Filling Features
Form T-9 is intended to be filled out only for those employees of the organization who spend most of their time at their main place of work. For those employees whose duties include constant travel (for example, drivers), there is no need to write business trip orders.
It should be noted that there is no need to ask employees for prior consent for a business trip - management has the right to send any employee on a business trip at its discretion.
Exceptions are those who have children under three years of age, as well as mothers and single fathers - these categories of workers can be sent on a business trip only with prior consent.
General information
A business trip is a trip by a full-time employee with whom an employment contract has been concluded, by order of the employer, to another location (outside his permanent place of work) for official reasons.
For registration and payment, you will need to fill out an order on Form T-9. The following expenses are paid:
- daily allowance;
- expenses for renting residential premises;
- travel expenses to and from the site.
Other expenses may also be paid, such as, for example, telephone or postal fees, visas and passports, consular fees, etc.
The organization determines the duration of an employee’s stay on a business trip independently, taking into account the volume, complexity and other features of the official assignment.
Filling out an order in form T-9
Part 1
Conventionally, the T-9 form can be divided into 3 parts. The first thing that needs to be indicated in the business trip order: the name of the company indicating its organizational and legal status (IP, LLC, CJSC, JSC). Then the OKPO code is entered into the order (it is taken from the title documents), the order number for internal document flow, as well as the date it was filled out.
Part 2
The second part of this document includes basic information. Here you need to enter personal information about the employee: full name (full name), personnel number, position and structural unit (department) to which he belongs. Next, write the destination (country and city), the duration of the business trip (in calendar days), indicating its start and end date.
Pay attention to counting days
When filling out the T-9 form, it is important to correctly calculate the travel days - the trip must be calculated from the day of departure to the day of arrival. That is, if according to the travel document the departure time is 23:45, this day must be included in the business trip period (the same applies to the day of arrival). If a business traveler arrives at night at 00:05, this day should also be included in the trip.
Part 3
In the third section, you need to indicate the purpose of the business trip and be sure to indicate at whose expense it will be paid.
The purposes of the trip can be divided into two types.
Common goals:
- purchase of raw materials, equipment, materials for the organization’s activities;
- negotiations with partners, concluding new deals, agreements, contracts;
- personal participation of a company representative in controversial negotiations;
- searching for new suppliers and getting to know new markets;
- obtaining new skills, knowledge and skills, scientific research.
Narrowly focused goals
- control over the work of a branch, structural unit;
- training of young specialists;
- repair and maintenance of machinery and equipment in branches and structural divisions.
Just below, after the lines about the purposes and payment for the trip, you need to add a link to the document that served as the basis for the business trip. After the order is completed in accordance with all the rules, it must be submitted to the director of the organization for signature. Last but not least, the T-9 business trip form must be signed by the employee sent on a business trip. Opposite his signature is the date the order was created.
Taxi on a business trip
expenses, if they are confirmed by documents that comply with the requirements of current legislation. This is stated in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 10, 2016 No. 03-03-06/1/34183.
The date of expenditure on business trips is the date of approval of the advance report (clause 5, clause 7, article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The advance report must be accompanied by documents indicating the actual costs incurred and confirming the actual length of stay of the employee on a business trip. You can confirm payment for a taxi fare with a cash receipt or a receipt in the form of a strict reporting form. This is established by the Rules for the transportation of passengers and luggage by motor transport and urban ground electric transport, established by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 14, 2009 No. 112.
The BSO must contain the mandatory details established by these rules. This:
- name, series and receipt number;
- name of the freighter;
- date of issue of the receipt;
- cost of using a passenger taxi;
- Full name and signature of the person authorized to carry out settlements.
If the receipt received from the carrier does not contain at least one of the required details, taxi expenses may be excluded from the income tax base. For example, an electronic receipt will most likely not have an authorized signature. And this may serve as a reason for not accepting expenses.
Confirmation of travel expenses
When returning from a business trip, an employee is required to provide the organization’s accounting department with all documents confirming his expenses. It can be:
- travel tickets, receipts for toll roads, parking, etc.;
- receipts from gas stations about the amounts spent on gasoline (when traveling in a personal car);
- checks, bills, receipts from hotels or hotels about expenses for renting rooms;
- any other payment documents that cover expenses related to the business trip.
Based on these checks and receipts, you will need to either return part of the travel allowances received in advance or receive compensation for funds spent in excess of the advance.
How to arrange for an employee to go on a business trip in a personal car
The question of traveling on a business trip in a personal car has become especially relevant during the coronavirus period, since personal transport allows you to distance yourself and reduce the possibility of infection. Therefore, both employers and employees began to more actively consider this particular procedure for organizing travel to and from the place of business travel. Let's consider the main points that you need to pay attention to if an agreement is reached that the employee will go on a business trip in his own car.
Registration of the use of an employee’s personal car in the interests of the employer
Let us immediately note that the legislation does not limit the list of types of transport in which an employee can go on a business trip. In accordance with paragraph 7 of the Regulations on the peculiarities of sending employees on business trips, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 13, 2008 No. 749, it is possible for an employee to travel on the basis of a written decision of the employer to the place of business trip and (or) back to the place of work on transport located in property of the employee or property of third parties (by proxy).
Thus, the use of a personal car by an employee to travel to and from a business trip does not contradict the law. At the same time, it is necessary to document the fact that the employee’s personal car is used in the interests of the employer.
