the rest of the payment purpose text. In other banking documents, the selected code is entered in a specially designated field.
Spaces and any extraneous characters are not allowed between the alphabetic and numeric parts.
Conventionally, each CVBO can be divided into two parts, the first of which (two symbols) classifies it as a specific class of transactions, and the second (the remaining three digits) characterizes the economic essence of a specific operation.
10 – a group of numbers indicating that the transaction is related to the import of goods into Russian territory.
100 – means that delivery is made on an advance payment basis.
It turns out that the currency transaction code 10100 means the shipment of goods to the territory of the Russian Federation on the basis of prepayment to a foreigner.
Purchasing goods from a foreign counterparty, but on the terms of payment upon delivery.
The selected QVBO from the above two options determines which fields the accountant will fill out in the certificate of foreign exchange transactions and which documents he will submit to the bank. If prepayment is chosen, you need to specify the expected delivery time and return of the advance payment. If the currency transaction code is 11200, these two fields are not filled in, but you must send the currency controller a document confirming that the goods have crossed the state border of the Russian Federation.
{VO20100} and {VO20200}
These codes refer to one group of operations - the provision of services in the field of international cooperation, including under agency agreements. The choice of a specific combination of symbols depends on the terms of the transaction. If we are talking about prepayment, the first option is suitable; the accountant will prescribe the terms for the provision of services and the return of the advance.
If the parties have agreed on a partnership on post-payment terms, the currency transaction code 20200 will be appropriate. It is also necessary to provide the bank with a document confirming that the work has been completed and services have been provided, for example, an act signed by both parties.
The currency transaction code 61100 consists of two parts:
- 61 – indicates that we are talking about payments made by residents;
- 100 – describes the nature of the operation being performed.
This code is used in a situation where funds are transferred from one account to another, opened in another bank. Supporting documents (contract, invoices, etc.) are not required for this transaction. The money is credited to the transit account and transferred to the current account using the SVO.
Choosing the right KVBO is not an easy task for an accountant or economist who is taking his first steps in the field of currency control. The instructions of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation are extensive, and many of the explanations are difficult to understand. To reduce the likelihood of error to zero, before making a currency transfer, it is recommended to consult with specialists of the servicing bank.
KVBO for operations
Here are the codes that usually accompany operations:
- 10100. Prepayment for the export of a batch of products from the territory of Russia.
- 10200. Deferred payment for a shipment transported out of the country.
- 11100. Advance payment to a foreigner for products imported into the country.
- 11200. Settlements with a resident if he is given a deferred payment for a consignment imported into the country.
- 12060. Payment for goods sold by a non-resident. It is assumed that the products were sold abroad, without import into the Russian Federation.
- 13010. Payment from a foreigner to a resident for goods sold in Russia.
- 20100. Prepayment of services or goods in favor of a resident.
- 20200. Payment between a non-resident and a resident for services or work.
- 20400. Payments under agreements on assignments, guarantees to the resident.
- 20500. Payments under guarantee agreements to a non-resident.
- 21100. Advance payment for services or work in favor of a foreigner.
- 35030. Payment to the resident for other actions.
- 35040. Payment in favor of a foreigner for other actions.
- 41030. Lending to a resident by a non-resident.
- 42015. Payment of the principal debt to a non-resident, if the resident has corresponding obligations.
- 61100. Movement of currency from one account to another.
- 61135. Transfer of currency from a resident’s account to an account in another bank.
- 70060. The resident transfers remuneration to the foreigner for work.
- 99090. Other actions and translations not listed above.
This is a list of the most common KVBOs. The remaining codes are in Central Bank Instruction No. 181.
Other operations
KVBO is also needed when working with foreign currency:
- 01010 – sale of currency for rubles.
- 01030 – purchase of currency for rubles.
Code usage example
Products were purchased from a non-resident. It was transported to Russia based on the provisions of a foreign trade agreement. The required code depends on the selected payment type:
- 10100 – for prepayment.
- 10200 – postpaid.
What to do if the goods of a non-resident are located in Russia? Code 13010 is used. The validity of its use is confirmed by an invoice with the Russian address of the product location.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! Code 13010 is not suitable for fuel and other resources for vehicle operation. The purchase of fuel is accompanied by these KVBO: 22110 (prepayment transaction) and 22210 (postpayment).
Currency control
All transactions with foreign currency are under special control of the state. The main regulatory legislative act of December 10, 2003 No. 173-FZ. The regulation procedure is determined by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation and the Government (Clause 1, Article 5 No. 173-FZ).
The law primarily applies to residents and non-residents. Residents include, inter alia, legal entities created in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, and non-residents include legal entities created in accordance with the legislation of foreign states and located outside the territory of the Russian Federation (Article 1 No. 173-FZ).
