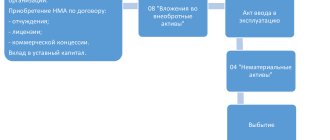
The software can be acquired by an organization with exclusive or non-exclusive rights to it. To register, you must have a license agreement or an agreement on the alienation of software to the buyer, an act of transfer of rights. In some cases, the license agreement may be replaced by sublicensing contractual documentation.
IMPORTANT! An exclusive right presupposes sole ownership of an asset, acquired through independent development of software for one’s own needs or through purchase under an alienation agreement.
Features of accounting and tax accounting software
The exclusive rights acquired by the organization must be classified as intangible assets. PBU 14/2007 imposes a number of requirements on such objects:
- there must be documentation indicating the existence of rights to use the software product;
- we will separate the asset from other assets of the enterprise;
- it is impossible to identify the material form;
- for the next year the institution has no plans to sell the software;
- economic benefits can be obtained from the process of using the program;
- the period during which the asset can be operated exceeds 1 year;
- it is possible to objectively and without significant errors determine the value of the initial cost.
Question: How to reflect in an organization’s accounting the acquisition of a computer program from the copyright holder on the basis of an agreement on the alienation of an exclusive right, if the acquisition costs are less than 100,000 rubles? View answer
Tax accounting places fewer requirements on incoming intangible assets (Clause 3, Article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- availability of documentation confirming the right to own and use the object;
- the prerequisites have been created for obtaining financial benefits from the operation of the asset;
- duration of use exceeds the threshold of 12 months.
The software is placed on the balance sheet at its original cost, which includes the costs incurred to purchase the licensed product. If the cost of the program does not exceed 100 thousand rubles, then, according to tax accounting rules, the asset may be considered non-depreciable. In accounting, the threshold for classifying objects as depreciable is at around 40 thousand rubles.
When a decision is made to charge depreciation on the purchased software, the service life is determined according to the technical documentation and is correlated with the standards of Art. 258 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This rule is fixed for tax accounting; in accounting, depreciation may not be charged if the service life of the intangible asset is unknown.
Software products acquired on the basis of a non-exclusive right cannot be depreciated. Clause 3 art. 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation confirms this position by the fact that such assets cannot be recognized as an integral part of intangible assets.
REMEMBER! Objects for which the enterprise has non-exclusive rights of use must be written off as other expenses.
When using the accrual method, expenses associated with the purchase of software products are recommended to be written off in equal parts over the entire period of operation. With the cash method, the expenses are entered into the amounts that were actually paid. For organizations operating on the simplified tax system, the right is provided to reduce the tax base at the expense of funds spent on the purchase of software.
To display the costs associated with the purchase of software, account 97 is used in accounting. Costs are subject to even write-off over the time allotted for using the program. The methodology for attributing the cost of software to expenses at all enterprises should be prescribed as a separate paragraph in local documents (accounting policies).
Is it possible to take into account expenses for a computer program for income tax purposes if an organization purchased it via the Internet?
Acquisition and creation of software products
Reflection in accounting of transactions for the acquisition of exclusive rights to use software products for activities subject to VAT.
| № | Debit | Credit | Contents of operation |
| Accounting entries when reflecting expenses for the acquisition of a computer program | |||
| 1 | 08-5 | 60, 76 | The cost excluding VAT of the purchased computer program is reflected (with the transfer of exclusive rights) |
| 2 | 19-2 | 60, 76 | VAT was taken into account (accrued) when acquiring exclusive rights to use a computer program |
| Accounting entries at the time of acceptance of the software product on the balance sheet | |||
| 1 | 04 | 08-5 | The software product is included in the organization's intangible assets. The computer program is intended for use for production (including VAT) purposes of the enterprise |
| 2 | 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” | 19-2 | Accepted for deduction of VAT on the software product accepted for accounting |
| Accounting entries when repaying debt to the seller (copyright holder) | |||
| 1 | 60, 76 | 51 | Reflected payment for the software product |
| Accounting entries when calculating depreciation | |||
| 1 | 20, 26, 44, etc. | 05 | Reflects the monthly amount of depreciation charges |
Reflection in accounting of the acquisition of exclusive rights to use software applications for mobile devices and their implementation under license agreements to end users.
