Do I need an advance invoice?
An invoice (hereinafter also referred to as invoice) is a document confirming:
The moment of determining the tax base for VAT – (clause 1 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
An invoice must be issued when determining the tax base for VAT. When receiving an advance - full or partial - the VAT base is subject to determination. Therefore, it is necessary to set the sf.
it is mandatory to issue invoices for advance payments . But there are a few exceptions to this rule.
When else can you claim a deduction?
However, nothing prohibits you from deducting VAT on a late invoice in your return for the following quarters. Indeed, by virtue of the norm of the same paragraph 1.1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, VAT deductions can be claimed in tax periods within 3 years after the registration of purchased goods.
For example, the last quarter in which you can claim a VAT deduction for goods accepted for accounting in the first quarter of 2022 will be the first quarter of 2024
If the invoice from the seller was received after the 25th day of the month following the quarter in which the purchased goods were accepted for accounting, you need to act differently. In this case, you can deduct input VAT in any period, starting from the quarter in which the invoice was received until three years after the goods were accepted for accounting.
What deadlines must be met when preparing an invoice?
A logical question is when an advance invoice is issued - on the day the funds are received or is some longer period given?
In paragraph 3 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation clearly states when an advance invoice and invoice are issued upon implementation:
The question often also arises: is it necessary to issue an advance invoice if the shipment for the listed advance payment occurred within 5 days from the date of the advance payment?
There are explanations from officials who say that in this case there is no need to make an advance payment (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated April 12, 2019 No. 03-07-08/28182).
But it should be taken into account that this point of view refers to a situation where both the advance payment and the shipment fall into the same reporting period. For VAT this is a quarter.
If an advance payment is received in one quarter, and shipment occurs within 5 days, but already in the next quarter, an advance invoice must be issued . Otherwise, the tax base for the quarter will be distorted, which will lead to an illegal reduction in the VAT tax payable.
What date to put in primary documents
In the letter of the Ministry of Finance dated September 29, 2022 No. 03-03-06/1/78815 about deductions, the wording has changed slightly, although it refers to ongoing services.
VAT deduction for continuing services should be applied in the quarter in which all the conditions established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are met, namely, if, before submitting a VAT tax return:
- services are registered;
- Based on them, primary documents and an invoice were received.
And the primary documents and invoice can be dated to the month of submission of the VAT return.
So if you did not have time to submit a declaration, then make an entry regarding the received invoice in the purchase book for the quarter in which the goods were accepted for accounting, in the usual manner.
Which form to use for an advance invoice
An invoice for the advance payment is issued using a regular account form. It was approved by Resolution No. 1137.
A sample advance invoice can be downloaded for free from the link below:
The main difference between a regular account and an advance account is the order in which data is entered into the document.
The header of the form is filled out in the same way as for a regular account:
- enter information about the payer, buyer, details of the payment order for which the advance was received. The lines “shipper” and “consignee” are crossed out;
- The order of filling out the table is different;
- The accountant for the advance is signed by the manager and chief accountant or persons authorized to do so.
You can download a sample of filling out an advance invoice from the link:
How should a buyer fill out a purchase book?
For a buyer, an invoice is an extremely important document. Only if it is available, filled out correctly and registered can you receive a deduction of input VAT.
After transferring the advance payment and receiving the corresponding invoice from the supplier, the document should be registered in the purchase ledger. This must be done in the quarter in which the advance is listed. Columns 4, 6, 8 and 9, as well as 10 to 12, are not filled in, and column 7 reflects information about the advance payment .
Once the advance invoice has been received, the VAT on the advance payment can be claimed as a deduction. But you can not do this, but wait until the shipment is made, and claim VAT for deduction from the shipping invoice. However, if the first path is chosen, the VAT previously deducted on the advance invoice will have to be restored. This must be done in the period when the goods, work or services for which the advance payment was transferred are received and capitalized. If VAT on the advance payment was not claimed for deduction, then there is nothing to recover.
When a shipping invoice is received, it should also be recorded in the purchase ledger. This can be done after the goods, works or services received under it are accepted for accounting. However, it is not necessary to register the document immediately - this can be done at any time within three years from the date of receipt of goods. This opportunity is used when they want to deduct input VAT on these goods in one of the following quarters.
How to enter advance invoices into sales and purchase books
It is the responsibility of the seller/performer to issue an invoice for the advance payment. He records the advance invoice in the sales ledger as usual .
The transaction type code for advance account payment is 02 . It shows the total amount including tax and the tax amount. The column with the indicator “sales cost excluding VAT” is crossed out.
Upon receipt of an advance invoice from a supplier, the taxpayer has the right to deduct VAT and include this advance invoice in the purchase book.
