What is a daily work schedule
Daily work is usually called the performance by an employee of his labor duties continuously for 24 hours in accordance with the internal labor regulations (ILR) and the terms of the employment contract.
The concept of “daily work” is not defined in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. However, in practice, employers often have to organize. such work. Employees of the Ministry of Emergency Situations, doctors, security guards, and workers of other professions can work on daily schedules.
In order to legally organize work in a company on a daily schedule, you must comply with the following requirements (Article 91, Article 103, Article 110 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
All three conditions must be met simultaneously, otherwise the establishment of such an operating mode will be unlawful. The rights of workers should not be violated when working on daily schedules.
Neglect of these rules can lead to fatigue, depression and illness, which will inevitably affect the productivity of employees and the efficiency of the company as a whole. Violations committed by the employer when organizing daily work and drawing up a schedule may result in fines for him.
The requirement that the duration of rest between shifts should be twice as long as the duration of work, established by clause 10.24 SP 2.2.2.1327-03. 2.2.2. “Occupational hygiene...” has not been applied since 2022 due to the abolition of these sanitary and epidemiological rules by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 8, 2020 No. 1631.
Find out further what else an employer needs to remember when engaging employees to work on daily schedules.
Employee rest during a 24-hour shift
An important point in this case is that a shift schedule is established for employees. This means that regular weekends such as Sunday and Saturday, if a shift falls on them, will not be considered days off. The peculiarity is that the daily schedule can be implemented not only with the help of shift work. This can also be done through flexible scheduling. This is explained by the provisions of Article 102 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The law allows shifts to last 24 hours. Such a program assumes that a citizen fulfills his duties at his position during the day without leaving work. This period includes both day and night. This schedule differs significantly from the hours of those workers who work a 5-day work week. When such a schedule is established, the employee will rest on the days following the shift. In addition, rest periods are established during the shift. When establishing rest, it is necessary to take into account the provisions of labor legislation. He says that the duration of rest between shifts should be 2 times longer than the shift itself.
How to set a daily work schedule for an employee
If you decide to introduce a daily work schedule in your company, you should register such a schedule in the PVTR. Or in an employment contract with an employee, if this schedule is individual or your company is a micro-enterprise that refused to accept local acts.
The text of the PVTR and/or employment contract should indicate (part 1 of article 100, part 2 of article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- length of the working week and shift;
- alternating working days and weekends;
- start and end of shift;
- time of breaks during the shift (for meals, rest, etc.);
- indication of one shift per day.
Then draw up a shift schedule taking into account the legal requirements described in the previous part of the material.
Shift schedules must be brought to the attention of employees no later than one month before they come into effect (Article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Rest standards
According to the law, daily work hours are allowed if the specifics of the enterprise require it. The schedule is usually set by the employer - as a rule, it is a day in two or a day in three.
“In accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the duration of rest should be 2 times longer than the work shift,” says Lyubov Zorina, head of the personnel department of a large plant. “In other words, if an employee works 24 hours, then before the next shift he must rest for at least 48 hours.”
2 main rules of the “day”
Employees should be familiarized with the new work schedule no later than a month before its introduction. Unfortunately, some employers violate this rule and transfer the employee to a new regime without warning.
During the work shift, each employee is given time for lunch - a total of about 1.5-2 hours, divided into half-hour breaks. This personal time can be spent at your discretion. By the way, no one forbids using these 2 lunch hours at a time, instead of taking “smoke breaks” in parts.
Which employees cannot be transferred to a daily work schedule?
For most workers, any shift duration can be set, including daily (part 1 of Article 93, part 1 of Article 100, part 1 of Article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). But certain categories of employees have restrictions on the permissible duration of daily work (Rostrud Letter No. 3567-6-1 dated December 2, 2009). For example, the maximum duration of a disabled employee’s shift is determined by a medical report (paragraph 4, part 1, article 94 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Therefore, before including workers in the daily work schedule, check whether labor legislation allows a particular employee to be involved in shift work lasting 24 hours (days), and whether he is prohibited from working at night.
