What the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation says about VAT deduction on a cash receipt
Hidden text
- the goods were purchased at retail (even if the VAT amount is highlighted as a separate line in the cash receipt);
- the company wishes to include VAT as an expense when calculating income tax.
A common situation was considered. An employee is given money on account for the purchase of office supplies, for example. There is no invoice. The employee draws up an advance report and attaches a cash receipt with the VAT amount highlighted on a separate line. The company is wondering whether the accountant has the right to deduct VAT. If this is not possible, then can VAT be included as an expense when calculating the taxable base for income tax?
It should be noted that from July 1, 2022, all sellers of goods and services switched to online cash registers, which means that absolutely all cash register receipts will include information about VAT and the tax rate - this is the requirement of the law “On the use of cash registers”. technology in the Russian Federation."
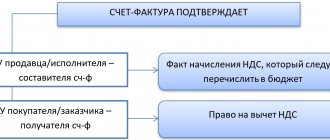
The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation emphasizes that, according to the instructions of paragraph 1 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, VAT can be deducted on the basis of the following documents:
- Invoice issued by the seller.
- Documents proving payment of VAT withheld by tax agents.
- Documents that prove the fact of payment of VAT when importing goods into the territory of the Russian Federation.
- Any other documents in cases where a deduction can be made for VAT paid by the organization as part of entertainment or travel expenses, as well as directly to the budget.
Based on the instructions of paragraph 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the financial department concluded that VAT deduction is impossible when purchasing goods at retail. Even the fact that VAT is listed as a separate line on the cash receipt does not allow taxpayers to make a deduction. The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation does not allow the accounting of VAT as part of income tax expenses - clause 2 of Art. 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for the possibility of including the amount of tax in the cost of goods. But according to paragraph 1 of Art. 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in other cases, amounts of value added tax presented at the time of purchase of goods cannot be taken into account as part of income tax costs
.
Income tax
According to the norms of Art. 170 of the Tax Code, input VAT can be attributed to the value of assets and taken into account in expenses that reduce income tax only in transactions not subject to VAT, when applying the VAT exemption under Art. 145 of the Tax Code, as well as when acquiring assets for sale outside the territory of the Russian Federation. A situation in which there is no documentary evidence of the right to deduction is not named in the Tax Code, which means in such cases this amount will not participate in the calculation of income tax (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 24, 2007 No. 03-07-11/126 ).
As a result, in this situation a permanent difference arises, which means that it is necessary to reflect a permanent tax liability in accounting in accordance with the norms of PBU 18/02 (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 19, 2002 No. 114n).
VAT deduction on a cash receipt - the opinion of the courts
The courts turned out to be not as categorical on the issue of deducting VAT on a cash receipt as the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation. For example, the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court indicated that when selling goods at retail for cash, the requirements for issuing invoices are recognized as fulfilled when the seller issues the buyer a cash receipt (or other document of the proper form) (clause 7 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Accordingly, the buyer has the right to deduct VAT if payment for goods was made taking into account value added tax. See Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated May 13, 2008 No. 17718/07, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated August 20, 2007 No. KA-A40/7956-07.
When is VAT allowed to be deducted?
In the event that an LLC or individual entrepreneur who owns a store pays VAT, the purchase amount will include the amount of value added tax.
If the following conditions are met, input VAT is allowed to be deducted: (click to expand)
- the company has documents indicating the existence of the right to deduct VAT;
- the purchased goods were capitalized on the company’s balance sheet;
- goods were purchased for the purpose of carrying out production activities, resale or any other operations that are subject to value added tax.
As for the first point about the availability of documents proving the right to a tax deduction, this condition previously caused disputes with the Federal Tax Service. The Tax Service believes that the right to deduction is confirmed by only one document - the invoice issued by the seller. See Letter of the Ministry of Science of the Russian Federation dated May 13, 2004 No. 03-1-08/1191/ [email protected] The Ministry of Finance agreed with the decision of the Federal Tax Service, as evidenced by:
- Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated August 25, 2017 No. 03-07-14/54643;
- Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 12, 2022 No. 03-07-09/634;
- Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 2, 2022 No. 03-07-14/45605.
Important!
At the time of purchasing goods in a store, an invoice issued by the seller is not required. Typically, sellers issue only a sales receipt and a cash receipt.
As stated in the text of paragraph 7 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in the case of selling goods for cash, the requirements for issuing invoices and drawing up settlement documents are considered fully met if the buyer received a cash receipt or other document of the established form from the seller (for example, a strict reporting form). Accordingly, current tax legislation allows taxpayers to deduct VAT if:
- the product was purchased at a retail outlet;
- the seller did not issue an invoice;
- In the cash register and sales receipt, the VAT amount is highlighted as a separate line.
If there is no invoice
Quite often, the accountable person, when making purchases with advance funds issued, fails to obtain an invoice from the seller.
