Cash transactions are operations related to the receipt, issuance, storage of cash and the preparation of cash documents. Cash transactions are conducted according to the rules established by the Central Bank: Directive dated March 11, 2014 N 3210-U and Directive dated October 7, 2013 N 3073-U. These rules are called cash discipline, and this concept includes:
- maintaining cash documents documenting cash flows;
- compliance with the cash balance limit;
- limitation of cash payments between business entities within the framework of one agreement in an amount of no more than 100 thousand rubles.
who conduct business exclusively through non-cash payments should not observe cash discipline The need to complete cash transactions is not affected by the presence of a cash register or the selected tax regime. There is only one rule here - if there are any cash movements, then cash discipline must be observed.
Cash documents
Cash transactions are documented with the following documents:
- Receipt of cash at the cash register - cash receipt order in form 0310001. Such an order is filled out for each receipt of money at the cash register, but if it is cash issued by a cash register check or a strict reporting form, then the order is issued for the total amount of cash received per day.
- Issuing cash from the cash register is an expense cash order in form 0310002. When receiving such an order, before issuing money, the cashier must check the signature of the accountant (or manager, in the absence of an accountant), the presence of supporting documents and verify the identity of the recipient of the money.
- The data on incoming and outgoing orders is entered into the cash book using form 0310004. At the end of the day, the remaining cash in the cash register is displayed. If no cash transactions were carried out during the working day, then no entries are made in the cash book.
- The book of accounting of funds issued and received by the cashier in the form 0310005 is kept only in the case when the organization has several cashiers. She arranges the transfer of cash between the senior cashier and the cashiers during the workday.
- The issuance of cash for the payment of wages, scholarships and other payments to employees is formalized not only by a cash receipt order, but also by statements: settlement and payment statements in form 0301009 and payment statements in form 0301011.
Cash accounting in the 1C:ERP system
The cash register card determines in which cash book the transactions for recording cash in the cash register will be reflected. A cash book can be generated based on cash transactions of a specific cash desk. It is possible to create a separate cash book for divisions that are not allocated to a separate balance sheet.
To plan the movement of cash using a payment calendar for the cash register, the collection period is indicated - the number of days from the moment cash is issued from the organization's cash desk until the moment it is credited to the current account.
The receipt of cash is registered in the “Treasury → Cash registers → Receiving cash orders” workplace. For the document “Cash receipt order” a list of typical business transactions is defined.
The basis for processing cash receipts in 1C:ERP 8 can be settlement documents “Invoice for payment”, “Customer order”, “Sales of goods and services (issued without an order)”, agreements with counterparties and various orders for receipt (returns from suppliers, movement orders, returns from accountable persons).
The issuance of cash is processed in the “Treasury → Cash Desk → Expenditure cash orders” workplace. For the document “Cash expenditure order” in 1C:ERP 2.4 a list of typical business transactions is defined. The basis for writing off the DS is the document “Application for expenditure of funds”.
If requests for spending funds are not used, then orders and invoices (if they are issued without an order) can act as orders for payment. In this case, it is recommended to use the general journal of payment documents to transfer payments.
When conducting mutual settlements in the context of contracts, the basis for transferring an advance or repaying a debt to a supplier may be an agreement with the supplier.
Operations for the issuance of cash to another cash desk are formalized with an expenditure cash order, then the receipt is recorded. Until confirmation of actual receipt at another cash desk, funds are monitored “in transit.”
Moving an organization's cash
In order to formalize the movement of an organization's cash between its cash desks and operational cash desks, several scenarios are supported in the 1C:ERP system.
Scenario 1
The document “Cash outgoing order” with the type of operation “Issue to the cash register of cash registers” and the document “Incoming cash order” with the type of operation “Receipt from the cash register of cash registers” is drawn up. This opportunity ensures the formation of entries Dt 50 Kt 50 in regulated accounting “directly”, which eliminates the need to prepare additional documents “Withdrawal of funds from the cash register of the cash register” and “Depositing funds into the cash register of the cash register”. It is recommended to use if the receipt and withdrawal of funds are carried out during the day.
Rice. 1 Cash receipt order
Scenario for registering the movement of an organization’s cash between its organization’s cash desk and the operating cash desk “directly”:
Rice. 2 Moving the organization’s cash
Scenario 2
The document “Incoming cash order” with the type of operation “Receipt from another cash register” and the document “Outgoing cash order” with the type of operation “Issue to another cash register” are drawn up. Additionally, you need to fill out the documents “Depositing funds into the cash register of the cash register” and “Withdrawal of funds from the cash register of the cash register”. It is recommended to use if the receipt and disbursement of funds can be carried out on different dates. When using this scenario, cash movement transactions are reflected through account 57.01 “Transfers in transit.”
