VAT on advances received from the supplier
Let's consider the situation with VAT, when the buyer made an advance payment to the supplier. Within 5 days from the date of receipt of the prepayment, issue an invoice for the advance payment in two copies (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Give the first one to the client, register the second one in the sales book.
Please indicate VAT on the invoice. To calculate it, use the formula:
VAT = Advance × 20/120
The rate of 20/120 is changed to 10/110 if goods are sold with VAT of 10% (for the list see clause 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If an advance is received for the supply of goods with different VAT rates, then calculate the tax at the general rate of 20/120.
Calculate VAT on advance payment for the transfer of property rights using the formula:
VAT = (Advance Costs for the acquisition of rights) × 20/120
Charge VAT on the day you receive the advance. This day will be the moment of determining the base for calculating the tax.
The advance amount from the invoice falls into column 3 of line 070 of section 3 of the VAT return. The amount of VAT on the advance payment falls into column 5 of the same line.
In addition, we create the following entries in accounting:
Dt 51 Kt 62 - the buyer made an advance payment;
Dt 76/62 Kt 68 - VAT was charged on the advance payment.
Advances issued
An advance payment is an advance payment to the supplier against future deliveries, work performed or services performed. Transferring an advance payment to a supplier does not mean receiving economic benefits, since the supplier may, for various reasons, fail to fulfill its obligations under the contract: fail to ship goods, fail to provide a service. In this case, the advance payment is returned to the buyer’s account if it was transferred through a bank, or to the cashier if received in cash.
In general, there is no obligation to return the deposit from the supplier.
To account for VAT on advances in the chart of accounts, there is a subaccount on account 76, most often its code is 76.AB.
The buyer can accept VAT as a deduction only if the following conditions are met:
- Presence of an advance payment clause in the contract;
- Documents confirming the transfer of prepayment;
- The supply of goods (services, etc.) is intended for use in activities subject to VAT;
- Availability of a supplier's SF with a dedicated tax.
The buyer does not have the right to accept VAT as a deduction if all of the above conditions are not met. Acceptance of VAT deduction is not an obligation, but a right of the purchasing organization.
If an organization decides to use VAT deduction from an advance issued, then after the provision of the service and the closing of this advance, it will be obliged to restore this VAT to the budget.
Example
Let's say Altavista LLC transfers an advance in the amount of 23,600 rubles. (including VAT). Then Altavista LLC receives goods worth RUB 23,600 from this supplier.
The rate and amount of incoming VAT are indicated in the supplier's invoice.
Advances issued - postings
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Sum | Document |
| 60.2 | 51 | Transfer of advance payment | 23 600 | Payment order ref. |
| 19 | 60.2 | VAT on advance | 3 600 | Advance invoice (received) |
| 68 | 76(advances) | VAT deduction from advance payment | 3 600 | Book of purchases |
| 10 | 60.1 | The received goods are registered | 20 000 | Invoice |
| 19 | 60.1 | Incoming VAT reflected | 3 600 | SF supplier |
| 60.1 | 60.2 | Advance offset | 23 600 | Accounting information |
| 60.2 | 68 | Recovered VAT from advance payment | 3 600 | Sales book |
VAT on advances received after shipment
After receiving the advance payment, shipment occurs. The period between advance payment and delivery of goods is not limited. Be sure to include this condition in the contract.
When transferring goods to the buyer, simultaneously charge VAT on the shipment amounts and deduct the VAT paid on the advance payment earlier (clause 8 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 6 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Deductions can also be made from advances from previous tax periods. For example, the advance was received in the 1st quarter of 2022, and the shipment occurred in the second quarter. Then submit the advance for deduction in the 2nd quarter of 2022.
When transferring goods, issue a “shipping” invoice in duplicate. Give one to the buyer, and register the second in the sales book. Register the previously issued “advance” invoice in the purchase book.
The shipment of goods is accompanied by the following accounting entries:
Dt 62 Kt 90.1 - revenue received from the sale;
Dt 62.02 Kt 62.01 - advance payment from the buyer is credited;
Dt 90.3 Kt 68 - VAT is charged on sales;
Dt 68 Kt 76/62 - accepted for deduction of VAT on advance payment.
Only that part of the VAT on the advance payment that corresponds to the VAT on the shipped goods can be deducted. Let's say, if the advance payment is 100%, but only 50% of the goods have been shipped, you will deduct only half of the VAT on the advance payment. The remaining VAT will be deducted after the last batch has been shipped. In the declaration, indicate the VAT accepted for deduction in column 3 of page 170 of section 3.
Keep records of exports and imports in the Kontur.Accounting web service. Simple accounting, payroll and reporting in one service
Refund of advance payment to buyer
The seller can return the advance to the buyer. The reasons for this are different - from an agreement of the parties to a court decision. VAT on the returned advance can be deducted after the return is reflected in accounting and the contract is terminated.
