Irregular working hours are often used by employers to regulate so-called “overtime”, but at the same time it causes a lot of debate.
Employers, as a rule, are confident that irregular working hours are not limited in time. Of course, this is a very common mistake associated with a lack of understanding of the legal standards for work and rest and, at the same time, an unreasonable desire to save on payments from the organization’s payroll fund. That is, the establishment of irregular working hours is a kind of optimization of personnel costs. Of course, this is a convenient position, which is approved by financial controllers, but does not always comply with labor laws.
Meanwhile, last year an attempt was made to limit the number of hours of “overtime” to 120 hours per year [1], but at the moment the relevant law is still under consideration. Moreover, the State Duma Committee on Federal Structure and Local Government Issues recommended that the lower house of parliament reject this bill.
Let's try to figure out how fair the interpretation of the law on long working hours in favor of the employer is in relation to commercial organizations, in which the temptation to abuse the right on the part of the employer most often arises.
HOW LONG IS AN IRREGULAR WORKING DAY?
As we know, the law defines work and rest standards, based on which the work schedule is established for employees. Working conditions during irregular working hours are still an assessment category for the employer. And he often understands an irregular day as having a beginning but no end. Of course, this approach to interpreting the law is beneficial to the employer, but, as a rule, it is disadvantageous to the employee. Does this mean that the truth is on the employer’s side?
In our country, the standard working time is 40 hours per week (Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), that is, with a five-day working week, one day accounts for 8 hours of working time. However, there are cases when this norm can be exceeded without violating the law. Such cases, as we know, include overtime and irregular working hours.
There is a clear limit in the law for overtime work - no more than 120 hours per year. Moreover, it is prohibited to engage an employee in overtime work lasting more than 4 hours for two days in a row. This is due to the fact that during overtime, the balance between work and rest is disrupted, which ultimately leads to ineffective work and unsatisfactory performance results.
Unlike overtime work, there are no such restrictions in relation to irregular working hours, that is, neither the restrictions established by law for engaging in overtime work, nor the guarantees and compensation associated with such work, apply to the work of employees with irregular working hours[2] .
Let's try to figure out why the legislator still allocates irregular working hours as a separate category of excess work, as a kind of special working time regime. According to Art. 97 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, work in irregular working hours is work outside the established working hours. That is, we are talking about extra-standard, additional work that goes beyond the working day. The legislator in Art. 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation made a reservation about the occasional involvement in such work, but this did not solve the problem of unfair use of labor. There are currently no criteria or signs of episodicity in regulatory legal acts. And the compensation that an employee receives in return for his excess labor costs is sometimes clearly lower than these labor costs.
We especially note that the introduction of an irregular working day for employees does not mean that they are not subject to the rules determining the start and end times of work, the procedure for recording working hours, etc.2 These employees are generally exempt from work on weekly rest days and holidays. Therefore, it is possible to attract employees who have irregular working hours to work on their days off and non-working holidays only by applying the provisions of Art. 113 and 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Part-time job
There is no law prohibiting part-time workers from using irregular working hours. However, in practice, its establishment is possible only when the part-time worker is free from performing work functions on some days, since in another case a part-time working day has been introduced for him.
The latest changes regarding irregular working hours were made to Art. 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in 2022. Then the legislator introduced a new rule according to which employees working on a part-time basis can establish an irregular working day only if the following conditions are met:
- a part-time working week is established by agreement of the parties;
- this part-time work week is established with a full-time work day.
Thus, at the moment, an irregular working day, according to Art. 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in the latest edition cannot be established for part-time workers, unless it is a part-time working week.
WHO CAN HAVE LONG WORKING DAYS?
The list of positions of employees with irregular working hours is not defined by regulatory legal acts, therefore, as a rule, it is established in the local regulatory act of the employer, for example, internal labor regulations or regulations on recording working hours.
The exception is the establishment of irregular working hours for drivers. So, according to Part 2 of Art. 329 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the specifics of the regime of working time and rest time, working conditions of certain categories of workers, whose work is directly related to the movement of vehicles, are established by the Ministry of Transport of Russia.