The scenario for registering the transfer of DS between the organization's cash desk and the operating cash desk using accounting accounts 57.01 “Transfers in transit” is presented in the diagram.
Rice. 3 Transfers on the way
Cash inventory
It is possible to carry out an inventory of cash in the cash registers of the enterprise. For inventory of cash, a document of the same name is provided (Treasury → Cash Desk → Inventory of Cash).
Using the “Fill” command, information about the organization’s cash balances is filled in in the tabular part of the document in accordance with the cash book and organization specified in the document. The information is filled in in the “Accounting” column. In the “Actual” column in the 1C:ERP configuration, enter the amount of cash recorded in the cash register after recalculation (taking inventory). Based on these data, discrepancies (surpluses or shortages) are recorded. The document indicates the item of cash flow, as well as the items of income and expenses to which these surpluses and shortages should be attributed.
Rice. 4 Cash inventory
If it is intended to compensate for the shortage of funds at the expense of the cashier, then an item with the distribution option “Do not distribute” is indicated as an expense item. As an expense analytics, you should use analytics for individuals and indicate information about the cashier to whom the shortage should be attributed.
To reflect the cash refund transaction in 1C:ERP 8, it is necessary to draw up the document “Cash receipt order” with the operation “Other receipt”. The document should indicate the same DDS items, income and expense items that were indicated during the inventory of cash at the cash desk.
Working with cash book sheets
A cash book can be generated separately for each organization, as well as for each separate division - both allocated and not allocated to a separate balance sheet.
For each separate division in 1C:ERP 2.4, you can maintain a separate cash book with its own numbering of sheets. Information about all cash books is stored in the list “Treasury → Cash → Cash books”. Information about the cash book is displayed as a grouping in the list “Master data and administration → Master data → Enterprise cash registers”.
The cash book indicates the name of the structural unit used in printed forms. For unique numbering of payment documents of a separate division within one cash book, you can specify a prefix. You can maintain continuous numbering of payment documents within one organization, without isolating payment documents of separate divisions.
Information about which cash book is used when conducting cash transactions in a specific cash desk and separate division is indicated in the “Organization Cash Office” card.
Rice. 5 Cash desk of the enterprise
Cash book sheets are created in the “Cash books” list. When creating a cash book sheet, transactions on those cash registers that relate to the specified cash book are taken into account.
When creating a cash book sheet, the correctness of reflection of payment documents in the cash book is additionally controlled.
Rice. 6 Cash book sheet
If the balance according to the information base (Balance according to register data) does not coincide with the final balance in the cash book sheet, then a warning will be issued that not all issued cash payment documents are registered in the cash book.
The cash book sheet is formed by the cashier daily based on the results of registering cash transactions during the day.
The cash book sheets marked in the list can be printed as a cash book. It is also possible to print the title page and the last page of the cash book (Title page and last page).
Rice. 7 Title page of the cash book
By default, transactions in the cash book are reflected in the currency of regulated accounting, but the possibility of accounting in foreign currency is also supported. To do this, you need to install the functional option “Master data and administration → Master data and sections setup → Enterprise → Currencies → Multiple currencies.”
Monitoring and analysis of operational information on all cash movements of an enterprise is carried out using the report “Treasury → Treasury reports → Control of cash transactions.”
How to start numbering sheets of a cash book other than number 1?
To change the numbering of cash book sheets, you need to use the “Group change of details” processing. Processing can be accessed via the “All functions” or “Technician functions” menu. Using the specified processing, you need to set the required number on the first sheet of the cash book at the header details “Sheet numbers” and “Sheet number of the tabular section”. You need to perform these steps by first turning on Developer Mode in “Advanced settings → Special processing capabilities.”
Cash limit
The cash limit is the maximum allowable amount of cash that can be kept in the organization's cash register at the end of the working day. Each enterprise sets the specific amount of this limit by internal order, based on its revenue amount using special calculation formulas given in the appendix to Directive No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014. Cash in excess of the established limit should not be in the cash register; it must be deposited at the bank. An exception to this rule is allowed on paydays, as well as on weekends and non-working holidays, if the organization carried out cash transactions on these days.