In particular, it is impossible to involve pregnant women, minors (except for those who participate in the creation and/or performance of artistic works), workers engaged in work with harmful and/or dangerous working conditions, where short working hours are established, for daily work. and some other categories of workers (Article 92, Article 94, Article 96 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Payment for work in accordance with the daily work schedule
When an organization uses shift or daytime work hours, this has special features when calculating wages. Including:
- it is necessary to pay for the hours during which the citizen actually performed his labor functions (this is the rate or salary for the position held),
- work performed at night must be paid at an increased rate, i.e. at the rates specified in the provisions of Article 154 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation,
- if a shift falls on a public holiday or public holiday, then it must be paid at double the rate, but the exception is situations when a citizen is given an additional day off for the day worked - the first two hours above the norm, payment is made at double rate, the rest of the time - at a multiplier of 1 ,5.
It is important to consider that changes to the above provisions can be made through the development of local regulations. At the same time, it is unacceptable to reduce the standards established by law (i.e., changes must be exclusively in favor of the employee).
Establishing a daily work schedule in an organization has some features. The actual hours worked are calculated and overtime hours must be taken into account. The management of the organization must take into account some features:
- it is necessary to keep records of overtime that occurs for each employee, which is provided for in Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation,
- it is possible to involve citizens in overtime work of no more than 120 hours (this value is set for an annual period),
- work on holidays and days off cannot be classified as overtime work.
To establish the exact amount to be paid to the employee, it is necessary to carry out the calculation before the end of the year.
Night work in accordance with the Labor Code
Legislative acts reflect the categories of citizens who can work after 22:00. The Labor Code states that the night lasts from 22:00 to 06:00. Night mode affects the normal functioning of the body. For this reason, the law introduces restrictions on the performance of work during the reporting period. In particular, the following cannot work at night:
- citizens who have not reached the age of majority,
- pregnant women.
It should be noted that some people may work at night if they agree to do so. To do this, written consent must be obtained. These categories include:
- women with children under three years of age,
- one of the parents raising a child under five years of age,
- people who act as guardians,
- citizens with disabilities
- and those raising children with disabilities who have been allowed by the medical commission to work at night.
The management of the organization is responsible for familiarizing employees with this provision of the employment contract. A document on familiarization with the rights of employees is drawn up against their signature, provided that night shifts are carried out constantly. When night shifts are established one-time, it is necessary to obtain the consent of employees each time.
When hiring a citizen, he initially needs to know about the possibility of working on the night shift, if there is one at the enterprise. In this case, it is necessary to obtain from the employee a certificate of the ability to work at night. The format of this act is reflected in the Order developed by the Ministry of Health.
If the management of a company engages a citizen who cannot work at night to work at night, this entails the application of administrative measures.
When an enterprise has established a shift schedule, it is unacceptable for a citizen to immediately mark 2 or more shifts in a row on the schedule. Also, after night work, the employee should not be asked to perform his duties during the day.
How to create a daily work schedule
Let's show with an example how to create a daily work schedule.
Example
Initial data: operating mode ─ every other day, accounting period ─ month, standard working hours in July 2022 ─ 176 hours.
The actual time worked is calculated based on the length of the shift (24 hours) and the number of shifts per month. For example, with eight shifts per month, this time will be 192 hours (24 hours x 8 shifts), and overtime is 16 hours. (192 hours – 176 hours).
Sample daily work schedule
How can one legally allow daily work as an ambulance driver?
A work shift starting after 22.00 is called a night shift. Night staff appeared due to the peculiarities of the technologies of many industries: for example, steelmaking shops cannot be stopped for a minute. Labor Code on Night Work The legislator formulated a list of categories that are allowed to work after 10 p.m., payment conditions, and defined the term “night work.” The Labor Code states that the period of time from 22.00 to 6.00 is considered night (Part 1 of Article 96 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Night mode affects biorhythms and threatens the normal functioning of body systems.
Summarized accounting of working hours with a daily work schedule
As a general rule, the normal length of the working week cannot exceed 40 hours per week (Part 2 of Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). According to the daily schedule, employees may not work up to standard in one month, but overwork in another month. In this regard, employers use summarized recording of the working time of employees working on a daily work schedule.
Summarized working time tracking allows you to:
- implement a schedule of the duration of the working day and working week on average for the accounting period;
- balance underwork or overtime in such a way that the sum of hours worked during this period is equal to the standard hours for this period for this category of workers.
The accounting period cannot exceed one year, and for recording the working time of workers engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions - 3 months (Part 1 of Article 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The procedure for calculating the norm of working time for certain calendar periods of time (month, quarter, year) depending on the established duration of working time per week is approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated August 13, 2009 No. 588N.
