Invoice under simplified tax system
All organizations and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system are not VAT payers, which means they do not need to issue an invoice. However, if certain situations arise, such a document will be needed.
These include situations where “simplified” people pay VAT: (click to expand)
- Import of goods;
- Operations under a simple partnership agreement, or trust management of property and concession agreement;
- When a company performs the duties of a tax agent, for example, rents state or municipal property.
In all of the above situations, organizations are required to issue an invoice (
Simplified VAT when purchasing state property
When selling state property, the tax base, according to clause 3 of Art. 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, corresponds to the amount of income from the sale including VAT. In this case, it is not the seller of state property who must pay the tax, but its buyer, who is recognized as a tax agent. It is he (in this case, the “simplified” buyer) who is obliged to calculate VAT under the simplified tax system, withhold it from income payable, and transfer it to the budget.
However, sub. 12 paragraph 2 art. 146 of the Tax Code provides the opportunity for a “simplified” buyer not to withhold VAT on the income of the seller of state property if the conditions for the purchase of state and municipal property established by Art. 3 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On the peculiarities of the alienation of real estate in state ownership...” dated July 22, 2008 No. 159-FZ:
- As of July 1, 2015, the property rented by the simplifier had already been leased to him for at least 2 years.
- He has no arrears of rent or other related payments (fines, penalties).
- The property is not included in the approved list of property intended for rental and free from the rights of third parties.
- On the day of concluding the repurchase agreement, the simplifier is listed in the register of small and medium-sized businesses.
Invoice with o
You are not required to issue an invoice from the company using the simplified tax system. Only companies exempt from VAT put this mark. Organizations that are considered exempt from VAT are recognized in accordance with Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Companies that apply the simplified tax system do not qualify as such “exempt” payers, since they are not initially payers of this tax. Accordingly, there is no need to issue a “simplified” invoice marked “without VAT”.
Some counterparties still insist on an invoice. Such companies should keep in mind that they will not receive a deduction for “input” VAT on such an invoice. And why they continue to demand such invoices is not clear.
“Simplers” are not obliged to fulfill such a request. They have the right to explain to their counterparties that in order to post the purchased goods, documents such as an invoice for payment, an invoice and a statement will be sufficient. And if the counterparty continues to insist and it is impossible to convince him, then you can issue the required document. Please indicate that the purchase does not include VAT.
Such registration of an invoice will not entail obligations to pay tax, as well as the preparation and submission of a VAT return, since the tax will not be highlighted in the invoice (
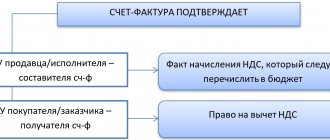
Obligation to issue invoices
The most important requirement for receiving a deduction is that the supplier issues an invoice correctly. This follows from the provisions of Articles 169, 171, 172, 176 of the Tax Code. At the same time, only sellers - VAT payers have the obligation to issue documents, who must draw them up within five calendar days from the date of receipt of an advance payment or shipment of goods, performance of work, provision of services (clause 1, 3 of Article 168, clause 3 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
As a general rule, companies using the simplified system are not VAT payers. According to paragraph 2 of Article 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the only exception is the tax payable when importing goods into the customs territory of the Russian Federation, as well as paid in accordance with Article 174.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It follows that these persons should not issue invoices.
note
The Constitutional Court determined that a deduction on an invoice issued by an organization on the simplified tax system according to the rules of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is possible if the tax is transferred to the budget. In this case, the “special regime” has the right to enter into legal relations regarding the payment of tax (Definition of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation of March 29, 2016 No. 460-O).
This point of view is also shared by the Ministry of Finance in letters dated October 20, 2011 No. 03-07-09/34, dated May 16, 2011 No. 03-07-11/126, etc. As well as the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated July 24, 2008 No. 3- 1-11/239 and Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated April 5, 2010 No. 16-15/035198. In addition to the absence of the obligation to issue invoices to their customers, simplified companies do not maintain a purchase book, a sales book and do not have to submit a VAT return. And they carry out settlements with customers without allocating VAT amounts in the primary documents.
Zero VAT on the invoice
Organizations using the simplified tax system should also not put a real VAT rate of 0% in the invoice. Only companies that are VAT payers can apply this rate. In addition, it must be confirmed by specific documents that organizations submit along with the VAT return to the tax office.
