What are accounting entries?
Every day millions of payments are made around the world. They are made by both ordinary people and businesses. Any business must take into account its own payments to keep them under control. Therefore, any payment is accounted for through accounting entries.
Accounting entries are accounts drawn up on actual papers, reflecting the amount of a business transaction that is subject to accounting.
Any information about actions performed on accounts is marked with a double entry, i.e. in the debit of one account and in the credit of another, for an identical amount. With its help, all accounts assume a single interconnected structure.
The relationship between debit and credit settlements, formed in the process of double entry, is called a correspondent accounts account, and the accounts participating in this relationship are called correspondent accounts.
To understand the concept of accounting for debit and credit accounts, the following features of account accounting were introduced into accounting:
- asset – reflects the values owned by the organization;
- liability – displays the organization’s debt to creditors;
- active-passive account – displays one-time debit and credit debt.
What is writing off accounts receivable with an expired statute of limitations and in what order this procedure is carried out - read the link.
Accounting entries for beginners with answers: table and examples
The basic rules for maintaining accounting entries for beginners can be expressed as follows:
- the asset has no loan balance;
- the liability has no debit balance;
- An active-passive account has both a debit and a credit balance.
Visually, in our table with answers it looks like this:
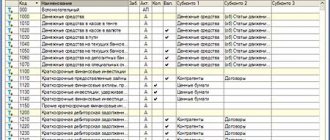
The relationship between active and passive accounts with debit and credit.
On the balance sheet, the asset is on the left and the liability is on the right. Active-passive accounts can be displayed at a time in the balance sheet. They can be simple or complex:
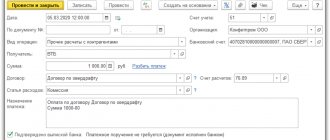
- simple posting - an operation is carried out based on two accounts, debit and credit; Example: materials received from a supplier in the amount of 1 million rubles. Debit 10 – 1 million rubles. Loan 60 – 1 million rubles. Account 60.10 is passive, thus, the increase is recorded as a credit to this account, the debt to suppliers increases;
- complex posting - an operation is carried out based on several accounts at the same time; this is possible by configuring the debit of one account, the credit of several, and vice versa.
It is worth noting that the sum of the debit and credit lines must converge to zero. Complex wiring has at least three accounts.
For example: raw materials were purchased for 300 thousand rubles, incl. VAT 18%. VAT allocated - 45.7 thousand rubles. Debit 10 – 254.2 thousand rubles. Debit 19 – 45.7 thousand rubles. Credit 60 (Payment for contractor services) – 300 thousand rubles.
After determining the structure of a business transaction, creating a posting will not be difficult even for a novice accountant. Below you can clearly study examples of postings for basic business transactions.
What are provisions for doubtful debts in accounting and tax accounting? The detailed answer is contained in the publication at the link.
Problem solving: Accounting. Cross-cutting task
Transcript
1 Problem solving: Accounting. End-to-end task Based on business transactions, open synthetic accounting accounts and record the amounts of initial balances in them. After recording each transaction in the journal, record it in the accounts. Calculate the actual cost of manufactured products, financial results from the sale of products, other operations, income tax, and net profit of the enterprise. Display ending account balances. Based on the accounts, prepare a turnover sheet, a balance sheet at the beginning and end of the reporting period, a financial performance statement, and a cash flow statement for the reporting period. Statement of balances on synthetic accounts for the city Name of accounts Amount, rub. accounts debit credit 01 Fixed assets Depreciation of fixed assets Intangible assets Depreciation of intangible assets Materials Main production Finished products Cash desk Current accounts Settlements with suppliers and contractors Settlements with buyers and customers Settlements for taxes and duties Settlements for social insurance Settlements with personnel for wages Settlements with accountables persons Settlements with various debtors and creditors Profits and losses Authorized capital Additional capital Retained earnings (uncovered loss) Business transactions for the quarter Subject Contents of business transactions Amount, rub. The supplier's invoice was accepted for the received equipment, 1 requiring installation (including 18% VAT), including VAT. The equipment for the workshop under construction was handed over for installation. The contractor's invoice was accepted for the completed 3 construction works of the workshop (including 18% VAT). VAT Obsolete equipment written off: 4 initial cost amount of accrued depreciation as of the date of write-off residual value written off cost of capitalized spare parts at price