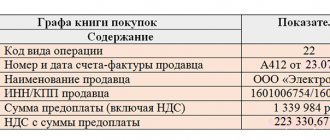
Confirm the advance refund with documents, for example, a payment order with allocated VAT for transferring money to the buyer. Register the payment in column 7 of the purchase book.
In accounting, make the following entries:
Dt 62 Kt 51 - return of advance payment to the buyer;
Dt 68 Kt 76 - accepted for VAT deduction.
You can use the deduction within a year; the right to a tax refund for three years does not apply.
Enter VAT for deduction in line 120 of section 3 of the declaration.
VAT on advance payment issued from the buyer
After transferring the prepayment, you will receive an “advance” invoice from the supplier. Based on it, you have the right to deduct tax. But follow the conditions from clause 12 of Art. 171 Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- the invoice is issued in accordance with the requirements;
- there is a document confirming payment;
- There is a condition for prepayment in the contract.
When transferring the advance payment, the buyer should have the following entries in his accounting:
Dt 60 Kt 51 - advance payment transferred to the supplier;
Dt 68 Kt 76 - VAT on the “issued” advance is accepted for deduction.
Record the received “advance” invoice in the purchase book. Indicate VAT on the advance payment in line 130 of section 3 of the tax return.
You can accept an “advance” invoice for deduction only in the quarter in which it was received. It cannot be transferred to the future. The rule on transferring deductions for a period of up to 3 years does not apply to advances (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-07-11/67480 dated October 17, 2017).
Reflection of advance transactions in the declaration: postings, restoration
In accounting, VAT is charged on the advance received from the buyer using the following entries:
To reflect the accrual of VAT on advance payments, the chart of accounts provides a subaccount “VAT on advances received (prepayments)” to account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” and account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”. This allows:
- keep in accounting data on advances received and VAT on them (according to Kt 62, 76);
- in the balance sheet, reflect the amounts of advances received (excluding VAT, accounted for on the Dt of the relevant accounts) as accounts payable.
Please note that the previously received advance payment at the time of sale of goods (services or work) is counted towards the prepayment amount. An invoice is issued for the shipped product (service or work). On the date of offset of advances, the company accepts for deduction VAT on advances received. Please note that the deduction is made in the amount of tax calculated on goods (services or work) shipped for which advances were received. It is understood here that if VAT on advances is charged at a rate of 20/120%, and the product (service or work) is shipped at a rate of 10%, then VAT on advances received is credited at a rate of 10/110%.
In the VAT return, the advance received is reflected in section 3 on line 070 in column 3, and the amount of tax on the advance is reflected in column 5.
The deduction of VAT on advances received is reflected in section 3 of the declaration on line 170 in column 3 for the tax period in which the goods were shipped.
Reflection in accounting of VAT on the advance paid to the supplier is reflected by postings.
Account 19 is used for the purpose of separating VAT from an advance, when the issuance of an advance and the deduction of VAT are separated in time. If advance VAT on the reporting date is not accepted for deduction, then the tax reflected in account 19 is recorded in the balance sheet as a current asset separately from the “receivables” for the transferred advance payment.
To separate VAT from advances issued, you can use separate subaccounts “VAT on advances issued (prepayments)” to account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” or to account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”. Thereby:
- the accounting stores data on advances paid, including VAT (according to Dt 60, 76);
- the balance sheet shows “receivables” (minus VAT accounted for in the KT of the relevant accounts) in the form of advances issued.
VAT on advances received, accounted for under Dt 62-VAT (76-VAT), is not indicated in the balance sheet, as well as VAT on advances issued, accounted for under Kt 60-VAT (76-VAT). In the balance sheet, tax amounts are reduced by the “debtor” in the form of advances issued and the “creditor” in the form of advances received.
Reflected in account 19 from the advance VAT issued, which was not accepted for deduction by the end of the reporting period, must be included in the balance sheet. This VAT is indicated in line 1220 “VAT on acquired assets.”
Advances issued are not reflected in the VAT return, but the tax on these advances accepted for deduction is indicated in section 3 on line 130.
Please note that for the advances listed by the suppliers, the buyer acts according to the following scheme:
1) receives an invoice for the advance payment, records it in the purchase book, and accepts the advance VAT for deduction;
2) after shipment of goods (services, works), records the shipping invoice in the purchase book;
3) indicates the previously registered advance invoice in the sales book, thus recovering VAT from the advance payment issued.
Kontur.VAT+ allows you to avoid discrepancies in the quotas and reconciles invoices for transactions with advances for all quarters.
Find out more
Regarding the recovery of VAT from an advance received, the situation is as follows. The seller, having received an advance payment, charges VAT on it. Having sold the goods (service, work), he draws up an invoice for the sale and accepts VAT from the previously received advance for deduction. That is, in this case the term “restoration” is incorrect to use. The seller records an advance invoice in the sales book, and later, after shipment of the goods (service, work), an invoice for sales. At the same time, the seller registers an invoice for the advance payment in the purchase book, thereby deducting advance VAT. Oh, that is, the deduction, VAT on the advance received is not limited, the main thing is that the deduction is declared in the quarter in which all the conditions for the deduction are met.
