Enterprise assets: concept, management principle
A company's assets are property resources that it owns and uses in production activities to make a profit and develop its business. They may not have a material form, they may be presented in the form of funds in a current account or in the form of some object.
Important! Starting from January 2022, companies have a PPA - the right to use an asset. These are assets that a company has leased and uses to make a profit. They do not belong to the company by right of ownership, but they generate income for it.
Asset management is relevant for any company. Therefore, it is carried out on an ongoing basis.
In this case, assets must meet the following requirements:
- Participate directly or indirectly in the main activities of the company and generate profit (income).
- Have a valuation.
- Belong to the company on the right of ownership (in the case of leased assets - on the right of use).
- The company can exercise control and management of assets.
Who controls?
Large companies with a network of branches and representative offices, as a rule, manage assets through a specially created structural unit.
Medium and small businesses do not have the production capacity to organize a separate asset management body. It is acceptable for them to assign management functions to the accounting department, which, in turn, can distribute control over certain types of assets to other departments.
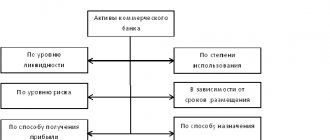
Composition and structure of assets
The company's resources are different: they are distinguished by their form, scope of application, turnover, as well as the sources of their receipt and formation of value. There are several classifications of assets in terms of their significance for the company.
Assets in accounting
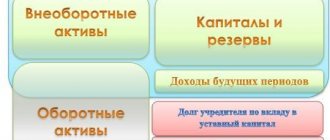
This classification implies the distribution of assets into two groups according to how they are reflected in the balance sheet - current and non-current. Current assets are not used in production for more than one year or one operating cycle if it exceeds a calendar year. During one cycle they are completely processed. They are considered the most liquid and are presented in the form of materials and inventories. This also includes money.
Non-current - used for a long period, transferring their value to the cost of production in parts, gradually. These are fixed assets in the form of buildings, equipment, transport, and intangible assets.
Asset form
The following classification involves division into groups according to form.
Physical assets have a material form, they can be touched and measured. For example, manufactured finished products, office or warehouse space.
Intangible assets are presented in the form of results of intellectual work, other developments, computer programs, logos, etc.
Financial assets are cash and cash equivalents, which are actually a means of payment.
Liquidity principle
In economics, it is customary to divide a company’s assets into 4 groups according to the degree of liquidity.
Absolutely liquid - money in current and foreign currency accounts, cash in hand. First of all, they act as a means of settlement with counterparties.
Highly liquid - those that are converted into cash without losing their market value and in the shortest possible time - up to 1 month. For example, short-term financial investments, short-term accounts receivable.
Liquid – with a maturity of up to 6 months. They can be cashed out quickly enough to be able to pay off your obligations, but there is a risk of losing value (impairment).
Illiquid (or low-liquidity) assets have a long sales period. Represented by fixed assets and intangible assets of the company.
Difference between current and non-current assets
Both non-current and current shares are used by the enterprise to generate income. The difference between them lies in how and for how long the property is used.
As mentioned above, non-current assets are property that is involved in the production process for more than one year. Its cost is included in the cost of finished products in parts. According to the Accounting Regulations No. 6/01 and 14/2007, as well as Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 66n, non-current assets include buildings, transport, production equipment, financial investments, development results, and other non-current assets.
Current assets include property that is directly used in the production process. Their cost is initially included in the cost of finished products. This category includes goods, materials, cash, and deposits.
Goals and objectives of asset management
Asset management represents a system of methods and principles for managing a company's property, as well as the process of making management decisions in relation to such assets.
The main (strategic) goal is to increase the value of the enterprise’s assets and increase the value of the business as a whole. To do this, it is necessary to implement a number of second-level goals:
- Maintaining a balance of assets according to the degree of liquidity. A sufficient level of solvency is achieved by combining assets of different liquidity. For example, the presence of a large volume of highly liquid assets (cash on hand) does not bring additional profit; they also lose value under the influence of inflation. However, they provide a high level of solvency for the company.
