Almost all costing instructions indicate the need for a monthly inventory of work in progress. Checking the actual reserves confirms the reporting calculations and production costs of the closing period. However, the inventory of work in progress, unlike other assets, is not properly covered in the methods. This is understandable: in controlling “work in progress”, specialists are guided by the company’s accounting policy and technological specifics. The question is important, so we will consider issues related to the inventory of work in progress, using the example of a machine-building enterprise.
COMPOSITION OF WORK IN PRODUCTION AND REGULATIVE DOCUMENTS FOR INVENTORY
According to clause 63 of the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n (as amended on March 29, 2017), work in progress includes :
- products that have not gone through the full production cycle provided for by the technology;
- incomplete products that have not passed testing and technical acceptance.
To conduct an audit of work in progress within the framework of the law, specialists must know the general rules of inventory, the procedure for regulating inventory differences and recording the results. Let us present the regulatory documents that should be followed:
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 No. 49 (as amended on November 8, 2010) “On approval of Methodological Guidelines for the Inventory of Property and Financial Liabilities” (hereinafter referred to as Guidelines No. 49);
- Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated August 18, 1998 No. 88 (as amended on May 3, 2000) “On approval of unified forms of primary accounting documentation for recording cash transactions and recording inventory results.”
The procedure for taking inventory of work in progress
A general list of cases when a mandatory inventory of property is required, incl. WIP, given in clause 27 of Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 34n. The most common of them is a check before annual reporting.
Before submitting annual reports, it is imperative to conduct an inventory of all assets and liabilities (Article 11 of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ).
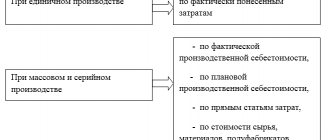
But we will tell you one more case, which is not on the list, although such inventory is carried out 12 times more often. It is also necessary to take inventory of work in progress in cases where your accounting policy requires that work in progress be assessed at the cost of raw materials, materials and semi-finished products. Such an inventory is needed to determine the cost of finished products for the month. Accordingly, such an inventory must be carried out monthly.
What and how to take into account when checking work in progress is determined by the characteristics of production and its technological processes. This should be described in detail in the enterprise's accounting policies.
But the general inventory mechanism here is the same as for other assets.
- To carry out an inventory, an order from the manager is issued indicating the purpose and objects of the inspection, its start and end dates, the composition of the commission and the deadline for submitting the results to the accounting department of the enterprise.
- Next, the commission and financially responsible persons check the work in progress in accordance with the general rules described in the regulatory documents.
- The commission records the result of the inventory in the act.
OBJECTIVES OF WIP INVENTORY
The objectives of conducting an inventory of work in progress are as follows:
- check the actual presence of work in progress and assess its condition;
- compare the actual availability of work in progress with accounting data;
- check data on operational accounting of the movement of components and parts between departments and the total amount of costs in work in progress;
- control the completeness and timeliness of delivery of finished products to the warehouse and documentation of such delivery;
- check the completeness of the necessary technical documentation for finished products;
- check the correct distribution of costs by type of product and clarify the cost of manufactured products;
- determine the actual completeness of the backlog, the availability of assembly parts;
- prevent theft, concealment of marriage and other abuses;
- check the correctness of registration of output and calculation of piecework wages.
Results
Capital investment in accounting is a concept that is inextricably linked with long-term investments and the fixed capital of a company.
Accounting for capital investments is carried out according to the rules prescribed by FSBU 6/2020 “Fixed Assets” and FSBU 26/2020 “Capital Investments”, effective from 2022, as well as the chart of accounts (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n). Until the end of 2021, the algorithm for accounting for capital investments was regulated by PBU 6/01 and Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 13, 2003 No. 91n. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
SELECT WIP FOR CHECKING
Inspections of work in progress depend on a number of factors:
- type of production;
- complexity and range of manufactured products;
- the procedure for operational accounting and storage of interoperational backlogs;
- other features of technology and production organization.
