Business trip expenses: what the employer pays for
When sending an employee to perform work functions in another locality in Russia, at the company’s expense it is necessary:
- purchase travel tickets, regardless of the type of transport. The only exception is a taxi - a trip in it, as a rule, is not compensated;
- pay for housing - this could be a hotel room or rental housing, provided that there are documents proving the corresponding expenses;
- issue daily allowances - they are calculated for each day of a business trip, including each day when the employee was on the way to another location and back. The exception is for one-day trips - if in the morning the employee went to another locality to fulfill the received official assignment, and returned in the evening (before 12 o'clock at night). No daily allowance is paid for them;
- other expenses, as agreed with management. For example, an organization’s internal documents may provide for compensation for entertainment expenses, costs for renting a car and/or a personal driver, for the services of VIP lounges at airports, communication services, and other issues.
As for trips abroad, the employer is also responsible for paying consular fees, issuing money for a visa, paying for insurance, and paying other mandatory payments when crossing the border.
In addition, the employer is obliged to maintain the posted employee’s salary, since in fact the person performs his work duties outside the organization. In this case, the salary is paid for each day of the business trip, including the days when the employee was on the road.
According to the general rules, if documents confirming expenses during a trip are presented, then they can be fully taken into account when calculating income tax or tax on the simplified tax system.
How much is the employee reimbursed?
It often happens that the purchase of tickets and booking a hotel room is handled directly by the company administration, which means that the employee does not receive money for this. And there are no questions with them. But if money for travel expenses is given to a person, then you need to understand what standards are used to reimburse them.
By law, travel expenses allow an employee to get to their destination, buy food, pay for accommodation, and afford other things previously agreed upon with the head of the company. And since the person went to perform an official assignment, he should be compensated for all expenses incurred and agreed upon with his superiors, and not consider the amount issued as income. That is, neither income tax nor insurance premiums are withheld from them. But this is provided that the company has approved a regulatory document (regulations on business trips), which provides for compensation standards, as well as the procedure for this procedure.
The only expense item that is standardized at the legislative level is the amount of daily allowance. In particular, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that daily allowances issued in the following amounts are not subject to personal income tax and insurance contributions:
- 700 rubles - per day of travel around the country;
- 2500 rubles - per day of a business trip abroad.
This does not mean that the employer cannot pay more. Maybe. But in this case, the company will have to withhold income tax and insurance premiums from the excess amount.
We also note that the subordinate is not required to report on what he spent the daily allowance on and whether he spent it at all. This is the item of travel expenses that is taken into account when taxing company profits without documents confirming that the money was spent.
Issuance of money on account
To receive money for targeted expenses, the employee sends an application to the manager. He indicates in it a specific amount, purpose and period for which he wants to receive it. The application form can be arbitrary or strict if it is approved in the regulations on settlements with accountable persons (if any). After the manager approves the application, it goes to the accounting department, which checks for balances on past advances.
Instead of an application, the basis for issuing money on account may be an order from the manager or another administrative document with his signature. If the settlement provision (if any) states that the order is mandatory, then it must be drawn up even if there is an application. From December 2022, you can issue several cash advances to one or more accountable persons with one order.
If money is issued for travel expenses, the manager issues an order to send the employee on a business trip. Then the employee writes an application with a preliminary calculation of the required amount.
Daily allowance abroad and in Russia: sizes
Since almost all travel expenses abroad and within the country can be taken into account when taxing company profits in full, we will dwell in more detail only on daily allowances, for which a personal income tax-free limit has been introduced.
About 5 years ago, the government required employers to provide employees with travel expenses that were no less than specified minimum amounts. But then they abandoned this, maintaining the standards only for state delegations. According to Government Decree No. 729 dated October 2, 2002, each federal civil servant is entitled to no more than 100 rubles per day if he goes on a business trip around the country. If you have to perform duties outside the Russian Federation, then the daily allowance is 50-70 dollars, depending on the specific country (Appendix No. 1 to Government Resolution No. 812 of December 26, 2005). Please note that these standards are not mandatory for employees of regional government agencies, local governments, and municipal institutions. For them, allowable travel expenses are determined locally.