It should be borne in mind that the advance account does not have the right to use the deduction for 3 years . That is, if VAT on a regular account can be deducted within 3 years from the date the account is issued, then VAT on an advance account can be deducted only in the quarter in which it is issued.
When making a shipment for which an advance was paid, the supplier again issues an invoice (already shipping) and registers it in the sales book with the transaction type code - 01 . To avoid double tax, the supplier simultaneously registers an invoice for the advance payment in the purchase book with the transaction type code - 22 .
The buyer accepts the shipping invoice from the supplier and registers it in the usual manner in the purchase book. If the buyer entered the previously accepted invoice for the advance payment into the purchase book and accepted VAT for deduction, then in order for the tax deduction not to be doubled, it is necessary to restore the previously accepted VAT for deduction on the advance payment.
Registration of SF for advance payment from supplier
Regulatory regulation
The organization has the right to accept for deduction VAT presented by the supplier when transferring an advance payment to him (clause 12 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
VAT on advances issued to suppliers is deductible if the conditions are met (clause 9 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- the contract provides for advance payment;
- payment was made against future supplies for activities subject to VAT;
- a correctly executed advance SF is available;
- Payment documents are available confirming the transfer of the advance to the supplier.
For the amount of input VAT accepted for deduction:
- in the purchase book, a registration entry is made for the advance SF with the transaction type code 02 “Advances issued”;
- In accounting, the entry Dt 68.02 Kt 76.VA “VAT on advances and prepayments issued” is generated.
In this case, it is necessary to take into account the following features associated with the acceptance of VAT for deduction on advance invoices from suppliers:
- accepting VAT for deduction is a right, not an obligation, therefore it is not necessary to accept VAT for deduction for each tax return, especially if the shipment from the supplier occurs in the same tax period;
- transferring the deduction for advance SF for three years is impossible , because it is provided only for VAT deductions when purchasing goods (works, services). Those. the deduction for advance SF must be made in the period when the right to it arose (clause 2 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated 01/09/2017 N SD-4-3 / [email protected] );
- if the date of preparation of the advance tax return falls on the next quarter , and not on the tax period of payment, then the deduction on such an invoice is illegal, even if it was received before the deadline for submitting the VAT return (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 24, 2017 N 03-07-09 /17203).
Accounting in 1C
The document Invoice received transaction type For advance payment is generated on the basis of the document Write-off from the current account by clicking the Create based on and - Invoice received .
The document Invoice received for an advance can only be created if the transactions of the payment document reflect the advance issued to the supplier, for example:
- Dt 60.02 Kt
The document Invoice received for advance payment is automatically filled in with the data from the document Write-off from the current account :
- Invoice No. and from – number and date of the invoice received from the supplier;
- Received – the actual date of receipt of the invoice from the supplier;
- The transaction type code is “Advances issued.”
If the document has the Reflect VAT deduction in the purchase book , then when it is posted, entries will be made to accept VAT for deduction.
Postings according to the document
The document generates transactions:
- Dt 68.02 Kt 76.VA – acceptance of VAT deduction from the advance payment transferred to the supplier.
The document generates movements in the VAT Purchases :
- registration of advance SF supplier with the transaction type code “Advances issued” for the amount of accepted VAT for deduction.
Purchase Book report can be generated from the Reports – VAT – Purchase Book section. PDF
VAT declaration
The VAT return reflects the amount of VAT deducted from the advance payment transferred to the supplier:
In Section 3, page 130 “The amount of tax presented to the taxpayer-buyer when transferring the amount of payment, partial payment on account of upcoming deliveries...”: PDF
- the amount of VAT accepted for deduction.
In Section 8 “Information from the purchase book”:
- invoice received, transaction type code ““.
See also:
- Reinstatement of VAT when offsetting advances issued to suppliers
- Invoice received for advance payment
- p.130 Advances transferred to suppliers
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Related publications
- Acceptance of VAT for deduction by a tax agent when renting state (municipal) property Let's consider the procedure for accepting VAT for deduction when renting property from...
- Acceptance of VAT for deduction when offsetting advances received from buyers Let's consider the features of reflecting in 1C the acceptance of VAT for deduction when...
- Acceptance of VAT for deduction during construction and installation work using a self-employed method Let's consider the features of reflecting in 1C the acceptance of VAT for deduction, earlier...
- Calculation of VAT on advances received from buyers to a current account Let's consider the features of reflecting in 1C the issuance of an advance invoice to the buyer and...