Organizing summary recording of working time is a right, not an obligation of the employer. Therefore, he can use regular (non-summarized) working time recording for employees working on a daily schedule (Part 1, Part 4 of Article 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
What work schedules are used in practice?
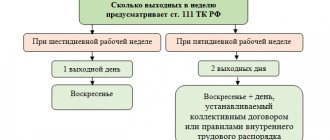
Five days or six days
Working on a “5 through 2” or “6 through 1” schedule is one of the most common in Russian practice. Sunday must be a day off
, and the second day off in a five-day week is negotiated separately. For example, in trading, the holiday often falls on Monday.
The length of the working day for a five-day work week is 8 hours, and for a six-day week it is not clearly established, but in practice it is usually 5 days of 7 hours, and on the sixth day - 5 hours. The main thing is that the total length of the working week should not exceed 40 hours.
With a five-day or six-day work week, employees are not required to go to work on weekends. But sometimes this is required by the employer. In this case, working on days off is possible subject to the following conditions:
- employee consent (in writing);
- consent of the trade union (in some cases);
- availability of the employer's order in writing.
For work beyond the established schedule, an increased wage or an additional day of rest is provided.
If an employee’s employment or collective agreement stipulates an irregular working day, he will have to go to work by order of the employer and on days off, and his consent is not required.
Shift work
A shift work schedule involves a person working at different times on different days. Shift work is introduced if:
- the presence of an employee around the clock is required - security activities, medicine, etc.;
- it is necessary to use existing production assets more efficiently - convenience stores, service enterprises, round-the-clock work in industrial enterprises.
Most often they work shifts according to the following schedules:
- “2 through 2”, “3 through 3” , etc. These are usually 12 hour shifts (resulting in approximately 42 working hours per week). This is how they work in trade, transport, catering, etc.;
- “in three days . This means that a person works one 24-hour shift, after which he rests for 3 days. This is often done in medicine or security.
Despite the fact that shifts are set to a certain length, the employer must still determine the time for rest and meals (from 30 minutes to 2 hours).
The working time of each employee working on a shift schedule must be taken into account individually. Moreover, it is necessary to keep separate records of time worked during the day and at night (additional payments are due for night work).
You cannot install 2 shifts in a row. In addition, when planning shifts, it is worth considering a minimum weekly uninterrupted rest of 42 hours.
Floating, sliding, flexible
A flexible, sliding or free work schedule is a schedule in which the working time is agreed upon individually
.
The start and end times of work, as well as the total duration of the working day, are agreed upon. After this, the employee will not be able to independently change the schedule without agreeing with the employer (even though the schedule is called free).
The legislation distinguishes 2 parts of a flexible schedule:
- fixed time – those hours that the employee must be at the workplace;
- variable time – hours during which an employee can be present at the workplace at his own discretion.
The main thing is that the employee works the agreed amount of working time. Remuneration is calculated based on the actual time worked, or in other ways as agreed.
A flexible work schedule can only be established with the consent of both parties - the employer and the employee. The employer's consent is not required only in cases where the employee has a child under 14 years of age or a disabled child.
For some professions, a flexible schedule is a prerequisite (in particular, for emergency responders on communication networks).
Shift method
Shift work is a way of organizing work when an employee does not return to his place of residence after work due to the fact that the place of work is far from home.
. Most often, the rotation method has a seasonal basis.
They work on a rotational basis mainly in the fields of mining, logging, construction, maritime transport, etc.
The duration of the shift (that is, the period when the employee lives outside the home) cannot be more than 1 month, but the law allows this period to be extended to 3 months in agreement with trade unions.
When working on a rotational basis, working conditions differ from usual ones. They usually work on a shift schedule; the duration of one shift cannot be longer than 12 hours.
For such work, workers receive an agreed payment for the hours worked, plus a special allowance for the rotation method. This allowance is paid for all days on duty, as well as for days spent traveling there and back.
If the place of work on a shift is in the Far North or equivalent areas, then the employee receives additional allowances for working conditions. He also has the right to additional days of vacation.
Distant work
Remote work is the dream of many, because you don’t have to waste time and money getting to your workplace. This is not available to everyone; only certain types of activities (such as the work of programmers) can be transferred to remote work.
Formally, hiring an employee for remote employment is no different from hiring an employee in an office.
. The employee must provide the same documents, an employment contract is concluded with him, an employment order is issued and a personal card is filled out.
The main difference is that when working remotely, an employee is located outside the employer’s location, or away from stationary workplaces and uses the Internet for work.
