State duty is a fee that must be paid by persons who apply to specialized authorities. The list of persons who must pay the state duty, as well as organizations that have the right to demand it, is indicated in Article 333.17 of the current Code. For example, some local governments and even officials may charge a state fee. Provided that they were given these rights by specialized acts. Although, for example, consular authorities of the Russian Federation cannot charge for their services.
State duty payers - who are they?
There are different types of state fees that certain individuals must pay. But before we look at each type, it doesn’t hurt to consider who exactly can pay the duty:
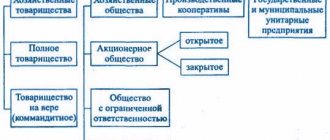
- Organizations;
- Individuals.
There are several reservations regarding the circumstances under which state fees can be paid by legal entities. To obtain the right in question, they must comply with the following conditions:
- Carry out the action required by law.
- Be a defendant in legal proceedings. The decision was made in favor of the plaintiff, who in this case is exempt from having to pay the fee.
Now we can consider the most common types of state duties.
16.1. Transport tax
Transport tax is a regional tax, obligatory for payment on the territory of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation in whose territory it was introduced by the law of the corresponding constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
Transport tax from January 1, 2003 is established by the Tax Code (section 9 “Regional taxes and fees”, chapter 28 “Transport tax”) and the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation on tax.
When introducing a tax, the legislative (representative) bodies of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation determine the tax rate within the limits established by the Tax Code, the procedure and terms for its payment.
When establishing a tax, the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation may also provide for tax benefits and grounds for their use by the taxpayer.
Taxpayers are persons who, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, have registered vehicles that are recognized as subject to transport tax.
For vehicles registered in the name of individuals, acquired and transferred by them on the basis of a power of attorney for the right to own and dispose of the vehicle until the official publication of Chapter. 28 of the Tax Code, the taxpayer is the person indicated in such a power of attorney.
The objects of taxation are vehicles registered in accordance with the established procedure in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation: cars, motorcycles, scooters, buses and other self-propelled machines and mechanisms on pneumatic and caterpillar tracks, airplanes, helicopters, motor ships, yachts, sailing ships, boats, snowmobiles, motor sleighs , motor boats, jet skis, non-self-propelled (towed vessels) and other water and air vehicles.
The list of vehicles that are not subject to transport tax is established in paragraph 2 of Art. 358 NK.
The tax base is determined depending on the type of vehicle (Table 16.1).
Table 16. 1.
Features of determining the tax base for transport tax.
The tax period is a calendar year.
Tax rates are established by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in the amounts specified in Art. 361 NK. Tax rates can be increased (decreased) by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, but not more than five times.
It is allowed to establish differentiated tax rates for each category of vehicles, as well as taking into account the useful life of the vehicles.
Tax calculation procedure. The amount of tax, unless otherwise provided by the Tax Code, is calculated for each vehicle as the product of the corresponding tax base and tax rate.
Taxpaying organizations calculate the tax amount independently. The amount of tax payable by individual taxpayers is calculated by the tax authorities on the basis of information submitted to the tax authorities by the authorities carrying out state registration of vehicles on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Procedure, deadlines for tax payment and tax reporting. Tax payment is made by taxpayers at the location of vehicles in the manner and within the time limits established by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
Taxpayers who are organizations submit a tax return to the tax authority at the location of the vehicles within the period established by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
Taxpayers who are individuals pay transport tax on the basis of a tax notice sent by the tax authority.
18.2. Simplified taxation system
Simplified taxation system for organizations and individual entrepreneurs in accordance with the provisions of Chapter. 26.2 The Tax Code involves the payment of UTII, calculated based on the results of economic activities for the tax period, and is applied along with the general taxation system (general taxation regime) provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation on taxes and fees.
The transition to a simplified taxation system or a return to other taxation regimes is carried out voluntarily by organizations and individual entrepreneurs.
The use of a simplified system of taxation by organizations provides for their exemption from the obligation to pay corporate income tax, corporate property tax and unified social tax.
The application of a simplified taxation system by individual entrepreneurs provides for their exemption from the obligation to pay personal income tax (in relation to income received from business activities), property tax (in relation to property used for business activities) and Unified Social Tax (on income received from business activities, as well as payments and other remuneration accrued by them in favor of individuals).
Organizations and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified taxation system are not recognized as VAT taxpayers, with the exception of value added tax:
– payable when importing goods into the customs territory of the Russian Federation;
– paid in accordance with the implementation of operations in accordance with a simple partnership agreement (agreement on joint activities) or an agreement on trust management of property on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Organizations and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified taxation system pay insurance premiums for compulsory pension insurance in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation. Other taxes are paid by them in accordance with the general taxation regime.
The tax is calculated as a percentage of the tax base corresponding to the tax rate.
The tax rate is set at:
– 6% – if the object of taxation is income;
– 15% – if the object of taxation is income reduced by the amount of expenses.
Changes for 2022
On January 1, 2022, in accordance with Federal Law No. 374-FZ dated November 23, 2020, changes to Art. 333.33 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, new fees are introduced for applicants:
- for state registration of the transfer of ownership of a real estate property in connection with the reorganization of a legal entity in the form of transformation - 1000 rubles;
- for entering data about a legal entity into the register of financial platform operators - in the amount of 35,000 rubles;
- for granting a license for the production of ethyl alcohol for the production of the pharmaceutical substance ethyl alcohol (ethanol) - 9.5 million rubles.
