General concepts
Successful business conduct is impossible without a detailed analysis of the financial and economic indicators of the economic activity of an economic entity.
In order to assess the property and financial position of an organization and make the right management decisions in a timely manner, it is necessary to determine important solvency and profitability ratios. One of the key calculation indicators is the calculation of the value of net assets on the balance sheet. The organization's net assets (NA) are the amount of funds of an economic entity, determined by calculation, which will remain at the disposal of the company after full repayment of debt obligations. In other words, the value of net assets is calculated as the arithmetic difference between the total indicators of the company’s property, material and financial assets and assumed liabilities.
Note that calculating the value of net assets on the balance sheet is mandatory for organizations. The indicator is calculated once a year based on accounting data. Indicators are reflected in the third section of the report on changes (movements) of capital; net assets are (in the balance sheet) line 360 of this reporting form.
Certificate of net assets: form and content
Since a unified form for the certificate has not been approved at the federal level, the Company retains the right to present information in free form. However, a certificate of net assets, a sample of which is approved by the meeting of members of the Company, must contain:
- legal name of the Company,
- document registration data,
- time of determining the net asset value;
- financial information on the amount of net assets, with a breakdown of current and non-current assets;
- information about the period for which the financial statements data were used to prepare the certificate;
- signatures of officials.
Formula for calculating net assets
The key procedure for calculating the value of net assets on the balance sheet is determined by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and is presented in a separate order No. 84n dated August 28, 2014. Please note that previously a different procedure was in effect, but it is not currently used.
This formula for net assets on the balance sheet is applicable to the following range of economic entities:
- public or non-public joint stock companies;
- state or municipal unitary enterprises;
- limited liability companies;
- production cooperatives or housing cooperatives;
- business partnerships.
Net assets formula:
NA = (AO - DU - ZA) - (OB - DBP),
Where
- JSC - the amount of non-current and current assets of an economic entity as of the reporting date;
- DE - debt of the founder incurred to the enterprise for the formation of the authorized capital;
- FOR - debt on own shares generated upon issue;
- OB - the sum of the company's short-term and long-term liabilities;
- DBP - future income in the form of state financial support or gratuitous transfer of property assets.
How to calculate net assets according to balance sheet lines?
To calculate the net asset value on the balance sheet, the calculation lines use the following:
NA = (line 1600 – DU) – (line 1400 + line 1500 – DBP).
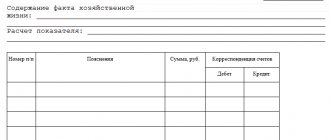
Calculating the amount of net assets in the balance sheet (the lines indicated above) using a pencil calculator is not enough. This calculation must be documented. However, a unified form for reflecting calculated data is not provided for in Order No. 84n. Organizations are required to independently develop a form and regulate it in their accounting policies.
Note that before the approval of Order No. 84n, the old form was in force (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 10 and the Federal Commission for the Securities Market of Russia dated January 29, 2003 No. 03-6/pz). In the new instructions, the Russian Ministry of Finance has not prohibited the use of this form, therefore, firms can use it to prepare calculations of net assets in the balance sheet (the document lines contain all the necessary information).
We fill out a certificate of the book value of assets
There is no form for a certificate of the book value of assets approved by current legislation, therefore there are no requirements for its completion. How then to compose it?
The most common way is to fill out a certificate within the meaning of the old balance sheet form (0710001), which is no longer relevant at the moment. Its essence lies in line-by-line filling of non-current and current assets, expressed in monetary units, at the beginning and end of the year.
If desired, you can draw up a certificate with a more detailed breakdown of the assets of the enterprise or issue a shortened version of the document. You will find a practical example of such filling on our website.
Since the law does not provide for the form of a certificate of the book value of assets, it is allowed to be drawn up in any form. For example, the text part of the certificate may begin with the following words: “As of ... the total value of the enterprise’s assets is ... rubles.” Further, if desired, you can open the list of assets of the enterprise in the form of a table for a specific date.
Useful publications
- Help calculation for sick leave, sample How to correctly fill out the application form for sick leave: calculation of benefits After receiving sick leave from an employee...
- Procurement act, sample How the OP-5 form is used in practice The document in question, first of all, acts as a tool to ensure the legality of transactions between...
- Application for offset, sample Example of an application for offset of counter homogeneous claims to the bailiff of the OSP for the Mikhailovsky district of the Amur region from ...
- Integrated cost indicators Directories and standards Real estate UPVS (1) UPVS - Collections of aggregated indicators of the replacement cost of buildings and...
