Individual entrepreneurs usually choose preferential tax regimes. This allows them to optimize costs and submit fewer reporting forms. The general taxation system for individual entrepreneurs is not the best option. As a rule, her choice is dictated by necessity. And in some cases it is not there at all, because you can end up on OSNO not of your own free will.
This will happen if you go beyond the restrictions established within the tax regime for the income of individual entrepreneurs, the number of employees or types of activities. Or if you don’t switch to a simplified tax system in time. However, the general taxation system for individual entrepreneurs may be relevant if he works with large buyers who pay VAT. Let's figure out what the OSNO regime is and what kind of reporting needs to be submitted here.
Personal income tax on entrepreneur income
An individual entrepreneur pays personal income tax on the amount of income he receives from business activities. He has the right to reduce them by professional deductions in the amount of costs that he can confirm with documents. If there are no documents, an individual entrepreneur on OSNO has the right to deduct 20% from his income. The result is a tax base to which a personal income tax rate of 13% is applied.
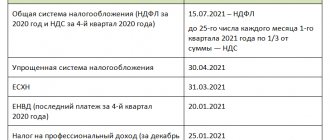
The procedure for paying tax is described in Article 227 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. During the year, the entrepreneur makes 3 advance payments at the following times:
- for the 1st quarter - no later than April 25:
- for the 3rd quarter - no later than July 25;
- for the 4th quarter - no later than October 25.
At the end of the year, the individual entrepreneur must recalculate personal income tax based on how much income he actually received and paid in advances. Additional tax payment must be made before July 15 of the following year. And by April 30, an individual entrepreneur on OSNO is required to submit a 3-NDFL declaration to the Federal Tax Service.
Free tax consultation
Algorithm for calculating and paying personal income tax for individual entrepreneurs on OSNO
Note!
From the beginning of 2022, the procedure for calculating personal income tax by entrepreneurs has changed. Previously, advance payments were calculated by specialists from the Federal Tax Service; now individual entrepreneurs must do this themselves.
Below is a step-by-step algorithm for calculating and paying personal income tax for individual entrepreneurs on the OSN, which was relevant until 2022:
- The individual entrepreneur received his first income of the year.
- Calculated the amount of estimated income for the whole year (minus expenses).
- Filled out and submitted the 4-NDFL declaration to the Federal Tax Service (with information about the expected income).
- I received notifications from the Federal Tax Service with the calculated amounts of advances for the payment of personal income tax.
- Paid advance payments on time (specified in notifications).
- At the end of the year, I compiled and submitted the 3-NDFL declaration.
- Paid or returned the tax calculated according to the 3-NDFL declaration.
VAT
OSNO is one of two taxation systems that requires payment of VAT. Tax is calculated on the cost of goods, works and services sold. The standard VAT rate is 20%, but there are a number of preferential goods that are taxed at a rate of 10%. These are food, goods for children, printed periodicals, and some medical products. The full list is presented in paragraph 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In addition, in some cases there is a zero VAT rate. It is used for export, international transport and cargo transportation. There are also a number of transactions that are not subject to VAT (Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Among them are the sale of certain medical goods and services, care for the disabled, activities with children in clubs and others.
The VAT allocated in the incoming invoice can be deducted by the buyer. It is because of this opportunity that entrepreneurs often choose the main tax regime. This allows their counterparties to reduce the tax payable. The individual entrepreneur himself can also take advantage of the deduction and reduce VAT by the amount of “input” tax charged to him by suppliers.
VAT is calculated at the end of each quarter. The amount received is divided into 3 equal parts and paid before the 25th day of each month of the next quarter.
VAT returns are submitted 4 times a year - before April 25, July 25, October 25 and January 25. The peculiarity is that this report is submitted only in electronic form. You cannot fill out a paper form and bring it to the Federal Tax Service or send it by mail. In this case, it is considered that the declaration has not been filed. This rule also applies to “zero” VAT returns.