Notes
- Due to the scale of production, the busyness of accounting and control personnel and limited time, a complete inventory is not always possible or appropriate.
- You can control volumes and confirm accounting data using monthly or quarterly sample inventories of work in progress.
- It is optimal if the revisions are sudden. This will allow timely identification of problems and control of the accounting discipline of financially responsible persons in production.
It is advisable to carry out a selective inventory in the following cases:
- of materials and components from which products are made, surpluses and shortages have been identified, facts of theft have been confirmed (for example, during a warehouse inventory);
- shop officials have identified systemic problems with other objects and orders (for example, the problematic unit is a delivery shop or its share of costs in the work in progress exceeds 30%);
- overestimated or underestimated raw material consumption rates have been recorded, there is a need to confirm the standards;
- orders, work-in-process items have been in the workshop without movement for more than two months, there is no write-off of materials to order, no work is carried out on order, this type of product is not manufactured;
- the workshop's balance sheet includes obsolete and canceled designs, manufacturing defects (not put into storage; no decision has been made on what to do with such assets);
- significant deviations of the actual picking list from the planned one were discovered;
- the estimate of actual costs consistently exceeds the planned one by more than the permissible percentage of deviations (for example, 10% or more);
- it is necessary to control production times, completeness of products that are manufactured to order (as a rule, these are large objects, equipment with a large estimated cost, orders from customers important to the company);
- the deadline for delivery of finished products to the warehouse is overdue;
- additions to the output of workers who are paid piecework wages are recorded;
- after changes in document flow, “primary” and reporting of production departments, transition to automated workstations, after installation of weighing devices, automatic dispensers, counters.
Target selective inventories to the following WIP items, product groups, and orders:
- old orders and products, work on which began a year or more ago, mothballed WIP objects;
- work in progress balances from closed, canceled or suspended orders;
- products launched for the first time, experimental products, orders and products after design or technological changes;
- semi-finished products and assemblies that have not been assembled, have a high cost and are highly labor-intensive to manufacture;
- products, semi-finished products, components, the timely production of which determines the timing of other important orders;
- WIP facilities at the first and last sections of the technological chain;
- products and orders are under the control of top management or the owner.
IT IS IMPORTANT
Even if WIP inventories are selective, within a year it is necessary to cover with monitoring all groups of semi-finished products that the company produces, all types of technological operations and all production areas.
We carry out an annual inventory
At the end of the year, the preparation of annual reporting data begins, an important part of which is the inventory of the construction company’s property. In this regard, let us remind you how to carry out an inventory and reflect its results in accounting and tax accounting.
Basic rules The need to conduct an inventory of property and liabilities before preparing annual reports in order to ensure the reliability of accounting data is established in paragraph 2 of Article 12 of the Federal Law of November 21, 1996 No. 129-FZ “On Accounting”.
However, this does not mean that all property needs to be recalculated and rewritten on December 31, 2008. You can start the annual inventory earlier (after October 1). And it is generally allowed to take inventory of fixed assets once every three years. ORGANIZATIONAL POINTS To carry out the inventory, a permanent inventory commission must be created. In addition, if necessary (if it is necessary to simultaneously conduct a census of property in different places in a short time, for example, in different warehouses, sites, etc.), working inventory commissions are also created.
The order appointing the commission (indicating its personnel and inventory deadlines) is approved by the head of the organization and registered in the control book.
The unified forms of these documents were approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated August 18, 1998 No. 88:
— order (decree, order) to conduct an inventory (form No. INV-22); — logbook for monitoring the implementation of orders (decrees, instructions) on inventory (form No. INV-23).
The inventory commission should include representatives of the administration, accountants, and other specialists (engineers, economists, technicians, etc.). It is possible to involve representatives of the internal audit service (if available) and independent audit firms.
Please note that the absence of at least one member of the commission during the inventory serves as grounds for declaring the inventory results invalid. Therefore, you should not attract employees who are constantly traveling and on business trips.