In accordance with the Regulations on the Peculiarities of Working Hours and Rest Time for Car Drivers[3], an irregular working day may be established:
• drivers of passenger cars (except taxis);
• drivers of expedition vehicles and survey parties engaged in geological exploration, topographic-geodetic and survey work in the field.
The number and duration of work shifts according to work schedules (shifts) for drivers with irregular working hours are established based on the normal length of the working week, and weekly rest days are provided on a general basis.
It should be noted that the irregular working hours regime has interesting features:
• it can be set for a specific position, and not for the structural unit as a whole;
• involvement in work beyond the standard time must be determined by production needs;
• the types of work performed overtime should not differ from normal work performed within the framework of an employment contract, job description or work instruction.
How many hours will you have to work
An important point that worries employees who have agreed to such working conditions is how long they will have to work. Indeed, today legislative and regulatory documents do not clearly stipulate the period of time that should be considered non-standardized. Therefore, each side tries to interpret them in its own way.
The administration is trying to make the most of the employee’s potential in order to resolve all their issues, regardless of the time the worker spends at the workplace. For the employee, the interest lies in receiving additional vacation and possible cash bonuses, but at the same time remaining at work for a minimum amount of time after the end of the working day.
Analyzing practical situations when it is necessary for individual employees to remain at work, we can highlight the following nuances:
- The duration of work outside the main working hours should approximately equal the compensation due. For example, if an employee receives 3 days of vacation, then he should not work more than 24 hours a year. It is easy to calculate that this amounts to no more than 2 hours per month. If this time is longer, the number of vacation days must be increased proportionally.
- If an employee’s presence is required for a small amount of time (for example, 15–20 minutes before the start or the same amount of time after the end of the work period), part of this time can be compensated with a monetary bonus (for the intensity of work).
- Performing functional duties after the end of the shift is not considered overtime work, is not taken into account and is not paid. In other words, even if you worked 10 hours, you will only be given 8 hours on your report card. Therefore, it is important to document compensation standards.
Remember, the duration of functional activity outside the main time must correspond in total to the compensation due for this. Determined by agreement between the citizen and the company.
HOW TO ESTABLISH AN INVENTIONAL WORKING DAY?
The provision for working on irregular working hours must be fixed in the employment contract with the employee. Here is an example wording:
2.1. The employee is assigned an irregular working day. 2.2. The annual additional paid leave for an employee’s irregular working day is six calendar days.
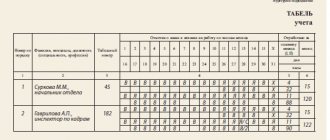
The local regulatory act that establishes the list of positions with irregular working hours is, as a rule, internal labor regulations (see example).
In order for an employee who has an irregular working day to be involved in extra work, a written or oral order from the employer or his own understanding of the need for this is sufficient. By the way, in order to attract an employee to work overtime, the employer must meet a number of conditions, including obtaining the employee’s consent.
It must be remembered that the employer has the right to involve employees with irregular working hours to work outside normal working hours only to perform work stipulated by the employment contract, and cannot assign other work. That is, if an employee works as a clerk, he cannot be involved in performing the work of a driver or secretary (for this you will already need to conclude an employment contract for part-time work).
Important nuances
1. An employee who has an irregular working day cannot refuse to work outside the working day (shift), if necessary. The employer may regard such a refusal as a failure to fulfill labor duties and subject the employee to disciplinary action.
2. Irregular working hours are episodic involvement in excess work. That is, in order to maintain a balance between working time and rest time, you can work beyond the norm from time to time, and not every day.
3. Performing work in excess of the standard does not mean that you can perform any work not specified in the job description. The employee no longer has any more responsibilities; only the time spent on work increases.
4. An undoubted advantage for an employee working irregular working hours is the establishment of additional paid leave of at least three days. This leave can be added to the annual main paid leave or replaced with monetary compensation (at the request of the employee).
5. If you need to establish an irregular working day for a specific employee, you must follow the procedure for documenting such a regime.