Personal income tax reporting for individual entrepreneurs
Here it is important to note three types of reports relating specifically to personal income tax:
- KUDIR for individual entrepreneurs on OSNO - the individual entrepreneur must keep a book where he reflects all business transactions (remember that only if KUDIR is maintained, the entrepreneur is released from the obligation to keep accounting records);
- 4-NDFL – information about estimated income (surrendered, as we said earlier, by entrepreneurs who either just registered as an individual entrepreneur or switched to OSNO from other regimes);
Important! 4-NDFL is submitted once. But, in principle, there may be a situation where it is necessary to file an adjustment return. Such a need arises in the event of a sudden change in business conditions, due to which the estimated income changes up or down by more than 50%.
If your estimated income has increased significantly, then it is not necessary to resubmit 4-NDFL - everything that you do not pay in advance, you will pay during the final payment at the end of the year. But if there is a sharp decrease in income, it is still better to file a 4-NFDL - this is beneficial for the individual entrepreneur. Based on the new information, the tax authorities will recalculate the advances, and you will no longer overpay them during the year.
- 3-NDFL - the personal income tax declaration itself is submitted once based on the results of the past year until April 30 of the next year.
Property tax for individuals
Property tax is levied on real estate that an individual entrepreneur on OSNO uses in his business. This could be an apartment, a room, a residential building, including an unfinished construction project, an outbuilding or structure, a garage, or a parking space. The tax rate varies from 0.1% to 2%.
Property taxes are calculated by tax inspectors. The entrepreneur receives a notification and makes payment no later than December 1 of the following year. This tax is not reported.
Personal income tax for employees
If an individual entrepreneur is an employer or hires individuals under civil contracts, he must transfer personal income tax to the budget from the payments he makes to them.
The tax is paid from the amounts accrued to the individual. The order is:
- income subject to personal income tax is calculated;
- the amount of tax is calculated taking into account the deductions due to the employee (Articles 218-220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- the amount received is withheld from income and transferred to the budget no later than the next day.
Certain types of income have their own tax payment deadlines. For example, personal income tax on sick pay or vacation pay must be transferred by the end of the month in which they were paid. Personal income tax reporting for employees is submitted in the form of calculation 6-NDFL - at the end of each reporting quarter, no later than the last day of the next month.
Free accounting services from 1C
Content
- How is personal income tax calculated for individual entrepreneurs?
- Income received
- Tax deductions
- Advance payments
- Personal income tax rate for individual entrepreneurs
- Calculation of personal income tax at the end of the year
- Personal income tax reporting for individual entrepreneurs
- Conclusion
Income tax is different for legal entities:
- Individual entrepreneurs pay personal income tax;
- Legal entities pay income tax.
Today we will talk about the peculiarities of paying personal income tax by individuals registered as individual entrepreneurs. And there are quite a lot of features here.
We are all accustomed to the fact that personal income tax is a tax that the employer withholds from our salaries (I’m talking about ordinary employees now). For individual entrepreneurs, the calculation and payment of this tax on income received from business activities looks different.
So, first things first!
Insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs for themselves
Every entrepreneur, regardless of the tax regime he has chosen, pays the following contributions for his insurance:
- Medical. In 2022 - 8,766 rubles.
- Pension. The contribution amount consists of two parts. The first part is fixed - 34,445 rubles for the full year 2022. If an entrepreneur’s income does not exceed 300,000 rubles, he pays only this part. If his income is greater, then he pays 1% on the excess amount. Individual entrepreneur on OSNO to calculate this amount reduces the income received for professional deductions.
Medical contributions and the first part of pensions are paid during the calendar year. The estimated portion of pension contributions must be transferred no later than July 1 of the following year. Reporting on individual entrepreneurs' own contributions is not submitted.
How is PFDL calculated in 2022 for individual entrepreneurs?
The tax for the year is calculated using the following formula:
Personal income tax = (Received income of an individual entrepreneur - Tax deductions) x Tax rate - Advance payments
Individual income received
To determine the personal income tax base, all income of an individual entrepreneur received by him in cash and in kind, in the form of material benefits, as well as when the right to this income arises, is taken into account. Income received both on the territory of the Russian Federation and abroad is subject to accounting.
An individual entrepreneur must determine the tax base separately for each type of income for which different tax rates are provided.
A complete list of income taken into account when calculating income tax is given in Art. 208 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Tax deductions
When calculating the amount of tax to be paid, an individual entrepreneur can use all types
tax deductions. The main deduction for individual entrepreneurs is professional and represents the possibility of accounting for all expenses incurred in the process of carrying out business activities.