The order to conduct an inventory is given to the chairman of the commission.
BENEFITS FOR NORTHERN PEOPLE In the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas, the inventory of goods, raw materials and materials can be carried out not in the 4th quarter, but during the period of least balance of valuables (for example, in the summer). This is provided for by the norms of paragraph 27 of the Regulations on maintaining accounting and financial statements, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n, and paragraph 1.5 of the Methodological guidelines for the inventory of property and financial liabilities, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 No. 49.
PROCEDURE FOR CONDUCTING INVENTORY So, on time, the commission came to the warehouse or arrived at the site. Before starting work, you must obtain from financially responsible persons (for example, foreman, storekeeper, etc.):
- the latest receipts and expenditure documents at the time of the inventory or reports on the movement of material assets or funds (endorsed by the chairman of the commission with the indication “before the inventory, on such and such a date”);
- receipts stating that by the beginning of the inventory, all expenditure and receipt documents for property were handed over to the accounting department or transferred to the commission and all valuables were capitalized, and those that were disposed of were written off. In some unified forms, such a receipt is already provided, for example, in the cash inventory report (Form No. INV-15) or in the inventory list of inventory items (Form No. INV-3).
And only after this, in accordance with paragraph 2.7 of the Inventory Guidelines, it is imperative to check the actual availability of property by counting, weighing and measuring it.
The commission and financially responsible persons must work together and at the same time. It is impossible for the commission to work in their absence and, conversely, for the responsible employee to have access to the object being inspected without members of the commission. Therefore, if it is impossible to carry out an inventory in one day, it is necessary to seal the premises at the end of the working day.
For construction organizations, the provisions according to which:
- for materials and goods stored in undamaged packaging of the supplier, the quantity of these valuables can be determined on the basis of documents with mandatory verification in kind (for sampling) of part of these valuables; — determine the weight (or volume) of bulk materials solely on the basis of measurements and technical calculations; - when inventorying a large number of weighted goods, the weight sheets are kept separately by one of the commission members and the financially responsible person, and at the end of the working day (or at the end of re-weighing), the data from these sheets is compared and the verified total is entered into the inventory. In this case, measurement reports, technical calculations and statements of plumb lines are attached to the inventory. “Construction” features Companies need to take into account the following specific features of the industry. INVENTORY OF UNCOMPLETE CONSTRUCTION... ...is carried out in accordance with the rules defined in paragraphs 3.32-3.34 of the Inventory Guidelines. In this case, separate inventories are compiled:
- for completed construction projects, actually put into operation in whole or in part, the acceptance and commissioning of which are not documented with the appropriate documents; - for completed but for some reason not put into operation objects, indicating the reasons for the delay in formalizing their commissioning; — for objects of unfinished capital construction; — for objects stopped under construction; — for design and survey work on unfinished construction.
In the last two cases, the inventory provides data on the nature of the work performed and its cost, indicating the reasons for the termination of construction. When filling them out, the relevant technical documents (plans, drawings, estimates, financial estimates), certificates of completion of work, stages, logs of work performed at construction sites and other documentation are used.
When conducting an inventory of unfinished capital construction, the inventory must indicate the name of the object and the volume of work performed on it (for each individual type of work, structural elements, equipment, etc.) In this case, you should check:
— the presence of equipment in unfinished capital construction that was transferred for installation, but has not actually begun installation;
— the state of mothballed and temporarily stopped construction facilities, identifying the reasons and grounds for their mothballing.
IT CAN'T DO WITHOUT THE HELP OF MANAGEMENT The head of a construction organization must take care to create the necessary conditions so that the commission can carry out a complete and accurate check of the availability of property within the established time frame: provide labor for hanging and moving cargo, provide technically serviceable weighing facilities, measuring and control instruments, measuring containers and other necessary tools.