VAT on advance payment issued after shipment
Upon receipt of the goods, the supplier will provide you with a “shipping” invoice. At this moment, the “advance” VAT previously accepted for deduction must be restored, and the “shipping” tax must be accepted for deduction. VAT recovery occurs according to the following algorithm:
- we build wiring Dt 76/60 Kt 68 for the amount of recoverable VAT;
- We record an “advance” invoice in the sales book;
- We enter VAT on the advance payment in line 090 of section 3 of the declaration.
In the buyer’s accounting at the time of shipment we make the following entries:
Dt 10/41... Kt 60 - inventory items are capitalized;
Dt 19 Kt 60 - VAT is allocated from the cost of inventory items;
Dt 68.2 Kt 19 - VAT accepted for reimbursement;
Dt 60.01 Kt 60.02 - advance payment to the supplier is credited;
Dt 76 Kt 68.2 - VAT on prepayment has been restored.
The supplier may return the advance. In this case, it must be restored in the period in which the money was returned. Make the following entries in your accounting:
Dt 51 Kt 60 - prepayment from the supplier has been returned;
Dt 76 Kt 68.2 - VAT on prepayment has been restored.
Step-by-step instruction
Attention! The VAT rate has been changed from 01/01/2019 from 18% to 20% and from 18/118 to 20/120.
On September 30, the Organization’s bank account received an advance payment from the buyer of Architectural Workshop LLC for office furniture in the amount of RUB 354,000. (including VAT 18%). An advance invoice is issued to the buyer on the same day.
Let's look at step-by-step instructions for creating an example. PDF
| date | Debit | Credit | Accounting amount | Amount NU | the name of the operation | Documents (reports) in 1C | |
| Dt | CT | ||||||
| Receipt of advance payment from the buyer | |||||||
| September 30th | 51 | 62.02 | 354 000 | 354 000 | Receipt of advance payment from the buyer | Receipt to the bank account - Payment from the buyer | |
| Calculation of VAT on advance payment and issuance of tax invoice to the buyer | |||||||
| September 30th | 76.AB | 68.02 | 54 000 | Calculation of VAT on advance payment and issuance of tax invoice to the buyer | Invoice issued for advance payment | ||
| — | — | 54 000 | Reflection of VAT in the Sales Book | Sales book report | |||
For the beginning of the example, see the publication:
- Issuing an invoice to the buyer and receiving an advance from him
When VAT is not charged on advances
VAT is not charged on advances in the cases listed in paragraph 1 of Art. 154 Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- the organization that received the advance payment is not a VAT payer;
- goods sold are exempt from VAT;
- goods sold are subject to VAT at a rate of 0% (for export);
- the duration of the production cycle of the goods sold is more than 6 months (the duration of the cycle must be confirmed by a certificate from the Ministry of Industry and Trade of the Russian Federation, and the product itself must be included in the List from the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 468 of July 28, 2006);
- place of sale of goods outside the Russian Federation.
With Kontur.Accounting, VAT accounting becomes easier. Keep records of advances received and issued, calculate VAT, issue deductions and offsets. Regularly enter transactions into the system to receive an automatically generated tax return at the end of the quarter. It can be submitted to the tax office for free directly from the service. Also in the Accounting Department you can conduct employee payments and accounting, generate reports, check counterparties and receive expert advice. New users receive 14 days of service as a gift.
When an advance invoice is not issued
There are cases when the above algorithm does not work. Thus, an “advance” invoice is not issued if the shipment took place no later than 5 calendar days from the date of receipt of the advance payment. This opinion was expressed by the Russian Ministry of Finance in letter dated January 18, 2017 No. 03-07-09/1695 (see “If shipment is due within five days after receiving the advance payment, then there is no need to issue an invoice for the advance payment”).
In addition, you can do without an “advance” invoice if the buyer is not a VAT payer or is exempt from paying this tax. This is directly stated in subparagraph 1 of paragraph 3 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Experts from the Ministry of Finance confirmed that this rule applies to “simplified” buyers (letter dated March 16, 2015 No. 03-07-09/1380; see “When receiving advance payments from an organization that uses the simplified tax system, invoices do not need to be drawn up”) . On our own behalf, we would like to add that this standard also includes “imputed workers”, entrepreneurs on the PSN, payers of the unified agricultural tax and those who have received an exemption under Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Finally, an “advance” invoice is not issued when exporting goods that are taxed at a zero rate. The fact is that, according to paragraph 1 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, prepayment for goods that are taxed at a zero rate is not included in the tax base. Consequently, an “advance” invoice is not needed here (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia 01/10/18 No. 03-07-08/142; “When exporting goods with a zero VAT rate, an advance payment invoice is not drawn up”). The same rule applies in a situation where an advance payment is made as part of transactions that are completely exempt from VAT under Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Submit a VAT return online with documents confirming export Submit for free