As for private enterprises, the managers of such companies themselves decide what the daily allowance should be. But the majority tries to comply with the norms that are not subject to personal income tax and insurance contributions: no more than 700 rubles per day when traveling within Russia and up to 2,500 rubles outside its borders. Let us repeat: no one forbids giving more, it’s just that you will have to pay tax (Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and insurance premiums (Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) on the excess amount. Please also note that for persons occupying different positions and specialties, different daily allowance rates may be established. But this must be stated in the organization’s regulatory document.
Please note that daily allowances are paid for each day of a business trip, for days en route and for periods of forced downtime. However, they do not replace wages; the employer is obliged to pay the average wage while the employee works in another locality.
How are travel expenses compensated for a one-day business trip?
Sometimes subordinates are sent on short business trips lasting one day, or even several hours. In this case, the company compensates travel expenses for transport, as well as for other purposes, if agreed upon.
However, in this case, daily allowances are not paid if the employee travels to another locality in the Russian Federation. In return, he may be paid compensation, but its amount is specified in the company’s internal documents. And if the employer is a budgetary institution, then in the regulations of the government or other authorities.
As for foreign one-day business trips, both for private companies and for the public sector there is a daily allowance limit of half the prescribed norm. This was stated in paragraph 20 of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 13, 2008 No. 749 and paragraph 30 of the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of July 18, 2005 No. 813.
In addition, amounts spent on rental housing are not reimbursed, since there is no need to stop somewhere on one-day business trips. However, in exceptional cases, when objective reasons force the employee to spend some time in a hotel, the company will also have to pay for accommodation.
Let us note right away that during a one-day business trip, the employer is still obliged to pay the employee the average salary. But if a business trip falls on a weekend or holiday, then payment must be made in accordance with Art. 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in double size. Or the employee can receive an additional day off (time off) and pay in a single amount.
Accounting for travel expenses: calculation and registration
Many companies and individual entrepreneurs, in the course of their activities, are faced with the need to send employees on trips away from their place of permanent work in order to carry out certain assignments.
Such a trip is called a business trip (Article 161 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, the employer is obliged to preserve for the posted worker his workplace, average earnings, and also reimburse the costs incurred by him, the list of which is established by law. In order to correctly and reasonably account for travel expenses, the accountant must have properly executed documents confirming the fact of the business transaction.
Accounting for travel expenses can be divided into 2 main stages:
- preliminary calculation and issuance of money on account to the business traveler;
- approval of the employee’s advance report on the amounts spent.
In order to pay an advance to an employee for business trip expenses, the accountant needs to calculate it based on internal documents:
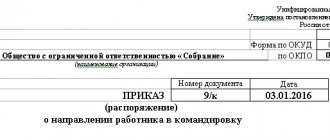
- an order or instruction from the manager to send a company employee on a business trip, which indicates the employee’s full name, duration and purpose of the trip (to perform a work assignment);
- a written decision of the manager on an employee’s trip on a business trip using official or personal transport (if accepted).
Based on what is written in these two local documents, as well as the business travel regulations developed and adopted by the company, the accountant calculates a cash advance, which includes:
- the cost of tickets for travel to and from the business trip;
- payment for hotel accommodation;
- daily allowance for each day you are on a business trip;
To learn whether to pay an employee a daily allowance for days on the road if the ticket includes meals, read the material “A business trip ticket includes meals—should you pay an employee a daily allowance for days on the road?” .
- other expenses permitted by management.
Is it possible to take into account taxi expenses of a business traveler when taxing, read the article “Reflecting taxi expenses in tax accounting (nuances).”
The daily allowance does not depend on travel and housing costs. This separate expense item is defined as the funds needed to perform work and stay during a business trip (for food).
Daily allowances are not limited by law, and every commercial organization has the right to establish their amount by internal act. At the same time, you need to remember that there is a limit above which personal income tax must be calculated and withheld from the employee, as well as insurance premiums must be calculated. In 2020-2021, this limit is 700 rubles. per day for business trips in Russia and 2,500 rubles. - for business trips abroad.
Daily allowances are paid for all days on a business trip, including weekends and non-working holidays, as well as travel days and forced stops (clause 11 of the regulation on the specifics of sending employees on business trips, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 13, 2008 No. 749). The employee does not need to report for the use of daily allowances.
Other expenses may include expenses for mobile communications, the Internet, and payment for goods and services necessary for work.
