In what cases do foreign exchange transactions appear?
Currency transactions are difficult for an accountant if they are performed for the first time or not very often. The regulatory framework for performing such operations is quite extensive. Accountants should pay attention to Federal Law-173, PBU 3/2006 and Federal Law-402.
Currency transactions appear in the following cases:
- the use of currency values as means of payment in international circulation;
- conversion of money from one currency to another by individuals or legal entities;
- forwarding, importing, transporting currency values in the territory of the native country or abroad.
Entrepreneurs carry out currency transactions when importing and exporting goods, making international transfers, and performing cash and settlement transactions.
Purchasing currency
An organization has the right to purchase foreign currency only through an authorized bank (Article 11 of Law No. 173-FZ of December 10, 2003).
To purchase foreign currency, draw up a payment document (clause 3.1 of Bank of Russia Instruction No. 138-I dated June 4, 2012). A single form of payment document is not established by law. As a rule, banks have the necessary forms. In the payment document, before the text part in the “Purpose of payment” detail, indicate the type of transaction code from the list of currency and other transactions (clause 3.2 of Bank of Russia Instruction No. 138-I dated June 4, 2012). When purchasing currency, indicate the currency transaction code 01 030 (Appendix 2 to Bank of Russia Instruction No. 138-I dated June 4, 2012).
For information on purchasing foreign currency for an employee’s business trip, see How to record non-cash purchases of foreign currency for a business trip abroad.
To reflect the currency purchase transaction in accounting, you can use account 57 “Transfers in transit.” This is possible if the issuance of a payment document to the bank for the purchase of currency does not coincide with the date of its receipt in the foreign exchange account. However, if the debiting of rubles from the account, their sale and crediting of currency occur on the same day (this can be determined from bank statements), then account 57 need not be used.
When transferring rubles to purchase foreign currency, make the following entry:
Debit 57 (76) Credit 51 – money was transferred to purchase foreign currency.
Reflect the receipt of purchased currency to your current account as follows:
Debit 52 Credit 57 (76) – currency is credited to the foreign currency account (based on the bank statement).
Capitalize the received currency at the official rate in effect on the date the money is credited to the organization’s foreign currency account. In this case, make entries in the accounting registers both in the currency of settlements (rubles) and in the currency of payments.
This procedure follows from paragraphs 4–6, 20 PBU 3/2006, paragraph 24 of the Regulations on Accounting and Reporting and the Instructions for the Chart of Accounts (accounts 52, 57, 76).
The exchange rate at which the bank buys it usually differs from the official one. If the currency is purchased at a higher price than the Bank of Russia rate, another expense arises from the currency purchase operation (clause 11 of PBU 10/99). If cheaper - other income (clause 7 of PBU 9/99).
Most banks will have to pay a commission to purchase foreign currency. In accounting, include this amount as part of other expenses (paragraph 7, paragraph 11 of PBU 10/99).
An example of recording a foreign currency purchase transaction in accounting
Alpha LLC entered into a foreign trade contract. To execute it, Alpha needs US dollars. There is no money in the organization's foreign currency account. Therefore, on January 30, Alpha instructed the bank to purchase the necessary currency ($1,000). To do this, we drew up a settlement document and transferred 31,000 rubles to purchase foreign currency.
On February 2, the bank bought foreign currency at the rate of 30.50 rubles. per dollar and credited it to the organization’s foreign currency account minus a commission in the amount of 200 rubles.
The US dollar exchange rate on February 2 (conditionally) was 29.70 rubles. for a dollar.
The organization's accountant made the following entries in the accounting records.
January 30:
Debit 57 Credit 51 – 31,000 rub. – money is transferred to purchase foreign currency.
February 2:
Debit 52 Credit 57 – 29,700 rub. (1000 USD × 29.70 rubles/USD) – currency is credited to the organization’s foreign currency account;
Debit 91-2 Credit 57 – 200 rub. – commission fee is withheld by the bank;
Debit 91-2 Credit 57 – 800 rub. (1000 USD × (30.50 rubles/USD – 29.70 rubles/USD)) – reflects the difference between the currency purchase rate and the Bank of Russia rate;
Debit 51 Credit 57 – 300 rub. (31,000 rubles – 1000 USD × 30.50 rubles/USD – 200 rubles) – the balance of unspent money is returned.
Control of currency transactions in Russia
The execution of foreign exchange transactions in Russia is controlled by Law No. 173 Federal Law and regulations of government bodies. Currency transactions in Russia are controlled by:
- exchange control agents;
- currency control authorities.
Currency control agents include Russian financial companies, the state organization Vnesheconombank, fiscal authorities, brokers and dealers.
Currency control bodies - the Central Bank, the Government of the Russian Federation, executive authorities.
Banking institutions ensure that currency transactions strictly comply with the law. Bank employees have the right to request documents to confirm the legality of using currency assets or crediting money to the company account. The legality is confirmed by contracts, agreements on transactions, and other documents.
Registration of a foreign exchange transaction is carried out after submitting a package of documents. The company must report and provide all supporting documents to the bank branch.
Note! Foreign exchange transactions will be prohibited if the bank suspects something. They can refuse either due to the lack of necessary documents or if errors are identified in their preparation.
Opening a foreign currency account outside Russia
Residents of the Russian Federation open without restrictions accounts (deposits) in foreign currency and the currency of the Russian Federation in banks located outside the territory of the Russian Federation (Clause 1, Article 12 of the Law of December 10, 2003 No. 173-FZ “On Currency Regulation and Currency Control” ).
Exceptions are provided for by Law No. 79-FZ of May 7, 2013 “On the prohibition of certain categories of persons from opening and having accounts (deposits), storing cash and valuables in foreign banks located outside the territory of the Russian Federation, owning and (or) using foreign financial instruments." These are persons holding a number of government positions and their spouses and minor children.
The tax inspectorate must be notified of the opening (closing) of bank accounts outside the Russian Federation or changes in the details of foreign currency accounts. This must be done within a month according to the approved form (clause 2 of article 12 of Law No. 173-FZ). The format of the notification in electronic form was approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated November 14, 2013 No. ММВ-7-14/ [email protected] , the form of notification on paper was approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 21, 2010 No. ММВ-7-6/ [email protected] ]
For being late or submitting a notification in an unspecified form, a fine for the organization is provided in the amount of 50,000 to 100,000 rubles, for failure to submit a notification - in the amount of 800,000 to 1,000,000 rubles. For the same violations, fines are provided for officials in the amount of 5,000 to 10,000 rubles and from 40,000 to 50,000 rubles, respectively (clause 2, 2.1 of article 15.25 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
To open a foreign currency account outside Russia, you should familiarize yourself with the requirements of the bank of the country in which you want to open an account.
You can easily open an account in a country that is a member of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) or the Financial Action Task Force (FATF). In other cases, you will first have to register the fact of opening an account with your tax office.
Include the fee for opening a foreign currency account as part of other expenses:
DEBIT 91-2 CREDIT 51
– paid for the bank’s services for opening a foreign currency account.
What applies to foreign exchange transactions at the legislative level?
Currency transactions are defined by Law No. 173-FZ of December 10, 2003. Article 1 lists the basic terms and the concept of foreign exchange transactions. According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, foreign exchange transactions include:
- acquisition, alienation by a resident from a non-resident (or vice versa) of any currency, securities, their use for payment;
- purchase, alienation of currency values between residents (this can be a gift, purchase and sale, inheritance);
- import into Russia and export from Russia of securities, currency, including rubles;
- acquisition, alienation of securities and currency between non-residents;
- transfer of securities and currency from a Russian account to a foreign one or vice versa;
- transfer of Russian currency from Russia abroad or vice versa, making a transfer to a resident’s account or as to one’s own;
- transfer by a non-resident of currency or securities from a Russian account to a foreign one.
Residents are individuals with Russian citizenship or people who permanently reside in the Russian Federation. Residents include organizations and companies registered in Russia, foreigners with a residence permit, and consular missions of the Russian Federation located abroad.
Non-residents are foreigners, representative offices of foreign states, interstate and intergovernmental organizations (their branches) in Russia. Non-residents can be companies registered and operating in other countries.
Law No. 173 Federal Law establishes that there are no restrictions on currency transactions between non-residents and residents. Article 9 of this law establishes restrictions only on foreign exchange transactions for payments for goods that were purchased from a Russian company. Payment can be made in rubles.
What it is
Foreign funds cannot be placed together with rubles. To do this, create a separate account into which only currency, and one specific type, is placed. It is a mistake to believe that it can only be euros and dollars. There are other currencies that a significant number of banks work with. True, some financial institutions actually provide services in only two designated monetary units.
SEA BANK allows you to open a foreign currency account (dollar) for conducting foreign economic activity.
The available list of transactions, as well as the entire procedure for opening an account, is strictly regulated by federal laws. The Central Bank of the Russian Federation also takes part in lawmaking in this area.
Classification of foreign exchange transactions
Classification of currency transactions is carried out according to different criteria. The object includes transactions with rubles, foreign currency, foreign and Russian securities. Operations are classified by subject:
- between non-residents;
- between currency residents;
- between currency residents and non-residents.
Foreign exchange transactions are divided into groups according to the nature of the transaction:
- export-import operations;
- transactions on the client’s bank foreign currency account;
- foreign exchange trading;
- international lending;
- the country's acquisition of foreign currency.
There is another classification of currency transactions performed:
- by deadlines (current, capital, cash transactions with currency);
- active and passive operations (in accordance with accounting);
- operations performed by residents and non-residents;
- aimed at achieving different goals (performed in the entrepreneur’s own interests or in the interests of clients).
There are other types of foreign exchange transactions:
- such transactions that take place through a bank or cash desk;
- purchase of intangible assets, fixed assets, inventories for foreign currency;
- expenses and income in foreign currency;
- fixed assets.
A separate group includes currency conversion transactions, which are carried out for the purpose of exchanging one currency for another. In this case, the difference in rates at the time of the currency transaction must be taken into account. Exchange rates change every day. When converting foreign currency into rubles, an exchange rate difference is formed. Such exchange rate difference must be attributed to the company's expenses or income.
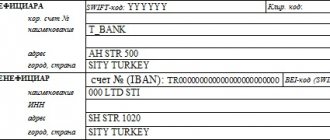
Sale of currency - postings in 1C 8.3 Accounting
Selling currency in 1C 8.3 Accounting example.
The balance in the foreign currency account at the end of January is 4,000 USD.
On February 6, the Organization submitted an application to the bank for the sale of currency in the amount of 1,000 USD.
On February 7, rubles received from the sale of foreign currency were credited to the current account.
Conditional rates of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for example:
- January 31—69.00 RUB/USD;
- February 06—RUB 63.00/USD;
- February 07 - 65.00 rub./USD, bank rate -64.00 rub./USD.
Selling foreign currency
In accordance with the Order on the sale of currency, the authorized bank buys currency from the Organization. Currency is purchased at the bank's internal commercial rate.
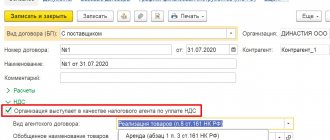
Fill out the sale of currency with the document Write-off from current account transaction type Other settlements with counterparties in the Bank and cash desk section - Bank - Bank statements - Write-off button.
Please indicate:
- Amount - 1,000 USD: currency amount sold.
- Settlement account — 57.22.
Selling currency in 1C 8.3 wiring example
Calculation of differences during revaluation:
Receipt of proceeds from the sale of foreign currency
Receipt of proceeds from the sale of foreign currency is reflected in the document Receipt to the current account transaction type Receipts from the sale of foreign currency in the Bank and cash desk - Bank - Bank statements section.
Please indicate:
- Amount is the ruble equivalent of the currency amount, calculated automatically after filling in . Amount (val.) : 1,000 USD x 64.0000 = 64,000 rubles;
- Settlement account — 57.22;
- Amount (val.) - 1,000 USD : amount in foreign currency sold to the bank;
- Settlement rate - 64 rubles/USD : bank rate when selling currency, set manually based on the bank statement;
- The exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation is set from the Currency .
Selling currency in 1C 8.3 Accounting transactions
Calculation of differences during revaluation:
Calculation of heading deviation differences:
Currency conversion in 1C 8.3 posting example:
- Currency transactions in 1C. Convert Euros to Dollars
- Convert Dollars to Euros
We looked at currency transactions in 1C 8.3 Accounting, how to reflect the purchase of currency in 1C 8.3 with transactions, how to reflect the sale of foreign currency in 1C 8.3 with transactions.
Test yourself! Take the test:
- Test. Purchasing currency
Current currency transactions
Current foreign exchange transactions include certain actions. For example, the following actions:
- issuing or receiving loans in foreign currency;
- transfers to the Russian Federation or from the home country of money in foreign currency for the purpose of import or export operations;
- transfers to Russia, from the country of interest and any payments related to the receipt of income;
- transfers of funds in the form of bonuses, wages, pensions and other payments;
- transfers of money for the purpose of purchasing non-property rights or property objects;
- investment carried out in the form of purchasing securities or acquiring shares in the capital of companies.
This is important to know! Transactions that are not on the list cannot be considered current currency transactions.
Features of foreign exchange transactions in the foreign exchange market
Not only companies, but also individuals and banking institutions can carry out currency transactions. Companies are allowed to use cash currency when their employees go on business trips (overseas).
The procedure for performing currency transactions has changed and simplified since July 1, 2016, because some provisions of Law No. 173-FZ have lost force.
The requirement to carry out operations aimed at purchasing foreign currency through authorized banking institutions remains valid. Such banks must have a license to carry out any currency transactions.
Individuals have the opportunity to carry out various foreign exchange transactions on the domestic market. Individuals buy currency for their own needs.
When carrying out transactions with currency, certain requirements for personal identification are established. There is no information in the law about restrictions on the amount of currency purchased.
Accounting, posting currency transactions
Participants in currency transactions must keep records of them. Information about such transactions is contained in account 52. The debit of the account for the last month takes into account all foreign exchange receipts, as well as non-cash currency balances at the beginning of the month.
The accountant keeps records separately for different types of currencies. Transactions must be reflected in Russian rubles. If it is necessary to submit reports in foreign currency, then the documentation is duplicated. Exchange rates change daily, for this reason the recalculation date should be set correctly. For example, transactions that passed through the cash register are reflected on the day they were performed and on the reporting date. Non-current assets must be recorded at the time expenses are recognized.
The current account reflects the accounting of cash proceeds in foreign currency, interest received and other transactions. A special transit account is opened for the client by an authorized banking institution. The transit account displays the purchase and sale of currency. A regular transit account is needed to reflect funds for which the banking institution has not yet received information. Such an account confirms the “origin” of funds, the relationship to a legal agreement.
Account 55 is involved in foreign exchange transactions only in certain cases. Currency on deposits, letters of credit, and other forms of payments is taken into account. Account 57 reflects foreign currency amounts intended for sale, as well as rubles for the purchase of foreign currency.
Different entries can be used in currency accounting:
- D57 K52, D51 - reflects currency transfer, revenue credited to the account;
- D57 K51, D52 - “reverse” transaction of purchasing foreign currency for rubles;
- D50 (52) K52 (50) - availability of currency at the cash desk or return to a banking institution;
- D52 K62, 66, etc. - crediting currency from buyers to the account, other receipts;
- D60, 66, 67, etc. - payment to suppliers in foreign currency, performance of other transactions with counterparties;
- D91(57) K57(91) - financial result from completed foreign exchange transactions.
Errors when processing currency transactions provoke problems with regulatory authorities. To prevent such problems from arising, you need to entrust accounting work to experienced specialists.
Currency accounting settings in 1C
To conduct currency transactions in 1C 8.3 Accounting you must:
- add foreign currency to the Currencies in the Directories section - Purchases and sales - Currencies;
- open a foreign currency bank account in the organization's card using the link Bank accounts ;
- determine the use of account 57 “Transfers in transit” in the accounting policy settings: section Main - Settings - Accounting policy.
If the receipt of currency and the transfer of funds for its purchase, as well as the sale of currency and the crediting of funds from its sale are not carried out on the same day, use account 57 “Transfers in transit” (1C chart of accounts).
If transactions for the purchase and sale of currency are carried out:
- regularly , we recommend checking the Use account 57 “Transfers in transit” when moving funds;
- one-time , then you can limit yourself to manually selecting account 57.02 (57.22) in the Settlement account in the document Write-off from current account .
How to reflect transactions on a foreign currency account in 1C:
- Currency account in 1C 8.3 step by step instructions
- Foreign currency account
- Transfer from transit foreign currency account to current account
- Sale of currency
- Revaluation on foreign currency accounts in 1C
1C: Accounting 8
“1C: Accounting 8” is the most popular accounting program that can take accounting automation to a whole new level. A convenient product and services connected to it will allow you to effectively solve the problems of the accounting department of any business!
- Support of different tax systems, maintaining accounting and tax records, submitting reports;
- Inventory accounting, batch accounting, settlements with counterparties, extracting primary documents;
- Payroll calculation, accounting of cash transactions;
- Integration with other 1C programs and websites;
- Working with electronic certificates of incapacity for work (ELS).
Try 30 days free Order
Did you like the article?
Want to receive articles like this every Thursday? Keep abreast of changes in legislation? Subscribe to our newsletter