Bookmarked: 0
In order to record the results of an inspection at an enterprise, a special document is used - an inspection report. The range of possible inspections is wide and includes fire, tax, technical, sanitary and other inspections.
The inspection report sheet is filled out and signed by a commission of three or more participants in at least two copies. If necessary, copies of other documents are attached to the act: lease agreement, extracts from registers, employment contract and other papers.
The members of the commission are government inspectors, company employees (the composition is approved by a separate order in advance, or is assembled on site from among those present), or third-party experts with whom they have entered into an agreement. An inspection report is enough to understand where the company’s weak points are and how to correct them. For example, retail chains, restaurants and cafes are regularly inspected.
Individual employees are also checked, which in some cases leads to the disclosure of theft. Then the act serves as the basis for disciplinary or administrative sanctions, as well as dismissal. The legislative basis for internal inspections is Art. 193 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Timely internal inspections help prepare for the visit of the state inspection, so company managers quickly get used to working with inspection reports.
General information
For convenience and understanding, we will divide checks into state and internal.
The first ones are characterized by:
- Established form of inspection report
- Mandatory nature
- Far-reaching consequences: fines, license revocation, criminal prosecution
What a sample state inspection report should look like is written in Federal Law No. 294-FZ “On the protection of the rights of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs in the exercise of state control (supervision) and municipal control” dated December 26, 2008, as well as in departmental orders. We advise you to study the laws and see whether the inspector’s papers comply with the established standards.
State inspection acts are not very different in form from internal inspection acts: when a company checks “itself” using its own or private experts. However, private individuals have much more freedom in drawing up acts. Each company has its own inspection report template in its archives - the law does not prohibit this. The main thing is to include mandatory elements in the act.
Below is a universal scheme of the inspection report, which allows you to correctly compose the paper according to your taste and needs.
How is the check carried out?
Inspections can be carried out not only according to a set schedule, for example, every six months. It is possible that there will be a need to conduct an unscheduled inspection. If any shortcomings were discovered during the inspection, they should be reflected in the report. The document must also contain information about what measures were taken to eliminate violations of industrial safety rules. In addition, a period is determined within which the problems must be corrected. Naturally, after this a re-check is carried out. Typically, the verification procedure is carried out in accordance with the rules of a particular institution. But there are standards that apply to many organizations. So, the inspector checks:
- signs containing emergency fire extinguishing service telephone numbers and information from employees responsible for compliance with safety rules;
- evacuation plans, which should be located on each floor in visible places;
- the presence and operation of signs with the word “Exit”. Moreover, these indicators should light up;
- emergency exits to ensure they are cluttered;
- fire shield, namely, whether it has all the necessary devices;
- fire extinguishers, their availability and expiration date;
- condition of various electrical appliances and sockets.
Fire suppression systems are typically inspected every six months. Automatic systems are subject to quarterly inspection. Inspection of such systems can be divided into three main stages:
- Visual inspection . Here, specialists try to find visible faults in the system. For example, this could be the appearance of corrosion, separation of elements, or leakage.
- Preventive actions . Existing rust is removed, parts are lubricated and, if necessary, completely replaced.
- Functionality check . Test runs are not excluded here, which makes it possible to determine the fluid pressure in the pipes. The automation is checked for the absence of false alarms.
( Video : “Fire safety training Fire technical minimum”)
How to correctly fill out a fire safety inspection report in 2021
As already mentioned, there is no need to adhere to strict rules when drawing up such a document. Some companies develop special forms for these purposes, which are approved by accounting policies. At the same time, do not forget about the rules for drawing up documents of this kind. So, there must be a “header”, the main part and the ending. Naturally, all responsible persons sign their autographs here. You can enter information not only by hand, but also on a computer.
It can be assumed that regular inspections of fire extinguishing systems minimize their failure. But this possibility cannot be excluded. Accordingly, if any problems are identified, this must be reflected in the report. Moreover, not only the problems themselves are indicated, but also the measures that were taken to eliminate them.
How to fill it out correctly
The upper part of the act - the “header” - is devoted to information about the company within which the inspection takes place, or about the third-party organization that conducts it. Here they write the name of the legal entity, INN and OGRN numbers, and the address of the company.
Then follow the name of the act, day, month, year and locality where the events take place. Perfectionists indicate the local start and end times of the inspection and drawing up the report.