The work schedule of a remote employee is discussed with him individually, but it must comply with the Labor Code. As a rule, employers agree with employees on a work schedule, when the employee must be present at the workplace (at his location) at certain hours and on certain days.
Since, from the point of view of the law, remote work is no different from “regular” office work, insurance premiums and personal income tax are paid for the employee, and he has the right to the same social package as others (vacation, sick leave, etc. ).
Freelancers
Freelancers are usually called those who do not have a permanent place of work and provide themselves with work independently. Most often, IT sector specialists work through freelancing, but freelancers can be called, for example, builders who independently seek orders for themselves.
Most of those who call themselves freelancers work without official registration. They do not earn insurance coverage (then it will be more difficult to retire), and do not have paid vacations or sick leave.
If we consider “official” freelancers, then in Russia they have to register as individual entrepreneurs
(IP). Now in 4 regions you can already register as self-employed, it will be more profitable.
In the case of work through the registration of an individual entrepreneur, no regulations stipulate either the length of the working week or the length of working hours per day. In practice, most freelancers work as much time as they wish (or depending on the availability of orders and time) - that is, much more than 40 hours a week.
In order to provide services as a freelancer, through an individual entrepreneur or simply as an individual, it is best to enter into a contract or service agreement with the customer. This document specifies the content of the work and the timing of its completion.
It is best not to “run” from the law, but to work with official registration. When working as an individual entrepreneur, it will be enough to pay 6% of income and insurance premiums (about 36 thousand rubles per year).
How to pay for work on a daily schedule
For employees working on a daily schedule, you can establish any wage system: time-based, piece-rate, etc. There are no special instructions or prohibitions in this regard in labor legislation.
Payment is made for actual hours worked or volume of work completed. For night work, it is necessary to pay extra for each hour of night time at least 20% of the salary/hourly rate (Article 154 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 22, 2008 No. 554). Holidays on which a scheduled shift falls are paid at no less than double rate or single rate if the employee takes time off for a “holiday” shift (Part 3 of Article 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
We will separately dwell on the procedure for paying for deficiencies and overtime of employees formed at the end of the accounting period.
When paying for defects, it is necessary to take into account the provisions of Art. 155 Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
If an employee has worked more than the established hours at the end of the accounting period, he or she will be overtimed. It should be paid as overtime:
- for the first 2 hours - at least one and a half times the amount, and if this work has already been paid in a single amount when paying wages, then you need to pay at least up to one and a half times the amount;
- subsequent hours - at least double the amount, and if they are already paid for in a single amount, you should pay at least up to double the amount.
At the employee’s request, he can take time off for overtime hours: no less than the time worked overtime (Part 1 of Article 99, Part 1 of Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated August 31, 2009 No. 22-2-3363).
In order not to make a mistake in calculating and paying overtime, it is important for the employer to pay attention (Parts 6 and 7 of Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- to scrupulously count the overtime of each employee;
- control over the volume of overtime ─ per year, overtime work should not exceed 120 hours (Part 6 of Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Work on weekends and holidays does not apply to overtime (Part 3 of Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
When calculating hours of overtime and underwork, it should be taken into account that the standard hours for different employees for the accounting period may differ. The standard hours exclude the time when the employee did not work, but he retained his place of work - he was on vacation or on sick leave, or underwent a medical examination. In such cases, the employee’s standard working time must be reduced by the number of hours of such absence falling within working hours (Letter of the Ministry of Labor dated May 21, 2019 No. 14-2/OOG-3606).
If you have any unresolved questions, you can find answers to them in ConsultantPlus.
Full and free access to the system for 2 days.
How many shifts per month can you work 24 hours a day?
According to the current legislation, it can be understood that even if working hours are allowed to be organized “every other day,” the employer does not have the right to force an employee to work beyond the established maximum permissible working hours. At the same time, he can use the consolidated recording of working hours for quite a long time - up to a year. In this case, overwork can be compensated for by breaks - days when the employee is absent from the workplace. However, if we consider precisely the question of how many shifts per month you can work 1/1, if in fact the employee does not go on sick leave, does not receive vacation, but goes to work strictly according to schedule, then the restrictions have already been established here, especially if the month is reporting period...
