The deflator coefficient is a coefficient that is set each year based on changes in consumer prices over the past year. This indicator is used for different purposes, for example:
- to adjust taxes;
- to set limits;
- to calculate UTII tax;
- to calculate the trade fee;
- for other purposes
Important! For 2022, deflator coefficients were established by Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia No. 595 dated October 30, 2018 “On the establishment of deflator coefficients for 2022.” This order established the following deflator coefficients:
| Deflator coefficient | Meaning |
| deflator coefficient for UTII | 1,915 |
| deflator coefficient for personal income tax | 1,729 |
| patent deflator coefficient | 1,518 |
| deflator coefficient for property of individuals | 1,518 |
| deflator coefficient for simplified tax system | 1,518 |
| deflator coefficient for trade tax | 1,317 |
Deflator coefficient for UTII tax
The tax on UTII is calculated using the deflator coefficient K1 and the correction coefficient K2. In order to understand what role they play in calculating the UTII tax, let's look at how this tax is calculated. The formula for calculating UTII is as follows:
UTII = DB x (Physical education 1 month + Physical education 2 month + Physical education 3 month) x K1 x K2 x tax rate, where
DB – basic profitability. Basic profitability is established by law. It depends on the type
activities of an organization or individual entrepreneur. Types of activities and their basic profitability are specified in paragraph 3 of Article 346.29 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Fizpok – physical indicators. For example, a physical indicator for veterinary services is the number of employees who provide veterinary services to the population, including the individual entrepreneur himself (if it is an individual entrepreneur). Physical indicators are also specified in paragraph 3 of Article 346.29 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Physical indicators are added up for the first, second and third months of the quarter, respectively.
K1 is a coefficient that adjusts the tax depending on inflation.
K2 is a coefficient that adjusts the base profitability up or down depending on its value. It is established by regional authorities.
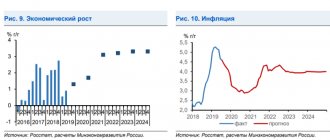
These coefficients are needed to adjust the amount of tax depending on the market situation. This is stated in Article 346.29 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Recent years have been characterized by a constant increase in the K1 coefficient, because inflation is growing. As the ratio increases, taxes increase. For example, in 2022 K1 was equal to 1.798, and in 2022 it was already 1.915.
Deflator coefficient for PSN
The patent tax for a year is calculated using the formula:
PSN = PVD x tax rate, where
PPV – potential income depending on the type of activity. The amount of potential income is set by regional authorities, however, according to federal legislation, its size cannot be more than 1,000,000 rubles, taking into account the deflator coefficient.
The tax rate is set by regional authorities. A patent can be taken out for a year or several months. A patent for several months is calculated using the formula:
PSN = PVD x tax rate x number of months / 12, where
The number of months refers to the number of months of the period for which the patent was issued.
Since a deflator coefficient is involved in calculating the cost of a patent, the potential income that the regions set in 2022 should not exceed 1,518,000 rubles.
1,000,000 x 1.518 = 1,518,000 rubles
Deflator coefficient for 2022 for UTII
The K1 deflator coefficient for organizations and entrepreneurs on UTII adjusts the size of the basic profitability for all types of activities on the imputation. In 2022, the coefficient is 1.915, for 2020 its size is 2.005 (Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated December 10, 2019 No. 793). Thus, the tax burden of most companies on UTII will increase.
There is also a K2 coefficient. On the contrary, it is designed to reduce the amount of tax, since its amount cannot be more than 1. But the coefficient K2 is set by local authorities for certain categories of taxpayers. There is no single K2 indicator.
Let us recall that the State Duma proposed, when calculating the deflator coefficient for UTII for 2022, to take into account changes in consumer prices in an amount not exceeding the inflation rate. Earlier it became known that the Bank of Russia lowered its annual inflation forecast from 4.0–4.5 to 3.2–3.7%. However, the calculation of the coefficient for UTII was still made based on 4.7%.
Deflator coefficient for personal income tax
For personal income tax (NDFL) purposes, the deflator coefficient is used to calculate a fixed advance payment for foreign patents . This payment is calculated according to the formula:
APf = AP x K1 x Kr, where
AP – established advance amount
K1 – deflator coefficient.
Kr – regional coefficient, which is set by local authorities
According to Article 227 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, AP = 1,200 rubles.
Deflator coefficient for simplified tax system
In a simplified taxation system, a deflator coefficient is needed to determine the income limit . The income limit is needed to determine the possibility of switching to the simplified tax system and applying the simplified tax system in the future. As you know, in order to start applying the simplified taxation system, a number of conditions must be met, namely:
- the number of employees should not exceed 100 people;
- the income limit of an organization or individual entrepreneur should not exceed 150,000,000 rubles;
- the residual value of fixed assets of an enterprise or individual entrepreneur should not exceed 150,000,000 rubles;
- the share of participation of other persons in the authorized capital of the organization should not exceed 25%;
- organizations that have branches cannot apply the simplified taxation system
According to paragraph 4 of Article 346.13 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the maximum value of the limit must be indexed annually by a deflator coefficient. In 2022, the maximum limit increased to 150,000,000 rubles. At the same time, the effect of paragraph 2 of Article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation was immediately suspended until the end of 2022 by Federal Law No. 243-FZ of 07/03/16. This clause provides for the indexation of the limit by the deflator coefficient, so in 2022 the limit will not be adjusted. It remains in the same position and is equal to 150,000 rubles.