- Accounts payable on the balance sheet What is net debt Net debt shows the company's ability to pay all debt at the time of analysis.…
| Organizations are recommended to provide information on the availability of assets recorded in off-balance sheet accounts in Form No. 1 “Balance Sheet”. This data is filled in based on the instructions given in the Chart of Accounts, as well as taking into account the specific list of off-balance sheet accounts used by the organization. The reference section of the balance sheet provides information about the values that are taken into account in off-balance sheet accounts. These are values that are temporarily at the disposal of the organization (leased fixed assets, material assets in safekeeping, in processing, etc.), conditional rights and obligations. In addition, off-balance sheet accounts account for assets and liabilities that are written off the balance sheet, but which must be monitored over a certain period of time. Line 910 “Leased fixed assets”Line 910 “Leased fixed assets” reflects the cost of fixed assets leased by the organization. The amount on line 910 is equal to the balance of off-balance sheet account 001 “Leased fixed assets”. If fixed assets were received by the organization under a leasing agreement, then line 911 “Including leasing” is filled in. Line 920 “Inventory assets accepted for safekeeping”In the reference section of the balance sheet, line 920 “Inventory assets accepted for safekeeping” reflects the cost of inventory assets that are in safe custody in the organization. Such values include:
The amount on line 920 corresponds to the balance on off-balance sheet account 002 “Inventory assets accepted for safekeeping.” Line 930 “Goods accepted for commission”Line 930 “Goods accepted on commission” of the reference section of the balance sheet by commission agent organizations reflects the cost of goods accepted on commission under a commission agreement. The amount on line 930 is equal to the debit balance on account 004 “Goods accepted on commission.” Line 940 “Debt of insolvent debtors written off at a loss”Line 940 reflects the amount of receivables written off at a loss due to the expiration of the statute of limitations and deemed uncollectible. Such debt should be recorded on the balance sheet in account 007 for five years from the date of its write-off in order to monitor the possibility of collecting it in the event of a change in the property status of the debtors. The procedure for recording debt collection is given in the description of account 007. The amount on line 940 is equal to the debit balance on account 007 “Debt of insolvent debtors written off at a loss.” Line 950 “Securities for obligations and payments received” and line 960 “Securities for obligations and payments issued”The articles “Securities for obligations and payments received” (line 950) and “Securities for obligations and payments issued” (line 960) reflect the amounts allocated by the organization to accounts 008 and 009. This includes information on the availability and movement of guarantees received and issued, respectively, to ensure the fulfillment of obligations and payments, as well as security received by the organization for goods transferred to other organizations (individuals). The amount on line 950 corresponds to the balance on account 008 “Securities for obligations and payments received.” The amount on line 960 corresponds to the balance on account 009 “Securities for obligations and payments issued.” Line 970 “Depreciation of housing stock” and line 980 “Depreciation of external improvement objects and other similar objects”Lines 970 and 980 of the balance sheet reference section are filled in by organizations that have fixed assets for which depreciation is not charged. These can be housing facilities, external landscaping, forestry, road facilities, specialized shipping facilities, etc. These lines can also be filled in by non-profit organizations that have fixed assets. For these objects, depreciation is charged, the amount of which is reflected in account 010 “Depreciation of fixed assets.” The amount on lines 970 and 980 is equal to the balance on account 010 for housing facilities and others, respectively. |
Analysis of indicators
Having completed the arithmetic calculations, we move on to analyzing the result obtained. With a positive amount of net assets in the balance sheet, we can conclude that the company is profitable and has high solvency. And, accordingly, the higher the indicator, the more profitable the enterprise.
Negative net assets are an indicator of the low solvency of an enterprise. In other words, a company with a negative NAV will most likely go bankrupt soon; the company will simply have nothing to pay off its debts. However, in such a situation, exceptional circumstances must be taken into account. For example, the company has just been formed and has not yet covered its costs, or the company received a large loan for expansion.
An increase in net assets can be achieved by increasing the authorized, reserve or additional capital or by reducing the founder’s debts to the enterprise.
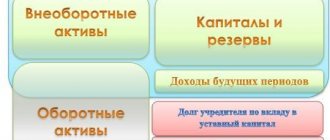
Assets: concept and types
Note! The assets of a company are usually understood as all its property and funds.
The assets, in turn, are divided:
- For non-current (property and non-property assets). Their main difference is their low ability to be converted into cash.
- Current assets, which turn into cash faster than non-current ones, that is, have greater liquidity. These include:
- accounts receivable - those that were formed as a result of failure to fulfill their obligations by counterparties under concluded agreements;
- products available in stock;
- funds in current accounts, etc.
Important! It is believed that an enterprise is more solvent when the size of current assets significantly exceeds the size of non-current assets.
More complete information on the topic can be found in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.
Net assets are a narrower concept. The formula for calculating their cost is established at the federal level.
Current and non-current assets
The assets of any company are divided into two types:
- Negotiable. These include:
- inventory, including products ready for sale;
- cash in the organization’s cash desk and in its current bank accounts;
- accounts receivable, i.e. everything that can be converted into monetary value in a short period of time.
Details about current assets.
- Non-negotiable. These are fixed assets and non-property assets, which are much more difficult to convert into monetary form (buildings, equipment, production, information systems, etc.).
Details about non-current assets.
A good indicator is if current assets are higher than non-current assets - in this case, the company is considered successful in terms of financial activities and solvent, which means that the likelihood of achieving its goals is much more serious.
Compilation rules
The legislation does not provide a unified form for drawing up this document, so each enterprise independently chooses a template and issues a certificate using it. Often the guideline is the requirements of the institution for which it is being formed. For example, the bank may require adding a clause regarding the availability of transport.
The certificate must include the following points:
The last point is the most important of all. The accountant must describe in detail everything related to the company's assets. If there is too much information, it is recommended to put it in a table. The signature of the director and chief accountant is required, otherwise the certificate will not be considered valid.
Registration of a certificate
The certificate can be written by hand or typed on a computer, on an ordinary A4 sheet or on the company’s letterhead (the latter option is preferable because it a priori includes the company’s details).
It is important to strictly observe only one condition - the document must be signed by the head of the organization (or a person who is his official representative), as well as the chief accountant. In this case, the signatures must be “live” - the use of facsimile autographs, i.e. printed in any way is unacceptable.
Today it is not necessary to certify a certificate using various types of stamps - this should be done only when the norm for the use of seals and stamps for endorsing papers is enshrined in the internal local legal acts of the company.
The certificate is usually made in one original copy, but if there is any need, additional certified copies can be made.
Information about the certificate is entered in a special accounting journal, and if it is intended for a third-party institution, also in the outgoing documentation journal.