Currency legislation and cash transactions: understanding the terms
The situation when a merchant may have foreign currency in his cash register is rare.
The thing is that payments in foreign currency between Russian organizations are prohibited (Clause 1, Article 9 of the Law “On Currency Regulation and Currency Control” dated December 10, 2003 No. 173-FZ). For example, if a Russian pays for a purchased product with Russian rubles, not rubles, or dollars or another currency, she will break the law. The punishment for this is provided for in Art. 15.25 Code of Administrative Offences. Read more about liability for violation of currency laws in the material “What is the liability for illegal currency transactions.”
The term “currency transactions” is contained in subsection. 9 clause 1 art. 1 of Law No. 173-FZ and includes the acquisition and alienation of currency values, the import and export of currency, etc. And the concept of cash transactions is given in paragraph 2 of the instruction of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated March 11, 2014 No. 3210-U on the procedure for conducting cash transactions and stands for cash acceptance, recalculation and issuance.
There are very few situations when the terms “currency” and “cash” transactions are used together. This is due to the fact that the bulk of foreign exchange payments, according to Law No. 173-FZ, must be carried out in non-cash form. Individual cases when currency does end up in the company's cash register are stipulated in the same law. These, for example, include the case of issuing currency from the cash register to an employee for a business trip abroad (subclause 9, clause 1, article 9 of Law No. 173-FZ).
Let us dwell in more detail on the procedure for accounting for cash transactions in foreign currency for this case.
Accounting nuances
In the Russian Federation, the main accounting currency is the domestic ruble .
Accounting for property, liabilities and business transactions is carried out in rubles. It does not matter the type of currency that was actually used in any transaction. To correctly reflect in accounting a business transaction that was not carried out in Russian currency, it is necessary to correctly calculate the amount of this transaction in rubles. This can be done step by step by following these steps:
- Set the posting (recalculation) time.
- Find out the official exchange rate of the Bank of Russia at the time of making the transaction.
- Multiply the currency amount by the official exchange rate.
- Calculate the difference in exchange rates.
The most popular source of foreign currency entering the company's cash desk is the receipt of foreign cash from an account at the relevant banking institution. It is worth noting that foreign cash can only be used to pay travel expenses for your employees .
You can find out detailed information about cash transactions and the latest changes from the following video:
Currency cash transaction: we issue currency for a business trip
In order to issue an employee with currency to pay for travel expenses, the company must have a foreign exchange office, enter into a financial liability agreement with the cashier, and follow the procedure for conducting cash transactions.
In 2022, when conducting cash transactions, it is necessary to adhere to the procedure established by the instruction of the Bank of Russia dated March 11, 2014 No. 3210-U.
NOTE! From November 30, 2020, the rules for conducting cash transactions were changed by the Central Bank's instruction dated October 5, 2020 No. 5587-U. For example, in an application for the issuance of accountable money, it is not necessary to indicate the amount of the advance and the period for which accountable amounts are issued. The organization sets the deadline independently. The requirement to submit an advance report within three days has been removed. Employers were also allowed to issue one order for several cash payments to one or more employees. In this case, you need to indicate the name, amount and period for which the money is issued for each employee.
ConsultantPlus experts told us what other innovations in the procedure for recording cash transactions came into effect on November 30, 2020. Get trial access to the K+ system and go to the review material for free.
For more information about who can now check the cash register and what sanctions exist for violating cash regulations, see the material “Are your cash discipline in order?”
Usually, foreign currency is not stored at the cash desk, so you need to buy it first. If the company has a foreign currency account, the purchase will be made cashless through the servicing bank. To receive foreign currency, the company will have to fill out an application in the form proposed by the bank or a letter of any type in which to indicate the following information (paragraph 3 of clause 2.1 of Chapter 2 of the Bank of Russia Directive No. 2054-U dated August 14, 2008 on conducting cash transactions with cash foreign currency in banks):
- Company name;
- date of receipt of currency;
- bank account details;
- information about the recipient (full name, passport details);
- amount and name of currency.
The letter must also indicate the date of its preparation and put a stamp; it must be signed by persons entitled to the first and (if any) second signature.
Accounting for cash transactions in foreign currency: step-by-step instructions for the receipt of currency at the cash desk
A company or any other enterprise has the right to receive cash in foreign currency at the cash desk only in cases permitted by law. This happens under the following conditions:
- withdrawing money from an account in foreign currency at an authorized banking institution for the purpose of issuing travel allowances to employees traveling outside the Russian Federation;
- return of the possible balance of unused foreign currency by the employee after returning from the trip.