2 possible use 4 financial result from write-off of equipment The organization's invoice was accepted for the work accepted according to the act 5 for the installation of equipment (including VAT 18%) including VAT Completed fixed assets were accepted into operation: 6 Workshop building Production equipment Released from warehouse and materials consumed (at actual cost): 7 for the manufacture of products in the main production for the repair of workshops' operating systems, economic needs of workshops for general business needs for packaging of sold products Depreciation of fixed assets accrued: 8 production equipment of buildings, structures and general equipment 8 depreciation of intangible assets accrued , used for 9 general production needs. Invoices from suppliers and third parties were received: 10 for routine repairs of the office building (including VAT 18%) including VAT for utilities by the main production 10 workshop (including VAT 18%) including VAT for utilities services and communication services of departments 10 for general business purposes (including VAT 18%) including VAT Cash received from the current account to pay salaries, travel expenses, business expenses 12 Paid from the organization's cash desk: wages, benefits for temporary 12 disability in reporting to travel and business expenses Money received into the current account: 13 from buyers for sold products to pay off debts from other debtors Paid from the current account: supplier bills for paid equipment, 14 materials, utilities Personal income tax contributions to the Pension Fund alimony withheld according to writs of execution Accrued wages, benefits: 15 workers of main production
3 workers and employees for the maintenance and management of 15 workshops, managers, specialists and employees of departments 15 general economic purpose temporary disability benefits From the accrued wages and other payments, deductions were made: 16 personal income tax on writs of execution. Insurance contributions from the salaries of workers and employees were calculated in the amount of 30 .2%: 17 for the manufacture of products in the main production for maintenance and management of workshops for the management of general business units Deduction of VAT amounts on purchased values and 18 services Expenses for business trips are reflected Overhead expenses are written off for inclusion in 20 cost of production (to determine the amounts): 20 general production expenses of workshops general business expenses of the organization Finished products were received into the warehouse at actual cost (WIP at the end of the month amounted to 85,400) determine 22 Finished products were shipped to customers: 22 at actual cost at the sold cost indicated in the settlement documents 22 (including VAT 18%) including including VAT Commercial expenses related to 23 sold products have been written off. The financial result from the sale of 24 products has been determined and written off. The organization rents out vacant premises: 25 rent has been charged (including VAT 18%) including VAT expenses related to the rental of property the financial result from other income and 25 expenses is reflected Profit tax for the quarter (20%) Reformed the balance sheet 27.1, subaccount 90 “Revenue” is closed, subaccount 90 “Cost of sales” is closed, subaccount 90 “VAT” is closed, subaccount 90 “Business expenses” is closed subaccount 91 “Other income” subaccount 91 “Other expenses” is closed The net profit (loss) for the reporting year is reflected
4 4
5 p/p Solution Journal of registration of business transactions Contents of business transactions 5 Amount, rub. The supplier's invoice was accepted for the received equipment, 1 requiring installation (including 18% VAT), including VAT. The equipment for the workshop under construction was handed over for installation. The contractor's invoice was accepted for the completed 3 construction works of the workshop (including 18% VAT). VAT Obsolete equipment written off: 4 initial cost amount of accrued depreciation as of the date of write-off residual value written off cost of capitalized spare parts at the price 4 of possible use financial result from write-off of equipment Accepted the organization's invoice for the work accepted under the act on 5 installation of equipment (including VAT 18%) including VAT Completed fixed assets were put into operation: 6 Workshop building Production equipment Materials released from the warehouse and consumed (at actual cost): 7 7 for the manufacture of products in the main production for the repair of workshop operating systems, economic needs of workshops general business needs for packaging of sold products Depreciation of fixed assets has been accrued: 8 production equipment of buildings, structures and inventory for general 8 purposes Depreciation has been accrued for intangible assets used for 9 general production needs Invoices from suppliers and third parties have been received: 10 for routine repairs of an office building (including VAT 18% ) including VAT for utilities by the main production workshop (including VAT 18%) 10 including VAT for utilities and communication services of general business units (including VAT 18%) Dt Kt
6 10 including VAT Cash received from the current account to pay salaries, travel expenses, business expenses 12 Paid from the organization's cash desk: wages, benefits for temporary 12 disability in the reporting for travel and business expenses Money received to the current account: 13 from customers for sold products to repay debts from other debtors Paid from the current account: supplier bills for paid equipment, 14 materials, utilities, personal income tax contributions to the Pension Fund alimony withheld according to writs of execution Wages and benefits accrued to: 15 workers of primary production workers and employees for maintenance and management of 15 workshops for managers, specialists and employees of departments 15 general economic purpose temporary disability benefits From accrued wages and other payments, deductions were made: 16 Personal income tax on writs of execution Insurance contributions from wages of workers and employees were calculated in the amount of 30.2%: 17 for the manufacture of products in the main production for the maintenance and management of workshops for the management of general business units Deduction of VAT amounts on purchased values and services Expenses for business trips are reflected Overhead expenses are written off for inclusion in 20 cost of production (determine the amounts): 20 general production expenses of workshops general business expenses of the organization Capitalized finished products to the warehouse at actual cost (WIP at the end of the month amounted to 85,400) determine 22 Finished products were shipped to customers: 22 at actual cost at the cost sold specified in the settlement documents 22 (including VAT 18%) including VAT Selling expenses were written off, related to
