The amount of wages depends on how many days an employee works in a month. If the month is worked in full, then the employee is entitled to a salary in the amount of the established salary. And if he did not work in full for a month, then his wages will need to be calculated. In addition, the salary will also depend on whether the employee worked on weekends or not. In this article we will look in detail at how the company calculates salaries for less than a full month.
When an employee has worked for a full month, he is entitled to a salary, and it does not matter how many working days there were in the month - 17, 18 or even 23. When an employee did not get a job at the organization from the beginning of the month or was on vacation, he does not work for a full month and his salary will depend on how much time the employee worked.
Payroll calculation if an employee just got a job
When hiring an employee not from the first day of the month, for example, in the middle or at the end, salary calculations are carried out in the same way as when calculating for an incomplete month.
Let's take a closer look at the example
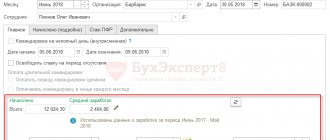
Ivanov I.I. I got a job at Continent LLC not from the beginning of the month, but from August 4, 2022. Ivanov’s salary is set at 50,000 rubles. From August 4 to August 31 there are 20 working days. Let’s calculate Ivanov’s salary for the first working month:
50,000 / 23 x 20 = 43,478.26 rubles.
We take 23 to be the number of working days in August according to the production calendar.
Important! An employee's salary is one of the main conditions for cooperation between the employee and the employer. It must be specified in the employment contract with the employee.
Remuneration systems and part-time work
Let's look at how partial month calculations are used in various remuneration systems.
An example of calculating wages for a full and part-time month for a salaried employee
Salary, tariff
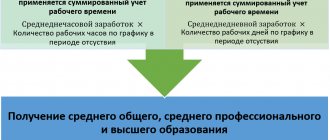
Remuneration for work time, or time-based, is a salary, tariff rate (hourly, daily). The salary is reduced proportionally, in accordance with the working time actually used in the month. The tariff rate is multiplied by the days or hours actually worked, depending on whether the rate is hourly or daily.
Example: according to an employment contract, an employee is given a salary of 25,000 rubles per month for a five-day working week. In April 2022, from April 1 to April 10 inclusive, he took leave at his own expense and worked 14 working days. There are 22 working days in a month. Credited 25000 / 22 * 14 = 15909.04 rubles.
Salary is calculated similarly according to the tariff rate (hourly or daily). If an employee has a daily wage rate of 1200 rubles/day under an employment contract, then after working 14 days he can count on an accrual amount of 1200 * 14 = 16800.00 rubles.
Piecework
Piecework wages for the number of finished products involve a price for each unit. Having worked for less than a full month, an employee, as a rule, manages to produce fewer units of production, and the accrual of payment will be less.
Example: the production standard for products is 10 products per day. An employee who meets the standard will produce 220 products in April. The price for each product is 130 rubles, which means that 28,600 rubles will be charged per month. If, as in the previous example, he worked only 14 days, the salary will be 14 * 10 * 130 = 18,200.00 rubles.
Commission and combined
The commission payment system is often used in trading. Employee remuneration is a percentage of sales, of income from transactions concluded by the employee. Partial work for the month is taken into account in wages “automatically”: the shorter the work time, the less significant the income from sales and the percentage of it.
If combined remuneration is used, including both salary and a percentage of transactions, a total calculation for the month is made taking into account the reduced salary.
Example: as in previous cases, an employee worked for 14 days in April, having, according to the employment contract, a salary of 25,000 rubles, plus the commission part of the salary - 6 percent of the amount of income from the transaction he concluded. During his work in April, he brought the company income of 550 thousand rubles. For the month he was accrued:
- 550,000 * 6% = 33,000.00 rubles as a percentage of sales;
- 25000 / 22 * 14 = 15909.04 rubles based on salary for less than a month.
33000.00 + 15909.04 = 48909.04 rubles total wages for less than a full month.
If there are holidays at the beginning of the month
There are often situations when an employee gets a job on a day other than the first day of the month, but only because the first days were holidays.