INVENTORY OF MATERIAL VALUABLES Inspection is carried out by financially responsible persons in places where valuables are stored, including at individual construction sites, sites, auxiliary production and service farms. In this case, a number of features also need to be taken into account.
Firstly, open storage materials are widely used in construction - sand, gravel, crushed stone, etc. Their inventory is carried out by geodetic measurement, that is, before the inventory, such materials are given the correct geometric shape (usually a cone, parallelepiped or cube), after which the height is measured, as well as the length, width (or diameter of the base) and the volume of material is calculated using geometric formulas.
Metal of various profiles used in construction (reinforcing and angle steel, channel, etc.) is also inventoried “mathematically”: the total length of each profile is calculated and multiplied by the theoretical weight of a unit of length in kilograms (using special reference tables).
The actual presence of concrete and reinforced concrete structures and products (for example, wall panels, floor slabs, foundation blocks, etc.) is determined by multiplying the quantity of each type of product (according to actual recalculation) by the design volume of each product in cubic meters. We should not forget about workwear, safety shoes and protective equipment, as well as special tools and equipment.
Secondly, according to paragraph 1.3 of the Inventory Guidelines, a construction company must conduct an inventory not only of its inventories, but also of the inventories that are included in its accounting on balance sheet or off-balance sheet accounts. These include:
— leased property; — valuables in safekeeping (for example, when materials received from a supplier do not correspond to the ordered assortment); — materials received for processing (equipment accepted for installation, customer-supplied raw materials). Separate inventories are compiled for them. Documentation Information about the actual availability of property and the reality of obligations is entered into inventories or acts. For most types of property and liabilities, there are unified forms (forms No. INV-1, INV-3, INV-4, INV-17, etc.) INVENTORY DESCRIPTIONS AND ACTS... ...are drawn up in at least two copies. You can fill them out either manually or on a computer.
Erasures and blots in inventories are not allowed. The correction is made by proofreading in all copies: the incorrect entry is crossed out, and the correct entry is placed above it, certified by the signatures of all members of the inventory commission, as well as the financially responsible person.
When filling out inventory lists, the names of valuables and their quantity must be indicated according to the nomenclature and in the units of measurement that are accepted in accounting. At the end of each page of the inventory, the number of serial numbers of material assets must be indicated in words, as well as the overall total of the quantity in physical terms recorded on this page (regardless of the units of measurement). When the inventory is completed, on the last page of the inventory the remaining unfilled lines are crossed out.
Completed inventory lists must be signed by all members of the inventory commission and the financially responsible person.
The unified inventory forms provide for a receipt from the financially responsible person, which confirms the following facts. Firstly, that the inspection of the property was carried out by the commission in his presence. And, secondly, that he does not have any claims against the members of the commission and the property listed in the inventory has been accepted for safekeeping.
If, after the inventory, the financially responsible person discovers an error in the inventory, he must immediately report this to the chairman of the commission to verify this fact. If it is confirmed, appropriate corrections are made to the inventory.
Upon completion of the inventory, control checks of the correctness of the inventory can be assigned. They are carried out with the participation of commission members and financially responsible persons and always before the opening of the inspected facility (the warehouse, site, etc. where the inventory was carried out).
One copy of the inventory list is transferred to the accounting department of the construction company, the second remains with the financially responsible persons. COMPATIBLE SHEET The accountant, having received the inventory lists, evaluates them and compares the actual availability of property according to the inventory data with the accounting data.
After checking the inventory data with the accounting data, if discrepancies are identified, the accountant must draw up matching statements (forms No. INV-18 or No. INV-19). Moreover, only those values for which deviations were found are entered as separate items in the matching sheet, while others are entered in one line, in the total amount. The amounts of surpluses and shortages are indicated based on the “accounting” assessment of the corresponding values. For values that do not belong to the organization, separate comparison statements are compiled.
SIMPLIFYING THE WORK WILL NOT BE BENEFIT Please note: you cannot fill out the inventory sheet using accounting data. After all, then the control function of the inventory will be disrupted, which can lead to distortion of results and abuse.