Invoice for the balance of the advance - at the end of the tax period?
| Can an organization, having shipped part of the goods on account of the received advance payment (five days after receiving the advance payment), issue an invoice for the remaining advance amount at the end of the tax period, if all operations were carried out in the same tax period? Experts from the Legal Consulting Service GARANT Nadezhda Vasilyeva and Olga Monaco answer. |
| Clause 1 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation determines that the moment of determining the VAT tax base for the seller is the earliest of the following dates (unless otherwise provided by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation): — day of shipment (transfer) of goods (works, services), property rights; - the day of payment, partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer of property rights. Consequently, upon receipt of an advance payment (advance), the taxpayer is obliged to calculate VAT on this amount and, on the basis of paragraph 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, no later than five calendar days from the date of receipt, draw up the corresponding invoice. The amount of tax in this case is calculated in the manner established by paragraph 4 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 1 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). According to paragraph 14 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, if the moment of determining the tax base was the day of receipt of advance payment on account of upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services, transfer of property rights), then on the day of shipment of these goods (performance of work, provision of services, transfer of property rights) rights) against the previously received prepayment, the moment of determining the tax base also arises. Invoices issued and (or) issued upon receipt of payment (partial payment) for upcoming deliveries of goods (work, services) or transfer of property rights are registered by the taxpayer in the sales book in accordance with paragraphs 3 and 17 of the Rules for maintaining the sales book used in calculations for value added tax, approved. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137. Based on a literal reading of the norms of paragraph 14 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, there are no exceptions to the general rule for cases where prepayment and shipment take place in the same tax period. This opinion is shared by the tax authorities, explaining that upon receipt of payment (partial payment) for the upcoming delivery of goods (work, services), an invoice for the amount of such advance payment must be issued without fail, even if the shipment of goods (work, services) made no more than within five days after making advances (letters of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 10, 2011 No. KE-4-3/3790, dated February 15, 2011 No. KE-3-3/354). However, according to the Ministry of Finance of Russia, if the shipment of goods (work, services) is carried out within five calendar days, counting from the day of receipt of the advance payment (partial payment), invoices for such advance payment are not required to be issued to customers (letters from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 12.10. 2011 No. 03-07-14/99, dated 03/06/2009 No. 03-07-15/39). When using these clarifications, it must be taken into account that such a conclusion does not follow from paragraph 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, but is based on the fact that upon shipment, the supplier will in any case issue an invoice, so issuing an advance invoice at the same time does not make sense , but only increases and complicates document flow. In addition, letters from the Ministry of Finance of Russia are advisory in nature, do not contain legal norms or general rules specifying regulatory requirements, and are not regulatory legal acts. The opinion of the judiciary on this issue is fundamentally different from the position of the regulatory authorities. Arbitration courts, in the case where prepayment and shipment occur in the same tax period, generally do not recognize such payments as advance payments for the purpose of calculating VAT, while they rely on the position of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation, which is that an advance payment cannot be recognized , received by the taxpayer in the same tax period in which the shipment took place (Resolutions of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated March 10, 2009 No. 10022/08, dated February 27, 2006 No. 10927/05, resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga District dated December 22, 2008 No. A55-3598/08 , FAS Moscow District dated January 23, 2013 No. F05-15410/12, dated April 23, 2010 No. KA-A40/3908-10, dated July 17, 2008 No. KA-A41/5427-08, FAS Far Eastern District dated November 28, 2008 No. F03 -4597/2008). If you follow this position, the seller must issue invoices for the received advance payment only if the shipment of the goods for which it was received will take place in the next tax period. Thus, in our opinion, the above position of the Federal Tax Service of Russia is the most consistent with the norms of Chapter 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which do not make the obligation of taxpayers to charge VAT and issue invoices upon receipt of an advance payment dependent on the period (terms) of subsequent shipment of goods (works, services) ). If an organization adopts a different procedure for issuing invoices for advances received, different from that recommended by the Federal Tax Service of Russia, namely, it issues an invoice for the remaining amount of the advance at the end of the tax period, then with a high probability this approach may cause a tax dispute. And in this case, there is a high probability that the organization will have to defend its position in court. The texts of the documents mentioned in the experts’ response can be found in the GARANT legal reference system. |
Results
If an advance is transferred to a supplier in one tax period, and an invoice for the advance is received in the next, you can deduct VAT on the advance in the period when the invoice is actually received. However, this will require fulfilling a number of conditions, the main of which is to confirm the date of actual receipt of the invoice.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated May 25, 2017 No. 625
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
We continue the series of lessons (previous part) on working with VAT in 1C: Accounting 8.3 (revision 3.0).
Today we will look at: “Accounting for VAT on advances paid to suppliers.”
Most of the material will be designed for beginner accountants, but experienced ones will also find something for themselves. In order not to miss the release of new lessons, subscribe to the newsletter.
Let me remind you that this is a lesson, so you can safely repeat my steps in your database (preferably a copy or a training one).
