The principle of operation of NPOs
Non-profit organizations operate on the basis of Art. 2 Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 7-FZ dated January 12, 1996. Non-profit organizations are created to work in areas related to charity, society, culture, as well as:
- scientific fields;
- sports;
- spiritual development of the individual (not related to obtaining material benefits).
Some NPOs provide legal and legal support to individuals and legal entities. Despite the fact that such organizations are created to perform work not related to obtaining material benefits, they are also allowed to engage in business. At the same time, it is impossible to distribute the profit received between the participants of the organization, which remained unchanged in 2022 (Clause 7, Article 2 of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 7-FZ). All proceeds are used for the purposes stated in the charter and expenses incurred in the process of achieving them.
The specifics of accounting for non-profit organizations in 2022 directly depend on whether the company is engaged in business or does not receive any benefits.
Can a non-profit organization provide paid services?
Based on the definition of entrepreneurial activity given in paragraph 2 of Art. 2 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, we can conclude that as part of its implementation, a company can not only produce goods or perform work, but also provide certain services. It follows from the very essence of entrepreneurship that the provision of such services is carried out on a reimbursable basis. The legislator does not prohibit NPOs from engaging in entrepreneurial activities, and therefore does not exclude the possibility of them providing paid services. There is only one limitation: the money received must be used to achieve the goals of the NPO, and not distributed among its founders (participants).
It is worth remembering that the paid services provided must be directly related to the goals of creating a company (Clause 2, Article 24 of Law No. 7). For example, an association that unites teachers and professors has the right to develop and sell teaching aids and textbooks, provide exam preparation services, or provide tutoring. At the same time, it will not be able to produce food or provide services for holding special events. Violation of this rule may entail the recognition of the concluded contract for the provision of services as void (clause 2 of Article 168 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), and also become the basis for the forced liquidation of the company on the basis of a court decision made at the request of a government agency or local government body (clause 4 Article 61 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Accounting for non-profit organizations that do not conduct business activities in 2022
The accountant of a non-profit organization credits receipts to account 86 and debits to account 86. Account 90 is not used by non-profit organizations of this type, and account 91 is used only in connection with operations involving the sale of assets (see paragraph 2, clause 1 of PBU 9 /99 and paragraph 2 of paragraph 1 of PBU 10/99).
In 2022, tax accounting of non-profit organizations for fixed assets is regulated by FAS 6/2020 “Fixed assets”, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 17, 2020 No. 204n. At the same time, PBU 6/01 “Accounting for fixed assets” is considered invalid. Now accountants use:
- FSBU 6/2020 “Fixed assets”;
- FSBU 26/2020 “Capital investments”.
Until the beginning of 2022, depreciation was not accrued on the fixed assets of non-profit organizations (clause 17 of PBU 6/01). Depreciation of fixed assets was recorded on off-balance sheet accounts using the following entries:
- depreciation accrued – 010;
- depreciation (accounted for) written off – 010.
In 2022, the clause in FAS 6/2020 “Fixed Assets” was removed, which allows us to talk about equating non-profit organizations with other organizations required to calculate depreciation. In this case, standard entries are used: debit 26 (20, 25...), credit 02 - depreciation has been accrued.
Important ! The accounts used in 2022 must be taken into account in the accounting policies of NPOs (internal law regulating all financial procedures, containing a description of the features of NPO activities, applicable general and special requirements, the presence of which is determined by the legal status and industry specifics of the organization’s work, etc.).
Since 2022, the new federal standard 27/2021 “Documents and document flow in accounting” has also been used.
Otherwise, nothing has changed; you can use the previous postings, but adjusted for the accepted adjustments.
Who can establish an NPO
The founders, that is, the creators of an economic entity, must meet several mandatory requirements at once. Only legally capable and adult citizens can act as creators. Legal entities already registered in the Russian Federation have the authority to establish an NPO. The right to create is reserved to public legal entities. This is the Russian Federation, the constituent entities and municipalities of our country.
The number of founders is not limited by the current legislation. Consequently, any number of founders can participate when registering a new entity. But the requirements for the number of participants of an NPO are established depending on the organizational and legal form. Please note the following regulations:
- When creating a public organization, there must be at least 3 participants (Article 123.5 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- When establishing a union, 2 or more participants are assigned (Article 123.9 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
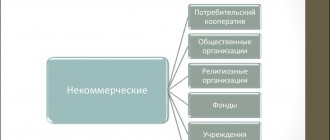
The creation of a non-profit organization is possible only in three cases (Article 13 of Law No. 7-FZ):
| Establishment of a new entity | Creation of a completely new legal entity |
| Reorganization of an entity having a similar type of organizational and legal form | A new legal entity is created on the basis of an existing entity with a specific legal entity. The organizational and legal form remains unchanged |
| Reorganization of a subject having a different general fund | The creation of a new legal entity is carried out by transforming the old NPO with changing the organizational and legal form to another |
Accounting in non-profit organizations engaged in entrepreneurship in 2022
Keeping records in non-profit organizations working for the purpose of obtaining material benefits is considered a difficult task, since the accountant needs to focus on:
- distribution of income and expenses between activities related to charity, social work and entrepreneurship;
- tracking the wording of the purpose of received and directed financial flows in contracts and documents that are primary.