To understand how many shifts you can work in a month, you should refer to the production calendar and find out the number of hours of work expected in those months according to the production calendar. For example, in June the norm is 167 working hours. This means that in just one month you can work a maximum of six full 24-hour shifts, or six 24-hour shifts and one 23-hour shift. In other months, the number of hours you work may be more or less, so the exact number of shifts per month you can work 1/1 will depend on the month you choose.
In this case, some overtime work is permitted provided it is paid as overtime. Overtime is calculated based on the results of the reporting period. And total overtime work cannot exceed 120 hours per calendar year. If it is recorded that an employee in this mode worked more than the allotted time, the excess working time is still subject to payment, but the employer may be held administratively liable in accordance with Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
How many years to keep the daily schedule
The storage periods for work schedules are established in clause 402 of the List of standard management archival documents, approved. By Order of Rosarkhiv dated December 20, 2019 No. 236:
| 402. | Time sheets (schedules), working time logs | 5 years | Under harmful and dangerous working conditions – 50/75 years |
The daily schedule of employees with harmful and/or dangerous working conditions must be stored:
- 50 years if it is completed by office work after 01/01/2003;
- 75 years if it was completed before 01/01/2003.
The storage period of the schedule must be calculated from January 1 of the year following the year in which the schedule ended (Part 1, Article 17, Article 21.1 of the Federal Law “On Archiving in the Russian Federation” dated October 22, 2004 No. 125-FZ, clause 4.1 and clause 4.8 of the Instructions, approved by Order of the Federal Archive of December 20, 2019 No. 237, Letter of the Federal Archive of March 13, 2020 No. R/M-479).
Why do you need a time sheet?
The working time sheet, approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee dated January 5, 2004 No. 1, helps the personnel service and accounting department of the enterprise:
- take into account the time worked or not worked by the employee;
- monitor compliance with the work schedule (attendance, absence, lateness);
- have official information about the time worked by each employee for calculating wages or preparing statistical reports.
It will help the accountant confirm the legality of accrual or non-accrual of wages and compensation amounts for each employee. The HR officer must track attendance and, if necessary, justify the penalty imposed on the employee.
A time sheet refers to the forms of documents that are issued to an employee upon dismissal along with a work book upon his request (Article 84.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It is worth noting that the unified forms of timesheets N T-12 and N T-13 are not required for use from January 1, 2013. However, employers are required to keep records (Part 4 of Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Organizations and individual entrepreneurs can use other ways to control the time employees spend at work. But in fact, the form format developed by Gostkomstat is quite convenient and continues to be used everywhere.
According to the Instructions for the use and completion of forms of primary accounting documents:
- the work time sheet for 2022 is compiled and maintained by an authorized person;
- the document is signed by the head of the department and the HR employee;
- after which it is transferred to the accounting department.
As we can see, the rules do not establish the position of the employee who keeps the time sheet. Management has the right to appoint anyone to perform this task. For this purpose, an order is issued indicating the position and name of the responsible person. If an order to appoint such an employee is not issued, then the obligation to keep records must be specified in the employment contract. Otherwise, it is unlawful to require an employee to keep records. In large organizations, such an employee is appointed in each department. He fills out the form within a month, gives it to the head of the department for signature, who, in turn, after checking the data, passes the form to the personnel officer. The HR department employee verifies the information, fills out the documents necessary for his work based on it, signs the time sheet and passes it to the accountant.
In small companies, such a long chain is not followed - the accounting sheet is kept by a personnel employee, and then immediately transferred to the accounting department.
What can an employer be punished for?
The employer should take the registration of work on a daily schedule seriously, as well as compliance with the procedure for remuneration according to such a schedule. Otherwise, administrative liability may follow under Parts 4 and 5 of Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. For example, they may be punished for failure to pay for deficiencies due to the employer’s fault or for paying for work on a daily schedule late/not in full.
If an employer, in an employment contract with an employee who works on a daily schedule, does not specify the working hours and rest hours, when they differ from the general rules of work in the company, he may be brought to administrative liability under Parts 4 and 5 of Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
They may also be punished for the lack of a daily schedule, if such a work schedule is established in the company, or for any violation of the procedure for drawing up a schedule (under Parts 1, 2 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Administrative responsibility under Art. 13.20 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation may threaten an employer who violates the rules for storing the daily schedule.
How work is regulated day after day in accordance with the Labor Code
Both employers and employees for whom certain work and rest hours have been established must be aware of the norms of current legislation affecting the issues of recording working time and the distribution of working time. In particular, understanding these standards will help an employee effectively defend his rights if his employer makes unlawful demands on him. The employer, in turn, referring to the legislation, will be able to organize working hours day by day so that there are no problems with regulatory authorities and fines. And, of course, an understanding of the principles of labor legislation in the context of work according to the daily routine is necessary for personnel department employees and immediate managers of the enterprise.
