Employee training at the expense of the employer according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Article 196 of the Labor Code states that the decision to pay for an employee’s professional training is made by the employer. The head also has the right to independently determine the conditions and procedure for study. All adopted rules must be recorded in the collective agreement and other internal acts.
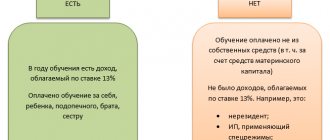
Is it necessary to withhold personal income tax when an organization pays the cost of training an employee?
In most cases, employee training is a right, but not an obligation, of the employer. However, there are exceptions specified in Part 4 of Article 196 of the Labor Code. The employer must organize professional training for certain categories of employees:
- Medical employees (Article 79 of Federal Law No. 323).
- Civilian workers (Articles 48 and 62 of Federal Law No. 72).
- Notaries and their assistants (Article 30 of the Fundamentals of the Law “On Notaries”).
- Auditors (Article 11 of Federal Law No. 307).
The employer is obliged to organize training even if this is considered a condition for the employee’s continued employment.
Carefully! Student!
Often, educational institutions send students to practice. In some places it is customary to work with specific enterprises. Universities enter into agreements obliging them to accept students (sometimes it’s the other way around - companies fight to get future specialists to work for them). Most state universities, institutes and vocational schools send students to work freely, and they negotiate their internship on their own.
In any case, it is not a professional who comes to the organization, but only a student who must experience theoretical knowledge in practice, so there are some restrictions. Typically, the student is assigned a mentor who is responsible for his training and guidance. He also gives grades, writes comments in the workshop diary and a review of the results of the work.
How to hire a student
The procedure is different depending on whether the trainee came on his own or through the direction of an educational institution with which there is already an agreement, and what kind of internship, educational or industrial, he is undergoing.
If the student came on his own, then you can simply conclude a fixed-term employment contract with him, indicating that it is valid for the duration of the internship; as confirmation, the student will provide information about this from the place of study. Article 59 of the Labor Code even has a separate paragraph confirming this right.
Important! Small businesses, including individual entrepreneurs, can enter into fixed-term employment contracts with any employees if the number of the employer’s staff does not exceed 35 people (retail and consumer services - 20).
In this case, the student is registered for work as an ordinary employee, with certain restrictions (since the training has not been completed, as a rule, the employer does not give the opportunity to work without the supervision of a mentor).
- A work book and T-2 registration card are created (if not).
- Safety instructions are provided.
- PPE and overalls are provided if necessary.
- If the work requires a mandatory medical examination, the student must also undergo it.
The same should be done if a clause on accepting a student for work is in the contract with a university or technical school and if the student is undergoing practical training.
Note! Training is a practice that does not imply active participation in work; it only acquaints the student with the work process, technology, working methods and does not require him to perform any work functions. Production is actually work as usual with involvement in the process.
If there is an agreement with an educational institution or the employer is ready to conclude one, then admission to practice is carried out on its basis. Moreover, the internship time is paid depending on the established conditions. The student comes with a referral that contains a link to the contract, type of internship, its duration and other basic data.
Work process and dismissal
It should be noted that the student is subject to certain restrictions of the Labor Code. For example, reducing working hours.
Minors cannot be sent on business trips, put on night shifts or work on weekends and holidays. It is also prohibited to engage them in overtime, harmful or dangerous work (Article 268, Article 96, Article 99, Article 265 of the Labor Code). The student is dismissed in the general manner, or the internship simply ends in accordance with the previously issued direction, depending on whether an employment contract was concluded with him or not.
Types of employer expenses for training
The conditions under which tuition fees are paid are recorded in the following documents:
- Collective agreement.
- Additional agreement to the employment contract.
- Separate training agreement.
The obligation to record the conditions of training is prescribed in Articles 196 and 199 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Employee training, paid for by the employer, is divided into three main types:
- Basic professional.
- Additional.
- Professional education.