For example, an employee gets a job immediately after the New Year or after the May holidays. He, like other employees, will work the same number of days this month; accordingly, he will receive his salary in full, despite the fact that he did not get a job from the beginning of the month.
Let's take a closer look at an example: (click to expand)
Kolosova N.P. are hired at the beginning of the new year. His first working day is January 9, 2022, since 1 to 8 are public holidays. Kolosov’s salary was assigned 35,000 rubles. Kolosov is entitled to his full salary for January. Despite the fact that he was registered at work only on the 9th, he worked all working days of the month, since the 1st to the 8th were weekends.
However, if a situation arises when an employee writes an application for leave of his own free will from January 9, 2022, the calculation will be different. In this case, the employee is not entitled to a salary, since he has not worked a single day. From January 1 to January 8 there were holidays, and from the 9th to the end of the month he was on vacation.
Nuances
When making calculations, you need to pay attention to a number of nuances. A new employee who does not have time to work a full month is paid the same as for existing employees, taking into account the actual time worked. Only working days according to the production calendar are always taken into account.
If there are holidays at the beginning of the month (January) and a new employee started working after the end of this period and worked until the end of the month, he must be paid in full for the month.
According to Art. 2-7, art. 130-2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee is guaranteed a minimum wage. If the month is not fully worked, the actual salary may be less than the minimum wage. This will not be a violation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. If an employee is assigned a part-time working day and has worked an incomplete month, payment for the incomplete month will be made based on the rate established by the contract (1/4, 1/2).
If the employee worked on weekends
Even if an employee did not work fully for the whole month, for example, due to illness, he can work on weekends or holidays. But this does not mean that some days can be replaced by others, that is, if an employee was sick for 3 days and worked on weekends for 3 days in the same month, this will not mean that he worked the entire month. That is, it is impossible to simply pay him the required salary; it is necessary to make a calculation.
Let's take a closer look at an example: (click to expand)
Employee Turkina M.A. in October 2022, I took vacation at my own expense on the 4th, 5th and 6th. At the same time, in October she worked 3 days off – October 14, 21 and 28.
She worked 22 days in October, that is, as much as indicated in the production calendar, but she simply cannot pay the salary. Let’s calculate Turkina’s salary based on the fact that her salary is 30,000 rubles.
Work on weekends in the organization is paid at double the rate.
30,000 / 22 x 19 + 30,000 / 22 x 3 x 2 = 25,909.09 + 8,181.82 = 34,090.91 rubles.
Features of calculation for a shift schedule
Payroll calculation according to a shift schedule can be formed as follows:
There is a certain store that is open from 8 to 22 pm. The work schedule is 2 days every other. One shift of a salesperson is 14 hours. The first saleswoman begins her work in the current billing period on the 2nd, and the second - on the 4th. There are only 30 days in a month, so the first one worked 16 days, and the second one 14. However, the first saleswoman missed 4 of her shifts due to illness, and the second one had to replace her during this period of time. The employer has established a fee for one shift in the amount of 1200 rubles.
We first calculate the amount of wages that should have been initially:
- Salary of the first employee: 16*1200 = 19200 rubles.
- Salary of the second employee: 14*1200 = 16800 rubles.
However, the first saleswoman did not work 4 shifts, so we subtract the cost of these shifts from her salary:
19200 - 4*1200 = 14400 rubles will be received by the first employee for less than a month.
Accordingly, the second’s salary will increase proportionally:
16800 + 4*1200 = 21600 rubles.
Other grounds
A person may not be present for the full period:
- If there are holidays in the paid period. If a person works for a salary, then the presence of any number of holidays is not reflected in the amount of payments. When an employee was absent for some time during the “holiday month,” the calculations are made according to the first scheme, as usual. In this case, state rest days are not taken into account as non-work.