The role of the deflator coefficient among the “simplified people”
In order to switch to the simplified tax system, as well as to maintain the possibility of applying this special tax regime, the organization’s income should not exceed the maximum amount (for individual entrepreneurs, there is no income limit at the time of transition to the simplified tax system).
The transition of an organization to the “simplified” system from the beginning of a new calendar year is permitted provided that, based on the results of nine months of the year in which the notification is submitted, income from the sale of goods (work, services) and property rights, together with non-operating income (according to tax accounting data) does not exceed 45 million rubles. This amount of income - the limiter for the transition to the simplified tax system - is subject to indexation no later than December 31 of the current year by the deflator coefficient established for the next calendar year. This means that in order to switch to the simplified tax system from January 1, 2015, the income limit (45 million rubles) must be adjusted by the deflator coefficient established for 2014 (it is equal to 1.067 - Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation dated November 7, 2013 No. 652 ). The deflator coefficient established for 2015 in the amount of 1.147 is subject to application to adjust the income limit of 45 million rubles in order to establish the possibility of switching to the simplified tax system from 01/01/2016.
For your information
The tax authority must be notified of the transition to the simplified tax system from the beginning of the new calendar year no later than December 31 of the year preceding the year of application of the special regime. Persons who have not done this within the prescribed period do not have the right to use the simplified tax system ( clause 19, clause 3, article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ).
| Income limit | |
| For 9 months of 2014 for the transition to the simplified tax system from 01/01/2015 | 48,015 thousand rubles. (RUB 45 million x 1.067) |
| For 9 months of 2015 for the transition to the simplified tax system from 01/01/2016 | RUB 51,615 thousand (RUB 45 million x 1.147) |
Please note: if an organization that has decided to switch to the simplified tax system applies the taxation system in the form of UTII in relation to certain types of activities, income from those types of activities in respect of which taxation is carried out in accordance with the general taxation regime is subject to control ( clause 4 of article 346.12 of the Tax Code RF ).
After the transition to the “simplified” system, the obligation to control the amount of income remains (for individual entrepreneurs): at the end of the reporting (tax) period, income taken into account for the purpose of calculating the single tax should not exceed 60 million rubles. ( clause 4 of article 346.13 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ). This income limit is also subject to adjustment by the deflator coefficient established for the corresponding year. (Reporting periods are the first quarter, six months and nine months of the calendar year; the tax period is the calendar year.)
| Income limit | |
| For the reporting (tax) period of 2014 for the application of simplified taxation system | 64,020 thousand rubles. (RUB 60 million x 1.067) |
| For the reporting (tax) period of 2015 for the application of simplified taxation system | 68,820 thousand rubles. (RUB 60 million x 1.147) |
The correctness of the presented calculations is confirmed by financiers (see letters dated January 13, 2014 No. 03-11-06/2/248 , dated December 13, 2013 No. 03-11-06/2/54977 ).
If, along with the simplified tax system, the taxpayer uses the taxation system in the form of UTII in relation to certain types of activities, the maximum amount of income for the use of the simplified tax system should be calculated based on “simplified” income. That is, in this case, the same approach is used as when controlling the maximum amount of income at the time of transition to the simplified tax system. The Tax Code does not say this directly, but this is precisely the opinion of the Ministry of Finance ( letters dated March 27, 2013 No. 03-11-06/2/9647 , dated May 28, 2013 No. 03-11-06/2/19323 ).
For an individual entrepreneur, the question of how to determine the maximum amount of income under the simplified tax system may be relevant if he applies the tax system for certain types of activities. The answer is provided directly in the Tax Code: when determining the amount of income for the purposes of complying with the income limit, income under both special tax regimes is taken into account. Moreover, this principle operates in order to control the legality of the application of not only the simplified tax system ( paragraph 2, paragraph 4, article 346.13 ), but also the PSNO ( paragraph 5, paragraph 6, article 346.45 ). Under PSNO, income from sales for all types of business activities to which the specified taxation system is applied should not exceed 60 million rubles. (Please note: this income limit is not adjusted.)
Reminder
“Patent” types of activities include the provision of public catering services through catering facilities with a customer service area of no more than 50 square meters. m for each such object ( clause 47, clause 2, article 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ).
The Ministry of Finance interprets the stated requirements as follows (see letters dated October 10, 2014 No. 03-11-11/51237 , No. 03-11-11/51236 ). Income received during a calendar year as part of the implementation of “patent” types of activities should not exceed 60 million rubles, and in combination with “simplified” income - the maximum amount of income determined according to the rules of Chapter. 26.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (in 2014 - 64,020 thousand rubles, in 2015 - 68,820 thousand rubles).