| № | Debit | Credit | Contents of operation |
| Accounting entries when reflecting expenses for the acquisition of a software application for mobile devices. The organization acquired, under a copyright agreement, the exclusive right to use a software application for mobile devices from an individual who is not an employee of the organization. The author, a citizen of the Russian Federation, provided the organization with information confirming the expenses he incurred. | |||
| 1 | 08-5 | 76 | The amount of remuneration to the author of a software application for mobile devices is reflected (with the transfer of exclusive rights). The remuneration amount takes into account the cost of work and intellectual property rights |
| 2 | 08-5 | 69 | The accrued amount of insurance premiums from royalties is reflected. The tax base for calculating insurance premiums is determined as the amount of remuneration to the author, reduced by a regulatory deduction in the amount of 20% of the amount of remuneration in accordance with Part 7 of Article 8 of the Federal Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ. Based on clause 2 of part 3 of Article 9 of the Federal Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ, contributions to the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation from remunerations of authors who are not employees of the customer organization are not accrued |
| Accounting entries at the time the software application is accepted onto the balance sheet | |||
| 1 | 04 | 08-5 | The software application for mobile devices is included in the intangible assets of the organization |
| Accounting entries when withholding personal income tax (NDFL) | |||
| 1 | 76 | 68 subaccount “Calculations for personal income tax” | Personal income tax (NDFL) has been withheld from the amount of royalties, taking into account a professional tax deduction in the amount of 20% of accrued income in accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 221 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Accounting entries when transferring funds to the author of the software application | |||
| 1 | 76 | 51 | Reflected payment for the software product |
| Accounting entries when calculating depreciation. Sales of software is the main activity of the organization | |||
| 1 | 20 | 05 | Reflects the monthly amount of depreciation charges |
| Accounting entries when reflecting revenue for the implemented software application for mobile device users. The sale of licenses for software applications for mobile devices is carried out by a payment agent, which is a cellular operator. Mobile device users pay for the software application by sending a paid SMS message. Sending a paid SMS message means acceptance of the terms of the license agreement by mobile device users | |||
| 1 | 62, 76 | 90-1 | Reflected (accrued) revenue from the sale of a software application to mobile device users for the current (reporting) period based on the payment agent’s report, taking into account all taxes |
| 2 | 90-3 | 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” | Debt to the budget for VAT on turnover was accrued for the implementation of a software application for mobile devices |
| Accounting entries upon receipt of funds | |||
| 1 | 51 | 62, 76 | Proceeds from the sale of a software application for mobile devices are listed |
Reflection in accounting of transactions for the acquisition of non-exclusive rights to use software products under license agreements.
| № | Debit | Credit | Contents of operation |
| Accounting entries when reflecting expenses associated with the acquisition of software products | |||
| 1 | 97 | 60, 76 | The cost excluding VAT of the purchased licensed copy of a computer program is reflected (without transfer of exclusive rights). The head of the organization has established the useful life of the purchased software product |
| 2 | 19 | 60, 76 | VAT is taken into account (accrued) when acquiring non-exclusive rights to use a computer program |
| 3 | 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” | 19 | Accepted for deduction from the VAT budget |
| Accounting entries when reflecting expenses associated with the installation and configuration of a purchased computer program by a third party | |||
| 1 | 20, 26, 44, etc. | 60, 76 | A one-time payment for installation, configuration and visit of a third-party specialist is reflected as part of expenses for ordinary activities |
| 2 | 19 | 60, 76 | VAT is charged on the cost of services provided by a third party |
| 3 | 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” | 19 | Accepted for deduction from the VAT budget |
| Accounting entries for the monthly reflection of expenses associated with subscription services for a purchased computer program by a third party | |||
| 1 | 20, 26, 44, etc. | 60, 76 | Monthly payment for subscription services for the program by a third party is reflected as part of expenses for ordinary activities |
| 2 | 19 | 60, 76 | VAT is charged on the cost of services provided by a third party |
| 3 | 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” | 19 | Accepted for deduction from the VAT budget |
| Accounting entries when transferring funds | |||
| 1 | 60, 76 | 51 | Reflected payment for the software product |
| 2 | 60, 76 | 51 | Payment for third-party services for installation and configuration of the purchased software product is reflected. |
| 3 | 60, 76 | 51 | Reflects monthly payment for third party services for subscription services of the purchased software product |
| Accounting entries when paying off expenses associated with the purchase of software products | |||
| 1 | 20, 26, 44, etc. | 97 | The cost of a computer program over its useful life is written off evenly as production costs (selling expenses) (monthly from the start of using the software product) |
Reflection in accounting of transactions for the acquisition of non-exclusive rights to use software products - reference and information databases. The buyer makes an advance payment to the software seller.