If you have access to ConsultantPlus, check whether you have correctly taken into account travel expenses when calculating your income tax. If you don't have access, get trial of online legal access.
The employee receives an advance at the organization's cash desk or by non-cash transfer to a card and, before the end of 3 days after returning to his permanent place of work, reports to the accounting department for the money received.
How to calculate travel and daily expenses
An invoice for travel tickets or the use of a hotel room, of course, can be sent to the organization. But most often, workers independently purchase the travel and accommodation services they need, and then provide documents confirming the costs.
However, even before sending an employee on a work assignment to another locality, the accountant needs to at least approximately calculate how much to pay in advance. To do this, the cost of round-trip tickets, the estimated cost of a hotel room, the amount of daily allowance for the number of days of a business trip, and other planned costs are taken into account.
To calculate the daily allowance, it is necessary to determine how many days a person will be outside the “home” locality and add to them the days on the way. For example, engineer Ivanov A.S. goes to another city for commissioning work. It departs on 12/09/2018 (Sunday) at 5 a.m. and returns on 12/16/2018 (also on Sunday) at 9 a.m. The total number of days on a business trip will be 8 days. If the trip is domestic, then the daily allowance limit, not subject to personal income tax, will be 700 rubles. The amount of daily allowance that must be paid to engineer Ivanov will be:
700 × 8 = 5600 rubles.
If the trip is foreign, then travel expenses will increase as follows:
2500 × 8 = 20,000 rubles.
Please note that the day of departure is determined from 00 to 24 hours, the same as the day of arrival. It is important to take this into account when making final payments, for example using travel documents. If there are no tickets, for example, the employee used a personal or company car, then the duration of the business trip is calculated based on the dates specified in the memo at the end of the trip.
Since the employee still writes a statement for travel expenses (it is the basis for the cash order), you can ask him to independently estimate how much he will need, and then check his calculations. This option will be convenient, including if a person goes to a business trip in a personal car, so he will have expenses, for example, to buy gasoline. The template for filling out the application is at the end of the article.
After the estimate is approved by the chief accountant and manager, you can issue an advance for travel expenses in cash or to a bank card. The issuance of funds is carried out taking into account the standards established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. Read more about the requirements of the financial regulator in a separate material from PPT.ru.
As for payments in foreign currency, they are also not prohibited. To do this, travel expenses are calculated according to general rules, but then the amount received is exchanged for currency. Moreover, either the posted employee himself or someone else can exchange rubles for foreign currency. In both cases, you must attach a receipt from the bank confirming the money exchange transaction.
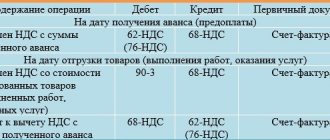
Postings for calculating travel expenses and mutual settlements with accountable persons
The duration of the trip is 5 days.
Duration of stay at the hotel is 5 days. The cost of hotel accommodation is 3,540 rubles. per day incl. VAT.
Travel costs in both directions are 5,900 rubles. incl. VAT.
At the end of the business trip, the employee submitted an advance report for the business trip in connection with general business purposes.
Payment of daily allowances
Payment of daily allowances is also exempt from personal income tax - personal income tax within the limits of standards: 700 rubles for each day of a business trip within the country and 2,500 rubles - outside the country. If the organization has established the amount of daily allowance in excess of these amounts, then the employee must pay personal income tax on the excess.
Thus, the daily allowance for a business trip will be 5 x 700 = 3,500 rubles.
Expenses for renting residential premises are paid to the employee in full if supporting documents are available. The amounts of living expenses do not relate to the employee’s income, therefore personal income tax is not charged on them. Insurance contributions (to the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund, Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund) are not charged from these payments.
We invite you to read: Selling a car under the simplified tax system “income minus expenses” (nuances)
If for some reason the employee was unable to document his living expenses, then they are reimbursed to him according to the standards. In this case, the standard values are also not subject to tax.
The cost of staying in a hotel according to the conditions of the problem will be 5 x 3,540 = 17,700 rubles. Including VAT RUB 2,700.
Travel expenses to and from the business trip are reimbursed to the employee in the amount of the cost of travel by air, rail, water, and general road transport (except taxis), including insurance payments for state compulsory passenger insurance, pre-booking services, and payment for bedding.