In the context of everyday labor regulation, special attention should be paid to the following provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- Article 57 strictly requires information about working conditions, including the current work schedule, to be indicated in the employment contract.
- Article 99 deals with the concept of overtime, which can often be considered as working 24 hours a day.
- Article 100 discusses the very concept of working hours and the general principles of its establishment in the context of labor relations.
- Article 102 regulates the principles for establishing flexible working hours, which are most often used to organize daily work.
- Article 104 regulates the principles of practical application of synthetic recording of working time, as well as situations in which the maximum duration of the accounting period is reduced.
- Article 152 provides for the legal regulation of remuneration of workers in the case of overtime work.
Let's sum it up
- The daily work schedule involves the employee performing his or her job duties continuously for 24 hours in accordance with the internal labor regulations and the terms of the employment contract.
- To ensure that work in this mode does not violate the norms of labor legislation, the employer must simultaneously fulfill three conditions regarding the duration of working hours and rest time.
- It is prohibited to include pregnant women, minors and some other categories of persons in daily schedules.
- Payment for work on a daily schedule should take into account the time actually worked by the employee, as well as additional payments for work at night, holidays, etc.
Employee rest during a 24-hour shift
Earning money on the Internet
Search for effective personnel
There are organizations and enterprises in which employees work in shifts, and the shift schedule is every three days, and the work shift is 24 hours. Many people ask: “Am I entitled to a break and rest for sleep? How long should they last? Let's try to figure out what kind of rest an employee should have during a 24-hour shift.
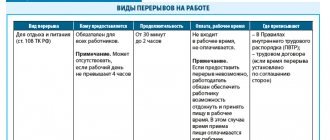
According to Art. 108 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, during the working day (shift), the employee must be given a break for rest and food lasting no more than two hours and no less than 30 minutes, which is not included in working hours.
The time for granting a break and its specific duration must be established by the internal labor regulations of the organization in which the employee works, or by agreement of the parties between the employee and the employer.
Duty with sleep right
The time for granting a break and its specific duration are established by internal labor regulations or by agreement between the employee and the employer. Since during the break for rest and food the employee is free from performing work duties, he has the right to use this time at his own discretion, including for sleep (cassation ruling of the judicial panel for civil cases of the Murmansk Regional Court dated December 15, 2010 in case No. 33- 3151). As an exception to the general rule of Part 1 of Art. 108 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the law establishes that a break for rest and food may not be provided only at work where, according to the conditions of production (work), providing a break for rest and food is impossible (see part three of the same article). In this case, the employer is obliged to provide the employee with the opportunity to rest and eat during working hours.
Duration of work at night according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, conditions and payment procedure
For persons working extended (12 or more hours) shifts with the right to sleep (dispatchers, energy system duty personnel, medical workers, etc.), it is necessary to equip a place for sleeping and eating hot food. Designing a shift work schedule for an industry or enterprise and increasing the duration work shift is allowed in accordance with the procedure established by law. But it is still not clear what “with the right to sleep” means? So, logically, it can be without the right to sleep? I hope the question is clear? Labor Code of the Russian Federation of December 30, 2001 N 197-FZ Article 91. The concept of working time. Normal working hours. Article 94. Duration of daily work (shift).
For this category of workers, the employment contract reflects this fact and the impossibility of reducing the night period.
Working at night without the right to rest
Shapoklyk wrote: Dear labor security guards! With the summarized accounting of working hours, there is such a schedule for a day or three. It is usually worked by security guards, boiler room operators, as well as all those who have a very long way to get from home to work :) The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not contain any prohibition on working for 24 hours. But my opinion is that if some kind of industrial accident suddenly happens to an employee injury - it doesn't seem like much. Therefore, from a labor safety point of view, is it possible to work for 24 hours without a 1-2 hour sleep break? If there are any regulations regarding requirements for breaks in the workplace? I only managed to dig up this: Sanitary and epidemiological rules SP 2.2.2.1327-0310.25.
About 24-hour duty
To service a continuously operating post (responsibility center), the administration forms a group of workers. The general working time fund (24 hours a day at one workplace) is distributed among employees of this group in accordance with the requirements of labor legislation, the terms of collective and labor agreements.