7 products sold The financial result from the sale of 24 products was determined and written off The organization rents out vacant premises: 25 rent was charged (including VAT 18%) including VAT expenses associated with leasing the property, the financial result from other income and 25 expenses Accrued profit tax for the quarter (20%) Reformation of balance sheet 28 Reflected net profit (loss) for the reporting year Account cards Account 01 Fixed assets Beginning balance Turnovers for the period Final balance Account 01.2 Disposal of fixed assets Turnovers for the period Turnovers for period Final balance 0 Account 02 Depreciation of fixed assets Initial balance Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance
8 Account 04 Intangible assets Beginning balance Turnovers for the period 0 Turnovers for the period 0 Final balance Account 05 Amortization of intangible assets Beginning balance Turnovers for the period 0 Turnovers for the period Final balance Account 07 Equipment for installation Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance Account 08 Investments in non-current assets Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance 0 Account 10 Materials Beginning balance
9 Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance Account 19 Value added tax on acquired assets Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance 0 Account 20 Main production Beginning balance Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance Account 25 General production expenses Turnovers for the period Turnovers for period
10 Final balance 0 Account 26 General business expenses Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance 0 Account 43 Finished products Initial balance Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance Account 44 Selling expenses Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance 0 Account 50 Cash desk Initial balance Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance
11 Account 51 Settlement accounts Initial balance Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance Account 60 Settlements with suppliers and contractors Initial balance Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance Account 62 Settlements with buyers and customers Initial balance Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance
12 Account 68 Calculations for taxes and fees Initial balance Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance Account 69 Calculations for social insurance and security Initial balance Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance Account 70 Settlements with personnel for wages Initial balance Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance Account 71 Settlements with accountable persons Initial balance Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance
13 Account 76.1 Settlements with various debtors Initial balance Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance Account 76.2 Settlements with various creditors Initial balance Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance Account 80 Authorized capital Initial balance Turnovers for the period 0 Turnovers for the period 0 Final balance Account 83 Additional capital Initial balance Turnover for the period 0 Turnover for the period 0 Final balance Account 84 Retained earnings (uncovered loss) Initial balance Turnover for the period 0 Turnover for the period Final balance Account 90 13
14 Sales Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Account 91 Other income and expenses Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Account number Account 99 Profit and loss Beginning balance Turnovers for the period Turnovers for the period Final balance 0 Name of accounts Turnover balance sheet Balance at the beginning of the period 14 Turnovers for the period Balance at the end of period 01 Fixed assets Disposal of fixed assets Depreciation of fixed assets Intangible assets
15 05 Amortization of intangible assets Equipment for installation Investments in non-current assets Materials Value added tax on acquired assets 20 Main production Overhead expenses General business expenses Finished products Selling expenses Cash desk Settlement accounts Settlements with suppliers and contractors Settlements with buyers and customers Settlements for taxes and duties Settlements for social insurance and security Settlements with personnel for wages Settlements with accountable persons Settlements with various debtors Settlements with various creditors Authorized capital Additional capital Retained earnings (uncovered loss) Sales Other income and expenses Profit and loss Total
How to prepare accounting entries for specific business transactions?
Examples of accounting entries for wages
Payroll transactions reflect the following: Debit personal income tax, other deductions and payment of wages, credit - accruals. Accounting entries are made for each employee.
Payroll accounting is carried out on the basis of the following important principles:
- accurate recording of the number of employees and the time they worked;
- correct withholding amounts, including budgetary and extra-budgetary funds;
- monitoring the performance of work by employees;
- correctness when posting labor transactions in accounting.
Table with examples of salary postings:
Payroll posting table.
Renting premises in the accounting department
All actions with the leased property are reflected by both the lessor and the tenant.
To fill out a lease agreement, an agreement form drawn up on the basis of the principles of Chapter 34 of the Civil Code is used. The contract specifies the validity period. If the period is not specified, it is considered that the contract was concluded for an indefinite period. In Russia, when renting for a period of more than a year, state registration is required.