By virtue of Art. 188 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, when an employee uses personal property with the consent or knowledge of the employer and in his interests, the employee is paid compensation for the use, wear and tear (depreciation) of tools, personal vehicles, equipment and other technical means and materials belonging to the employee, as well as reimbursement of expenses, associated with their use. In this case, the amount of reimbursement of expenses is determined by agreement of the parties to the employment contract, expressed in writing.
In this regard, the employee must sign an additional agreement to the employment contract, which defines:
- the procedure for using the employee’s personal car in the interests of the employer;
- amount of compensation for use, wear and tear (depreciation);
- procedure and amount of reimbursement of expenses.
In addition, when drawing up an order to send an employee on a business trip, it must indicate that the employee’s personal car is used to travel to and from the business trip.
Reimbursement of employee expenses
Just as in any other case, the employer must reimburse the employee for travel expenses to and from the business trip. This requirement is provided for in Art. 168 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
It should be taken into account that the employee uses personal transport and will not provide travel documents. In such a situation, to confirm the expenses incurred, the employee must submit the following documents to the accounting department:
- route sheets (they indicate the travel route) or other documents that can confirm the vehicle’s route;
- cash receipts confirming gasoline expenses.
Regarding reimbursement of expenses, the following nuance must be taken into account. According to the Federal Tax Service of Russia, if a personal car is used for business purposes, then according to paragraphs. 11 clause 1 art. 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, expenses for compensation for the use of personal cars for business trips can be taken into account within the limits established by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 02/08/2002 No. 92 “On establishing standards for the organization’s expenses for paying compensation for the use of personal cars and motorcycles, within which, when determining the tax base for corporate income tax, such expenses are included in other expenses associated with production and sales" (letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated May 21, 2010 No. ШS-37-3/2199 "On the accounting procedure for tax purposes profit from the cost of travel for an employee on a business trip").
The said resolution established the following expense standards:
- 1,200 rub. per month if the engine is 2,000 cc. cm or less;
- 1,500 rub. per month if the engine is more than 2,000 cc. cm.
In other words, the employee will have to be reimbursed for travel expenses in full, however, it will be possible to take into account expenses in expenses when calculating income tax only in the specified amounts.
But if you are ready for disputes, you can try to defend the right to take into account the full amount paid to the employee for travel as expenses when determining the amount of income tax in court.
In accordance with paragraphs. 12 clause 1 art. 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when taxing profits, other expenses associated with production and sales include the company’s expenses for business trips, in particular for the employee’s travel to the place of business trip and back to the place of permanent work. Tax legislation does not establish any restrictions on types of transport. At the same time, the costs of travel for an employee to the place of business trip and back by personal transport can be considered as economically justified (Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Let us note that courts often take the side of organizations in such disputes (for example, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga-Vyatka District dated August 28, 2006 in case No. A29-8205/2005A).
Liability to third parties
When deciding to send an employee on a business trip using personal transport, employers are also concerned about the issue of liability to third parties if the employee causes an accident.
According to the general rule established by Art. 931, 935 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, damage to a person injured in an accident is compensated by compulsory motor liability insurance. But if the amount of insurance compensation is not enough, the culprit, at his own expense, pays the person injured in the accident the difference between the insurance compensation and the actual amount of damage.
It should be taken into account that, by virtue of paragraph 1 of Art. 1068 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a legal entity compensates for damage caused by its employee in the performance of labor (official, official) duties. Therefore, if the amount of damage is significant, there is a risk of recovery of damages from the employer (for example, the Appeal ruling of the Supreme Court of the Republic of Bashkortostan dated December 1, 2015 in case No. 33-21123/2015, the Appeal ruling of the Supreme Court of the Republic of Karelia dated September 29, 2015 in the case No. 33-3693/2015).
Send
Stammer
Tweet
Share
Share
Return report
Upon return, you must complete and submit a report to the organization’s accounting department.
An advance report is a primary accounting document that confirms the expenditure of the amounts allocated to the employee, to which documents confirming the expenditure of accountable funds must be attached. It is drawn up according to the unified form No. AO-1. Documents confirming expenses must be attached to it.
The report must be submitted no later than 3 business days upon return for final payment.
Base
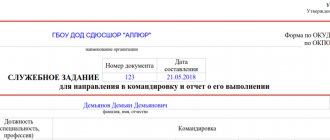
The order to send personnel is issued based on the decision of the immediate supervisor. A sample order for the business trip of employees in the T-9 form is drawn up on the basis of a job assignment, which indicates the place of business trip, the date and time of the trip, as well as the goals and objectives of the trip.
Let us remind you that it is no longer necessary to draw up a job assignment (Regulation approved by Government Decree No. 749 dated October 13, 2008 (as amended on December 29, 2014)), but if this is accepted in your organization, a sample T-9 form can be viewed and downloaded in our article.
Related documents
After the responsible person has issued an order to go on a business trip, additional forms may still be issued for the document.
Attention: some of them, by law, are no longer required to be issued. On the other hand, this is mandatory if this step is directly indicated in the company’s accounting policies.
Additional documents include:
- Travel certificate. This document must be stamped as a mark of the visit to the receiving company. The document is not mandatory for use;
- Service assignment. The T-10 format form contains a list of tasks that the employee needs to complete on a business trip. Now recognized as optional. Sometimes a list of tasks for a business trip is included in the travel certificate form.
- Record book for employees on a business trip. In such a log you need to make notes when an employee goes on a business trip and returns from it. Currently, keeping this book is not considered mandatory.
- Service note. Usually it is drawn up by an employee to justify what daily allowance should be provided when traveling on business. Sometimes upon arrival it is necessary to draw up a new memo - for example, to pay for spent fuel and lubricants for your own car.
Tags: Business tripOrder