This classification is specified in articles 10, 73, 76 of Federal Law No. 273. The type of training determines the calculation of compensation, as well as the guarantees provided to the employee. Studying can be carried out without interruption from work. Otherwise, the employer retains the employee’s average salary and position. If the place of study is located in another area, the organization accrues travel allowances to the employee according to the standard scheme (Article 187 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The guarantees provided to a student employee are listed in Articles 173-176, 187 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- Payment for additional leave provided during training.
- Reimbursement of transportation costs associated with travel to an educational institution.
- The employee retains his average salary.
Each operation related to registration and payment of training must be confirmed by primary documentation (Part 1 of Article 9 of Federal Law No. 402). It is also necessary to confirm the fact that the educational service was received. An act signed by the employer and a representative of the educational institution is suitable for this. The main requirement for a supporting document is the presence of all details. Education documents are proof of the provision of services. For example, a diploma.
What amounts should be compensated (paid) to an employee with whom a student agreement ?
Types of training
Actually, there is no strict classification, this is a conditional list, but it allows you to highlight the features of different types:
- Internal certification.
- Hiring a student or trainee.
- Confirmation, advanced training, certification or testing of knowledge in accordance with legal requirements.
- Advanced training, seminars, trainings, additional education.
- Obtaining education in a new profession due to production needs or career development.
The first, second and in some cases the fourth point are internal types of training. The third, fifth, sixth and fourth (most often) are external.
Rules and features of working out for training
IMPORTANT! A sample order for referral to training from ConsultantPlus is available here
Payment for training is a kind of investment by the employer. That is, the manager expects to receive bonuses from this operation in the future. This is not at all a manifestation of the employer’s altruism.
However, it is easy to imagine a situation in which a manager invests, but receives nothing due to an ungrateful employee. An employee, after completing training, may well quit and get a job at another company with his professional baggage updated at someone else’s expense. How to prevent this? The employer may specify in the contract the obligation to work for training. That is, an employee who has improved his qualifications at the expense of the company cannot just leave. He undertakes to serve a certain period of time. The possibility of setting such a condition is stipulated in Articles 197 and 199 of the Labor Code.
If an employee refuses compulsory service, he is obliged to reimburse the employer’s expenses for paying for educational services.
This rule is spelled out in Articles 207 and 249 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. To protect his interests, the manager must correctly formalize the agreement with the employee.
Legal registration of mining
The manager cannot oblige an employee to work off his expenses based solely on an order to send the employee for training. To do this, you will need to indicate the processing condition in one of the following documents:
- Employment contract.
- Additional agreement.
- Student agreement.
The document must include the following information:
- Specialty or area of study.
- Terms and cost of educational services.
- Obligation to work or compensate employer expenses.
The working period is determined on an individual basis. It can range from several months to several years. It all depends on the agreements between the manager and the employee. Typically, the period is determined based on the following factors:
- Cost of educational services.
- The values of the acquired knowledge.
- Duration of training.
The terms must be fixed in the agreement between the parties.
Features of collecting expenses from an employee upon dismissal
You can recover expenses from an employee for previously provided educational services only if he resigns for an unexcused reason. This rule is stipulated by Articles 207 and 249 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. However, the law does not specify the reasons that can be considered valid or disrespectful. These nuances are determined on the basis of existing judicial practice. For example, valid reasons for dismissal are:
- Staff reduction.
- The employee has received a medical certificate according to which he cannot continue to work in his previous position, but the employer cannot provide a suitable position.
- Conscription of an employee for military service.
An unjustified reason in this context is the employee’s unauthorized initiative or his guilty actions.
Risk 2. The contract was concluded for advanced training
The student agreement stipulates a number of mandatory conditions (diagram below). They also indicate what new qualification the student will receive (Article 199 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, the employer who conducts the training himself or the educational organization does not always issue the employee with a document confirming that he has acquired a new profession.
If the contract did not indicate that the employee was receiving a new specialty, and the employee was not issued a training document, it will be difficult to recover expenses. In this case, the court may declare the student agreement invalid.