An example of an incorrect determination of the purpose of funds in the accounting policy is as follows.
The accountant needs to accept the money received as a reward for holding the event. They can be written in two ways - correct and incorrect. It is incorrect to write the following: “Fee for holding an entertainment event.” Correct: “Targeted contribution for organizing and holding an entertainment event.” In the first case, the tax service requires VAT, but targeted contributions to NPOs are not taxed, so the organization will not incur any additional expenses. VAT reporting is mandatory.
The accountant needs to focus as much as possible on the choice of wording: the use of vague, imprecise definitions in official documents should not be allowed. An example of inaccuracy is the assignment “Purchase of disposable tableware.” The exact wording should be: “Purchase of disposable tableware for a charity event in nature with the participation of children.” If we are talking about the purchase of office supplies, then instead of the simple “Purchase of office supplies,” they write “Purchase of office supplies for the administrative department.” Precise indication of target expenses helps the accountant not to get confused during tax accounting of expenses and income, and to quickly determine which account will be correct for directing money to it.
In addition, the accountant is obliged to check whether the costs incurred are justified. To do this, you need to check if you have:
- orders for the distribution of finances;
- letters and orders of NPO participants;
- requests from citizens and organizations for funds in the form of assistance from a non-profit organization;
- other documents.
In order to keep tax records separately, two different sub-accounts are created. For main social activities - 20-1 and 26-1, for entrepreneurial activities - 20-2 and 26-2.
In 2022, financial results are recorded as follows:
- basic public work – score 86;
- entrepreneurship - account 90, loss and profit are written off every year to account 86;
- sale of assets and performance of other operations - account 91, at the end of the year this account is closed to account 86.
At the end of the year, an NPO must submit two forms (this also applies to those organizations that do not conduct commercial activities) - a balance sheet and a report on the intended use of funds. If an organization conducts business activities, then, as before, it reports financial results.
Important ! NPOs still do not need to declare where and how funds flowed in 2022. The exception is organizations operating in a highly specialized field, whose activities are regulated by separate laws.
Separate accounting
Another feature of entrepreneurial activity in NPOs is maintaining separate records of both income and expenses, especially if we are talking about several areas.
“In form, we are a regional branch of an interregional public organization,” says Victoria Podolskaya , head of the Regional Public Organization “Equal Opportunities”. – There are several areas within the organization. The two largest projects are the integrated theater “Krug II”, in which people with special needs play, and the “Okoyom” workshops, in which “special” masters also work. The commercial activity of the Krug II theater is regular showings of our performances, for which tickets are sold, as well as commercial performances at various events.”
As a commercial service, the organization offers small theaters, creative groups, event organizers and photo studios the production of scenery and props from a variety of materials, tailoring and repair of costumes, production of art objects, accessories, gift and souvenir products. “Last year we began to develop workshops as an independent social and entrepreneurial project and even won a grant from the Mayor of Moscow for this,” adds Victoria Podolskaya. – We are planning to launch a project – a collection of designer clothing for people from 7 to 75 years old. The staff includes 17 craftsmen, teachers and administrative employees. We also employ children with special needs. Currently, 28 people with mental disabilities are employed in the theater and workshops.”
Profits are used for statutory purposes and development. “When we receive an order from another organization, we enter into an agreement and receive funds into the account,” says Podolskaya. – For other cases – a cash register. So far, our entrepreneurial activity is not yet very stable and generates income unevenly. Therefore, we combine different sources of funding, including grants and subsidies.”
Equal Opportunity continues to search for the optimal entrepreneurial model, and there are many difficulties. For example, while developing workshops, NGOs realized that handicrafts are an expensive pleasure for many buyers. We must look for ways to reduce production costs and the price of final products, to produce more, cheaper and faster. In addition, promotion on the market requires a budget; NPOs do not have enough funds for it. For now, employees are engaged in promotion themselves or with the help of volunteers. They mainly use social networks, their own website, e-mail newsletters and presentations at events.”
If you are interested in charity, you want to understand new technologies, read expert interviews with prominent figures in the NGO world and help wisely - subscribe to the sector newsletter Miloserdie.ru. The more we know, the better we help!