6. The established regime of irregular working hours makes it possible to keep an employee at work without registering overtime work and, accordingly, paying it at increased rates.
7. The employer does not need to keep records of overtime and monitor their limits.
8. Irregular working hours do not apply to work on weekends and holidays, only to working days for a specific employee.
9. If an employer abuses the right to hire workers during irregular working hours, the employee may file a complaint with the labor inspectorate or court (Articles 352, 356, 391 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). As a result, systematic overtime may be recognized as overtime work and the employer may be required to pay appropriate compensation. In addition, for violating labor law norms, the employer faces administrative liability under Art. 5.27 of the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offences.
What compensation is due?
Since information about an irregular schedule is significant and must be included in the employment contract, the employer must familiarize the future employee with this condition, as well as the compensation that he is entitled to for overtime working hours. In particular, according to Article 119 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, employees who work in this mode are entitled to additional paid leave. Its duration is determined by the collective agreement, but it cannot be less than three days.
An employee has the right to contact the employer with a request to replace additional leave for overtime with monetary compensation. This possibility is provided for in Article 126 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. However, providing this cash payment is the employer's right, not an obligation.
FAQ
Having understood the theory and examined practical examples, identifying the advantages and disadvantages of establishing irregular working hours and its differences from overtime work, we will answer the most frequently asked questions.
What is better: regular or irregular working hours?
This question cannot be answered unambiguously. Not only the legal, but also the human factor of your boss will be key. On the one hand, if the employment contract provides for an irregular work schedule, you have the right to additional days of vacation, which is good news, provided that there is a possibility that you will not be involved in working outside the standard schedule at all.
That is, it is better for the employer to provide for irregular working hours in the terms of the employment contract, and the employee should not categorically evaluate this fact. The main feature and difference from overtime work (overtime) is that irregular working hours are episodic, that is, they cannot be permanent, and may not be applied at all by the employer in practice. But if you still like certainty and tranquility, a normal working day and a standard 28 days of vacation per year are for you, but no one can guarantee the absence of overtime.
Working long hours has its benefits
Is it possible to take a vacation with irregular working hours?
Yes, the condition of an irregular work schedule in no case cancels the right to annual paid leave. Moreover, for employees hired within the framework of such a schedule, additional guarantees are established regarding the duration of vacation. Additionally, such employees are entitled to at least 3 calendar days per year.
Since the law does not establish a mandatory requirement for the number of undivided days of additional leave when dividing it into parts, as in relation to the main annual leave (Article 125 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the employee has the right to divide additional leave for an irregular working day according to the schedule at his own discretion.
How work is controlled under NSD
Control over the quality and quantity of work during an irregular work schedule on the part of the employer is no different from standard conditions. However, it is important for accounting departments to correctly keep records of overtime in order to avoid problems with regulatory authorities, as well as confusion with the concept of overtime work.
Working on an irregular schedule requires additional accounting from the accounting and HR departments
What to do if your employer forces you to switch to irregular working hours
Based on the fundamental principle of freedom of contract, the parties have the right to agree and adjust the terms of contracts at their own discretion. This also applies to an employment contract. The employer has the right to include a condition on an irregular schedule, and the employee has the right to refuse to enter into an employment contract with irregular working hours if the conditions do not suit him and choose another employer or renegotiate the conditions with the first one.
However, you should not be critical of this feature, as we said earlier - an irregular schedule may not be implemented in practice, while the employee will have guarantees.
If you have already concluded an employment contract and the employer insists on irregular working hours, it is important that this is documented, since such overtime is not paid like overtime, which means you may be left without any compensation or guarantees. It is important to check their availability when concluding an additional agreement to the employment contract.
Results
The issue of establishing and applying irregular working hours is relevant today for both employers and employees. Some want to save money, while others, on the contrary, want to receive additional guarantees or compensation.