In case of loss of travel documents, expenses are reimbursed to the employee at a minimum cost.
Transport costs according to the problem are 5,900 rubles, including VAT 900 rubles.
Advance report
Using an advance report, accountable persons confirm for the accounting department the spent amounts previously given to them in advance.
The advance report form is a two-sided unified form No. AO-1 and must be filled out in one copy, both by the accountable person and by the accounting employee. An advance report completed by the employee along with supporting documents (tickets, checks, documents from the hotel, etc.
After approval of the document, the accounting department generates entries for writing off accountable funds and makes the final settlement with the accountable person. If the advance received by the employee is not fully used, then the remainder is handed over to the company's cash desk. Conversely, the overdrawn amount must be paid to the employee by the accounting department.
The final calculation of travel expenses is shown in the table below.
| Type of consumption | Expenses, rub. per day | 24 hours | Expenses, rub. |
| Daily allowance | 700 | 5 | 3 500 |
| Hotel accommodation | 3 540 | 5 | 17,700 incl. VAT 2,700 |
| Directions | 5,900 including VAT 900 | ||
| TOTAL | 27 100 |
Dt71 “Settlements with accountable persons” 10,000 rubles.
Kt50 “Cash desk” 10,000 rub.
Accounting entry: daily allowances have been accrued according to the advance report.
Dt26 “General expenses” RUB 3,500.
Kt71 “Settlements with accountable persons” 3,500 rub.
Accounting entry: according to the advance report, living expenses are taken into account.
Dt26 “General expenses” RUB 15,000.
Dt19 “VAT refundable on purchased valuables” RUB 2,700.
Kt71 “Settlements with accountable persons” RUB 17,700.
Accounting entry: according to the advance report, transportation costs are taken into account.
Dt26 “General business expenses” 5,000 rub.
Dt19 “VAT refundable on purchased valuables” 900 rub.
Kt71 “Settlements with accountable persons” 5,900 rub.
As you already know, to record settlements with accountable persons, accounting account 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” is used. After completing the above accounting entries, the data for this account looks like this:
| 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” | |
| 10 000 | |
| 3 500 | |
| 17 700 | |
| 5 900 | |
| 10 000 | 27 100 |
| 17 100 | |
Dt71 “Settlements with accountable persons” 17,100 rub.
Kt50 “Cash desk” 17,100 rub.
If the settlement is made in full, then there should be no balance on account 71 “Settlements with accountable persons”.
| 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” | |
| 10 000 | |
| 3 500 | |
| 17 700 | |
| 5 900 | |
| 17 100 | |
| 27 100 | 27 100 |
In the recent past, the most common method of issuing money to a business traveler was issuing cash from the cash register. Money is issued by drawing up an expenditure cash order based on an application from an employee approved by the manager.
ATTENTION! You cannot issue accountable amounts to an employee who has not reported on previous amounts (clause 6.3 of the Bank of the Russian Federation Directive No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014). This instruction applies only to cash payments; accordingly, its requirements do not apply to the transfer of non-cash funds to a card.
How to properly process the issuance of money from the cash register, what requirements must be met, read the article “How to fill out a cash expense order (RKO){q}”.
Dt 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” (71-1, 71-2) Kt 50 “Cash” (50-1).
The use of subaccounts depends on the adopted working chart of accounts (clause 4 of PBU 1/2008).
To ensure consistency between the work of the accountant and the computer accounting programs used, it is advisable to approve the subaccounts recommended by the developers. For example, it is advisable to count. 71 use subaccounts:
- 71-1 - for payments in rubles;
- 71-2 - in currencies.
You can open sub-accounts for account 50:
- 50-1 “Organization cash desk”;
- 50-2 “Operating cash desk”;
- 50-3 “Money documents”.
When issuing money from the cash register, the posting will look like this: Dt 71-1 Kt 50-1.
When traveling abroad, it is allowed to issue money in foreign currencies. Reflect the receipt of money to the cash desk from a foreign currency account by posting Dt 50 Kt 52.
In this case, it is advisable to create a separate sub-account for account 50 for each type of currency. Reflect the issue from the cash desk in foreign currency for a foreign business trip by posting Dt 71-2 Kt 50 (sub-account corresponding to the currency).