Individual entrepreneurs and small businesses (enterprises with no more than 100 employees and no more than 400 million rubles in annual revenue from the sale of goods and services) from June 1, 2014 may not set a cash balance limit. A special order must be issued to ensure that a cash limit is not established. If such a decision is made, then all cash proceeds can be stored in the cash register without any restrictions.
We draw the attention of those individual entrepreneurs and LLCs that were already working with cash before June 1, 2014, which means they should have had an order to set a limit. This order needs to be reissued, because until June 1, 2014, Bank of Russia Regulation No. 373-P dated October 12, 2011 “On the procedure for conducting cash transactions with banknotes and coins of the Bank of Russia on the territory of the Russian Federation” was in force, which has already been cancelled. The previous order based on this Regulation is invalid. You can set the same limit, you just need to change the basis of the order to Directive No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014.
If you want to refuse to establish a cash limit, then you cannot simply cancel the previous order in the order about this. According to the tax authorities, the cancellation of the old order does not mean the cancellation of the limit as such, but only the cancellation of the previous calculated limit amount, which means that the new limit is equal to zero. In this case, any amount of cash in the cash register at the end of the day will be above the limit. Strange logic, which, nevertheless, can deprive the organization of 50,000 rubles (the amount of the fine for violation of cash transactions for an LLC). Based on this, the new order must contain wording like “Keep cash in the cash register without setting a limit on the balance in the cash register.” This phrase is also suitable for those who are issuing a cash limit order for the first time.
How to calculate the cash balance limit for 2020 - 2022?
How to calculate the cash balance limit? Bank of Russia Directive No. 3210-U provides for such a calculation two outwardly identical formulas, which differ fundamentally only in the characteristics of the volume of turnover (real or planned) of funds involved in the calculation:
- Sales revenue volume. It does not take into account funds accepted by the paying agent (subagent).
- Volume of cash disbursements. It does not include funds for paying employees salaries, scholarships, and social benefits.
The first volume in Bank of Russia instruction No. 3210-U is designated by the letter V, and the second by R. And the formulas for calculating the limit (L) with these letters look like this:
L = V / P × N;
L = R / P × N;
where the remaining 2 indicators (P and N) are very similar in meaning, but characterize, respectively, the process to which one of the indicators that determine the calculation formula (V or R) relates:
- P is the billing period (defined in working days with the condition that their number does not exceed 92), during which either volume V is received or volume R is issued;
- N is the number of working days between the days of depositing money to the bank (for indicator V) or receiving it from the bank (for indicator R).
When determining the number of days that make up the value of the indicator N, the facts of acceptance and issuance of funds not included in the volumes (V and R) are not taken into account. It has been established that the number of days that make up the indicator N should not exceed 7, and if there is no bank in the locality where the legal entity is located, then 14. Although the value of this indicator may depend on such things as:
- force majeure circumstances;
- location, structure and features of the legal entity’s activities.
An example of calculating the cash register limit taking into account the volume of receipts from ConsultantPlus: Cash revenue of Rassvet LLC from the sale of goods for the billing period from 09/01/2020 to 11/30/2020 (64 working days) amounted to RUB 2,385,648. Revenue is surrendered daily (once a day)... Read the continuation of the example in the legal reference system. And if you don't have access to K+, get a trial demo access for free.
See also: “How to calculate the cash balance limit?”
Limitation of cash payments
The limit for cash payments is 100 thousand rubles. within the framework of one agreement, it applies to payments between business entities, that is, individual entrepreneurs and organizations among themselves. With individuals who are not entrepreneurs, the limit on cash payments does not apply, as well as when issuing accountable amounts, salaries and other social payments to employees from the cash register.
If you pay for goods or services in cash, you can give the accountable person any amount for payment, provided that the limit of 100 thousand rubles within the framework of one agreement remains the same. For example, you sent your manager to different addresses: buy materials for production, pay for any services, order work. If for each of these transactions the amount does not exceed 100 thousand rubles, then you can give him up to 300 thousand rubles.
Another thing is how safe it is to transport and pay with large sums of cash? Non-cash payments are both more profitable (no bank commission when cashing out) and more secure.
Choose a profitable current account
Certificate of verification of cash at the cash register (form No. KM-9)
This act reflects the results of a sudden audit of cash in the operating cash desk.
As a rule, the results of the audit are compiled by the tax inspector and the cashier-operator. They are then brought to the attention of the head of the company.