Then the inspectors are listed: positions and full names. The basis for the inspection is indicated below: order, instruction, decision of the general director and the number of this paper. They write down who was present during the inspection (for example, if we are talking about a retail outlet, then they write down the sellers and the director.
Next, they describe the facts: what was checked, whether the state of affairs complies with the established standards, what shortcomings were identified. The level of detail in this section depends on the type of inspection and company regulations. For a relatively simple check, a small numbered list is sufficient.
Download a completed example of an inspection report to understand what the completed paper looks like:
What requirements must be met when drawing up an inspection report?
When drawing up an act, tax authorities must be guided by the Tax Code (clause 4 of Article 100), the regulations on the Federal Tax Service, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated September 30, 2004 No. 506 (clause 1), and the requirements for drawing up a tax audit report set out in Appendix 24 to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 05/08/2015 No. ММВ-7-2/ [email protected] (hereinafter referred to as the Requirements).
Here are the main requirements:
- drawing up an inspection report in 2 copies (clause 5 of the Requirements);
- compliance with the strictly approved form if the act is drawn up on paper (clause 4 of article 100 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 2 of the Requirements);
- signing of the act by the inspector on the one hand and by the taxpayer being inspected or his representative on the other hand (clause 2 of article 100 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 4 of the Requirements);
- 10 working days are allotted for drawing up a report from the date of completion of the inspection if, as a result of its results, violations were discovered (paragraph 2, paragraph 1, article 100, paragraph 6, article 6.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- delivery of a copy of the act to the taxpayer (his representative) within 5 working days from the moment it was drawn up.
Find out how to authorize a company employee to sign desk inspection reports here.
Should the inspector draw up a desk inspection report if the identified violations did not result in an understatement of the amount of tax payable? Find out the answer to this question in the ConsultantPlus Tax Guide by getting trial access for free.
What to pay attention to
We recommend that you immediately state in the act the purpose of the inspection and the results: whether it was achieved or not, so that the manager does not have to read the items on the list and draw conclusions on his own. For example, if you are preparing a store for an inspection visit, let it be written in the act.
We also advise you to indicate the further “fate” of the signed acts: to whom they were handed over and sent, in how many copies. A reliable way to insure against forgetfulness and the human factor. Punctuality is never excessive, so record the exact time of the inspection: systematic prolongation of the process indicates that it is time to change the composition of the commission.
And, of course, remember that each company has its own regulations on the storage and disposal of inspection reports. If you are new to the position, please read the rules carefully.
Why do you need a desk inspection report?
Upon completion of any desk audit, the tax authority must draw conclusions about whether the taxpayer has violated tax laws or not.
If facts of violation have been identified, then the inspector must formalize the results of the inspection in the form of a desk inspection report, this is what clause 5 of Art. 88 and para. 2 p. 1 art. 100 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The functions assigned to the desk tax audit report are as follows:
- It is a document included in the materials of the desk audit. Based on the conclusions set out in it, the head of the inspection or an authorized person makes a decision on whether it is worth holding the taxpayer accountable for the tax offense he has committed or not (Clause 1 of Article 101 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- And brings to the attention of the taxpayer the preliminary results of the desk audit, on the basis of which, according to clause 6 of Art. 100 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the latter may raise objections.
The timing of a desk audit can be found in the material “The inspection must complete a desk audit within 3 months .
Requirements for registration of the act
AT 9. Registration of inspection results. Inspection report and its characteristics
Based on the results of the inspection, during which violations of legislative acts are identified, an inspection report .
Based on the facts of identified violations, the inspector, within his competence, may draw up a protocol on an administrative offense and (or) issue a resolution in a case of an administrative offense .
The results of the inspection, during which no violations of legislation were identified, are documented in an inspection certificate .
The inspection report (certificate) is drawn up in at least two copies and signed by the inspector (the head of the inspection) no later than five working days from the date of completion of the inspection.
The results of the inspection are documented by the inspectors of each control (supervisory) body in a separate inspection report (certificate). If a joint inspection is carried out on the initiative of a regulatory (supervisory) body, one copy of the inspection report (certificate), after delivery (direction) to the inspected entity or its representative, is transferred to the regulatory (supervisory) authority that initiated the inspection.
The inspection report must ensure clarity and accuracy in the presentation of the identified facts.
It is not allowed to include in the inspection report various types of undocumented facts and data about the activities of the inspected entity.
Unspecified corrections are not permitted. In cases where errors (slips) are found in the inspection report (certificate), incomplete clarification of circumstances, or based on the results of additional and (or) counter checks, it is necessary to make changes and (or) additions to the inspection report (certificate), to such act (certificate) changes and (or) additions are made.
The inspection report, taking into account the specifics of conducting certain types of inspections, must indicate:
the basis for ordering the inspection, the date and number of the order to conduct it, positions, surnames and initials of the persons conducting the inspection;
the start and end dates of the inspection (if the inspection is suspended, its period is indicated), as well as the place where the inspection report was drawn up;
verified period;
positions, surnames and initials of employees of the inspected entity who are required to sign the act, with the obligatory indication of the period of their work in their positions in the inspected period, as well as other persons involved in the inspection;
name (last name, first name, patronymic) of the inspected entity (if the inspected separate unit does not have a name, the address of its location), location (place of residence) and subordination (if any), payer's account number, details of current (settlement) and other accounts ( if available);
availability of an inspection book (work production log), as well as information about the entry made in it about this inspection;
by whom and when previous inspections were carried out during the period under review on the same issues on which the inspection was carried out;
what financial and business transactions (documents), by what method and for what period were verified;
a description of the fact of violation of the law, the place and time of its commission, acts of legislation whose requirements were violated, and (or) liability for such violation provided for by legislative acts;
the amount of harm caused (if any) and other consequences of the identified violations;
positions, surnames and initials of persons whose actions (inaction) resulted in violations of the law by the subject being inspected;
other information necessary for reviewing materials about the violation committed and making a decision on the inspection report and (or) issuing a requirement (order) to eliminate violations.
The inspection report may contain proposals for eliminating identified violations.
The inspector is responsible for the accuracy of the facts and information about the violations identified, as well as the established amounts of damage specified in the inspection report.
For the accuracy of the documents, information and facts specified in the certificates, explanations and calculations submitted at the request of the inspector, the officials and representatives of the inspected entity who submitted the specified certificates, explanations and calculations are responsible.
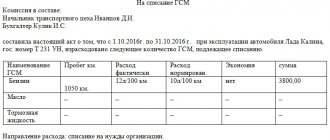
Homogeneous violations can be reflected in statements (tables ) attached to each copy of the inspection report, which indicate all the necessary data for each fact of violation: the amount of harm caused (if any), the period during which the violation was committed, dates and numbers of documents .
Integral parts of the inspection report (certificate) drawn up based on the results of the control measurement are an explanatory note, summary statements about the cost of the inspected construction, installation and (or) repair and construction work, the costs incurred and the amounts of overstatement established by the control measurements (if any).
If samples (samples ) were taken during the inspection, acts on the selection of such samples (samples) are attached to the inspection report, which must be signed by the inspector (inspection manager), the subject being inspected (its manager), and in his absence - by a representative of the subject being inspected on the day of sampling (sampling), as well as protocols of the studies (tests) and examinations (if any).
If necessary, certificates and calculations drawn up on the basis of verified documents, as well as copies or extracts from documents certified by the inspected entity in the prescribed manner, and explanations from a representative of the inspected entity may be attached to the inspection report.
The inspector may require written explanations about the reasons for the identified violations from the inspected entity, its representative, as well as from other persons whose actions (inaction) resulted in a violation of the law by the inspected entity. These explanations are attached to the inspection report
The inspection report (certificate) is signed by the inspector (the head of the inspection), as well as:
the head of the inspected entity or an individual entrepreneur, in their absence - another representative of the inspected entity, a person carrying out private notary, craft activities, activities in the field of agro-ecotourism;
the person who manages the accounting of the inspected entity (during inspections on issues related to the implementation of financial and business operations by the inspected entity).
The control measurement report and the mandatory annexes to it are signed by the participants in the control measurement.
The inspection report (certificate) within two working days from the date of its signing by the inspector (the head of the inspection) is handed over signature (sent by registered mail with acknowledgment of receipt) to the inspected entity or its representative.
If the relevant officials of the inspected entity to sign the inspection report (certificate), the control measurement report, an appropriate note is made in them and the inspection report (certificate), the control measurement report are sent to the inspected entity by registered mail with return receipt requested or handed over to the inspected entity or its representative for painting. In this case, a person who refuses to sign an inspection report (certificate), a control measurement report, has the right to state in writing the reasons for refusing to sign them.