In practice, both employees and employers incorrectly interpret and do not distinguish between the concepts of “irregular hours,” “overtime,” “overtime,” “additional work,” and so on. There are often cases of abuse of rights on the part of employers, in order to save money, when, with an established irregular working day, an employee is involved in working beyond the norm not occasionally, but systematically. Such circumstances are qualified as overtime work, which is subject to additional payment. Therefore, it is important for an employee to know his rights in order to stop their violation or protect them in a timely manner, and for an employer to avoid problems with regulatory authorities.
Definition of valid time
Labor legislation defines working hours as the time during which an employee must perform work duties. Normal working hours cannot exceed 40 hours per week. The employer is required to record the time actually worked by each employee. There are restrictions on overtime work, which is paid additionally and is often confused with irregular working hours. Irregular working hours should be distinguished from overtime.
For irregular working hours, one wage system is provided. In turn, overtime is paid for as work “above the norm” at a different rate.
List of positions
A specific list of positions for which an irregular regime is applied is established by the company administration. At the state level there are only recommendations to whom this can be applied. The list included:
- Leaders. This includes not only the top officials of the company, but also their deputies, heads of branches, divisions, and individual sections.
- Maintenance engineering and technical personnel. For example, computer engineers, technicians, operators, equipment adjusters usually begin their activities a little earlier than ordinary employees and finish after their departure with a control check of such property.
- Housekeeping staff. Supply of products, support of workplaces in working order, elimination of all technological problems.
- Employees whose activities cannot be normally regulated. For example, couriers, realtors, tutors who focus on clients.
- Hard workers who are expected to produce the final result, and not to be in the company. This category includes artists, writers, and other creative individuals.
It is advisable to indicate that for ordinary workers performing complex physical activities in shifts, the use of irregular work hours is unacceptable. This prohibition is associated with the physiological characteristics of the human body. And also, you should not ignore labor safety requirements regarding providing workers with the rest necessary for full recovery.
Remember, it is the employer’s responsibility to determine who will work irregular hours. An employee may refuse such a regime if working conditions allow this.
Design and work schedule
The concept of an extended regime of functional obligations applies only to those cases where the employee starts work earlier or is slightly delayed after its completion. These hours are not shown in the work schedule.
In practice, the number of hours worked over the required hours is not taken into account. So it turns out that a worker can be at the workplace continuously for up to 12 hours, while only 8 hours of worked time will be entered on his report card.
At the same time, he is entitled to a legal three days of vacation in addition to the main one. Other compensation issues will have to be adjusted with the employer. The subordinate’s obligation to stay after everyone has gone home and finish the task unfinished during the day occurs only if such a regime was agreed upon in advance.
Registration of irregular working hours
Employers are wondering: how to establish such a work schedule? Let's figure it out:
- Simply familiarizing an employee with a local regulatory legal act, a list of positions, where it will be indicated that he is entitled to NSD is not enough and is unlawful. Such orders should not be carried out verbally either.
- It is necessary to establish a list of positions for which irregular work hours will be established. The list can be drawn up in a separate document, introduced by order, or specified in a collective labor agreement. Also, if desired, you can develop a Regulation on irregular working hours, which will describe in detail the features and guarantees.
Payment
Functional activities outside the period established by the schedule require certain compensation. The legislator has established that it is mandatory to provide 3 days of vacation (in addition to the main one). At the same time, the worker decides independently to receive days of rest or monetary compensation for them. And this is not limited by law. With the exception of cases where such rest is due to pregnant women, minors, for work in harmful or dangerous conditions.
The regulations do not provide for other types of compensation. Here is a reference to local collective agreements of companies. In practice, in addition to real rest, companies often provide their subordinates with:
- increased salary within the salary range of a specific position;
- additional payments for work intensity (up to 100% of the official salary);
- increase the number of rest days (up to 7 days);
- one-time bonus payments for performing a specific amount of work;
- allowances for professional excellence;
- other types of compensation.
To understand what level of income a citizen working in this mode will receive, you should carefully read the provisions of the company’s collective agreement. You must immediately read the agreement with the company that you are proposing to sign.
Remember, the collective agreement applies to all company personnel. Therefore, if the rule on increased payment is not included in a bilateral document, it will still be implemented on a general basis.