A formal approach (drawing up inventories without leaving the accounting department, without conducting actual checks) is also unacceptable. In a hurry, when registering the results of a fictitious inventory, often all inventories are dated by one number (in the presence of a large number of objects being inspected and only one inventory commission).
This calls into question not only the results of the inventory, but also the entire reporting of the construction company.
SUMMARY All discrepancies must be explained in one way or another.
For example, if surpluses and shortages are detected, written explanations from financially responsible persons should be obtained. If the culprit of the shortage has not been identified, the relevant decisions of the investigative or judicial authorities confirming the absence of culprits must be attached to the final documents. If damage to valuables is detected, a conclusion from the technical control department or specialized organizations (quality inspections, etc.) is required.
The inventory commission must prepare proposals for resolving the identified discrepancies, which are submitted for consideration to the head of the construction company. Data from the results of inventories carried out in the reporting year are summarized in the statement of results identified by the inventory. Accounting for inventory results The procedure for accounting for deviations identified during inventory is as follows (it is defined in paragraph 3 of Article 12 of Law No. 129-FZ). The surplus property is accounted for, and the corresponding amount is credited to the financial results of the organization. Shortage of property and its damage are written off:
- within the limits of natural loss norms - for production or distribution costs; - above the norm - at the expense of the guilty persons; — if there are no perpetrators (if they are not identified or the court refuses to collect), the losses are written off to the financial results of the organization.
The results must be reflected in the records of the month in which the inventory was completed, and for the annual inventory - in the annual accounting report. IF SURPLUS IS DETECTED Surplus money and valuables are accounted for by the debit of the corresponding accounts - 50 “Cash”, 10 “Materials”, etc. and the credit of account 91 “Other income and expenses”. Moreover, the property is accounted for at market value.
In tax accounting, the market value of “extra” assets is included in non-operating income (Clause 20, Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). IF A SHORTAGE IS IDENTIFIED Let us emphasize that in order to correctly write off a shortage, a number of documents are required. These include:
— matching statement (form No. INV-18 or No. INV-19); — statement of results (form No. INV-26); — written explanations of the financially responsible person (or other employee responsible for the shortage); — order of the manager to recover damages from the guilty party; — a court decision to collect (or refuse to collect) damages from the employee; - a resolution to refuse to initiate a case (if the value of the missing or stolen valuables is less than 1000 rubles, which is recognized as petty theft, which is an administrative offense in accordance with Article 7.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation); — a decision to suspend the preliminary investigation due to failure to identify the person to be charged as an accused.
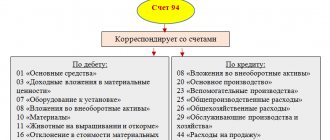
First, the missing property is written off to the debit of account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” from the credit of the corresponding accounts (for example, from account 10). Deviations in the cost of assets are also written off here if the organization uses account 16 “Deviation in the cost of material assets.”
Further actions will be as follows.
First of all, the shortage is calculated and written off within the limits of natural loss norms to the debit of cost accounts (20 “Main production” or 26 “General expenses”).
The norms of natural loss of non-metallic building materials (sand, crushed stone, gravel) during storage are given in Appendix No. 1 to the Decree of the USSR State Supply Committee dated June 15, 1984 No. 72.
Next you need to determine if there is a specific culprit. If there is (for example, a storekeeper or foreman), the shortage is recovered from the guilty person.