In the event that an identified violation can be hidden or, based on the identified facts, it is necessary to take urgent measures to eliminate them and bring to justice persons whose actions (inaction) resulted in a violation of the law by the subject being inspected, the inspector (the head of the inspection) draws up a separate interim inspection report .
The interim inspection report must contain:
the basis for ordering the inspection, the date and number of the order to conduct it, positions, surnames and initials of the persons conducting the inspection;
the start date of the inspection (if the inspection is suspended, its period is indicated), as well as the place and date of the interim drawing up of the inspection report;
name, location and subordination (last name, first name, patronymic, place of residence) of the inspected entity, payer's account number, details of current (settlement) and other accounts;
a description of the fact of violation of the law, the place and time (if established) of its commission, acts of legislation whose requirements were violated, and (or) the liability for such violation provided for by legislative acts;
an indication that the inspection report is interim;
other information necessary to consider materials about the offense committed.
Based on the interim inspection report, the controlling (supervisory) body may issue a decision and (or) requirement (instruction) to eliminate violations identified during the inspection. Based on the facts of identified violations, the inspector, within his competence, may draw up a protocol on an administrative offense and (or) issue a resolution on the case of an administrative offense.
The facts stated in the interim inspection report are included in the inspection report.
If there are objections to the act (certificate) of the inspection, the inspected entity or its representative makes a note about this before his signature and no later than 15 working days from the date of signing the act (certificate) submits objections in writing regarding its (her) content to the controlling (supervisory) organ.
The validity of the arguments set out in the objections is examined by the inspector (the head of the inspection) and a written conclusion is drawn up on them within 15 working days, which is sent to the inspected entity by registered mail with return receipt requested or handed over to the inspected entity or its representative against signature.
If necessary, in order to confirm the validity of the arguments set out in the objections, no later than 10 working days from the date of receipt of the objections, an additional inspection may be scheduled in relation to the inspected entity. Such an inspection is carried out by the controlling (supervisory) body that initially conducted the inspection. In this case, a written conclusion on the objections is sent to the inspected entity by registered mail with return receipt requested or handed over to the inspected entity or its representative against signature no later than 10 business days from the date of completion of the additional inspection.
Based on the act drawn up based on the results of the inspection, within 30 working days from the date of delivery (sending) to the inspected entity or its representative, a decision is made on the inspection report and (or) a requirement (order) to eliminate violations identified during the inspection.
In cases of detection of violations of legislation that pose a threat to the life and health of the population, as well as causing environmental harm, the emergence of a danger of causing environmental harm in the future, violation of requirements in the field of environmental protection, the head of the control (supervisory) body issues a requirement (order) to eliminate the violations, which is handed over (sent by registered mail with acknowledgment of receipt) to the inspected entity or its representative no later than three working days from the date of detection of violations.
A requirement (instruction) to suspend (prohibit) the activities of the inspected entity , workshops (production areas), equipment may be issued on the day the violation is discovered. This requirement (instruction) is signed by the inspector (the head of the inspection) with its subsequent approval by the head of the control (supervisory) body (his deputy) no later than the end of the working day following the day the requirement (instruction) was issued, and is handed over (sent by registered mail with acknowledgment of receipt ) to the inspected entity or its representative on the day the violation was detected.
The decision on the inspection report, the requirement (instruction) to eliminate violations are mandatory for execution by the inspected entity .
The inspected entity, within the time limits established in this requirement (instruction), informs the controlling (supervisory) body that conducted the inspection in writing about the fulfillment of each point of the requirement (instruction) to eliminate violations.
The head of the control (supervisory) body or his authorized deputy (the authorized head of the structural unit of the control (supervisory) body), who signed (approved) such a requirement (instruction), no later than two working days from the date of receipt of the message, has the right to schedule a control check of the elimination by the inspected entity of the identified violations.
The control (supervisory) body, when establishing during an inspection facts of harm, unjustified write-offs of funds and inventory in the amount of more than 1000 basic units, as well as when establishing other facts indicating signs of a crime, transfers the inspection materials to the criminal prosecution authorities in 10-day period from the date of the decision on the inspection report and (or) requirement (instruction) to eliminate violations.
Upon completion of the inspection, the control (supervisory) body that conducted the inspection has the right to inform the higher control (supervisory) body, the owner of the property of the inspected entity or his representative about the identified facts of violations of the law and make proposals to prevent them in the future.