Shift schedule required
The employment contract determines the duration of daily work (shift). Labor legislation does not prohibit the use of 24-hour shifts. Article 94 of the Labor Code clarifies that certain categories of workers cannot be hired under such conditions. For example, an employee under 18 years of age cannot be assigned to daily duty. Pregnant women are not allowed to work at night (Article 96 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). A number of fundamental requirements are contained in Article 103 of the Labor Code:
- the work of the duty officers must be organized in accordance with the shift schedule;
- The shift schedule is brought to the attention of employees no later than one month before it comes into force. This means that the employee must be familiarized with the duty schedule for December before November;
- Working two shifts in a row is prohibited. If the duty period lasts 24 hours, then it is unacceptable to engage an employee for two shifts in a row.
The absence of a shift schedule or an employee working two shifts in a row are classified by labor inspectors as administrative offenses. Responsibility for all types of violations of labor and labor protection legislation entails the imposition of an administrative fine under Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses:
- for officials - in the amount of five to fifty times the minimum wage;
- for persons carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity - from five to fifty times the minimum wage or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days;
- for legal entities - from three hundred to five hundred minimum wages or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days.
But if an official has previously been subject to administrative punishment under this article, then he faces disqualification for a period of one to three years.
How to create a shift schedule
It is convenient to draw up a shift schedule using the form provided for the working time sheet. For this purpose, in the unified form of report card No. T-13, columns 1 - 6 are used. But they are not enough - it is necessary to provide an additional column for the signature of each employee, certifying (with the date) that he is familiar with this document.
When working in shifts, the working hours include a working week with days off on a staggered schedule. This wording is enshrined in Article 100 of the Labor Code. The legislation does not explain the length of such a working week in days. Therefore, the employee’s employment contract fixes a conditional average indicator - the length of the working week in hours. But how to define it?
The legislation does not clarify the concept of “normal working hours”. However, within the meaning of Article 91 of the Labor Code, this is the time allotted for the performance of labor duties and agreed upon by the employment contract. This article introduces a maximum duration of normal working hours during the week - 40 hours. Therefore, when using a sliding schedule, the employer is forced to set the employee a certain length of the working week, also in hours. This inherently average annual figure cannot exceed 40 hours.
Working hours are regulated by the decision of the employer, taking into account the opinion of the elected trade union body or on the basis of a collective agreement (Articles 159, 160 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the length of time worked for the selected accounting period should not exceed the normal number of working hours. Therefore, during the accounting period, the employer keeps summarized* records of working time. And the established length of the working week is used when calculating vacation pay (clause 13 of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 11, 2003 No. 213).
Example 1
The employer will have to determine the length of the duty week. Weekly working time – 168 hours (24 hours a day, 7 days). If we distribute this load among five people on duty, then each of them will have to spend an average of 33.6 hours (168/5). But with four people on duty per employee, on average there will be 42 hours a week (168/4).
Normal number of working hours
The concept of the normal number of working hours is explained by the Ministry of Labor Resolution No. 65 of December 29, 1992 (hereinafter referred to as Resolution No. 65). The norm should be calculated on the basis of the calculated schedule of a five-day working week (clause 2 of Resolution No. 65). For the practical application of the rule contained in it, it is necessary to establish the length of the employee’s working week - 40 hours or less:
The new, amended version of Article 104 of the Labor Code, which came into force on October 6, 2006, essentially did not change this provision. Its wording does not contradict the explanations of the Ministry of Labor (Resolution No. 65). It cannot be said that the normal number of working hours now coincides with the weekly working hours set by a particular employer. It is still tied to the standard “five-day week”. This principle is used to determine the number of personnel required to ensure round-the-clock duty.
We draw up a staffing schedule
The company's need for duty must be reflected in the staffing table. This primary document requires indicating not only the name of the position of the duty officer (watchman, security guard, etc.), but also the required number of such staff units.
When planning the number of staff on duty, it is necessary to remember about the possibility of temporary disability and social guarantees. Each employee is entitled to an annual leave of 28 calendar days (Article 115 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). And, in addition, additional leaves may be granted to certain categories of workers or established by a collective agreement.