If the culprits are not found, the shortage is written off from the credit of account 94 to the debit of account 91. EXAMPLE During the inventory of inventory items at Monolit LLC, a shortage of construction sand was discovered in the total amount of 36,000 rubles. The perpetrators have not been identified. The shortage within the limits of natural loss norms is calculated to be 7,250 rubles. The manager decided to write off the amount of the shortfall to the financial results. The accountant will write down: DEBIT 94 CREDIT 10 - 36,000 rubles. — the missing sand is written off based on the matching sheet; DEBIT 20 CREDIT 94 - 7250 rub. — the shortage of sand was written off within the limits of natural loss; DEBIT 91 CREDIT 94 - 28,750 rub. (36,000 - 7250) - the shortage of sand in excess of the norms of natural loss was written off. In tax accounting, expenses in the form of shortages of material assets in the absence of perpetrators, as well as losses from theft, the perpetrators of which have not been identified, are included in non-operating expenses. But for this, the fact that there are no perpetrators must be documented by an authorized government body (subclause 5, clause 2, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Otherwise, losses are not taken into account for the purpose of calculating profit. CREDIT FOR REGRADING In accordance with paragraph 5.3 of the Methodological Instructions for Inventory, a construction company can make a mutual offset of surpluses and shortages as a result of regrading.
However, this can only be done as an exception if a surplus and shortage of inventory items of the same item are simultaneously detected:
- for the same audited period; - from the same person being checked; - in identical quantities.
Therefore, for example, if there is an excess of sand and a lack of crushed stone, it is impossible to carry out a misgrading test. It is also impossible to make an offset if an excess of sand is found at one construction site and a shortage at another.
Hello Guest! Offer from "Clerk"
Online professional retraining “Accountant on the simplified tax system” with a diploma for 250 academic hours . Learn everything new to avoid mistakes. Online training for 2 months, the stream starts on March 1.
Sign up
PREPARATORY ACTIVITIES
Before carrying out an inventory of work in progress, it is necessary to carry out a number of preparatory procedures in order for the process to produce effective results.
1. Before starting the inventory, we check:
- availability and correctness of accounting in analytical accounting registers for each type of product, order, WIP object;
- availability of design and technological documentation, engineering survey results, design documentation, patents;
- whether semi-finished products can be used in production;
- provision of labor for hanging and moving large parts and assemblies, technically sound weighing equipment, measuring and control instruments, and measuring containers.
If the WIP inventory is planned, you need to organize preparatory work in the workshops , which will simplify the work of the commission. It is necessary to order that in workshops:
- parts and assembly units were placed in an order convenient for counting;
- signed, hung tags on racks, containers, parts;
- outdated designs and canceled orders were placed separately;
- removed defective parts and waste;
- delivered all unnecessary materials, purchased components and semi-finished products to warehouses;
- parts, components and assemblies, the processing of which was completed in the audited workshop, were transferred to the next technological stage.
2. We select a competent commission.
The inventory commission includes:
- technical specialists of general plant services (technologists, designers, controllers);
- employees of the financial and accounting service - an accountant of the production group, an economist or the head of the economic planning and production dispatch departments, an accountant-auditor;
- employees of the company's internal audit and security services;
- representatives of independent audit companies, competent experts.
An important point: limited time is allotted for inventory; errors are difficult to detect and correct, so it is necessary to provide a sufficient number of working commissions and performers. Inspectors must have a good knowledge of the technological process.
- We receive from financially responsible persons of production departments:
- the latest incoming and outgoing documents at the time of inventory, production reports for workshops;
- receipts stating that all documents on the movement of work in progress have been submitted to the accounting department or transferred to the commission.
- We instruct the members of the inventory commission about the purposes, volumes and procedure for conducting the inventory.
Rules for filling out the WIP verification report form
The act form is developed at the enterprise and approved by order of the manager, with subsequent consolidation in the accounting policy. It can be based on the forms given in Appendices No. 6–15 to the guidelines approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 49.
The act must indicate:
- Title of the document,
- link to administrative document,
- inventory start and end date.
It is recommended to summarize the results of the check in a table for the convenience of recording work in progress by quantity and cost. At the end of the act there must be signatures of all members of the inventory commission.
The absence of the signature of at least one member of the commission makes the act invalid.
The acts are filled out separately for each separate division of the enterprise.
The WIP inventory form looks like this: