For accounting purposes, balance sheet and off-balance sheet accounts are provided. The first ones are maintained to reflect cash and non-cash money, borrowed funds, settlements, income and expenses, profits and losses.
Off-balance sheet accounts in budgetary institutions are opened to account for:
- material assets (MT), which are not their property, but are in temporary use (for example, fixed assets rented or free of charge; objects taken for processing or for safekeeping, etc.);
- BSO, vouchers to sanatoriums, holiday homes;
- obligations awaiting fulfillment.
Off-balance sheet accounts in the budget: general provisions
Budgetary accounting of MCs on the balance sheet is carried out in a simple way: receipts are subject to reflection on the debit side of the accounts, disposals - on the credit side. Corresponding records are not used when using them. Budgetary organizations can open additional off-balance sheet accounts to collect information necessary for management accounting and internal control over the safety of property.
Accounting for property assets on the balance sheet is carried out using the same primary documents and registers that are used in accounting for MC on the balance sheet. Inventory of off-balance sheet funds is carried out in the same way as for objects on balance sheet accounts.
Off-balance sheet accounting
To record assets and liabilities on the balance sheet, accounts 001 to 011 are intended (order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n):
- on account 001 reflects leased assets;
- sch. 002 is intended for accounting for inventory items accepted for storage;
- sch. 003 is used to account for materials taken for processing;
- on account 004 reflects goods accepted for commission;
- sch. 005 is used to account for equipment for installation;
- sch. 006 is needed for BSO accounting;
- on account 007 accounts for uncollectible receivables;
Find out step by step how to write off receivables with an expired statute of limitations in ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the system, sign up for a trial demo access. It's free.
How to take it off balance sheet, read the article “Writing off accounts receivable to an off-balance sheet account.”
- sch. 008 and 009 are needed to reflect received and issued payment security, for example, deposit amounts for returnable packaging;
- sch. 010 is used to reflect the depreciation of housing facilities, external amenities, as well as fixed assets of non-profit organizations;
- sch. 011 contains information about operating systems owned by the organization, but leased to another company.
If necessary, an organization can develop and implement additional off-balance sheet accounts or sub-accounts to existing ones. These innovations should be reflected in the working chart of accounts of the organization's accounting policies.
What are the specifics of off-balance sheet accounting? Transactions using off-balance sheet accounts are carried out using a simple system, without the use of double entry. That is, one business transaction corresponds to an entry only in the debit or credit of one off-balance sheet account. However, just like assets and liabilities reflected on balance sheet accounts, transactions with off-balance sheet assets or liabilities must be reasonable and documented.
Find out more about off-balance sheet accounting in the material “Rules for maintaining accounting on off-balance sheet accounts.”
Information about assets and liabilities held in off-balance sheet accounts does not fall into the main accounting report - the balance sheet (Appendix 1 to the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n). But the company may, at its discretion, indicate information about objects recorded on off-balance sheet accounts in an explanatory note to the accounting records (Appendix 1 to Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n).
IMPORTANT! A legal entity is required to maintain off-balance sheet accounting, since the reflection of certain business operations and values using off-balance sheet accounts meets the requirements for the reliability of reporting. If you ignore off-balance sheet accounting, the reporting will cease to be reliable, and this is a violation of Art. 15.11 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. The minimum fine in this case is 5,000 rubles. But an individual entrepreneur is not required to keep accounting records (Clause 2, Article 6 of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ). If an individual entrepreneur decides to conduct accounting on his own initiative, then he should adhere to the appropriate accounting rules, including, if necessary, reflecting values and liabilities on the balance sheet.
The safety of property and the status of liabilities on the balance sheet must also be periodically checked. How to do this - read the article “Is it possible to carry out an inventory for off-balance sheet accounts?”
Off-balance sheet account 01 in budget accounting
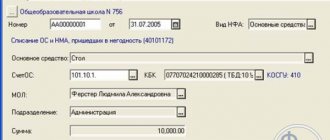
Used to account for fixed assets (fixed assets) received under lease agreements or free of charge with the right to operate without being assigned to operational management.
Let's look at a practical example.
For the celebration, the cultural institution rented costumes. According to the contract, the lessor gave 5 suits for two-month use. The rent amount was 12,500 rubles. After the holiday, the costumes were returned. Off-balance sheet account 01 was used in accounting:
- property objects were received for rent - Dt 01 (RUB 12,500);
- the leased property was returned - Kt 01 (RUB 12,500).
The basis for the operations was the lease agreement and the acceptance certificate.
Off-balance sheet account 04 in a budget institution
Budgetary organizations can write off debts recognized as unrealistic for collection, reflecting them on the balance sheet. To account for this type of debt, off-balance sheet account 04 written off debt of insolvent debtors is used (clause 339 of Instruction No. 157n). It is necessary to monitor the possibility of debt repayment. If collection resumes or funds are received to repay the debt, the debt is written off.
Let's look at a practical example.
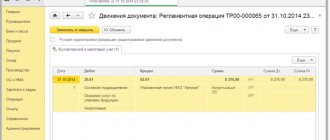
Limitation period for debt in the amount of RUB 4,570. expires on November 25, 2017. By order of the director, it must be written off on the basis of documents confirming the recognition of the debtor as insolvent. The following entries must be made in accounting using off-balance sheet account 04:
- write-off of debt recognized as unrealistic for collection - Dt 2,401 20,273 Kt 2,206 31,000 (RUB 4,570);
- simultaneously accounting for debt on the balance sheet - Dt 04 (RUB 4,570);
- account closure – Dt 2,401 30,000 Kt 2,401 20,273 (RUB 4,570).
Let’s say that in December 2022, the debtor returned the money given to him in advance for the supply of materials. The debt should be restored as follows:
- restoration of debt on accounts – Dt 2,401 20,273 Kt 2,206 31,000 (RUB 4,570);
- simultaneously writing off debt – Kt 04 (RUB 4,570)
Accounting for receivables and payables
To account for receivables and payables on the off-balance sheet, two accounts are provided: account 04 “Debt of insolvent debtors” and account 20 “Debt unclaimed by creditors”.
Debt is reflected in accounting at the moment when the commission for the receipt and disposal of assets makes a decision to write it off from the balance sheet.
Debt accounting is maintained in the card for accounting for funds and settlements:
- by type of revenue and debtor for accounts receivable;
- by types of payments and receipts and by creditors for accounts payable.
From account 04, the debt is written off by decision of the commission (in the event of death or liquidation of the debtor), when the debt collection procedure is resumed, or if money has been deposited into the account to repay the debt.
Off-balance sheet account 07 in budget accounting
It records two types of MCs:
- prizes, cups, banners intended to reward the winners throughout the entire period of their stay in the budget organization according to conditional assessment;
- souvenirs and valuable gifts at the cost of their acquisition.
Let's look at a practical example.
The sports institution purchased valuable gifts to be used as prizes for competition winners for RUB 26,500. Based on the results of the competition, the athletes received gifts. Transactions on their purchase and delivery should be reflected as follows:
- acquisition costs – Dt 4,401 10,290 Kt 4,302 29,000 (RUB 26,500);
- cost of valuables on the balance sheet – Dt 07 (RUB 26,500);
- payment for purchased MCs for gifts – Dt 4,302 29,000 Kt 4,201 11,000 (RUB 26,500);
- debiting donated prizes from the off-balance account – Kt 07 (RUB 26,500).
Off-balance sheet account 21
It is used when calculating fixed assets with a value not exceeding 3,000 rubles, except for real estate and library objects (clause 373 of Instruction No. 157n).
Fixed assets on an off-balance sheet account in the budget are taken into account according to the primary document, which confirms their entry at a conditional valuation or at book value, depending on the procedure provided for by the accounting policy of the budget organization.
The movement within the institution of fixed assets on off-balance sheet accounts is shown according to the primary documentation. For these purposes, the financially responsible person and (or) warehouse is changed.
Disposal of fixed assets is carried out according to an acceptance certificate or a write-off act at the cost of accepting them for off-balance sheet accounting.
Types of personal accounts
The following types of personal accounts can be opened for an institution at the territorial body of the Federal Treasury:
20 — designed to account for transactions with funds from budgetary institutions. This account reflects transactions with funds from subsidies received for the implementation of a state task (with the exception of subsidies for other purposes, capital investments), funds received from business activities, income from leasing property, as well as funds received to secure an application for participation in procurement and contract execution;
21 — a separate personal account of a budgetary institution intended to record transactions with subsidies for other purposes and capital investments (Articles 78.1, 78.2 of the Budget Code of the Russian Federation);
22 — a personal account of a budgetary institution intended to record transactions with compulsory medical insurance funds.
In the Federal Treasury Authority, to carry out operations for the health care institution FFBUZ “Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the Kirovsky District” of the city of Yekaterinburg, a single personal account has been opened for the receipt and expenditure of funds, to which are credited:
- subsidies for the implementation of government tasks (budget allocations);
- income received from other income-generating activities.
The institution is also engaged in entrepreneurial activities (providing sanitary and epidemiological services on a paid basis to legal entities and individuals, individual entrepreneurs, having concluded agreements with them).
To separately account for cash flows from different sources of financing and reflect transactions in accounting by type of activity, the type of financial security code (KFO) is used.
The procedure for accounting for subsidies is determined by the Instructions for the application of the Unified Chart of Accounts for public authorities (state bodies), local governments, management bodies of state extra-budgetary funds, state academies of sciences, state (municipal) institutions, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n (as amended on August 6, 2015; hereinafter referred to as Instruction No. 157n). In accordance with it, the code for the type of financial support for activities 4 (KFO 4) “Subsidies for the implementation of a state task” should be used.
For entrepreneurial activities, the code for the type of financial support for activity 2 (KFO 2) “Income from the provision of paid services” is used.
Off-balance sheet account 22
Used when MC is received from the supplier before receiving notification and photocopies of documentation for them. The received property can be used only with the permission of the authorized executive body, GRBS.
Budgetary institutions also use other off-balance sheet budget accounting accounts: 2-6, 8, 11-16.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Accounting for financial investments
- Account 31 “Shares at par value”. Accounting is maintained by a body with the powers of a shareholder or another authorized body. Shares are placed on off-balance sheet accounting simultaneously with their reflection in account 204.30 “Shares and other forms of participation in capital.” Accounting is maintained in the securities register.
- Account 40 “Assets in management companies.” The off-balance sheet takes into account assets that are listed in account 204.51 “Assets in management companies.” The value of the property is adjusted at the reporting date. Accounting is carried out by groups and types of non-financial and financial assets.
- Account 42 “Budget investments implemented by organizations.” Acceptance for accounting occurs based on data on the transfer of funds or transfer of assets. Investments are written off from the balance sheet upon completion of work and commissioning of capital construction projects. Analytical accounting of the account is carried out by recipients of funds.