This usually happens when making purchases at retail outlets and purchasing goods for a small amount. Moreover, if the seller is a VAT payer, then even if there is no invoice, the enterprise that accepted the report of the accountable person without an invoice still has the opportunity to take advantage of the VAT deduction. If VAT is highlighted as a separate line in a payment document (cash receipt or receipt order), then the enterprise will have the opportunity to take advantage of a deduction from this transaction made by an accountable person. After all, the Tax Code does not have a clear assessment for such a situation.
Moreover, the official position of government bodies is voiced clearly and categorically. If there is no invoice, then there is no right to deduction, even if the amount of tax is withheld by the seller of the product or service. Thus, in letters of the Ministry of Finance dated March 26, 2019 No. 03-07-09/20252, dated January 24, 2017 No. 03-07-11/3094, dated August 25, 2017 No. 03-07-14/54643, dated January 12, 2018 No. 03 -07-09/634 states that tax amounts on goods purchased from retailers without invoices indicating VAT to be deducted are not accepted for deduction. Even if the buyer has a cash register receipt with the allocated VAT amount.
At the same time, the financial department indicates that the advice provided in the above-mentioned letter and other similar letters is of an explanatory and recommendatory nature. The positive judicial practice that has developed today on the issue of challenging the tax authorities’ refusal to deduct the amount of VAT on an advance report without an invoice allows taxpayers to prove their right.
Court decisions that are positive for taxpayers (for example, resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Central District dated August 5, 2010 No. A64-3986/09 and the Moscow District Federal Antimonopoly Service dated August 23, 2011 No. F05-6832/11) are based on judicial practice summarized by the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation in a resolution dated May 13 .2008 No. 17718/07. In turn, the Supreme Arbitration Court relied on the opinion of the judges of the Constitutional Court. The decision of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated October 2, 2003 No. 384-O states that an invoice is not the only basis for using the right to deduction.
You can find out more about how law enforcement practice on this issue is currently developing in ConsultantPlus. Get trial access to the system for free and proceed to a selection of explanations from officials and examples from arbitration.
However, if in the check of a seller who is a VAT payer, the tax amount is not highlighted as a separate line, but there is an inscription “including VAT,” then the enterprise must calculate the VAT independently and reduce the cost of goods by this amount for profit tax purposes. This rule must always be applied, except for the cases specified in paragraphs. 2.5 tbsp. 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (letters of the Ministry of Finance dated April 24, 2007 No. 03-07-11/126, dated January 24, 2017 No. 03-07-11/3094).
In your accounting, include the amount of VAT not accepted for deduction:
- into the actual cost of purchased materials, goods and similar values (this follows from paragraph “a”, paragraph 11, paragraph “a”, paragraph 12 of FSBU 5/2019 “Inventories”);
- into expenses for ordinary activities, if the purchased works (services) are related to the ordinary activities of the organization (clauses 5, 6 of PBU 10/99 “Expenses of the organization”);
- into other expenses, if the purchased works (services) are not related to the normal activities of the organization (clause 11, 14.1 of PBU 10/99).
Make the following entries in your accounting:
| Contents of operations | Debit | Credit |
| Paid for materials (goods, work, services, etc.) through an accountable person | 60 | 71 |
| Materials purchased (goods, works, services, etc.) | 10 (41, 20, 25, 26, etc.) | 60 |
| VAT is reflected on the cost of materials (goods, works, services, etc.) | 19 | 60 |
| The amount of VAT not accepted for deduction is included in the actual cost of materials (goods and other valuables) or in expenses (for ordinary activities or other) | 10 (41, etc.) OR 20 (25, 26, etc.) OR 91-2 | 19 |
If the tax amount is not allocated at all, then the taxpayer can include the tax amount in expenses, i.e., not deduct VAT from the cost of the purchased goods when registering them (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia in Moscow dated January 10, 2008 No. 19-11-603, p. 2, Article 254, subparagraph 11, paragraph 1, Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). There is also positive judicial practice in this case - resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga-Vyatka District dated 06/09/2006 No. A29-13221/2005a.
In order not to argue with the tax authorities and not to lose the VAT deduction, we recommend that you issue a power of attorney to the accountable person to receive goods and materials. In this situation, the seller will issue shipping documents and an invoice to the company.
If you have an invoice in your accounting, make the following entries:
| Contents of operations | Debit | Credit |
| Paid for materials (goods, etc.) through an accountable person | 60 | 71 |
| Materials purchased (goods, other valuables) | 10 (41, etc.) | 60 |
| VAT is reflected on the cost of materials (goods, etc.) | 19 | 60 |
| Accepted for VAT deduction | 68-VAT | 19 |
ATTENTION! The documents must contain the name of the organization, not the full name of the employee. If the invoice is issued to an accountable person, the tax office will refuse the deduction because it will not be able to identify the buyer (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated January 09, 2017 No. SD-4-3 / [email protected] ).
How to properly issue a power of attorney is explained in detail in ConsultantPlus. Get trial access to K+ for free and go to the Ready-made solution.
VAT deduction on a cash receipt - conclusions
When an item is purchased at a retail store for cash, taxpayers are entitled to a VAT deduction based on the sales receipt, even if there is no invoice. The main thing is that the VAT amount is highlighted as a separate line in the goods and the cash receipt.