Often, an employer enters into an apprenticeship agreement to improve the employee’s qualifications. But this is risky, since the employee is trained in the same profession, he only updates theoretical and practical knowledge. The court may come to the conclusion that the employer must pay for advanced training and that these expenses cannot be reimbursed from the employee (Articles 196, 198 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, appeal ruling of the St. Petersburg City Court dated November 5, 2015 No. 33-18707/2015).
In one dispute, the employer was unable to prove that after advanced training the employee received a new specialty, a profession in which he subsequently worked. The apprenticeship contract did not indicate the new qualifications acquired by the employee. It was not reflected in the certificate received after the seminar. Therefore, the court found that the student agreement was concluded unlawfully (appeal ruling of the Khabarovsk Regional Court dated March 18, 2015 in case No. 33-1585/2015).
In rare cases, the courts take the employer's side. Thus, in one case, the company reached the Supreme Court, and it indicated that it was possible to recover the costs of advanced training from the employee. The main thing is that two conditions are met: the training contract establishes a period of service after training and the employee quits without good reason before the expiration of this period (determination dated April 17, 2022 No. 16-KG17-3).
Accounting for training expenses
Training expenses are accepted for tax accounting on the basis of Article 264 of the Tax Code. However, they are taken into account only if certain conditions are met (Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated March 23, 2009):
- The educational service is paid for in the interests of the company; such expenses are economically feasible.
- The employee undergoes training in the company with all necessary licenses.
- The employee works on the basis of an employment contract.
For accounting purposes, it is important to confirm all training costs. To do this, you will need the following documents (Letter from the Ministry of Finance dated November 9, 2012):
- Agreement with an educational institution.
- An order from a manager to send an employee to study.
- An educational program that specifies the number of teaching hours.
- Act on the provision of educational services.
- A copy of the document confirming completion of training (for example, a certificate).
IMPORTANT! If employee training does not promise economic profit for the company and is carried out in the interests of the employee himself, then associated costs are not taken into account when calculating income tax. That is, it will not be possible to reduce the tax base.
To reduce the tax base, it is important to prove two things: the economic benefit of the enterprise from employee training and the connection between the educational service and the company’s activities. For example, if an organization is engaged in cargo transportation, and an employee is sent for makeup training, such expenses will not affect the tax base.
How to reflect in accounting the compensation of training costs at the expense of the employer upon dismissal of an employee ?
Personal income tax and insurance premiums
Amounts of payment by a company for training employees in a foreign language under an agreement concluded with an educational institution may not be subject to personal income tax.
To do this, the conditions established by paragraph 21 of Article 217 of the Tax Code must be met. The requirements are similar to those for income taxation. Namely, employees must undergo training, professional development and retraining in Russian educational institutions that have the appropriate license, or foreign educational institutions that have the appropriate status.
Recommendations from officials
In order to include in expenses the cost of training employees in foreign languages, it is necessary that they use the acquired knowledge in their work. That is, it is important that services are initially provided in the interests of the organization, and not its employees. The presence of certain skills in a trained employee related to the subject of training must be enshrined in the job description of this employee. This follows from letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 10, 2007 No. 03-04-06-02/64 and the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated August 19, 2008 No. 21 -11/ [email protected]
Insurance premiums are also not paid. Neither in Social Insurance, nor in the TFOMS, nor in the Pension Fund. This rule also applies to social insurance against accidents at work and occupational diseases.
Such benefits are provided for at the legislative level (clause 12, part 1, article 9 of the Law of July 24, 2009, No. 212-FZ and sub-clause 13, clause 1, article 20.2 of the Law of July 24, 1998, No. 125-FZ). Officials do not argue with this either. For example, in a letter dated November 17, 2011 No. 14-03-11/08-13985, Social Insurance specialists indicated that payment for training conducted at the initiative of the employer, in order to more effectively perform job duties, regardless of the form of training, is not subject to taxation insurance premiums.