Professional deductions can be provided in the amount of:
- Actual expenses incurred, if they are economically justified and documented;
- In the amount of 20% of all income received for the year, if there is no documentary evidence of expenses.
The composition of expenses is determined by the individual entrepreneur independently, in the manner prescribed by Chapter. 25 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Note
: It is beneficial to use a deduction in the amount of 20% of the income received when the documented amount of expenses incurred is less than the deduction provided in the amount of 20%.
In addition to professional ones, an individual entrepreneur can apply property, social, standard, investment and “loss” deductions. The procedure for their application is similar to that for ordinary citizens (that is, all necessary documents must be attached to the declaration).
Note:
deductions can be used to reduce income taxed at a rate of 13% (except for income from equity participation in an organization). Thus, if an individual entrepreneur is a non-resident, he will not be able to claim deductions (including professional ones).
From the beginning of 2022, an additional personal income tax rate of 15% (Law No. 372-FZ of November 23, 2022). It applies to individual entrepreneurs’ income exceeding 5 million rubles. You must pay tax at a rate of 15% on income exceeding 5 million rubles.
Tax rates
The basic tax rate for personal income tax for individual entrepreneurs is 13%
. It applies to the amount of income of an entrepreneur up to 5 million rubles inclusive.
If an individual entrepreneur is a non-resident of the Russian Federation, he pays personal income tax at the rate 30%
.
For income exceeding 5 million rubles, the rate applies 15%
.
A 15% rate applies to income over 5 million rubles. For example, if the tax base of an individual entrepreneur for 2022 is 6 million rubles, then in total he must pay: (5 million * 13%) + (1 million * 15%) = 800 thousand rubles.
A working entrepreneur must calculate tax based on his own actual income, without taking into account payments made to him by his employer. The Federal Tax Service will aggregate data from the 3-NDFL declaration filed by the individual entrepreneur and the data provided by the employer. If the total amount of a citizen’s income exceeds 5 million rubles, the tax authority itself will calculate the additional personal income tax payment taking into account the increased rate and send a notification. This explanation was given by the head of the Department of Taxation of Personal Income and Administration of Insurance Contributions, Mikhail Sergeev, during the All-Russian Winter Online Business Congress “Taxes and Reporting in 2022”.
An example of calculating advances and taxes for the year
IP Ivanov I.I. uses OSNO. Let's calculate his tax for 2021.
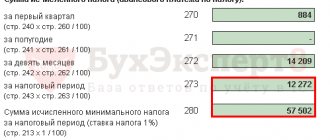
For the 1st quarter of 2022, the individual entrepreneur earned income in the amount of 400,000 rubles. His advance payment will be: 400,000 x 13% = 52,000 rubles.
For 6 months, the income of the individual entrepreneur amounted to 700,000 rubles. He must pay: 700,000 x 13% - 52,000 = 39,000 rubles.
The amount of income for 9 months is 1,000,000 rubles. The advance payment will be: 1,000,000 x 13% - (52,000 + 39,000) = 39,000 rubles.
In total, in 2022, IP Ivanov earned 1,200,000 rubles. His tax for the year will be 1,200,000 x 13% - (52,000 + 39,000 + 39,000) = 26,000 rubles. It must be paid by July 15, 2022.
Entrust reporting to specialists
Individual entrepreneur reporting forms
In conclusion, we list what kind of reporting an individual entrepreneur submits with his employees. It does not depend on whether the entrepreneur chose the main tax system, simplified tax system, UTII, unified agricultural tax or patent. If there is at least one hired employee, the individual entrepreneur is required to take:
- Calculation of insurance premiums. Submitted to the tax office at the end of the quarter by the 30th of the next month.
- Forms of personalized accounting. SZV-M is submitted to the Pension Fund every month, the submission deadline is the 15th of the next month. At the end of the year, before March 1, the SZV-STAZH is submitted along with the EDV-1 form.
- 4-FSS. Submitted to the Social Insurance Fund every quarter. Deadlines: in paper form - until the 20th day of the month following the end of the quarter, in electronic form - until the 25th day.
What reporting needs to be submitted to OSNO
Mandatory tax reporting forms
Tax returns. Individual entrepreneurs submit VAT and 3-NDFL returns using the common system.