Example 2
There are two options for calculating staffing levels per workplace with 24-hour operation, depending on the length of the working week. It is taken into account here that on pre-holiday days the length of the working day should be reduced by one hour (Article 95 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). And in addition, you can control that the amount of overtime during the year does not exceed 120 hours (Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Using this algorithm, it is easy to calculate that for a staffing level of 4 people with a maximum permissible “average” working time of 40 hours per week, overtime for an employee will be 370 hours per year. In other words, staff reduction will entail a violation of labor laws.
How to choose an accounting period
Summarized accounting is based on the fact that the employer has the right to increase the “control”, that is, accounting, period, from one week to a year (Article 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The accounting period is determined by the specifics of production. There are industries in which the workload on personnel is seasonal. For example, for boiler room attendants the main peak of employment occurs during the heating season, and for security guards in an educational institution - from September 1 to June 30. In such cases, vacations are planned during the production “lull”. And the accounting period is chosen so that its duration obviously exceeds the period of intensive work. In our examples, this accounting period will be a year. The point of a long accounting period is to minimize overtime within its limits and smooth out the seasonal overload of the employee. You can set the usual accounting period for these employees - a month. After all, work schedules will have to be drawn up for the entire accounting period at once (clause 3 of Resolution No. 65). And planning the employment of specific employees for the long term is a thankless task.
One more detail should be paid attention to: for the enterprise as a whole, only the duration of the accounting period and the date of its introduction are established. And for each newly hired employee, the accounting period will be counted from the moment of his hiring. Accordingly, he will have to determine the normal number of working hours on an individual basis.
Peculiarities of remuneration for duty officers
Remuneration based on a monthly salary for duty officers with cumulative recording of working hours is not entirely suitable. It unjustifiably complicates the work of accounting and does not fully take into account the economic interests of employees. It is much more practical to apply a per-shift rate, especially in situations where the schedule is compressed to replace an absent employee. The tariff applies to the shift as a whole. The daily shift is not divided into day and night parts. You will not have to pay extra for night work. In addition, there are no problems with payment for a month that is not fully worked.
Overtime is included in expenses
Overtime hours can only be identified at the end of the accounting period. They are paid at an increased rate: for the first two hours - no less than one and a half times the rate, for subsequent hours - no less than double (Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Overtime hours are recorded in the employee’s personal account - according to columns 26 and 27 of the unified form No. T-54. A long accounting period will be unprofitable for the employer if a large amount of overtime for the double rate accumulates. This consideration would argue for a short-term monthly reference period.
The question arises: is it possible to include overtime in labor costs for income tax purposes? The Ministry of Finance in a letter dated February 2, 2006 No. 03-03-04/4/22 gives a positive answer to it. But the employer has the right to take into account such expenses, including beyond 120 hours, only if the obligation to overtime work is provided for in the employment contract.
Line no. Indicators Calculation procedure If 40 hours a week If 36 hours a week 1 2 3 1 Established weekly working hours, hours Management decision 40 36 2 Annual working time fund for one post (responsibility center), hours 24 hours x 365 days 8760 8760 3 Norm of working time per employee per year, hours according to the production calendar of a 5-day week 1980 1781,6 4 Demand for workers, people page 2 / page 3 4,4 4,9 5 Duration of the employee's annual paid leave, hours 28 days / 7 days x page 1 160 144 6 Norm of employee working time for the year, taking into account vacation, hours p. 3.– p. 5 1820 1637,6 7 Demand for workers taking into account planned vacations, people page 2 / page 6 4,8 5,3 8 Number of staff, units rounding to whole units page 7 5 5 9 Annual resource of working time of full-time personnel, hours page 8 x page 6 9100 8188 10 Overtime per year for all personnel, hours page 2 – page 9 340 572 11 Overtime per year per full-time employee (on average), hours page 10 / page 8 No 114,4
it is important
The standard working time for certain periods is calculated according to the estimated schedule of a five-day work week with two days off on Saturday and Sunday, based on the following duration of daily work (shift):
- with a 40-hour work week – 8 hours,
- if the working week is less than 40 hours - the number of hours obtained by dividing the established working week by five days (clause 2 of Resolution No. 65).
it is important
The rule on postponing days off that coincide with holidays does not apply to a department operating around the clock (Resolution No. 65). But if the shift falls on a non-working holiday, then it is paid at a double rate (Article 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
* For some problems of summarized accounting, read PB No. 9, 2006.
E. Dirkova, auditor
| New generation berator PRACTICAL ENCYCLOPEDIA OF AN ACCOUNTANT What every accountant needs. The full scope of always up-to-date accounting and taxation rules. Connect berator |