Changes in taxation of NPOs in 2022
In January 2022, there were some changes regarding the taxation of non-profit organizations. Thus, from January 1, 2022, when determining income taxes, expenses on the value of property (including money) that were donated to NPOs are taken into account, provided that the organization is included in a special register of socially oriented enterprises (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation dated July 30, 2021 No. 1290). Besides:
- a new procedure for recording the number of socially oriented organizations is being applied (such organizations are still entered into the register by the Ministry of Economic Development after going through a number of procedures);
- the register of socially oriented organizations cannot include institutions founded by a state authority or local government;
- an organization that does not meet the requirements of the Ministry of Economic Development may be entered in the register with the permission of the state authority of the subject, but for no more than three years;
- a list of information that must be entered into the register has been approved;
- deadlines have been established and the procedure for making changes to the register has been determined;
- the register is made publicly available (it can be found on the website of the Ministry of Economic Development);
- to confirm the accuracy of information in the register, the UKEP is used;
- The situations in which an NPO can be removed from the register have been reviewed.
The procedure for maintaining a register of non-profit organizations that was used previously, including the one that was introduced for those affected by the coronavirus, is no longer valid.
Charity auctions
Photo from laprogressive.com
Cases often arise when NPOs do not understand that their activities are commercial. The most common example is “charity auctions”, at which NPOs sell various lots, and the income from this is considered a donation.
“In accordance with current legislation, any auction, including a charity one, is an open auction,” PHILIN experts explain. – A purchase and sale agreement must be concluded with the auction winners. It is the basis for the receipt of funds received by the NPO. Thus, we see that it is not a donation that is taking place, but an ordinary purchase and sale, which, in turn, is an income-generating activity for NPOs, and the funds received are profit, which is taxed, unlike a donation. Without knowing these nuances, an NPO may unexpectedly find itself in a situation where, during an audit, the regulatory authorities make a decision to collect unpaid tax from the money received, as well as penalties for late payment.”
Simplified taxation of NPOs in 2022
Non-profit organizations can switch to simplified tax administration. You can choose the simplified tax system at the time of submitting an application to the tax office for registration of an NPO, or you can change the adopted taxation system already in the course of business activities. Restrictions for the simplified tax system in force in 2022:
- number of employees (non-profit organization participants) – no more than 100 people;
- income for the next 9 months – up to 45 million rubles;
- residual price of funds – up to 100 million rubles;
- no branches;
- NPOs do not produce products considered excisable.
At the end of the year, the NPO submits a single simplified declaration. The organization does not pay taxes on profits, property, or VAT; a single tax is calculated for it. If taxation is carried out on income, its value is 6%, with “Income minus expenses” 15% of the difference is taken, and if there is none, then 1%.
Money (income) used for the purposes specified in the charter is not subject to taxes. An example of such income:
- grant;
- membership fee;
- donation;
- subsidy for targeted needs.
NPOs operating under the simplified tax system distribute income and expenditures of target amounts separately.
Important ! The simplified tax system for non-profit organizations has many advantages and has not lost them in 2022. Thus, the head of an NPO still acts as the chief accountant. This scheme is beneficial for organizations that sell goods, work for a fee and own taxable property.
Can non-profit organizations carry out activities that generate income?
In paragraph 2 of Art. 24 of Law No. 7 states that NPOs have the right to undertake income-generating activities while simultaneously meeting the following conditions:
- funds received in the course of carrying out income-generating activities are used to finance its statutory goals (money can be used to pay for the labor of persons with certain physical limitations, such as blindness, deafness, etc., to improve the material and technical base of the association and pay for utilities accounts, as well as for solving various socially significant problems);
- the possibility of performing such actions is recorded in the company’s constituent documents.
At the same time, according to clause 3 of Art. 24 of Law No. 7, an NPO is obliged to keep records of income and expenses arising as a result of its business and other profit-generating activities.
Features of taxation of NPOs on OSNO
Every year, NPOs will have to prepare a VAT return. In this case, the seventh paragraph of the declaration is filled out if the organization is engaged in activities that are not subject to VAT, it carries out operations that are not subject to VAT, and also:
- the results of activities are manifested outside the territory of the Russian Federation;
- a product is manufactured or supplied that takes more than six months to create or deliver.
Under the normal taxation system, the transactions carried out by NPOs are quite extensive. An example of taxation under OSNO looks like this.
The NGO is dedicated to the protection of rare animals. This is the main activity. But at the same time, the organization received income for the educational services it provided, which is not the main activity. The money was spent on purchasing serum to vaccinate a wild cat. Those new to tax accounting will try to immediately deduct taxes from the remaining amount. But in reality, funds received not from the main activity are not subject to taxes, since it is the way in which they are spent that is important. In this situation, it is targeted, corresponds to the charter, and contributes to the achievement of the goals enshrined in it. This rule remains unchanged in 2022.