In terms of providing benefits for paying state fees, two new grounds have been introduced for the obligation to pay state fees:
- in order to encourage rights holders of real estate to register rights that arose before the entry into force of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation of July 21, 1997 No. 122-FZ “On state registration of rights to real estate and transactions with it”, they are exempt from paying the state duty when applying for legally significant actions related to state registration of previously arisen rights;
- In order to reduce the financial burden on citizens affected by emergencies, an exemption from payment of state duty for state registration of ownership of residential premises or shares in them acquired by individuals in connection with the implementation of social support measures is provided to replace residential premises lost by them as a result of the emergency.
What is the state duty paid for?
The state duty is paid for the performance by state bodies of legally significant actions in relation to the citizen or organization that applied for their commission.
Legally significant actions for which a fee must be paid are listed in the Tax Code.
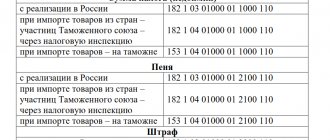
In Art. 333.17-333.33 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation indicates what the state duty is paid for:
- when applying to courts - both arbitration and general jurisdiction, to magistrates;
- when applying to the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation and constitutional (statutory) courts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation;
- when contacting a notary to perform notarial acts (for example, drawing up a power of attorney);
- for state registration of acts of civil status (registration of marriages, births, deaths, divorces, etc.);
- upon receipt of passports of Russian citizens and foreign passports;
- when acquiring Russian citizenship;
- for state registration of computer programs, databases;
- for state registration of medicinal products;
- for state registration of legal entities, political parties, media, issues of securities, property rights, vehicles;
- for the right to use the names “Russia”, “Russian Federation” and words and phrases formed on their basis in the names of companies;
- for the right to export cultural property;
- for issuing permits for the export from the territory of Russia, for the import into its territory of species of animals and plants falling under the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora;
- other legally significant actions, which transactions are subject to state duty, are specified in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The specifics of paying state duty depending on the type of legally significant actions performed, the category of payers or other circumstances are established by Articles 333.20, 333.22, 333.25, 333.27, 333.29, 333.32 and 333.34 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Taxes, fees and duties
In accordance with clause 1 of Article 333.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, payers of fees for the use of objects of wildlife and for the use of objects of aquatic biological resources are: a) organizations; b) individuals registered as individual entrepreneurs; c) individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs. In order for the listed persons to become fee payers, certain conditions must be met. Firstly, an organization or individual must have a license (permit) to use objects of the animal world or objects of aquatic biological resources. According to Article 33 and Article 37 of the Federal Law “On Wildlife,” objects of animal life are provided to legal entities and individual entrepreneurs for long-term use on the basis of a long-term license, and to citizens for short-term use on the basis of personalized one-time licenses. The second criterion for determining the payers of the fee for the use of aquatic biological resources is the territory. The use of aquatic biological resources should take place in internal waters, in the territorial sea, on the continental shelf of the Russian Federation and in the exclusive economic zone of the Russian Federation, as well as in the Azov, Caspian, Barents Seas and in the area of the Spitsbergen archipelago.
We recommend reading: Buy a Completed Krasnodar Exchange Card
The tax return is submitted to the tax authority no later than the 20th day of the month following the end of the tax period. If the declaration reflects transactions taxed at a rate of 0%, the taxpayer is obliged to attach to the tax return documents justifying its application, in accordance with Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
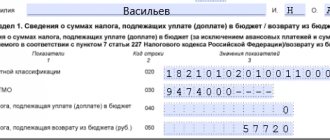
Payment order for payment of state duty: sample
It is clear that if a new payment order is generated, an unprocessed payment order will appear in the chronology, but this situation does not entail any punitive measures and is easily explained by the expiration of the document.
- when contacting judicial authorities to submit a request, petition, application, statement of claim, administrative claim, complaint;
- when applying for notarial acts;
- when applying for the issuance of documents (their duplicates);
- when applying for an apostille.
27 Jul 2022 jurist7sib 150
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Why When Submitting an Application to Artek All Shifts Are Not Displayed
- What Amount will be Provided to Honorary Donors in the Novosibirsk Region in 2022?
- Judicial Practice Regarding Housing and Utilities Debts of a Minor
- What is the Salary of a Kindergarten Teacher 2022 in Moscow
Increased originality
We invite our visitors to use the free software “StudentHelp”, which will allow you in just a few minutes to improve the originality of any file in MS Word format. After such an increase in originality, your work will easily pass verification in the anti-plagiarism systems of the university, antiplagiat.ru, RUCONTEXT, etxt.ru. The “StudentHelp” program works using a unique technology so that in appearance, the file with increased originality does not differ from the original one.
Thus, based on the available data, we can conclude that the amount of tax income received by the state from state duties is very insignificant, due to which it is necessary to address the issue of increasing the efficiency of the system of state duties. In my opinion, there are two ways to increase the amount of revenue from state duties:
- Revising the rates of state duties is the most difficult and time-consuming path, requiring material costs for calculating, optimizing and forecasting new rates; Reducing the number of benefits for paying state duties is the most optimal solution; the legislator has already taken this path, abolishing most of the benefits for paying state duties for performing notarial acts, which was enshrined in the second part of the Tax Code.
Receipt for payment of state duty: validity period
As we can see, the validity period of a receipt for payment of state duty in most cases is about 1 calendar year. But there are a number of situations, such as, for example, the return of an overpaid amount of state duty, in which the payment made can be returned within three years from the date of payment.
When talking about the validity period of the state duty in court cases, it is worth keeping in mind that the payment can be counted within 1 year, but it is worth filing a statement of claim no later than December 31 (or the last working day) of the current year.
We recommend reading: Maternal Capital Commitment From Grandparents