The act consists of:
· in triplicate - if the audit is carried out with the participation of a tax inspector. In this case, one copy of the act is submitted to the tax office;
· in duplicate - if the audit is carried out on the initiative of the enterprise administration. One copy of the act is transferred to the accounting department, the second remains with the financially responsible person (cashier-operator).
The unified form No. KM-9 was approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated December 25, 1998 No. 132.
Simplified cash discipline procedure
This concept means the opportunity for entrepreneurs and small businesses to refuse to set a cash limit, as well as the opportunity that only individual entrepreneurs have received since June 2014 - not to document cash transactions.
But although such a right exists, in reality it will not always be possible to use it. Clearly, this opportunity is available only to individual entrepreneurs without employees (or paying wages to employees by bank transfer), who, moreover, do not accept cash from anyone. Why? The fact is that Directive No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014 contains contradictory norms:
- Clause 4.1. Cash transactions are formalized by incoming cash orders 0310001, outgoing cash orders 0310002 (hereinafter referred to as cash documents). Individual entrepreneurs who, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on taxes and fees, keep records of income or income and expenses and (or) other objects of taxation or physical indicators characterizing a certain type of business activity, may not prepare cash documents.
- Clause 5. Acceptance of cash by a legal entity, individual entrepreneur, including from a person with whom an employment contract or a civil law agreement has been concluded (hereinafter referred to as the employee), is carried out using cash receipt orders 0310001.
- Clause 6. The issuance of cash for the payment of wages, scholarships and other payments to employees is carried out according to cash receipts orders 0310002, payroll slips 0301009, pay slips 0301011.
In paragraphs 5 and 6 there is no usual clause (except...) and it turns out that the requirements apply to individual entrepreneurs as well. Considering how often the Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Service can change their point of view on the same issue, it can be assumed that these provisions carry the risk of tax disputes. Therefore, while there are no official comments on these issues, it is safer to keep cash documents.
The second reason why individual entrepreneurs must continue to maintain cash documents is that filling out the book of income and expenses in all modes (except for UTII 2016, in which KUDiR is not maintained) is carried out on the basis of primary documents. Such documents confirming the receipt and expenditure of cash are orders in the form 0310001 and 0310002. Based on this, individual entrepreneurs maintaining KUDiR cannot refuse to maintain cash documents at all, because they will have no reason to make entries in the ledger.
It turns out that in reality, only individual entrepreneurs who do not pay salaries in cash, do not receive cash from anyone, and do not enter data into KUDiR (that is, only on UTII) can not keep cash documents. As you can see, the “simplified procedure for cash discipline” turned out to be very tricky. In fact, the only real simplification in conducting cash transactions so far is the ability not to set a cash limit.
If an individual entrepreneur decides to refuse to maintain cash documents (we have already pointed out the risks) and not to set a cash limit, then an order must be issued about this. While there is no such order, the individual entrepreneur must obey cash discipline.
How to get money from business? Registration of cash transactions
Business is going well, income is growing, free funds appear that the businessman can spend on himself. How to do it? For some LLC founders, it is a surprise that they cannot at any time receive money from the cash register for their needs or withdraw it from a cash account. But individual entrepreneurs can. But first things first.
First, about the legal status of the property of a legal entity. The authorized capital in the form of cash or other property does not belong to the founder of the LLC. Everything that was contributed during the registration of the company and everything that was earned in the process of its business activities is the property of the legal entity. A founder working in his own company can receive a salary in it as an ordinary employee if an employment contract has been concluded with him. Even if this is the only founder (participant) who himself manages the organization, he cannot dispose of the money of his LLC at his own discretion. By the way, the possibility of concluding an employment contract with the sole founder - the manager - still remains controversial, and you can find out about the latest opinion of the Ministry of Finance on this topic in this article.
Another opportunity (and the only one if the founder does not work in his organization) to receive money from the business is to use the profits received as dividends. We looked at the issues of taxation of wages and dividends of the founder of an LLC in the example of the article Individual Entrepreneur or LLC - what to register? But in this case, we are not interested in the issue of taxes, but in whether the founder can take cash from the cash register for his needs or withdraw it from the current account? No, it can’t, therefore the question of registering such cash transactions is not even worth it.
Now - about IP. On the one hand, an individual entrepreneur is liable for his obligations with all his property, except for that which cannot be recovered. But on the other hand, all property and money of an individual entrepreneur, including those received from business activities, are his property, which he can dispose of as he pleases (unless there are debts on taxes and contributions).