| № | Debit | Credit | Contents of operation |
| Accounting entries when issuing advance payment to the seller | |||
| 1 | 60 subaccount “Settlements for advances issued” | 51 | Accrued receivables to the seller for advances (prepayments) issued for the upcoming purchase of a licensed copy of the reference and information database |
| 2 | 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” | 76 subaccount “VAT on advances issued” | Accepted for deduction of VAT on advance payment (prepayment) issued to the seller |
| Accounting entries when reflecting expenses associated with the acquisition of software products - reference and information databases | |||
| 1 | 20, 26, 44, etc. | 60 subaccount “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” | The cost, excluding VAT, of an acquired licensed copy of a computer program (without transfer of exclusive rights) - a reference and information database - is reflected. The cost of the database is written off as a lump sum to production costs (selling expenses) |
| 2 | 19 | 60 subaccount “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” | VAT was taken into account (accrued) when acquiring non-exclusive rights to use the reference and information database |
| 3 | 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” | 19 | Accepted for deduction from the VAT budget |
| Accounting entries when reflecting the offset of an advance payment (prepayment) issued to the seller | |||
| 1 | 60 subaccount “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” | 60 subaccount “Settlements for advances issued” | The amount of debt to the seller for the licensed copy of the reference and information database purchased from him was repaid by offsetting the advance amount |
| 2 | 76 subaccount “VAT on advances issued” | 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” | Restored by reverse entry of VAT payable to the budget, previously claimed for deduction on an advance payment issued or |
| 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” | 76 subaccount “VAT on advances issued” | VAT payable to the budget, previously claimed for deduction on an advance payment (prepayment), has been reversed. | |
Reflection in accounting of the fact of acquisition (purchase) of a licensed copy of a computer program for production (including VAT) purposes through accountable persons.
| № | Debit | Credit | Contents of operation |
| Accounting entries at the time of issuing money for reporting | |||
| 1 | 71 | 50 | Advance payment of funds for the purchase of a software product is reflected |
| Accounting entries when reflecting expenses associated with the acquisition of software products | |||
| 1 | 97 | 76 | The cost excluding VAT of the purchased licensed copy of a computer program is reflected (without transfer of exclusive rights). The head of the organization has established the useful life of the purchased software product |
| 2 | 19 | 76 | VAT is taken into account (accrued) when acquiring non-exclusive rights to use a computer program |
| 3 | 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” | 19 | Accepted for deduction from the VAT budget |
| Accounting entries when paying for a software product to the seller | |||
| 1 | 76 | 71 | The amount of expenses incurred for the purchase of a software product was written off for settlements with accountable persons |
| Accounting entries when paying off expenses | |||
| 1 | 20, 26, 44, etc. | 97 | The cost of a computer program over its useful life is written off evenly as production costs (selling expenses) (monthly from the start of using the software product) |
Reflection in accounting of the creation of software by the organization's own resources.
| № | Debit | Credit | Contents of operation |
| Accounting entries when reflecting the costs of creating a computer program | |||
| 1 | 08-5 | 02 subaccount “Depreciation of fixed assets accounted for on account 01” | Reflects depreciation of fixed assets used to create a computer program |
| 2 | 08-5 | 05 | Depreciation of intangible assets used to create a computer program is reflected |
| 3 | 08-5 | 10 | The cost of the materials used is reflected |
| 4 | 08-5 | 70, 69 | Reflects the accrued amount of wages and contributions from the accrued wages of programmers involved in creating a computer program |
| Accounting entries when including a computer program in the intangible assets of an organization | |||
| 1 | 04 | 08-5 | The computer program is included in the intangible assets of the organization. The software product is intended to be used for production purposes of the enterprise |
| Accounting entries when calculating depreciation | |||
| 1 | 20, 26, 44, etc. | 05 | Reflects the monthly amount of depreciation charges |
Reflection in accounting of the organization's expenses for creating its own page on the Internet when obtaining exclusive rights to the site.