If an accountant decides to meet the buyer halfway and issue a document with zero VAT, the tax authorities have the right to charge it, not at a zero rate, but at a rate of 18%. This will happen because VAT is indicated in the invoice, and it is impossible to confirm that the company’s rate is zero.
Deduction on an invoice from a counterparty
An analysis of judicial practice shows that arbitrators in most cases consider it legal to deduct an invoice from a counterparty using the simplified tax system. Thus, the Constitutional Court, in its Ruling No. 460-O dated March 29, 2016, concluded that VAT payers have the right to deduct the tax, even if the invoice was issued by a “special regime officer.” The court indicated that “simplified people” can enter into legal relations regarding the payment of tax and, when issuing an invoice with VAT highlighted in it, are obliged to transfer it to the budget. The document issued to the buyer, in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, is the basis for accepting the tax amounts indicated in it for deduction from the buyer.
Similar conclusions were made by arbitration courts in the decisions of the Administrative Court of the East Siberian District dated June 8, 2016 in case No. A78-2859/2015, FAS of the West Siberian District dated February 24, 2012 in case No. A03-5151/2011. When making decisions in favor of companies on the possibility of deducting VAT, the judges proceeded from the fact that a company has the right to deduct tax paid to a supplier who is not a VAT payer if all the requirements for its acceptance, provided for in Articles 171 and 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, are met. The fact that the invoice was issued by a “simplifier” does not matter, because he will pay the tax to the budget.
As we see, the position of the courts runs counter to the opinion of the regulatory authorities. So if the inspectorate refuses to deduct VAT for a company on an invoice issued by a “simplified” person, then the buyer can defend his right to deduct only in court.
If you issue an invoice with VAT
Some organizations, on their own initiative, may issue invoices, highlighting VAT. In this case, they are required to pay tax to the budget and also submit a VAT return to the Federal Tax Service. This must be done before the 25th day of the month following the quarter in which the document was issued. For example, a company issued an invoice using the simplified tax system on February 10, 2022; accordingly, it must submit a VAT return by April 25, 2022.
It is important to understand that issuing an invoice with allocated VAT does not give the simplifier the right to a tax deduction on purchased goods. Only VAT payers have the right to such a deduction, and organizations using the simplified tax system are not such.
VAT deduction under the simplified tax system
It is worth noting that if a company’s supplier uses the simplified tax system, it will be very difficult to obtain a VAT deduction. Regulatory authorities have long held this position: if an invoice is received from a “simplified” person, then it cannot be used for VAT reimbursement. Another similar conclusion was made in the letter of the Ministry of Finance dated October 5, 2015 No. 03-07-11/56700. The department came to such conclusions earlier in letters dated May 16, 2011 No. 03-07-11/126, Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated April 5, 2010 No. 16-15/035198 and others.
Answers to common questions
Question: A simplified company, at the request of the buyer, issued an invoice, highlighting VAT. After that, in accordance with the requirements of the law, I paid this tax to the budget and filed a VAT return. When calculating the simplified tax system, will VAT be included in the tax base? (click to expand)
Answer: The tax base for simplifiers is income, which must first of all be economically profitable. Paid VAT is not a benefit for the company, and therefore should not be included in the base for calculating the simplified tax system. Accordingly, when calculating the tax, the simplified tax system does not need to be included in the VAT base.
Simplified Taxation System and VAT: purchase from a foreign person on the territory of the Russian Federation
entered into an agreement with a foreign manufacturer for the purchase of materials, while the sale of materials is carried out on the territory of the Russian Federation. What will happen to VAT in this case? It depends on whether the “foreigner” has a permanent establishment in the Russian Federation. A Russian company should pay VAT under the simplified tax system only if there is no such representative office. In this case, the Russian buyer is a tax agent who, in accordance with paragraphs. 1 and 2 tbsp. 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, is obliged to withhold VAT from the foreign counterparty and pay it to the budget.
Example
A Russian company, using the simplified tax system, entered into a contract with a foreign seller who does not have a permanent representative office in Russia for $12,000, including VAT. The contract is executed on the territory of the Russian Federation. In this case, the Russian company needs to withhold VAT from the “foreigner” under the simplified tax system in the amount of $2,000 and transfer it to the budget, and pay the remaining $10,000 for purchases.
To summarize: a “simplified” seller is required to pay VAT if the place of transaction is the Russian Federation and foreign sellers do not have the independent ability to pay VAT due to the fact that they do not have a permanent establishment in the Russian Federation.