If a conflict arises with the tax service, you can refer to arbitration practice. The judges are of the opinion that it is impossible to refuse a VAT deduction only because of the absence of an invoice if there is a cash receipt or other document of the established form.
To avoid problems with the Federal Tax Service, whose inspectors refuse to deduct VAT in the absence of an invoice at the time of the on-site inspection, it is better to carry out the purchase and sale operation in special contract departments of retail stores
– specialists will issue an invoice, cash receipt order or invoice to the buyer who paid in cash. When the VAT amount is highlighted as a separate line in the listed documents, VAT can be deducted.
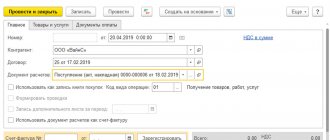
Account cash warrant
Access to the document in the section “Bank and cash desk” - “Cash desk” - “Cash documents”:
Let’s create a new document for cash withdrawal with the transaction type “Issue to an accountable person.”
The result of posting the document will be a posting reflecting the issuance of funds to the employee from the organization’s cash desk:
Common mistakes
Error:
The taxpayer accepted VAT as a deduction after purchasing goods for cash in a retail store. In the cash receipt, VAT was not highlighted as a separate line.
A comment:
If the seller did not issue an invoice when purchasing goods at retail, VAT can be deducted on the basis of a sales or cash receipt, but the VAT amount must be highlighted on a separate line.
Error:
The purchased goods were not recorded on the company's balance sheet. The taxpayer accepted VAT for deduction on the basis of a cash receipt with the amount of value added tax highlighted as a separate line.
A comment:
In order to have grounds for deducting VAT, it is necessary to capitalize the purchased goods on the balance sheet of the enterprise, retain documents confirming the right to deduct, resell the goods or use them in the course of production activities or in carrying out other transactions subject to VAT.
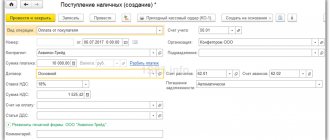
Advance report
Confirmation of expenses incurred and the use of accountable amounts is prepared in the document “Advance report”, which is available in the section “Bank and cash desk” - “Cash desk” - “Advance reports”:
When creating a new document, we fill in the following details in the header: the employee who received the amounts for the report, the organization that issued the funds, and the warehouse to which the inventory items purchased by the employee will be posted.
The tabular part of the document contains several bookmarks:
- Advances: we create a list of documents for which funds were issued for reporting:
- Goods: we enter information about inventory items purchased by the accountable person: nomenclature, quantity, price, VAT rate. Fill in information about the supplier. If the supplier issued an invoice, you should make a mark in the “SF” box and indicate its details. After the advance report is completed, the invoice will be generated automatically.
- Returnable containers: The tab is used for information about returnable containers that the accountable person received from suppliers.
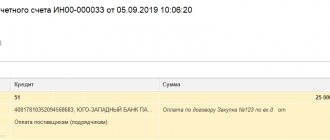
- Payment: details of amounts paid to suppliers for purchased goods or as prepayments. Filling out the cells of the bookmark is clear from the names: details of the expense document, name of the supplier and agreement with him. We describe the contents of the operation for filling out the printed form of the expense report. We indicate the payment amount. Settlement accounts 60.01 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” and 60.02 “Settlements for advances issued” will be filled in automatically.
- Other: we fill out the tab for the following expenses: travel expenses, travel expenses, gasoline costs, etc. We also fill out confirmation of receipt of services for purchased and issued monetary documents on this tab.
We fill in the details of the expense document for the printed form of the expense report. Similar to filling out the “Products” tab, if the supplier provided an invoice, check the box for its availability and fill in the details. After the advance report is completed, the resulting invoice will be generated in the system automatically.
We will enter the amount and the percentage of the VAT rate. The VAT amount and the total transaction amount will be calculated automatically.
We will fill out cost accounts for accounting and tax accounting and analytics. This information is necessary for the correct generation of transactions:
The printed form of the document is a unified form No. AO-01:
Answers to common questions about VAT deduction on a cash receipt
Question #1:
Can you be sure that the tax office, during an on-site audit, will not refuse to deduct VAT due to the lack of an invoice?
Answer:
The Federal Tax Service is of the opinion that VAT deductions can only be made if there is an invoice. Therefore, if the taxpayer only has a cash receipt in which VAT is highlighted as a separate line, claims from the tax inspectorate cannot be avoided, despite the fact that the opinion of the arbitration judges does not agree with the position of the Federal Tax Service. The only way to avoid claims is to complete the purchase of goods in a special contract department of the store, where sellers issue an invoice, delivery note and cash settlement for buyers who paid in cash.
Question #2:
There is a cash receipt for the purchase of goods in a retail store. Is it possible to deduct VAT without an invoice if the goods were not purchased for the purpose of using them in the business of the company?
Answer:
It is allowed to deduct VAT on the purchase of goods that were purchased for the purpose of resale or use in the economic activities of the enterprise. If the goods were purchased for other purposes, VAT cannot be deducted in any case.