| № | Debit | Credit | Contents of operation |
| Accounting entries when reflecting the costs of creating a website by a third-party contractor | |||
| 1 | 08-5 | 60, 76 | The costs of developing a website are reflected without VAT as part of the costs of creating an intangible asset. |
| 2 | 19-2 | 60, 76 | The amount of VAT on website development costs is reflected |
| Accounting entries when reflecting the costs of creating a website by employees of the organization in the performance of their official duties | |||
| 1 | 08-5 | 70, 69 | The accrued amount of wages and contributions from the accrued wages of employees involved in the development of the website (intangible asset) is reflected. |
| 2 | 08-5 | 02 subaccount “Depreciation of fixed assets accounted for on account 01” | The amount of depreciation of a fixed asset item is reflected as part of the costs of creating an intangible asset item |
| 3 | 08-5 | 10 | The materials used to create the website (intangible asset) have been written off. |
| Accounting entries when reflecting expenses for the initial registration of a domain name | |||
| 1 | 08-5 | 60, 76 | Costs for registering a domain name without VAT are reflected as part of the costs of creating an intangible asset object |
| 2 | 19-2 | 60, 76 | The amount of VAT on the costs of registering a domain name is reflected |
| Accounting entries when reflecting expenses associated with hosting a website on the Internet (hosting services) | |||
| 1 | 08-5 | 60, 76 | The costs of providing hosting services without VAT are reflected as part of the costs of creating an intangible asset object |
| 2 | 19-2 | 60, 76 | The amount of VAT on the costs of providing hosting services is reflected |
| Accounting entries when putting the site into operation | |||
| 1 | 04 | 08-5 | The site was put into operation as an object of intangible assets |
| 2 | 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” | 19-2 | Accepted for deduction from the budget of VAT on the object of intangible assets |
| Accounting entries when transferring funds | |||
| 1 | 60, 76 | 51 | Paid for website development |
| 2 | 60, 76 | 51 | Paid domain name registration |
| 3 | 60, 76 | 51 | Remuneration under the contract was transferred to the host provider |
| Accounting entries when paying off expenses | |||
| 1 | 20, 26, 44 | 05 | Reflects monthly depreciation on the site |
Continued >>
Postings in commercial structures
Operations where a commercial institution acquires the exclusive right to use a new program must be recorded in accounting by a set of correspondence:
- By the date of acquisition, to reflect the amount of expenses incurred, a transaction is generated between D08.5 and K60.
- At the moment when the program is installed and you can start using it, a record is created for the cost of the software with D04 and K08.5.
- Every month, when depreciation amounts are calculated, account 20 (or 26, 44) is debited while account 05 is credited.
If the program was purchased at a cost not exceeding 40 thousand rubles, then the accountant draws up the following set of transactions:
- When purchasing software, expenses are taken into account through correspondence D08.5 - K60.
- When the program is put into operation, account 04 is debited and account 08.5 is credited.
- The full cost of the software in tax accounting is immediately transferred to the enterprise’s expenses by entry between D20 (or 23, 26, 25, 44) and K04.
- Depreciation will be calculated in accounting; correspondence D20 (or 23, 26, 25, 44) - K05 is intended for this.
If an institution purchased the software and received non-exclusive rights to it, then:
- when making a one-time payment at the time of purchasing the software, account 97 is debited, account 60 is recorded as a credit;
- the software license is accounted for as a debit turnover in off-balance sheet account 012;
- Every month, part of the costs incurred is transferred to the expenses of the upcoming periods by posting D20 (or 23, 26, 25, 44) - K97.
IMPORTANT NUANCE! It is legally prohibited to use illegal versions of software. The use of pirated programs in work is punishable by civil and criminal law in Art. 1252 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and Art. 146 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
When carrying out the procedure for updating a software product or performing specialized maintenance, the money spent on this is shown in debit 20 (25, 23, 44, 26) and credit 60 of the account.
How are exclusive rights to software developed in-house reflected in accounting?
Write-off of costs for acquiring non-exclusive rights to software
Non-exclusive rights acquired under a license agreement are not recognized as intangible assets, and the costs incurred are taken into account in expenses for ordinary activities. The license to use the software is reflected on the balance sheet of the acquirer (for example, on account 012) in the valuation specified in the license agreement. After putting the software into operation, the costs of its acquisition are subject to write-off, the procedure for which is established by the company and enshrined in the accounting policy for accounting purposes. For example, the cost of purchasing software is reflected in the structure:
- expenses of future periods, if a fixed amount is established for using the software, paid at a time. The company can write off such payment evenly over the period of validity of the license;
- in current costs, if periodic payments are expected to be made for using the program in each reporting period.
In accounting, the acquisition of software and the write-off of costs for its acquisition are recorded using the following entries:
| Operations | D/t | K/t |
| When accounting for RBP: A one-time payment is included in deferred expenses for the purchase of software | 97 | 60 (76) |
| Part of the costs was written off in the reporting period | 20 (23, 25, 26, 44) | 97 |
| When taken into account in current costs: Periodic payments are reflected in the current costs of the reporting period | 20 (23, 25, 26, 44) | 60 (76) |