- When the contract stipulates a partial day. In this case, actual hours and days worked are paid. Often these are people who work part-time and want to earn extra money. For example, if a specialist has agreed with the manager to establish a schedule according to which he undertakes to work 5 hours a day for 30 days, and his minimum wage for a normal day is 45,000 rubles. So, in a month he would have to work 175 hours, but according to the new agreement it turned out to be 60. Then it turns out: 45,000 / 175 x 60 = 15,428 rubles.
- When going to work on a day off. According to labor legislation, it is allowed to go to work on a day of rest as directed by your superiors. If there are not enough hours in the paid period, then to increase earnings, workers also perform work on weekends.
According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, salary for a day off is calculated at double the average daily earnings rate.
The formula looks like this:
- salary is calculated for an incomplete period;
- after which the size for the weekend is calculated;
- the final payment will correspond to the sum of the above indicators.
Salary after vacation is calculated according to the usual scheme according to the first formula. Indexation of accrued wages is also carried out according to the general rules of Art. 134 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Minimum wage and incompletely worked month
The value of the minimum wage means the minimum allowable wage for a person for one month.
In accordance with the law, a person should not receive less than this value for a fully worked month. At the moment, the minimum wage is 6204 rubles.
Example
The person got a job 9 days before the end of the current pay period. Thus, he worked only 7 working days, with a total number of working days in the current month equal to 22 days. The salary is 18,000 rubles. Thus, his salary for less than a full month will be: 18,000/22*7 = 5,727.27 rubles.
This figure is lower than the minimum wage, so a reasonable question arises: does the organization need to pay the minimum wage , i.e. 6,204 rubles?
There is only one answer - no. The fact is that the minimum wage should be no lower than the value established by law only in the case when a person has worked a full calendar month. If for some reason he missed a certain number of working days, then he may receive less than what is indicated in the minimum wage.
In accounting, wage entries must be recorded very correctly and accurately. Women who are individual entrepreneurs can count on minimum payments. Specific amounts can be found in the article.
Are you expecting a baby? Then you will be interested to know how sick leave is paid for pregnancy and childbirth.
Calculation formulas
There are several ways to determine the amount of earnings for an incomplete period:
- Divide the monthly salary indicator (hereinafter referred to as the minimum wage) by the number of working days in the month (hereinafter referred to as the RDM). Multiply the resulting figure by the amount of days actually worked (hereinafter - FOD) - minimum wage / RDM x FOD. So, for example, if citizen P. worked for 17 days in July, with 21 RDM, and his salary is 60,000 rubles, then: 60,000 / 21 x 17. For 17 days, citizen P. will be given 48,571 rubles.
- You can also subtract the average salary for a certain period. In this case, the salary (hereinafter - O) is divided by the average number of days per month established by the state, after which the resulting figure is multiplied by the FOD - O / 29.4 x FOD. For example, a driver got a job on June 20 and worked for a total of 8 days. His minimum wage is 45,000 rubles. Thus, 45,000 / 29.4 x 8. The driver will be charged 12,244 rubles.
These are standard formulas used by accountants in organizations.
As already mentioned, the requirement for a salary not less than the subsistence minimum must be strictly observed by all employers. This amount is set as a minimum if the employee has completed the entire amount of work. Accordingly, if a citizen worked 5 days in a month, he will receive an amount corresponding to the hours of work.
For example: a seamstress works in an organization where the minimum wage is 40,000 rubles. Due to employment at the end of the month, she worked 5 days out of the required 22. The salary for the reporting period can be calculated as follows: 40,000 / 22 x 5. The actual salary for 5 days will be 9,090 rubles.
We recommend you study! Follow the link:
How to calculate an advance payment for an individual entrepreneur using the simplified tax system
Although the resulting amount does not reach the subsistence level, the organization does not violate the rights of the employee, since the seamstress worked for an incomplete period.
If the employee was not present for the entire monthly working period, then calculations are carried out according to the first formula. If a person did not show up, but by virtue of the law he is entitled to retain his wages, then its amount is calculated using the second formula, taking into account the average number of working days in a month. As a result, the employee receives the sum of indicators for the payroll and time while maintaining the salary.