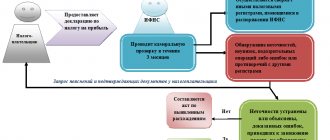
What is a tax register?
Registers are elements of tax accounting. They are conducted by companies that pay income tax. Personal income tax agents are also required to create registers.
All information necessary to establish the amount of income tax is entered into the registers (Article 314 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Then this information is systematized. On their basis, the tax base is determined.
Registers are consolidated forms for systematizing information, which are grouped on the basis of Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. However, they are not placed on the accounting accounts. The corresponding definition is given in Article 314 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Register data must answer, inter alia, these questions:
- On the basis of what documents is the tax base determined?
- What is the method of forming this base?
Article 314 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation indicates that registers are formed on the basis of the primary register. When filling them out, you need to eliminate these shortcomings:
- Errors and typos.
- Erratic entry of information.
- Availability of passes.
NRs are filled out exclusively in chronological order.
There are rules regarding the storage of HP. They must be protected from unauthorized attempts to correct them. If errors need to be corrected, the procedure requires documentary support. Corrections must be certified.
IMPORTANT! Information from registers constitutes a tax secret: information cannot be disclosed. Otherwise, liability is imposed.
Change mid-tax period
According to the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 03-03-06/1/45756 dated 07/03/2018, it is possible to reflect changes in accounting policies for tax accounting purposes (Article 313 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- when legislation on taxes and fees changes;
- when changing the accounting methods used.
Changing accounting methods is allowed only from the beginning of a new tax period, that is, from the beginning of the year. But if the legislation changes, it is allowed to change the accounting policy from the moment the new rules come into force. It depends on the organization on what principle to formulate its tax accounting policy. When new types of activities appear, changes must also be made to the regulations. In the middle of the tax period, the taxpayer has the right to change the accounting policy in two cases:
- the legislation has changed and these changes have entered into legal force;
- The company began to carry out a new type of activity.
What should the register look like?
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation contains practically no information regarding the type of register. The Code contains general information only. That is, the task of preparing documents is assigned to organizations.
But Article 313 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation specifies mandatory information that must be included in the register. In particular, these are the following points:
- Name.
- Period.
- The name of the operation performed.
- Results of the operation in rubles.
The document is certified by the signature of the responsible employee. The signature is accompanied by a transcript.
If this is a personal income tax register, it includes this information:
- Type of income.
- Personal income tax benefits that reduce the tax base.
- Payment amounts.
- Payment dates.
- Amount of calculated tax.
- Tax withholding date.
- Information about payment slips that confirm tax payment.
The rules relating to tax registers are almost identical to the rules relating to primary accounting. Therefore, some experts have a question about the possibility of replacing registers with accounting documentation. There are no prohibitions regarding this in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Moreover, Article 313 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides indirect permission for this. But the same article states that if accounting data is insufficient, it needs to be supplemented. Based on the results of the additions, the register is formed.
ATTENTION! Registers are maintained in both paper and electronic form. Electronic documentation is simply printed if there is a need for this (for example, a tax requirement).
How to make working with tax registers easier?
For small companies with a limited volume of standard business operations, there is an opportunity to significantly simplify the management of business accounting. At the same time, this will not affect the correct calculation of the tax base (for example, for income tax), and the requirements of Art. 313 on the organization of tax accounting will be completed.
Study the provisions of Art. 313 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the material “Art. 313 Tax Code of the Russian Federation (2015): questions and answers" .
To do this, the accounting policy must provide that individual accounting registers simultaneously serve as accounting registers. This is possible in the case when the procedure for accounting for objects or transactions for the purposes of both types of accounting is the same.
Let's look at an example:
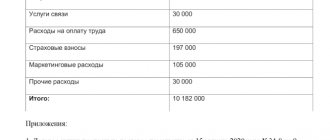
purchased an expensive metal-cutting machine with an initial cost of 6,300,000 rubles. in October 2015 and immediately put it into operation, establishing a useful life of 90 months. The accounting policy for accounting and accounting purposes provides for the calculation of depreciation using the linear method. In this case, the monthly amount of depreciation according to accounting data will coincide with the tax depreciation of this object and will be: 6,300,000 rubles. / 90 months = 70,000 rub.
It makes no sense to create a separate tax analytical accounting of depreciation amounts - one (general) register is enough for the purposes of accounting and tax accounting. When calculating income tax, expenses confirmed by accounting data will be included.
A different situation will arise if the company wants to quickly recognize the cost of fixed assets in tax expenses and provides for the use of bonus depreciation in its accounting policy.
We will talk about the consequences of such a step in the next section.
How to create registers
As already mentioned, the law does not prescribe a form for registers. It is determined by the organization independently. The developed form is fixed in the accounting policy. To do this, an order must be issued.