If funds for a business trip are issued in foreign currency, then exchange rate differences appear. Exchange rate differences will arise if the date of receipt of currency at the cash desk and the date of its issue do not coincide. It is necessary to determine the difference between the amounts recalculated at the official rate for each date - the date of receipt of money in the cash register and the date of its issue.
Reflect the positive exchange rate difference in accounting by assigning it to other income of the organization: Dt 50 (corresponding subaccount) Kt 91-1.
The negative difference goes to the organization's expenses: Dt 91-2 Kt 50 (corresponding subaccount).
After the end of the business trip, the employee reports for the accountable amounts received. To do this, he draws up an advance report or another document, independently finalized and approved in the accounting policy.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: If the lands are not demarcated, what level of ownership do they belong to?
Read everything about advance reports in the article “Features of advance reports in accounting.”
If there is an unused balance of travel allowances, the balance should be returned to the cash desk and reflected in the entry Dt 50 Kt 71.
The unspent balance can be transferred from the employee’s card to the organization’s current account: Dt 51 Kt 71.
The return of the balance to a special card account is reflected by posting Dt 55 Kt 71.
Travel expenses can be written off as follows:
- Dt 08 (10, 41...) Kt 71 - non-current assets, inventory and materials were purchased;
- Dt 19 Kt 71 - the amount of input VAT is reflected;
- Dt 20 (23, 26...) Kt 71 - expenses are charged to the cost of products (services, works);
- Dt 44 Kt 71 - expenses are recognized as commercial expenses or expenses for the main activities of a trading organization;
- Dt 91 Kt 71 - non-production expenses were approved and written off.
You can study this topic in more detail in the article “Accounting for settlements with accountable persons.”
What documents will be needed to confirm travel expenses?
No later than three days after returning from a trip, the employee is required to report on the amounts spent. Please note that all expenses must be documented and be reasonable. Otherwise, the employer may refuse to compensate them.
Documents confirming travel expenses include:
- travel certificate with notes on departure and arrival, if it was issued at the beginning of the trip;
- travel tickets, including those issued via the Internet;
- any receipts and invoices for accommodation, rental vehicles, services received or goods purchased that were purchased to perform a work assignment;
- an advance report indicating the costs, as well as the amount paid to the employee. If more was spent on a business trip than the amount of the advance payment issued, an additional payment is made. If according to the documents there is still money left, it must be returned to the cashier. Or the employer will independently deduct the required amount from wages (Article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Also an important document is a report (memo) on the completion of a work assignment during a trip. Otherwise, the feasibility of travel expenses will not be proven. Note that such a report can also become a source of information about the duration of a business trip if the employee traveled to the destination by personal or official transport.
How to reflect expenses in accounting and tax accounting
To begin with, let us remind you that for income tax expenses are taken into account on the day the advance report is approved. In this case, VAT on expenses is deductible provided that there is an invoice for them.
Expenses for the payment of average wages for the period of a business trip are included in labor costs. The remaining expenses during a business trip are required by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation to be considered as other expenses associated with production and sales.
How to reflect travel expenses in accounting? The correct order is:
- the operation when an advance is issued for a business trip is accompanied by posting Dt 71 Kt 50 (51);
- when the accountant wants to indicate that travel expenses (invoice) are taken into account, the posting should be: Dt 26 (08, 20, 23, 44) Kt 71.
Travel allowances issued in cash documents
Traveler's checks may be issued to posted employees. A traveler's check is an obligation of the issuer to pay the amount of the check to its owner. Accounting for traveler's checks is kept in account 50-3 “Cash documents”. The following entries must be made in accounting:
- Dt 50-3 Kt 60 (76) - purchase of traveler's checks;
- Dt 71 Kt 50-3 - traveler's checks issued.
Unfortunately, the use of traveler's checks is not common in the Russian Federation. They can only be exchanged for money, but even then not in all financial institutions. Therefore, this type of financial document is most convenient to use when traveling on business trips abroad. The use of traveler's checks as a means of payment has its advantages - both in the simplicity and safety of their use.
The organization can purchase and issue travel documents to the posted employee. The accounting of travel documents is carried out similarly to the accounting of cash checks in account 50-3.