Trade tax deflator coefficient
Trade tax is a tax that applies only in Moscow. It is regulated by Moscow Law No. 62 dated December 17, 2014 (as amended on November 29, 2017). This tax applies to organizations and individual entrepreneurs engaged in retail sales and wholesale sales. To do this they must use the following objects:
- stationary facilities with a sales area;
- stationary facilities without a sales area;
- non-stationary objects
This tax must be applied by organizations and individual entrepreneurs that use the simplified or regular taxation system. Those organizations and individual entrepreneurs that use UTII, are on the patent taxation system or the Unified Agricultural Tax, are exempt from paying this tax. To calculate this tax, you need to know the rates. Rates are set based on the trade facility (trade facility) or its area. In addition, rates depend on which administrative district of the city the property belongs to. For rates on retail markets, a deflator coefficient is used. Examples of Moscow rates taking into account the deflator coefficient for 2022 are given in the following table.
| Objects | Rates by administrative district, rubles per object (per quarter) | ||
| Administrative district 1 group | Administrative district 2 groups | Administrative district 3 groups | |
| stationary sales area of 50 m2 or less | 60 000 | 30 000 | 21 000 |
| stationary sales area of 50 m2 or more | · 1,200 rub/m2 if less than 50 m2 · 50 rub/m2 if more than 50 m2 | · 600 RUR/m2 if less than 50 m2 · 50 RUR/m2 if more than 50 m2 | · 420 rub. RUB/m2 if less than 50 m2 50 RUB/m2 if more than 50 m2 |
| if there is no sales area, except gas stations | 81 000 | 40 500 | 28 350 |
| other non-stationary objects | 40 500 | 40 500 | 40 500 |
| retail non-stationary trade (delivery and carry-out) | 40 500 | ||
| for management companies of urban retail markets | 65.85 RUR/m2 | ||
In 2022, the size of the trading fee of management companies of urban retail markets will increase by the deflator coefficient: 65.85 = 50 rubles x 1.317.
Administrative district of group 1 includes the territories of the Central Administrative District of Moscow.
Administrative district of group 2 includes:
- Northern administrative district, except Molzhaninovsky district;
- North-Eastern administrative district, except for the Northern region;
- Eastern administrative district, except for the Eastern, Novokosino, Kosino-Ukhtomsky districts;
- South-Eastern Administrative Okrug, except Nekrasovka;
- Southern Administrative District;
- Southwestern Administrative Okrug, except for Northern and Southern Butovo;
- Western administrative district, except Solntsevo, Novo-Peredelkino, Vnukovo;
- North-Western Administrative District, except Mitino, Kurkino
Group 3 administrative district includes:
- Zelenogradsky, Troitsky, Novomoskovsky;
- Northern region of the North-Eastern Administrative District;
- Molzhaninovsky district of the Northern Administrative District;
- Vostochny, Novokosino, Kosino-Ukhtomsky districts of the Eastern Administrative Okrug;
- Nekrasovka South-Eastern Administrative District;
- Northern and Southern Butovo of the South-Western Administrative District;
- Solntsevo, Novo-Peredelkino, Vnukovo Western Administrative District;
- Mitino and Kurkino of the North-Western Administrative District
Deflator coefficient for personal property tax
For personal property tax, the deflator coefficient is applied only if this tax is calculated based on the inventory value of the property.
Example. The inventory cost of the apartment is equal to 1,300,000 rubles, taking into account the deflator coefficient in 2022, its cost will be equal to 1,973,000 rubles (1,300,000 x 1.518). Currently, the calculation of property tax based on inventory value is valid only in some regions of the country. And starting from 2022, all property taxes for individuals will be calculated based on the cadastral value of the property.
Calculation procedure
The total income of a business entity is calculated by summing up a number of income, namely:
- proceeds from the sale of goods or services;
- revenue from non-operating income;
- advance payments received to the current account or cash desk of a business entity as an advance on contractual obligations.
The cumulative values are multiplied by the established deflator coefficient. The resulting value will determine the profitability limit.
| Year | The amount of the maximum income limiting the right to switch to the simplified tax system | The amount of the maximum income limiting the right to use the simplified tax system |
| 2020 | ||
| 2019 * | 90 million rubles | 120 million rubles |
| 2018 * | 90 million rubles | 120 million rubles |
| 2017 * | 90 million rubles | 120 million rubles |
| 2016 | 45 million rubles | 60 million rubles |
| 2015 | 45 million rubles | 60 million rubles |
| 2014 | 45 million rubles | 60 million rubles |
| 2013 | 45 million rubles | 60 million rubles |
* Please take into account: for 2022 - 2022, indexation of the income limit for the simplified tax system has been suspended, and for 2020 the deflator coefficient is equal to 1.