So let's get started
Situation to consider
We (VAT LLC) signed an agreement with Supplier LLC for the supply of goods to us in the amount of 150,000 rubles (including VAT).
According to the terms of the agreement, we must transfer an advance in the amount of 60% of the amount specified in the agreement, that is, 90,000 rubles.
- In the 1st quarter, according to the agreement, we transferred an advance to the supplier in the amount of 90,000 rubles.
- In the 2nd quarter, Supplier LLC shipped us goods for the entire amount specified in the contract (150,000 rubles).
It is required to formalize these transactions in the 1C: Accounting 8.3 (version 3.0) program, and also calculate VAT for each quarter.
The essence of the lesson
We will offset VAT on the advance payment (90,000) in the 1st quarter, reflecting it in the purchase book for the 1st quarter.
Then we will offset VAT on the entire amount (150,000) in the 2nd quarter, reflecting it in the purchase book for the 2nd quarter.
Finally, we will charge (restore) the VAT credited in the 1st quarter from the advance payment (90,000), reflecting it in the sales book for the 2nd quarter.
Total to be reimbursed:
- For the 1st quarter there will be VAT 90,000 * 18 / 118 = 13,728.81
- For the 2nd quarter 150,000 * 18 / 118 - 13,728.81 = 9,152.54
1st quarter
We carry out a bank statement
We enter into the program a bank statement dated 01/01/2016 for the transfer of an advance in the amount of 90,000 rubles for LLC “Supplier”:
The debit from the current account will be as follows:
Please pay attention to the following points:
- Transaction type “Payment to supplier”.
- A separate agreement (No. 1 dated 01/01/2016) within the framework of which settlements for this transaction will be carried out.
- Dedicated VAT at the estimated rate (18/118).
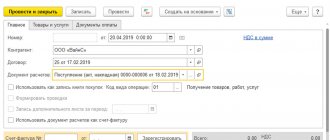
We enter an invoice for the advance payment to the supplier
Having received a copy of the invoice from Supplier LLC for the advance payment we have transferred, we enter it into the database:
Create a new document:
The generated advance invoice will look like this:
Please pay attention to the following points:
- Number and date indicated on the invoice from the supplier (No. 10 dated 01/03/2016).
- Type of invoice: “For advance payment”.
- Basis document: bank statement, according to which we transferred the advance from our current account to the supplier's account.
- The checkbox “Reflect VAT deduction in the purchase book” is checked.
- Transaction type code 02 “Advances issued”.
We post the created invoice (the “Post and close” button).
We analyze the postings and movements of registers...
- The deduction of VAT from the transferred advance was reflected in debit 68.02 in correspondence with credit 76.VA (VAT on advances and prepayments issued).
We skip the “Invoices Journal” register, it is not interesting to us (see the first lesson).
- An entry in the “ VAT Purchases ” register ensures that the advance payment issued is included in the purchases ledger.
What is said in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation about the deduction of VAT on an advance invoice
Based on paragraphs.
1st and 12th Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the buyer has the right to deduct VAT calculated when paying an advance on account of future deliveries. As a general rule, the right to claim VAT for deduction is available within three years from the moment such an opportunity arises (clause 2 of Article 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, specifically in terms of deductions for advances, this rule is not applicable, and transfer of the deduction to later periods (quarters) is not allowed (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 04/09/2015 No. 03-07-11/20290).
Find out more about the general procedure for deducting VAT on advances.
From 07/01/2021 a new invoice form is in effect, incl. adjustment, as amended by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 04/02/2021 No. 534. The update of the form was caused by the introduction of a goods traceability system. All taxpayers are required to use the new form, even if the goods are not included in the traceability system. We described in more detail the changes made to the invoice here.
You can download the new invoice form by clicking on the image below:
ConsultantPlus experts have prepared step-by-step instructions for preparing each line of the updated invoice. To do everything correctly, get trial access to the system and go to the Guide. It's free.
Prepayment in cash
When paying in cash, money is deposited into the cash register. The document that evidences the payment of cash as an advance payment is a cash receipt (Article 5 of Law No. 54-FZ of May 22, 2003). According to the Rules, the invoice for prepayment must indicate the details of the payment and settlement document, which are reflected in line 5 (subclause 3, clause 5.1, article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If, in order to accept VAT as a deduction when purchasing goods for cash (with or without prepayment), the numbers and dates of cash receipts are indicated in invoices, then formally the norm of paragraph 9 of Article 172 of the Tax Code, which refers to confirmation of the transfer of prepayment, will not be met, and Transfers are made only by bank transfer through a bank. Therefore, on line 5 of the “advance” invoice, when making an advance payment in cash, the seller should put a dash, and the buyer should not register such an invoice in the purchase book and should not deduct VAT from the cash advance payment.