The VAT return is submitted every quarter by the 25th day of the following month following the reporting period. For example, for the third quarter the declaration must be submitted no later than October 25. If there was no income, they submit zero. For failure to provide, a fine is provided under Article 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and the blocking of the current account.
The VAT return is submitted only electronically. A declaration on paper is not considered submitted (letter of the Federal Tax Service No. OA-4-17/ [email protected] ).
VAT declaration. The form was approved by order of the Federal Tax Service No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected]
3-NDFL declarations are submitted once a year until April 30. It indicates the entrepreneur’s income and tax deductions. Compiled in electronic or paper form. The declaration can be filled out using the “Declaration” program on the Federal Tax Service website.
Declaration 3-NDFL for 2022. The form was approved by order of the Federal Tax Service No. ED-7-11/ [email protected]
Book of accounting of income and expenses (KUDiR). Individual entrepreneurs on OSNO may not keep accounting records, provided that they keep records of income and expenses (Article 6 of Law No. 402-FZ). All financial receipts and expenses during the year are entered into KUDiR.
KUDiR can be maintained electronically using online accounting services. At the end of the year, the accounting book needs to be printed, numbered, signed and the individual entrepreneur’s seal put on it, if there is one. There is no need to send the KUDiR anywhere, but the tax office may require it during an audit. The fine for the absence of KUDiR is from 10 to 30 thousand rubles (Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Sample and rules for filling out KUDiR for individual entrepreneurs on OSNO in Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 86n.
Book of purchases and sales. The purchase book records invoices for the purchase of goods and services, and the sales book records invoices issued to counterparties during the tax period. The tax office uses them to check the VAT return.
The book of purchases and sales can be kept in handwritten or electronic form. Inspectors compare invoice data from counterparties to verify VAT refunds.
The form and rules for maintaining the book of purchases and sales are approved by Government Decree No. 1137.
Reporting forms, if there are employees
If an individual entrepreneur hires workers, the number of reports increases. They are submitted to the tax office, the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund.
Calculation of insurance premiums (DAM). This is information about all insurance premiums for employees. It also provides information on the average number of employees. The DAM is submitted to the tax office once a quarter until the 30th day of the next month (clause 7 of Article 431 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The form was approved by order of the Federal Tax Service No. ED-7-11/ [email protected]
6-NDFL. This is a report with the income of all employees from whom tax has been withheld. 6-NDFL must be submitted to the tax office every quarter before the 30th day of the month following the reporting period. For example, the second quarter report must be submitted by July 31. Annual report - until March 1 of the next year (clause 2 of Article 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The 6-NDFL report form and the procedure for filling out were approved by Federal Tax Service Order No. ED-7-11/ [email protected]
4-FSS. This is a calculation of insurance premiums for injuries, which is submitted to the Social Insurance Fund. If the individual entrepreneur does not pay such contributions, zero reports must be submitted.
The 4-FSS report is submitted once a quarter until the 20th day of the next month. If the report is in electronic form - until the 25th. The form was approved by FSS order No. 381.
SZV-TD. This is a report with information about hired employees. It is submitted to the pension fund upon hiring, dismissal or transfer of an employee to another position.
Submission deadlines (Article 11 of Law 27-FZ):
- upon hiring or dismissal - no later than the next day;
- when transferring to another position - no later than the 15th day of the next month.
The report form was approved by Resolution of the Pension Fund Board No. 730p.
SZV-M. This report on insurance payments must be submitted to the Pension Fund for employees under employment contracts and civil servants' agreements. Deadline: every month until the 15th. The form was approved by Resolution of the Pension Fund Board No. 83p.
SZV-STAGE. Annual reporting for employers on the length of service of employees. It must be submitted to the Pension Fund once a year before March 1 of the following year. The form was approved by Resolution of the Pension Fund Board No. 507p.
If there are more than 25 employees on staff, SZV-TD, SZV-M and SZV-STAZH are submitted electronically. If less - in electronic or paper form.
Reports to Rosstat. In 2022, all individual entrepreneurs must submit reports to Rosstat for continuous monitoring, which is carried out once every 5 years. Whether you need to submit reports or not, you can check in the future on the official website of Rosstat.
Reporting for individual entrepreneurs on OSNO, sorted by frequency