General work log: sample filling and step-by-step guidance for drawing up the document are in the article at the link.
The contract has two parts: main and additional. The additional one includes various payments, such as housing and communal services. In rare cases, housing and communal services fees are included in the general rent. By law, rental expenses are recorded in accounting on a monthly basis.
These expenses are considered as ordinary activities and are taken into account in accounts 20-29 and 44, depending on the activities of the organization.
Table of accounting entries for renting premises with answers:
Table: Accounting for the lessor when recognizing rental income as income from ordinary activities.
Table: Accounting for the lessor when recognizing rental income as other income.
Table: Tenant's accounting.
Examples of accounting entries for wholesale and retail trade
The economic activities of wholesale and retail organizations require the execution of many transactions; they are related to the sale of goods, finished products, as well as services.
Find out the procedure for writing off accounts payable with an expired statute of limitations in this article.
Posting table with trading examples:
Table: Receipt of goods from the supplier.
Table: Sales of goods at the time of payment.
Table: Sales of goods at the time of shipment (OPT).
Table: Sales of goods at the time of shipment (Retail).
Accounting entries for beginners under an assignment agreement
An assignment agreement is a replacement of a creditor under an obligation. There are three parties to the contract. The accounting of the parties is as follows:
- debtor – all debt transactions are reflected in analytical accounting. Costs identified during the validity of the assignment agreement are reflected in other expenses. Changing the lender will not affect financial accounting;
- assignor - the assignment agreement does not generate either income or expenses. But the fact of execution of the operation increases its liquidity;
- assignee - when assigning a debt, records it in debit as a receivable for the amount of the debt, then displays it as a credit in anticipation of the transfer of funds.
The following table with examples for an assignment agreement will help beginners make accounting entries:
Table: Postings under the assignment agreement.
Cash transactions in accounting
Cash transactions involve receiving, issuing and storing cash. Accounting for cash transactions is based on the regulations of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
What is depreciation of fixed assets in simple words? The answer is here.
When maintaining a cash register, the following documents are used:
- cash receipt order - to record cash receipts;
- expense cash order - to record cash expenses;
- cash book – takes into account all movements on the cash register.
Table of accounting entries with answers:
Table: Cash transactions in accounting entries.
Provision of services
An organization can either provide services to third parties or use the services of a third party. Accounting for accounting entries in this case will be different.
The main tasks are the following:
- reliable and complete information content of all transactions performed;
- providing information to all participants in the process;
- avoiding a negative outcome for these operations;
- proper documentation;
- competent reflection of expenses in the process of operations;
- receiving monetary profit from the transaction.
Table with answers for business transactions related to the provision of services to third parties:
Table: Provision of services to third parties.
Table: Obtaining services from a third party.
How to prepare accounting entries for fixed assets?
An organization that has fixed assets on its balance sheet is obliged to take them into account in the balance sheet. It is worth noting some features in this process:
- accepting a fixed asset for accounting, its initial cost is determined;
- a fixed asset has a useful life - this is the period during which it generates income;
- it is necessary to depreciate the fixed asset, i.e. write off its partial cost;
- revaluation is not mandatory, the organization has the right to carry it out;
- expenses for capital or current repairs of fixed assets are recorded on debit expense accounts;
- write-off of a fixed asset occurs in the event of non-receipt of profit or its disposal.
Table of accounting entries for fixed assets with examples:
Table: Accounting entries for fixed assets.
Closing of the year
According to the law, a period is defined for which all economic activities of the organization are carried out; this period lasts from January 1 to December 31. Based on this period, January 1 is the new reporting date, and December 31 is the final one.
You can read how to independently draw up an accounting certificate about correcting an error and writing off a debt here.
Closing the year sums up all the annual financial results of the organization. That is, it resets the balances on accounts 90 and 91, and closes account 99. As a result, the total, profit or loss is taken into account on account 84.
Closing is done on a full year basis. In accounting, the year end is shown as December 31st. After closing, the organization begins a new period with zero financial balances.
Table with examples:
Table: Closing transactions.
Examples of accounting entries for taxes and state duties
Tax expenses and state duties are displayed in the period of actual payment. Based on the purpose of the payment, you need to consider:
- write-off of costs for core activities;
- posting of costs to other expenses if they are not related to the main activity;
- accounting as part of the property.
Payment of taxes and state duties is carried out from the organization's current account. When paying, you must take into account all the payer's details and the correct purpose of the payment.