Registers can vary dramatically in appearance depending on the company. There are no restrictions in law regarding form. But the taxpayer must comply with the general rule - all information required for tax accounting is indicated in the registers. From the data provided it should be clear how the tax base was formed.
Data can be grouped in different ways. The use of tables and lists is allowed. However, the grouping tool used must be included in the accounting policy.
Despite certain freedom, the taxpayer must be aware of a number of restrictions. In particular, the register must contain mandatory details. If these details are not present, the register will be considered invalid.
Tax registers of separate accounting for VAT
Additional registers may be needed if the taxpayer is required to maintain separate VAT accounting. These are the following situations:
- You perform taxable and non-taxable transactions at the same time. In this case, registers will be needed for separate accounting of incoming VAT and for applying the 5 percent rule (calculating the share of non-taxable transactions).
- You have transactions subject to VAT at a rate of 0%. Registers will be needed for separate accounting of transactions and distribution of input VAT when applying deductions at the time of determining the tax base.
- Your operations have a long production cycle, but you don't want to pay "advance" VAT on them. Registers will be needed for separate accounting of transactions and input VAT.
- You receive subsidies or investments from the budget that have no intended purpose.
For such registers, the tax legislation does not provide special forms and rules for filling them out. All organizations develop them independently, based on their own characteristics, and prescribe them in their accounting policies. Separate accounting can also be confirmed by other documents: certificates of VAT calculation, prescribed maintenance methods, accounting certificates, primary records, orders of the head (resolutions of the Arbitration Court of the East Siberian District dated May 20, 2016 No. F02-2434/2016 and dated November 27, 2014 No. F02- 5554/2014 and the Ural District dated October 2, 2014 No. F09-6168/14).
Maintain tax registers for VAT in the Kontur.Accounting service. Organize separate accounting, receive and issue invoices, and the service itself will create books of purchases and sales and create a log of invoices. Regularly entering transactions into the service will help you almost automatically submit your VAT return at the end of the quarter. All new users can work in Accounting for 14 days free of charge.
Income tax registers
Registers are filled out on the basis of primary records and accounting accounts. They are required to establish the amount of income tax. Register forms are developed taking into account the specifics of the company's work.
As already mentioned, tax registers can be replaced by accounting documents. But sometimes you need to create registers separately. This is relevant for transactions, the results of which are reflected differently in tax and accounting records. If an organization deals with such transactions, it is worth developing registers.
It is necessary to take into account that sometimes accounting and tax accounting standards differ.
Accordingly, the documents for accounting must be different. This is where tax registers come in handy.
If an organization deals only with transactions that are equally documented from the point of view of both tax and accounting, separate registers are not required. They are simply replaced by accounting registers. A single form saves time and makes calculations easier.
To generate an income tax return, you will need at least two tax registers: for income and expenses. Information about income and expenses is needed to determine the amount of profit. It is this that is the tax base, on the basis of which the amount of tax is determined.
Two registers are the bare minimum that will be useful in calculations. Sometimes auxiliary registers are introduced. They are relevant when the organization is engaged in several areas of activity at once. Registers should be created when a company is faced with special transactions that require a special procedure for the formation of the tax base.
Tax accounting
Tax accounting is a system for summarizing information to determine the tax base for a tax based on data from primary documents, grouped in accordance with the procedure provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Maintaining tax records is the responsibility of all companies, including those applying special tax regimes.
It is tax accounting that makes it possible to generate complete and reliable information about the accounting procedure for tax purposes of business transactions.
Tax accounting is carried out in special forms - tax registers.
Taxpayer organizations independently form their own tax accounting system.
The procedure for maintaining tax accounting must be prescribed in the accounting policy for tax purposes, which is approved by order (instruction) of the head of the company and is the main document necessary for calculating taxes.
The goals of tax accounting are:
1) generation of complete and reliable information on the amounts of income and expenses of the taxpayer, which determine the size of the tax base for the reporting (tax) period;
2) providing information to internal and external users to monitor the accuracy, completeness and timeliness of calculation and payment of taxes to the budget;
3) providing internal users with information that allows them to minimize their tax risks and optimize taxes.
In this case, the internal user of the information is the administration of the organization.
External users of information are tax authorities, which assess the correctness of the formation of the tax base, tax calculations, and also monitor the receipt of taxes to the budget.
The means of achieving the goal of tax accounting is the grouping of data from primary documents.
Tax accounting consists only of the stage of summarizing information. Collection and registration of information by documenting it is carried out in the accounting system.