For information on the procedure for deducting VAT withheld by a tax agent, read the article “How can a tax agent deduct VAT when purchasing goods (work, services) from a foreign seller.”
Log book of received and issued invoices during intermediary operations
In relation to clause 5.1 of Art. 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, persons who do not pay VAT under Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, but conduct activities in the interests of another person under commission agreements, agency agreements and issue invoices, are required to submit to the Federal Tax Service the “Register of received and issued invoices” . This also applies to transport expedition contracts, income under which is determined in the form of remuneration and when performing the functions of a developer. The journal of received and issued invoices is submitted by the 20th day of the month after the reporting quarter.
Thus, organizations under the simplified tax system are required to keep a journal of invoices in the following cases:
In what cases during intermediary operations is an invoice journal not kept?
An invoice journal is not kept in the following cases:
- If the principal or principal of the organization under the simplified tax system is not a VAT payer, then there will be no invoices, because he is also a “simplified”. And if the principal or principal is with OSNO, then you need to keep a journal of invoices.
- If, under an agency agreement, an organization under the simplified tax system, as an intermediary, will make a transaction on behalf of the guarantor under a power of attorney and all documents will be on his behalf.
- If an organization under the simplified tax system is a principal or a principal and gives its goods for sale or an order for the purchase of goods, then an invoice journal does not need to be kept.
If a VAT non-payer intermediary sells goods only to individuals, and, therefore, does not issue invoices, then when carrying out such operations, a log of issued and received invoices is not kept, by virtue of the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated April 2, 2015 No. 03-07-14/18223 .
Accounting for “input” VAT under the simplified tax system in accounting in 1C 8.3
Input VAT is indicated as a separate line in the book of income and expenses, because it is a separate expense in the Tax Code. In accounting, the simplified version includes input VAT in the price. In accounting, this is the debit of account 41, and if you look at the posting in 1C 8.3, you will notice that the document contains VAT, but it is not in the postings. Due to the fact that in the form of the document “ Prices in the document ” there is a checkbox “Include VAT in the price”. 1C 8.3 includes input VAT automatically in the debit of account 41:
If a simplified taxation system is installed in the accounting policy settings in 1C 8.3, then by default in the document form “ Prices in document ” the checkbox “Include VAT in price” will be checked. The main thing is not to turn it off manually. And if the checkbox is turned on, then automatically the input VAT will be debited to account 41.01. In accounting, VAT is not recorded separately on account 19, but only on account 41:
How to display?
Issuing an invoice to a VAT tax agent:
- the invoice is issued on behalf of the seller: in the lines “Seller”, “Address”, “TIN/KPP” of the seller the details of the counterparty are entered, in the data of the buyer - the simplified one;
- the invoice is issued within five calendar days from the date of payment in two copies;
- one signed copy is transferred to the counterparty.
It is necessary to indicate the number and date of the payment and settlement document according to which payment for goods (work or services) was transferred.
Issuing an invoice under an agency agreement:
a simplifier as an agent, purchasing on his own behalf a product or service for a client on OSNO, together with supporting documents, receives an invoice from the supplier in his name;- the same invoice is issued to the buyer, where the customer’s details are indicated in the buyer’s data, and the supplier’s details remain in the seller’s data;
- the buyer is also given a copy of the seller's invoice (to receive a VAT deduction).
The invoice date for the customer must match the invoice received from the supplier. The invoice number is assigned in a simplified manner.
Accounting for “input” VAT under the simplified tax system in tax accounting in 1C 8.3
As for the book of accounting of income and expenses (KUDiR) for tax accounting, here the input VAT must be included in the expense as a separate line. Therefore, in order for the 1C 8.3 information base to “see” this separate line, VAT must be reflected separately as in the primary document from the supplier.
In 1C 8.3, you need to register the input invoice that the supplier submitted, while the invoice details are not reflected anywhere in tax accounting. If there is a document, then it needs to be registered. In KUDiR, the 1C 8.3 program does not include an invoice:
It is important to register invoices with input VAT because there are different situations. For example, an organization works on the simplified tax system, but suddenly a situation arises that the revenue limit under the simplified tax system is exceeded in the middle of the year or a founder appears - a legal entity with a share in the authorized capital of more than 25%. Accordingly, there is an urgent need to recalculate taxes according to OSNO. To do this, you need to pick up all the primary documentation and enter it into the 1C 8.3 program. And if all invoices have already been entered in advance, then only the accounting policy parameters need to be changed.