The inspected entity has the right to appeal the decisions of the controlling (supervisory) bodies on the inspection report, requirements (instructions) to eliminate violations, actions (inaction) of the inspectors to a higher controlling (supervisory) body or to a higher official to whom the inspectors are directly subordinate, and (or) general or economic court, unless a different procedure for appeal or a different period is established by legislative acts. Filing a complaint to a higher regulatory (supervisory) body or a higher official does not exclude the right to file a complaint in court.
Topic 3. The essence and content of the audit
STUDY QUESTIONS:
1. Audit as a form of independent control. Differences between an audit and an audit.
2. History of audit development
3. Organization of audit in the Republic of Belarus.
4. International auditing standards. National rules of auditing. Internal auditing standards.
5. Professional ethics of auditors.
6. Relationship between auditor and client. Rights, duties and responsibilities of the auditor.
| Material support for the lesson (visuals, teaching aids, etc.) | Literary sources |
| Methodological manuals [17], | [2-4,7, 10,11, 13-15] |
AT 9. Registration of inspection results. Inspection report and its characteristics
Based on the results of the inspection, during which violations of legislative acts are identified, an inspection report .
Based on the facts of identified violations, the inspector, within his competence, may draw up a protocol on an administrative offense and (or) issue a resolution in a case of an administrative offense .
The results of the inspection, during which no violations of legislation were identified, are documented in an inspection certificate .
The inspection report (certificate) is drawn up in at least two copies and signed by the inspector (the head of the inspection) no later than five working days from the date of completion of the inspection.
The results of the inspection are documented by the inspectors of each control (supervisory) body in a separate inspection report (certificate). If a joint inspection is carried out on the initiative of a regulatory (supervisory) body, one copy of the inspection report (certificate), after delivery (direction) to the inspected entity or its representative, is transferred to the regulatory (supervisory) authority that initiated the inspection.
The inspection report must ensure clarity and accuracy in the presentation of the identified facts.
It is not allowed to include in the inspection report various types of undocumented facts and data about the activities of the inspected entity.
Unspecified corrections are not permitted. In cases where errors (slips) are found in the inspection report (certificate), incomplete clarification of circumstances, or based on the results of additional and (or) counter checks, it is necessary to make changes and (or) additions to the inspection report (certificate), to such act (certificate) changes and (or) additions are made.
The inspection report, taking into account the specifics of conducting certain types of inspections, must indicate:
the basis for ordering the inspection, the date and number of the order to conduct it, positions, surnames and initials of the persons conducting the inspection;
the start and end dates of the inspection (if the inspection is suspended, its period is indicated), as well as the place where the inspection report was drawn up;
verified period;
positions, surnames and initials of employees of the inspected entity who are required to sign the act, with the obligatory indication of the period of their work in their positions in the inspected period, as well as other persons involved in the inspection;
name (last name, first name, patronymic) of the inspected entity (if the inspected separate unit does not have a name, the address of its location), location (place of residence) and subordination (if any), payer's account number, details of current (settlement) and other accounts ( if available);
availability of an inspection book (work production log), as well as information about the entry made in it about this inspection;
by whom and when previous inspections were carried out during the period under review on the same issues on which the inspection was carried out;
what financial and business transactions (documents), by what method and for what period were verified;
a description of the fact of violation of the law, the place and time of its commission, acts of legislation whose requirements were violated, and (or) liability for such violation provided for by legislative acts;
the amount of harm caused (if any) and other consequences of the identified violations;
positions, surnames and initials of persons whose actions (inaction) resulted in violations of the law by the subject being inspected;
other information necessary for reviewing materials about the violation committed and making a decision on the inspection report and (or) issuing a requirement (order) to eliminate violations.
The inspection report may contain proposals for eliminating identified violations.
The inspector is responsible for the accuracy of the facts and information about the violations identified, as well as the established amounts of damage specified in the inspection report.
For the accuracy of the documents, information and facts specified in the certificates, explanations and calculations submitted at the request of the inspector, the officials and representatives of the inspected entity who submitted the specified certificates, explanations and calculations are responsible.
Homogeneous violations can be reflected in statements (tables ) attached to each copy of the inspection report, which indicate all the necessary data for each fact of violation: the amount of harm caused (if any), the period during which the violation was committed, dates and numbers of documents .
Integral parts of the inspection report (certificate) drawn up based on the results of the control measurement are an explanatory note, summary statements about the cost of the inspected construction, installation and (or) repair and construction work, the costs incurred and the amounts of overstatement established by the control measurements (if any).