- Ensuring profitability. Using assets in the most efficient and profitable areas of activity increases their profitability. If an activity does not generate income, or its level is not high enough, it is necessary to take measures to improve the situation or eliminate it. Assets should be used where they benefit the company. If used in unprofitable activities, their profitability will be low.
- Ensuring the necessity and sufficiency of assets to carry out production activities. To operate a company, you need a workshop, equipment, raw materials and materials, as well as funds to pay for priority expenses. The lack of property and funds does not allow production to be carried out in the planned volumes. If your own capital is not enough, you should think about finding and attracting additional, borrowed sources of capital to form assets.
- Optimizing asset utilization. We are talking about work in three directions:
- ensuring the production cycle by managing asset flows;
- ensuring the necessary amount of assets to ensure continuous operations. Downtime in production means losses and lost income;
- minimizing defects and losses of raw materials and waste based on the results and during production.
How are inventories accounted for in account 10?
All legal entities are required to keep accounting records of material inventories - this is a mandatory requirement for their business activities (Clause 1, Article 2 of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ). In this case, business transactions reflecting the turnover of inventories are recorded on account 10 of the Chart of Accounts. Various sub-accounts are opened for it (for raw materials, fuel, containers, etc.). The corresponding business transactions are registered using supporting documents (invoices, orders, acts, etc.).
Management and optimization of the enterprise asset structure
It is necessary to optimize the structure of assets - when determining the optimal ratio of their various types, an assessment of the enterprise's liquidity is given, and ways to increase it and improve economic activity are determined.
The process itself takes three stages:
- The composition of non-current assets is analyzed. The part of active assets, most used in operating activities, and passive (auxiliary) assets is determined.
- The optimal ratio of active and passive non-current assets is calculated. At this stage, it is incorrect to believe that passive non-current assets need to be minimized. They include buildings, structures, and expensive equipment - without them, an effective and uninterrupted production cycle is not possible.
- Optimization of current assets. We also maintain a balance between highly liquid cash, accounts receivable and the availability of raw materials in warehouses. It is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the main type of economic activity, factors of the production cycle, as well as the liquidity of various types of current assets.
Principles of asset management and optimization
To properly organize the process of asset management and optimization, you need to consider the following factors:
- The totality of a company's assets is formed taking into account its development strategy, possible prospects, economic characteristics of the market, as well as the regional segment. Important!
Absence of contradictions with the goals of creating the organization itself. For example, it may seem strange to tax authorities that a large share of the assets of a company in the metallurgical sector consists of short-term financial investments in the absence of fixed assets. - The totality of assets is formed in such a way as to ensure the production of finished products, taking into account compliance with the structure of the enterprise. In the course of activity, the composition of assets must undergo some changes, adapting to the range of products produced. For example, if a confectionery company started baking cheesecakes, it would be necessary to purchase an oven and a freezer to store the products.
- Wise choice of assets. It is necessary to acquire assets taking into account the maximum possible benefit from their use. The low cost of equipment from a supplier may indicate poor quality, short service life, and rapid obsolescence. Too expensive equipment in most cases implies thoughtless spending on their acquisition without the opportunity to significantly increase profits from the use of such an asset. The balance of price and expected benefits is the main principle of choosing an asset to purchase.
- Balance in assets based on liquidity. It is worth noting that it can be difficult to comply with this principle - you need to analyze the existing property, draw up a list of assets that should in the future ensure the achievement of key performance indicators. And strive to bring the actual availability of assets to the planned one. The assets of any company must include both highly liquid assets (money in accounts) in order to timely pay off its obligations, and low-liquid assets (for example, fixed assets in the form of buildings, equipment) that ensure the production cycle. But in what proportions is a task for the manager.
- Interchangeability. It is necessary to form a set of assets taking into account their possible interchangeability. For example, one machine broke down. Spare parts for repairs or equipment capable of taking over the functions of the machine for repair should always be available. This is the only way to ensure continuity of production. Are assets not fungible? Then there is the risk of downtime, especially if the company only has assets that are used for a long time or are not updated.
Order size optimization involves determining inventory requirements
This area of analysis deals with the calculation of the standard indicator of the company’s need for certain material reserves - so as to optimize their purchases in the required volume when ordering from suppliers. In this case, the task of responsible specialists comes down to finding such a quantity of reserves that, on the one hand, is sufficient to maintain the production process, and on the other hand, is not too much in terms of the cost of their acquisition and maintenance.