Currency transactions between residents and non-residents are carried out through authorized banks (Clause 1.1, Article 19. No. 173-FZ).
As part of control, residents are required to provide authorized banks with the information specified in clause 1.1. Art. 19. No. 173-FZ, including:
- the expected timing of receiving foreign currency or Russian currency from non-residents for the fulfillment of obligations under contracts;
- expected terms of fulfillment by non-residents of obligations under agreements.
Documentation of control requirements is carried out on the basis of Instruction of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated June 4, 2012 No. 138-I. It contains the procedure for residents to provide control documents, the forms of these documents, as well as information for filling them out, in particular, the code for the type of currency transaction in the payment order.
Code when paying wages to a non-resident
The company's staff may include non-residents. A non-resident is any person without a Russian passport or citizenship. Within the framework of currency control, it does not matter how long the foreigner lived in Russia. In any case, he is considered a non-resident. When paying remuneration to a foreign person, codes are also used.
Payments in favor of a non-resident are indicated by code 70060. But to use this KVBO, it is not enough to provide only a payment order to the bank. Most likely, you will also need an employment agreement with a foreigner and a copy of his passport.
Remuneration for an employee is not only salary, but also other payments. And each payment is assigned its own code:
- 70200 – payments according to the advance report (for example, travel expenses).
- 70030 – social payments (for example, financial assistance).
- 70120 – payments made by court decision.
Upon payment, accompanying documents are sent to the bank. Their list depends on the type of operation. For example, a non-resident is accrued travel allowances. In this case, a business trip order is sent to the bank.
When is KVBO indicated?
The currency transaction code must be entered under the following circumstances:
- making a payment in foreign currency by a resident of Russia in favor of a non-resident;
- receipt of funds in rubles from a foreigner;
- writing off currency to a resident or foreigner;
- receipt of currency from residents or non-residents;
- carrying out settlements with a non-resident bank.
Companies and individual entrepreneurs must select a code when filling out banking documents: transfer applications (if funds are transferred in foreign currency), payment orders (if payments are made in rubles) and certificates of currency transactions.
Filling procedure
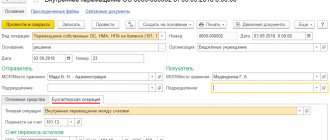
Before the text in the “Purpose of payment” field we write VO in Latin letters, followed by the transaction code from Appendix 2 of instruction No. 138-I, and we enclose all this in curly brackets.
Example. {VO01030} is a resident’s purchase of foreign currency for rubles.
Important! Latin letters are in capital letters only; spaces cannot be placed inside parentheses.
You will find codes for types of transactions in the material “Directory of codes for types of currency transactions (2020-2021)”.
The code is incorrectly selected and filled in - what to do?
If, when drawing up a payment order, the code for the type of currency transaction was incorrectly specified, the bank will return such a document. And he will be right, since he must control the submitted documents (Chapter 18 of instructions No. 138-I). In this case, the organization has only one option - to redo the payment card.
But there are a number of cases when you don’t have to draw up settlement documents at all. And if they are compiled, then you don’t have to write the code. And this should not be a reason for returning the document from the bank. Such situations are described in paragraph 3.3 and paragraph 3.4 of Chapter. 3 instructions No. 138-I.
Another option when an organization can be sure that the bank will accept its documents is to include clauses in the agreement with the bank stating that the bank will draw up payment orders for foreign exchange transactions on the basis of the documents that the organization provides.
Preparation of payment documents in foreign currency: where to start
In order to understand the details of processing a foreign currency payment, we will consider the most general case:
- the payment is made in foreign currency to a non-resident;
- payment is made under a foreign trade contract;
- the payment leaves the Russian bank to a foreign bank.
To begin correctly processing a payment in foreign currency, you must first register with the bank (clauses 4.1, 4.2 of Instruction No. 181-I):
- import contract, loan agreement, the amount of obligations under which is equivalent to 3 million rubles. and more;
- an export contract, the amount of obligations under which is equivalent to 6 million rubles. and more.
Until 03/01/2018, along with the contract, it was necessary to submit a transaction passport to the bank. But after the Central Bank’s instruction dated August 16, 2017 No. 181-I came into force, the passports were cancelled.
- take the payment form for the currency transfer that your bank uses. The general requirements for filling out such payments are established by instruction No. 181-I, but there is no uniform form for all - therefore the bank usually develops and approves its own;
- decide on payment details:
- who pays the commissions and fees for the transfer - the payer, the recipient, or both their part (in the practice of international payments there are different options);
- how currency will be purchased to complete the transaction: the company will buy it in advance itself or instruct the bank to exchange the required amount immediately on the basis of a payment order;
- Is there a currency clause in the contract that may adjust the payment amount?
invites you to a webinar about recent tax news: we will discuss it in detail on August 27.