If samples (samples ) were taken during the inspection, acts on the selection of such samples (samples) are attached to the inspection report, which must be signed by the inspector (inspection manager), the subject being inspected (its manager), and in his absence - by a representative of the subject being inspected on the day of sampling (sampling), as well as protocols of the studies (tests) and examinations (if any).
If necessary, certificates and calculations drawn up on the basis of verified documents, as well as copies or extracts from documents certified by the inspected entity in the prescribed manner, and explanations from a representative of the inspected entity may be attached to the inspection report.
The inspector may require written explanations about the reasons for the identified violations from the inspected entity, its representative, as well as from other persons whose actions (inaction) resulted in a violation of the law by the inspected entity. These explanations are attached to the inspection report
The inspection report (certificate) is signed by the inspector (the head of the inspection), as well as:
the head of the inspected entity or an individual entrepreneur, in their absence - another representative of the inspected entity, a person carrying out private notary, craft activities, activities in the field of agro-ecotourism;
the person who manages the accounting of the inspected entity (during inspections on issues related to the implementation of financial and business operations by the inspected entity).
The control measurement report and the mandatory annexes to it are signed by the participants in the control measurement.
The inspection report (certificate) within two working days from the date of its signing by the inspector (the head of the inspection) is handed over signature (sent by registered mail with acknowledgment of receipt) to the inspected entity or its representative.
If the relevant officials of the inspected entity to sign the inspection report (certificate), the control measurement report, an appropriate note is made in them and the inspection report (certificate), the control measurement report are sent to the inspected entity by registered mail with return receipt requested or handed over to the inspected entity or its representative for painting. In this case, a person who refuses to sign an inspection report (certificate), a control measurement report, has the right to state in writing the reasons for refusing to sign them.
In the event that an identified violation can be hidden or, based on the identified facts, it is necessary to take urgent measures to eliminate them and bring to justice persons whose actions (inaction) resulted in a violation of the law by the subject being inspected, the inspector (the head of the inspection) draws up a separate interim inspection report .
The interim inspection report must contain:
the basis for ordering the inspection, the date and number of the order to conduct it, positions, surnames and initials of the persons conducting the inspection;
the start date of the inspection (if the inspection is suspended, its period is indicated), as well as the place and date of the interim drawing up of the inspection report;
name, location and subordination (last name, first name, patronymic, place of residence) of the inspected entity, payer's account number, details of current (settlement) and other accounts;
a description of the fact of violation of the law, the place and time (if established) of its commission, acts of legislation whose requirements were violated, and (or) the liability for such violation provided for by legislative acts;
an indication that the inspection report is interim;
other information necessary to consider materials about the offense committed.
Based on the interim inspection report, the controlling (supervisory) body may issue a decision and (or) requirement (instruction) to eliminate violations identified during the inspection. Based on the facts of identified violations, the inspector, within his competence, may draw up a protocol on an administrative offense and (or) issue a resolution on the case of an administrative offense.
The facts stated in the interim inspection report are included in the inspection report.
If there are objections to the act (certificate) of the inspection, the inspected entity or its representative makes a note about this before his signature and no later than 15 working days from the date of signing the act (certificate) submits objections in writing regarding its (her) content to the controlling (supervisory) organ.
The validity of the arguments set out in the objections is examined by the inspector (the head of the inspection) and a written conclusion is drawn up on them within 15 working days, which is sent to the inspected entity by registered mail with return receipt requested or handed over to the inspected entity or its representative against signature.
If necessary, in order to confirm the validity of the arguments set out in the objections, no later than 10 working days from the date of receipt of the objections, an additional inspection may be scheduled in relation to the inspected entity. Such an inspection is carried out by the controlling (supervisory) body that initially conducted the inspection. In this case, a written conclusion on the objections is sent to the inspected entity by registered mail with return receipt requested or handed over to the inspected entity or its representative against signature no later than 10 business days from the date of completion of the additional inspection.
Based on the act drawn up based on the results of the inspection, within 30 working days from the date of delivery (sending) to the inspected entity or its representative, a decision is made on the inspection report and (or) a requirement (order) to eliminate violations identified during the inspection.
In cases of detection of violations of legislation that pose a threat to the life and health of the population, as well as causing environmental harm, the emergence of a danger of causing environmental harm in the future, violation of requirements in the field of environmental protection, the head of the control (supervisory) body issues a requirement (order) to eliminate the violations, which is handed over (sent by registered mail with acknowledgment of receipt) to the inspected entity or its representative no later than three working days from the date of detection of violations.