Thus, in most enterprises, determining the standard for inventory is a necessary part of analyzing the state of inventories, coupled with determining the factors influencing their volume.
Assessing the effectiveness of asset management at an enterprise
The effectiveness of using a company's existing assets can be assessed in three areas.
Horizontal analysis
. The change in the value of assets over several periods and the rate of growth in the value of assets by type are assessed. The source of data is the accounting registers for accounts. The analysis allows us to identify the directions and reasons for changes in the value of assets. The results are used to predict further changes and for strategic planning of key indicators.
Vertical analysis
. The structure of assets is analyzed in order to calculate the share of each type in the entire aggregate. It is carried out across the enterprise as a whole, and across structural divisions.
The results of vertical analysis are used for: ·
- assessing the efficiency of asset use based on types of activities;
- assessing the efficiency of asset use for the enterprise, and separately for divisions;
- analysis of asset turnover, as well as determination of key performance indicators.
Comparative analysis.
Used to compare company data with industry averages, as well as with industry values.
The results give an idea of the company's competitiveness and identify reserves for increasing the groups of necessary assets. Economic coefficients
. Based on data on the composition and value of the company's assets, financial indicators are calculated. For example: return on assets ratios, turnover ratios. Due to this, an understanding of the company’s solvency and profitability of activities is achieved.
To assess the effectiveness of asset management, economists use asset turnover indicators. They act as indicators of the business activity of an enterprise. The initial data for the calculation are information about the organization’s revenue for the period, as well as the average annual value of the company’s assets as a whole or by individual types. Information about revenue is taken from the income statement, about the amount of assets - from the balance sheet. As a rule, there are no standard values, since they depend on the industry characteristics of production.
The profitability of a company is usually judged by profitability indicators. In general, return on assets is calculated as the ratio of net profit to the average annual value of assets as a whole, or for individual types. The results show how much profit each ruble invested in the company's assets brings.
Heading:
Management Concepts and Techniques
Search
Valuation of assets on the balance sheet
Balance sheet is a document reflecting the presence and condition of the organization’s assets, their itemized and total value (the latter is entered in line 1600). By analyzing the value and structure of assets, one can draw a conclusion about the success of the enterprise, its ability to fulfill its obligations and make a profit.
Many indicators are used for analysis, some of which are discussed below.
Cost and average value of total assets
The cost of resources is an assessment, expressed in monetary terms, of the property of an enterprise that generates income or can generate it in the future. It consists of two positions: the amount of current and non-current assets (in the balance sheet these are lines 1100 and 1200, respectively). Thus, the value of total assets is determined as the sum of lines 1100 and 1200. In other words, this is the balance sheet currency: the total for the assets section, line 1600.
The average value of total resources (ASA) of an organization is found as the arithmetic mean between the value at the beginning of the year (A1) and at the end of the year (A2). This is written as a formula:
SSA=(A1 + A2)/2
To calculate the average annual cost, the same principle is applied: indicators are taken as of one accounting period, but from the balance sheets of different years. The divisor will be equal to the number of years under study (if for two years - 2, if for three - 3, etc.). The average indicators for current and non-current resources are calculated similarly.
Real assets ratio
Real assets include intangible assets, fixed assets, inventories (production) and costs in work in progress - everything that is involved in commercial activities. For analysis, a ratio is usually used - the ratio of the total value of real assets to their total value on the balance sheet. A successful manufacturing company should have a value above 0.5 (50%). Decrease means a drop in production capacity or a transfer of the enterprise to other, non-core activities.
Asset immobilization ratio
Immobilization of assets means their withdrawal from circulation. That is, the share of assets that are not involved in turnover and do not generate income, or are used for other purposes than their intended purpose, is assessed. The immobilization coefficient shows how efficiently the enterprise's resources are used. The indicator reflecting the state of immobilized funds is calculated as the ratio between the permanent (non-current) and current (current) assets of the enterprise.
The lower this indicator, the more liquid resources the enterprise has and, accordingly, the higher its solvency.