The process is described as follows:
| Steps | Description |
| 1. | An order is being drawn up from the manager to send a company employee on a business trip outside the Russian Federation |
| 2. | The document is sent to the accounting department |
| 3. | An accounting employee calculates the amount of business trip expenses |
| 4. | A letter issued by the company is provided to the authorized bank. It is drawn up in any form or according to a model developed by a credit institution |
| 5. | Receiving the ordered amount at the bank cash desk (currency) |
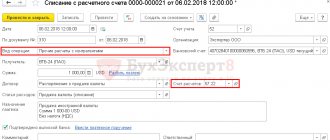
| 6. | The foreign currency arrives at the enterprise's cash desk and is recorded in a receipt order at the current exchange rate on the day of receipt. |
| 7. | Currency units are issued to an employee using a cash receipt order (RKO) |
Important! Amounts of money in cash orders are also recorded in currency. e., and in RUB . The latter are subject to recalculation at the rate of the Bank of the Russian Federation, current at the time of issue of foreign currency or its receipt.
How to arrange the issuance of currency and is it possible to make this work easier?
In accounting, the purchase and issue of currency described above will be reflected as follows:
- funds were transferred for the purchase of currency (Dt 57 Kt 51);
- currency was credited to the company's account (Dt 52 Kt 57);
- currency was capitalized in the cash register (Dt 50 “Currency cash desk” Kt 52);
- currency was issued to an employee for a business trip abroad (Dt 71 Kt 50).
For more information on how to correctly reflect currency transactions in accounting, see the material “Accounting for currency transactions (PBU, transactions)”
The issuance of currency from the cash register is carried out upon a written application from the employee or by order of the head of the company (clause 6.2 of the procedure, approved by instruction No. 3210-U) and is drawn up with an expenditure cash order (clauses 4–6 of this procedure), as well as entries in the cash book (two amounts: in foreign currency and in rubles at the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of the transaction).
You can avoid unnecessary hassle associated with foreign currency cash transactions when sending an employee on a business trip abroad. For example, issue an advance from the cash register in rubles, and the employee himself will purchase the necessary currency at the exchange office. Or the required amount in rubles can be transferred to the employee’s bank card - this situation is discussed in the letter of the Ministry of Finance dated July 17, 2015 No. 03-03-06/41128.
Cash assets of enterprises in foreign currency
The funds of enterprises in foreign currency include:
Are you an expert in this subject area? We invite you to become the author of the Directory Working Conditions
- cash in foreign currency at the cash desk, reflected in account 50 “Cashier”;
- company funds in foreign currency accounts opened with banks and accounted for in account 52 “Currency accounts”;
- company funds in foreign currency, in letters of credit, deposits, check books, etc., reflected in account 55 “Special accounts in banks”, in a separate sub-account;
- funds in foreign currency intended for crediting to bank accounts, but at the reporting date not credited for their intended purpose, reflected in account 57 “Transfers in transit”.
In the Russian Federation, the main accounting currency is the Russian ruble. Accordingly, accounting for the obligations, property and business transactions of the enterprise is carried out in rubles. This does not depend on the type of currency that is actually used in the transactions.
To correctly reflect business transactions carried out in foreign currency in accounting, it is necessary to determine the ruble equivalent of the transaction. This requires a sequential algorithm of actions:
Finished works on a similar topic
Course work Features of accounting for cash transactions in foreign currency 430 ₽ Abstract Features of accounting for cash transactions in foreign currency 240 ₽ Test paper Features of accounting for cash transactions in foreign currency 230 ₽
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
- determine the calendar date of the operation and recalculation;
- clarify the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation as of the date of operation and recalculation;
- multiply the amount in a currency by the exchange rate of that currency according to the Central Bank of the Russian Federation;
- determine the amount of the exchange rate difference when recalculating.
Note 1
The source of receipt of funds in foreign currency at the organization's cash desk may be the withdrawal of foreign cash from a current bank account. It should be noted that foreign cash can only be used to pay for travel expenses of employees.
Acceptance of currency by the organization's cash desk, as well as its issuance from the cash desk, is carried out similarly to ruble amounts. The absence of entries in the cash book about foreign currency accepted into the cash register may be regarded as non-receipt of cash to the cash register. Which may lead to the imposition of penalties on the organization.
To record transactions with cash foreign currency, a separate cash book is not opened, since according to the procedure for conducting cash transactions in Russia, each enterprise must maintain one cash book.
a practice report on this topic
The cashier must keep analytical records for each type of foreign currency that is in the cash register. Accounting for currency transactions and valuables, as well as accounting for ruble transactions, is carried out in the same system of accounts. But it is more expedient to take into account payments in the currencies of other countries separately, in separate sub-accounts. Since there is no separate account for accounting for the expenditure and receipt of currency, a separate sub-account “Cashier in foreign currency” is opened for account 50 “Cashier”. In these sub-accounts, the records must contain information about the exchange rate used to calculate the ruble equivalent of the transactions reflected in these records.