A requirement (instruction) to suspend (prohibit) the activities of the inspected entity , workshops (production areas), equipment may be issued on the day the violation is discovered. This requirement (instruction) is signed by the inspector (the head of the inspection) with its subsequent approval by the head of the control (supervisory) body (his deputy) no later than the end of the working day following the day the requirement (instruction) was issued, and is handed over (sent by registered mail with acknowledgment of receipt ) to the inspected entity or its representative on the day the violation was detected.
The decision on the inspection report, the requirement (instruction) to eliminate violations are mandatory for execution by the inspected entity .
The inspected entity, within the time limits established in this requirement (instruction), informs the controlling (supervisory) body that conducted the inspection in writing about the fulfillment of each point of the requirement (instruction) to eliminate violations.
The head of the control (supervisory) body or his authorized deputy (the authorized head of the structural unit of the control (supervisory) body), who signed (approved) such a requirement (instruction), no later than two working days from the date of receipt of the message, has the right to schedule a control check of the elimination by the inspected entity of the identified violations.
The control (supervisory) body, when establishing during an inspection facts of harm, unjustified write-offs of funds and inventory in the amount of more than 1000 basic units, as well as when establishing other facts indicating signs of a crime, transfers the inspection materials to the criminal prosecution authorities in 10-day period from the date of the decision on the inspection report and (or) requirement (instruction) to eliminate violations.
Upon completion of the inspection, the control (supervisory) body that conducted the inspection has the right to inform the higher control (supervisory) body, the owner of the property of the inspected entity or his representative about the identified facts of violations of the law and make proposals to prevent them in the future.
The inspected entity has the right to appeal the decisions of the controlling (supervisory) bodies on the inspection report, requirements (instructions) to eliminate violations, actions (inaction) of the inspectors to a higher controlling (supervisory) body or to a higher official to whom the inspectors are directly subordinate, and (or) general or economic court, unless a different procedure for appeal or a different period is established by legislative acts. Filing a complaint to a higher regulatory (supervisory) body or a higher official does not exclude the right to file a complaint in court.
Topic 3. The essence and content of the audit
STUDY QUESTIONS:
1. Audit as a form of independent control. Differences between an audit and an audit.
2. History of audit development
3. Organization of audit in the Republic of Belarus.
4. International auditing standards. National rules of auditing. Internal auditing standards.
5. Professional ethics of auditors.
6. Relationship between auditor and client. Rights, duties and responsibilities of the auditor.
| Material support for the lesson (visuals, teaching aids, etc.) | Literary sources |
| Methodological manuals [17], | [2-4,7, 10,11, 13-15] |
Structure and content of the inspection report
The inspection report contains:
- introductory part, which provides general information about the inspection being carried out, the company (its branch) in which it is carried out;
- a descriptive block with the disclosure of facts of violations of tax legislation, based on documentary evidence, presented with maximum clarity and systematization;
- the final part, i.e. conclusions about the results of the audit and the presence of a tax offense, information about the consequences of the identified deficiencies, as well as making proposals for their elimination.
An integral part of the act are the annexes drawn up to it. This is evidence confirming facts of violations related to the calculation and payment of taxes and penalties. These include the necessary explanations, additions, certificates, calculations of discrepancies between the data declared by the company and those established during the audit, and other documents drawn up by the inspection inspector.
What is a revision
First, let's define what a revision is.
When an enterprise conducts business activities, the need inevitably arises to control these activities, especially their financial side. To achieve this, there are a number of activities that an organization can carry out independently and establish the procedure for their implementation in its internal local acts. Audit (or inspection) is one of the most effective means of control. It allows you to obtain a control result in the “here and now” format and compare actual data with accounting data.
The audit is carried out in relation to such issues of the financial and economic activities of the enterprise as:
- availability and correctness of primary documentation;
- compliance of accounting data with information contained in primary documents and their correct interpretation for accounting purposes;
- checking the availability of property.
An audit can be carried out both by external regulatory bodies (for example, the Chamber of Control and Accounts) and by an internal commission of the enterprise, which has received the authority to do so on the basis of an order from the manager. After the completion of audit activities, there is a need to document its results. This is why the audit act exists.
Find out how to conduct a cash register inventory and draw up an audit report in ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.