OKVED for NPOs
The basis for opening a new NPO is an application drawn up in form P11001, approved by the order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation “On approval...” dated January 25, 2012 No. ММВ-7-6/ [email protected] Sheet I of the said application must contain information about the activity codes of the registered association, selected in accordance with the All-Russian Classifier of Types of Economic Activities (OKVED), put into effect by the order of Rosstandart “On adoption...” dated January 31, 2014 No. 14-st.
The application must indicate:
- code of the main activity of the association;
- codes of its additional activities.
For certain types of activities of NPOs, special codes are used. For example, code 87.90 can be used by organizations providing residential care services:
- in orphanages;
- children's boarding schools and hostels;
- temporary shelters for the homeless, etc.
If an NPO plans to conduct additional activities that qualify as entrepreneurial, it will need to indicate the corresponding codes in an additional window. It is worth remembering that the entrepreneurial activities of non-profit organizations
must be interconnected with the main direction of functioning for which they are created.
The selected OKVED codes must also be indicated in the charter of the NPO submitted for registration.
What mistakes can an NPO accountant make in 2022?
There are a number of errors that are considered typical in the accounting environment. Almost all accountants make them, no matter whether the NPO operates under a simplified taxation scheme, conducts business activities, or exists solely on a charitable basis. The following types of errors are common.
- A non-profit organization transfers excisable goods free of charge, but does not pay VAT. This is a violation of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 135-FZ dated 08/11/1995. This federal law applies if the NPO donates goods or performs work on a charitable basis. It seems that everything is fine, but the law does not apply to excisable goods. They are taxed according to the general rules.
- Individuals who are not employees of NPOs received donations from which personal income tax was not deducted. The Tax Code (Article 217) states that such payments are not subject to taxes. But it is also noted that the source of payments should be the state, and not NPOs. In some cases, money sent as assistance to an employee’s family may not be taxed, including one-time assistance (up to 2,000 rubles) and gifts (up to 2,000 rubles). Taxes in this category are not paid by organizations included in the official lists developed by the Government of the Russian Federation. But all other organizations are required to deduct personal income tax.
- NPOs do not think about proper accounting, the accountant does not have a report for the quarter, half a year and nine months, while the organization does not work according to a simplified approach. This is also a mistake. In a simplified format, only budgetary and public organizations are allowed to report, provided that they are not engaged in activities that bring material benefits or do not sell goods and services.
These errors are considered the most common, in addition to basic confusion with transactions and accounts.
Legislative restrictions on the implementation of entrepreneurial activities of NPOs
In accordance with paragraph. 2 p. 2 art. 24 of Law No. 7, the legislator may impose certain restrictions on the income-generating activities of individual NPOs. Examples of such restrictions include:
- a ban on participation in business companies in which third parties are members for charitable organizations (clause 4 of article 12 of the law “On Charitable...” dated August 18, 1995 No. 135);
- establishing a closed list of types of activities that political parties can engage in (information, printing and advertising activities, provided that they are aimed at promoting the party; production and sale of objects with their own symbols; sale and leasing/leasing of movable and immovable property belonging to the party , paragraphs 3 and 4 of Article 31 of the Law “On Political...” of July 11, 2001 No. 95);
- a complete ban on entrepreneurship for bar chambers (clause 10, article 29 of the law “On the Bar...” dated May 31, 2002 No. 63), etc.
Answers to common questions
In 2022, in terms of common questions that require answers, everything remains the same. Often NPOs do not have the funds to hire an experienced accountant, and this role is filled by the manager. In addition, regular changes in legislation do not reduce, but only increase the flow of questions. Here are just a few of them.
- In what cases does an NPO pay VAT in 2022? By answering this question, experts draw attention to the operations that the organization is engaged in. If an NPO works with goods subject to tax, then VAT is paid regardless of the intended purpose of the income received.
- Can an NPO deduct VAT on goods purchased for commercial activities? Yes, it can, but if there are taxable and non-taxable transactions, separate tax accounting is maintained. Refusal to keep two different accounts is a violation; the manager may be held accountable for deliberately understating taxes.
- Can an NPO withhold personal income tax from funds allocated to help military widows? Yes, personal income tax is withheld since the widows are not employees of the organization. If goods on which it is impossible to withhold tax were given as assistance, the tax service is notified of this within a month after the promotion.
- Is the sale of valuable items previously received as a gift subject to income tax? If the assets are not received for intended purposes, then they are also subject to income tax upon sale. The cost of property is not included in the expenses for reducing the tax base.
- What is the limit for settlements between non-commercial organizations if we are talking about cash? Under one agreement, the limit in 2022 is 100 thousand rubles. However, there is no limit set for settlements with individuals.
Accounting and taxation in an organization should be carried out separately for different types of activities - targeted and commercial. This will help avoid problems with the tax authorities in 2022.