The individual entrepreneur does not receive his salary from himself, but he can take cash from the cash register or from the current account at any time. The right to do this is given by Directive No. 3073-U. If money is transferred to an individual’s payment card, then such a transfer is not a cash transaction and is not documented in cash documents. The amounts that an individual entrepreneur can spend from the cash register or from a current account for his personal needs are not limited, but arrears in taxes and insurance contributions must not be allowed. If an individual entrepreneur refuses to maintain cash documents and issues an order to this effect (see the section Simplified procedure for cash discipline), then the receipt of cash is not formalized in any way. If cash documents continue to be maintained, then on the basis of payments of money in the cash receipt order it is necessary to indicate: “Issuance of funds to the entrepreneur for his own needs” or “Transfer of income from current activities to the entrepreneur.”
Cash receipt
When receiving money for goods, the cashier is obliged to punch the cash receipt and give it to the buyer. The check must indicate:
- name and tax identification number of the company;
- KKM serial number;
- serial number of the check;
- date and time of purchase;
- the price of the product;
- a sign of fiscal mode (these are special characters that confirm that the cash register is registered and its memory operates in fiscal mode).
In addition to the required elements, the check may contain other data that the company or entrepreneur considers necessary (for example, the name of the cashier).
Control over cash transactions
Until 2012, control of cash discipline was assigned to banks, but now this function is only of the tax authorities. This function is regulated by the Administrative Regulations approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of October 17, 2011 N 133n. What do tax authorities have the right to when checking cash discipline?
- Accounting for cash in the cash register.
- Printing reports from the fiscal memory of cash register equipment and used fiscal memory drives.
- Checking all documents documenting cash transactions: the cashier-operator’s journal, incoming and outgoing cash orders and their registration journal, cash book, etc.
- Actions to verify the issuance of a cash receipt, which, although not called a test purchase (since they relate to investigative control measures), can constitute visual observation, with or without the use of video and audio recording methods of the facts of purchase and payment for goods.
Violation of the procedure for working with cash and the procedure for conducting cash transactions, as well as violation of the requirements for the use of special bank accounts, entails the imposition of an administrative fine under Article 15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation:
- for officials (heads of an organization or individual entrepreneur) - from 4,000 to 5,000 rubles;
- for legal entities - from 40,000 to 50,000 rubles.
We recommend that you check the correctness of your accounting in a timely manner, and from time to time arrange a full audit of your business. For our users, this service is available free of charge:
Free business audit
Cash and accounting - what are the rules of reflection?
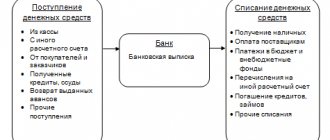
In accounting, cash transactions are reflected using account 50. Cash transactions are considered to be all actions performed with cash and monetary documents in a company and any entrepreneur.
What kind of operations these are, you will learn from our article “The concept and types of cash transactions (legal regulation).”
Account 50 is active, its debit reflects the receipt of assets, and its credit reflects the disposal. Depending on the type of business operation, account 50 can correspond with many accounting accounts.
So, for example, the posting of cash (withdrawal from a bank account) at the enterprise’s cash desk is reflected as follows: Dt 50 Kt 51. And vice versa, the delivery of cash to the bank from the enterprise’s cash desk is Dt 51 Kt 50.
The receipt of cash from the buyer in payment for goods/services is reflected as follows: Dt 50 Kt 62. Cash settlement with the supplier is formalized by posting Dt 60 Kt 50. In this case, it is necessary to comply with the limits for cash settlements between legal entities established by the Bank of Russia in clause 4 of the instructions from 09.12.2019 No. 5348-U.
Receipt of credit funds to the cash desk - Dt 50 Kt 66 (67), loan repayment by depositing cash from the cash desk - Dt 66 (67) Kt 50.
Payment of wages to employees from the cash register is Dt 70 Kt 50, and settlement in cash with the founders by paying dividends is Dt 75 Kt 50. The issuance of cash to the report is reflected by posting Dt 71 Kt 50, and the return to the cash register from the report of the balance of the unspent amount is reflected as follows: Dt 50 Kt 71.
The sale of fixed assets for cash is documented by posting Dt 50 Kt 62, and the receipt of proceeds from retail sales to the cash desk - Dt 50 Kt 90.
Details on conducting cash transactions in companies are contained in the BR Directive No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014 (hereinafter referred to as the Directive).