Tax accounting data must contain the following information:
- the procedure for forming the amount of income and expenses;
- the procedure for determining the share of expenses taken into account for tax purposes in the current tax (reporting) period;
- the amount of the balance of expenses (losses) to be attributed to expenses in the following tax periods;
- the procedure for forming the amounts of created reserves;
- the amount of debt for settlements with the budget for taxes.
Tax accounting data is confirmed by:
- primary accounting documents (including an accountant’s certificate);
- analytical tax accounting registers;
- calculation of the tax base.
One of the main tasks of tax accounting is to determine the amount of payments to the budget and tax debts to the budget on a certain date.
The subject of tax accounting is the production and non-production activities of an enterprise, as a result of which the taxpayer has obligations to calculate and pay taxes.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation defines the following principles of tax accounting:
- principle of monetary measurement. Tax accounting reflects information on income and expenses, presented primarily in monetary terms;
- principle of property separation. Property owned by an organization is accounted for separately from the property of other legal entities owned by the organization.
- the principle of continuity of the organization's activities. Accounting must be maintained continuously from the moment of its registration as a legal entity until its reorganization or liquidation.;
- the principle of temporary certainty of facts of economic activity. The principle of temporary certainty of the facts of economic activity is dominant. Income is recognized in the reporting (tax) period in which it occurred, regardless of the actual receipt of funds, other property or property rights (accrual principle). Expenses accepted for tax purposes are recognized as such in the reporting (tax) period to which they relate, regardless of the time of actual payment of funds or other form of payment.;
- the principle of consistency in the application of tax accounting rules and regulations. The rules and regulations must be applied consistently from one tax period to the next. This principle applies to all tax accounting objects;
- the principle of uniform recognition of income and expenses. This principle assumes that expenses are reflected for tax purposes in the same reporting period as the income for which they were incurred.
The following tax accounting options are available:
- tax accounting is maintained separately from accounting. This option is most appropriate for use in large companies, where such records are kept in a special division of the organization;
- tax accounting is maintained on the basis of accounting, which presupposes the maximum convergence of tax and accounting; special tax registers are maintained only in cases where tax legislation provides for other accounting rules;
- tax accounting is carried out by adjusting accounting data: tax registers reflect only the difference between accounting and tax accounting data in situations where such deviations arise;
- tax accounting is maintained in a special tax chart of accounts. This method involves the development and introduction of additional tax accounts to the working chart of accounts. This method is the most optimal and is most often used in small and medium-sized organizations.
Examples
There are two main forms of register. These are registers that reflect income and expenses. But if necessary, additional forms can be added to them. For example, one organization may have the following registers:
- Proceeds from sales.
- Expenses that reduce sales revenue.
- Non-operating income.
- Non-operating expenses.
There may be more registers. It all depends on the needs of a particular company. For example, you can enter these HP:
- Revenue from the sale of goods of own production.
- Revenue from the sale of goods that were previously purchased in bulk.
- Revenue from the sale of other products.
When registering each register, you must adhere to the provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For example, when filling out the “Sales Income” register, you need to remember that revenue should be recorded excluding VAT and excise taxes. The corresponding rule is given in paragraph 1 of Article 248 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
To fill out such a register, you need to use information from accounting. In particular, accounts 90 and 91. Accounting data and information in registers should not contradict each other.
Main types of accounting registers
Registers in accounting can differ not only in the way they are kept records, but also in appearance.
So, they are distinguished by the following varieties:
- By external design. There are documents in the form:
- Books. The most common and simplest way to maintain accounting registers. They are laced together and divided into columns. In addition, the chief accountant must sign the cover.
- Cards. They look like a single sheet with a lined table. Despite the simplicity of description and filling, they are:
- Consisting of two graphs. They are used in settlements with legal entities and individuals. Such cards are convenient because they allow you to see all your income and expenses for a certain period of time.
- Cards with three columns. They are designed to account for material assets. Along with the receipt and consumption of all goods, there is another column where the final balance is displayed.
- Forms with a large number of columns. They are designed to calculate all types of work for a specific product using accounting. They are convenient because they allow you to calculate the cost of production and determine the level of development of the entire enterprise. They are stored in a special box - a file cabinet. Moreover, in order to quickly find the required form, it has an alphabetical list.
- Free sheets. They are stored in folders. All data is prepared on plain paper. In addition, special reporting records are kept on them. This helps prevent the sheet or card from being lost or replaced.
- Machine storage media. They are floppy disks, films, etc. Their disadvantage is that they also require a paper original document.
As for the main types, they coincide with the categories of registers in terms of external design.
- Display in monetary terms. All transactions are recorded in the form of amounts of money.
- In the form of accounting accounts. Transactions of this kind are recorded in the form of correspondence accounts.
- Combined. Operations are displayed in different versions.
Entries to these registers are made according to one of two principles:
- Income and expenses are written on one line.
- All operations are listed in different columns.