Rubles are not the only monetary unit used in the Russian accounting system. Synchronously with entries in rubles, amounts on foreign currency accounts and transactions in foreign currency are reflected in the currency of mutual settlements at par. For this purpose, different ways of organizing records are used: second copies of accounting registers, recording data in fractions, including additional indicators.
During the period that foreign currency is in the organization’s cash desk, the exchange rate established by the Central Bank may change. As a result, exchange rate differences arise. Accordingly, entries made in the cash book for the receipt and expenditure of funds in foreign currency at different rates will give a discrepancy in the ruble balance according to the cash book and the actual cash balance in the cash register. Therefore, additional entries are made in the cash book to reflect exchange rate differences.
According to clause 7 of PBU3/2000, the value of foreign currency is recalculated into rubles on the date of the transaction or on the date of formation of the financial statements. The company prepares interim financial statements on an accrual basis from the beginning of the reporting year for the month, quarter, etc. In addition, the value of the balance of money in the organization’s cash register can also be recalculated as the exchange rate changes, according to quotes from the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. The method of recalculation is reflected in the accounting policy of the enterprise.
If a company rarely carries out cash transactions, then it is more advisable to take into account exchange rate differences as of the reporting date. Otherwise, you will have to recalculate the currency daily and fill out new sheets of the cash book. With daily movement of money in the cash register, it is better to recalculate as the exchange rate changes.
The reflection of exchange rate differences does not constitute the expenditure or receipt of cash foreign currency. This is just a change in its ruble equivalent depending on the fall or rise of the exchange rate against the Russian ruble. Therefore, such operations are formalized using memorial orders, and not with receipt or expenditure cash documents.
Results
Accounting for cash transactions in foreign currency is generally similar to ruble accounting. At the same time, you also need to comply with cash procedures (issue cash orders, make entries in the cash book, etc.). To issue currency, you need a foreign exchange office, and in accounting you need to use a separate subaccount to account 50 “Cashier”.
A non-cash transfer to the employee’s card of the amount required for a business trip in rubles can help avoid unnecessary hassle in accounting and organizing cash currency transactions.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Documentation on currency turnover
The organization's cash book is kept in a single copy. Each operation with e. is reflected in it in two amounts: in RUB (Central Bank quote) and in the corresponding foreign currency. Accordingly, daily totals in the ledger are recorded in the same two amounts.
The cashier must make all necessary records. Their absence relative to accepted (and issued) y. e. is regarded as a violation of cash discipline, which is fraught with penalties.
The cash register of any enterprise has a turnover of That is, it is no different from the turnover of the ruble mass.
Analytical records are kept for each type of foreign currency passing through the cash desk. The system of accounts generally accepted in the Russian Federation (Plan) of accounts is used. But it is reasonable to consider calculations in foreign currency separately:
- open subaccounts (special);
- include in the accounts on them the exchange rate used for conversion into the equivalent in rubles.
In addition to the cash book (form KO-4), the generally accepted order forms KO-1 and KO-2 are used. They must be registered in a special journal (form KO-3).
Postings in foreign currency
Company cash desks accept and issue currency in the same way as rubles. If there is no entry in the unified cash book about the foreign currency received, this may be regarded as non-receipt of cash to the cash register, therefore, fines will be imposed on the company.
The cashier is required to perform analytical accounting for any type of currency that is available in the cash register. Accounting for currency transactions and valuables is carried out using the same accounting system as accounting for ruble transactions and valuables.
It is recommended that transactions in foreign currency be taken into account separately, in special open sub-accounts.
In addition to standard entries, subaccount data must contain the exchange rate , which is used to calculate the equivalent in rubles of transactions associated with the operation.
Transactions in foreign currency must be reflected in accounting. To do this, you can resort to a variety of recording methods:
- Second set of accounting registers.
- Writing information in fractions.
- Creation of auxiliary indicators in document form.
During the time that the foreign currency remains in the company’s cash register, the exchange rate that was established by the Bank of Russia can change. In this case, exchange rate differences arise. When entries in the cash book for the receipt and expenditure of the same amount are created at different rates, the balance in rubles will be incorrect, not corresponding to the actual balance of money in the cash register. This is precisely why it is necessary to make auxiliary entries in the cash book that relate to the reflection of exchange rate differences.
The value of foreign currency in rubles is calculated either at the time of the posting or at the date of creation of the accounting report. Remember that the company is required to prepare interim financial statements every thirty days. In addition, the value of the money remaining in the cash register can be calculated as the exchange rate changes. What to choose is up to the organization to decide.
How to fill out a journal for registering incoming and outgoing cash documents - see this article. How to correctly draw up an order for the appointment of a chief accountant - read here.