Examples of postings are clearly shown in the following table:
Table: Postings for taxes and duties.
Loans issued
The organization has the right to issue a loan to a third party organization or individual. Such a transaction must be certified in writing on both sides as a loan agreement. The loan agreement usually specifies the interest level, the period of validity of the agreement, and the payment schedule.
If the interest level is not determined, you can take the current refinancing rate as a basis. The loan agreement can also be interest-free, which must also be stated in the agreement.
The loan can be issued either in cash or in kind; it is worth noting that VAT is not assessed for a cash loan. The amount of interest received is included in sales revenue or other income. This does not affect financial results.
Table: Accounting entries for loans and credits.
Acquiring
Acquiring is non-cash payments with the buyer through an intermediary, which is the bank, on the basis of a concluded agreement between the organization and the acquiring bank.
This operation has the following features:
- use of a POS terminal for processing bank cards;
- The POS terminal is listed on an off-balance sheet account (if provided by a bank), or as a fixed asset (if acquired as an asset of an organization);
- proceeds from the sale are credited to the account in an amount reduced by the amount of the acquiring bank's commission, but the entire amount of proceeds is indicated in the income;
- the acquiring bank's commission is included in the costs.
Accounting entries for acquiring in the table:
Table: Accounting entries for acquiring.
Accounting is equipped with a large number of entries; an experienced accountant knows that the reflected data must be correct and literate, in accordance with established rules. First of all, the accountant must understand the importance of this and be aware of the responsibility that lies with him.
If information is distorted or trying to avoid providing it, the manager and accountant will be held liable under Art. 15.11 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
How to prepare accounting entries correctly? Watch the following video for recommendations:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ng4Ifp0Mgog
Don't forget to add "FBM.ru" to your news sources
Last news
Accounting tasks. Part 02
Task No. 4024 (preparing accounting entries)
Prepare accounting entries for the following transactions:
- 1. Parts sold to customers, including VAT.
- 2. The cost of manufactured parts is written off.
- 3. VAT payable is reflected.
- 4. The costs of delivering sold goods to the buyer are reflected.
- 5. The information costs of the intermediary organization associated with the implementation are reflected.
- 6. The financial result from the sale of parts is reflected.
- 7. Received funds from the sale into the current account.
- 8. Aktiv LLC accrued rental payments for February 20___.
- 9. Aktiv LLC paid for the rent of warehouse premises for February 20__.
- 10. The organization reflected accrued interest on the issued long-term loan as part of other income.
Recommended tasks for the discipline
Accounting tasks. Part 09 (inventory)
Task No. 2482 (reflection of inventory results in accounting) During the inventory of fixed assets, it was established that the organization unlawfully...
Accounting tasks. Part 04
Task No. 2580 (cash flow transactions) Revenue from customers in the amount of 100,000 rubles was credited to the current account. VAT transferred to the budget in the amount...
Accounting tasks. Part 02
Task No. 4024 (preparing accounting entries) Prepare accounting entries for the following operations: 1. Parts sold to customers, including...
Accounting tasks. Part 03 (insurance premiums)
Task No. 5109 (calculation of insurance premiums) Problem from the workshop “PM 03. Carrying out settlements with the budget and extra-budgetary funds” (Tambov) Employee’s wages ...
Accounting tasks. Part 05 (fixed assets)
Task No. 712 (accounting for the sale of fixed assets) In April 2011, LLC “A” makes a decision and sells a fixed asset in connection with...
The solution of the problem:
1. Parts sold to customers, including VAT:
- 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”
- 90 "Sales"
2. The cost of manufactured parts is written off:
- 90 "Sales"
- 43 “Finished products”
3. VAT payable is reflected:
- 90 "Sales"
- 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”
4. The costs of delivering sold goods to the buyer are reflected:
- 90 "Sales"
- 44 “Sales expenses”
5. The information costs of the intermediary organization associated with the implementation are reflected:
- 90 "Sales"
- 44 “Sales expenses”
6. The financial result from the sale of parts is reflected:
- 90 "Sales"
- 99 "Profits and losses"
7. Received funds from the sale to the current account:
- 51 “Current accounts”
- 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”
8. Aktiv LLC accrued rental payments for February 20___:
- 91 “Other income and expenses”
- 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”
9. Aktiv LLC paid for the rent of warehouse premises for February 20__:
- 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”
- 51 “Current accounts”
10. The organization reflected accrued interest on the issued long-term loan as part of other income:
- 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”
- 91 “Other income and expenses”