What does dismissal by agreement of the parties mean?
An agreement between the parties (employee and employer) is a separate basis for the dismissal of an employee, established by an article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
As the name suggests, this is possible if the parties have agreed on all the essential points of termination of the employment relationship - the date of dismissal, additional compensation payments, etc. Compose HR documents using ready-made templates for free
If such agreement is not reached, then the employee has the right to resign of his own free will, having notified the employer at least two weeks in advance (Article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The employer may also be the initiator of the separation. To do this, it is necessary to have the conditions defined in the article of the Russian Federation (for example, reduction in number or staff, violation of labor discipline by the employee, etc.; for more details, see “How to fire an employee in 2022: step-by-step instructions for the employer”).
Pros and cons for the employee
In case of dismissal by agreement of the parties, the employee is not obliged to notify the employer two weeks in advance. Consequently, such a “resignation” is possible at any time, including “one day”. In certain situations, this can be considered a plus for both the employee and the employer.
Another advantage for the employee is the opportunity to receive additional monetary compensation upon dismissal “by agreement”. If an employee leaves of his own free will, such payments are not provided.
Among the disadvantages for the employee is the fact that the agreement of the parties is one of the most “strong” grounds for terminating an employment contract. It will be more difficult to challenge a properly executed agreement in court and be reinstated than if you were dismissed for other reasons. Especially if the employee received additional payments provided for in such an agreement.
Draw up and print an employment contract
Features of taxation
Paragraph 14 of the review of Judicial Practice of the Supreme Court states: in order for the amount of compensation upon dismissal by agreement of the parties to be recognized as expenses taken into account for income tax, the employer must prove the economic justification of such expenses.
That is, if the amount of the benefit turns out to be too large and inappropriate for the employee’s job functions, then the economic justification of the expenses must be proven directly by the employer.
If the dismissal occurs due to an employee committing a violation, the amount of the payment is always subject to taxation. To prove misconduct, the employer must provide documents confirming this fact.
Thus, compensation not exceeding three times the average monthly (in the northern regions six times) earnings are not subject to personal income tax. If the amount exceeds these amounts, but was previously agreed upon in the employment contract or collective agreement, then, in accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 217, the compensation will not be taxed.
Although, it is worth noting that in this matter the decision of the Constitutional Court, which takes into account only compensation regulated by Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, has great force, and therefore in the event of a trial, the decision will most likely be made in favor of the tax authorities.
Termination of an employment contract by agreement of the parties is no exception in tax matters. The same conditions and restrictions that apply to other reasons for dismissal remain in this case.
Benefits and risks for the employer
First of all, we note the low probability of conflict with an employee leaving by agreement of the parties. Such an employee receives an absolutely neutral entry in the work book, as well as additional cash payments. Consequently, the chances of future complaints and litigation are reduced (especially if the “compensation” is paid on time and in full).
If a conflict does arise, then the fact of the stability of the agreement, mentioned as a “minus” for the employee, as a basis for dismissal, turns into a “plus” for the employer. If this document is properly executed, the employee’s chances of being reinstated at work (and therefore receiving payment for forced absence and moral damages) are not great.
However, we cannot say there is a complete absence of risks in the event of termination of the employment relationship by agreement of the parties. Thus, if an employer delays payment of the amounts specified in the agreement, he faces a fine under Part 6 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation (for legal entities - up to 50 thousand rubles, for individual entrepreneurs - up to 5 thousand rubles).
Also, the fact that dismissal occurs “by agreement” does not mean that the employer will not be responsible for violations committed when preparing the relevant personnel documents (dismissal order, work book, etc.). In this situation, a fine can be issued on the basis of Part 1 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation (for legal entities - up to 50 thousand rubles, for individual entrepreneurs - up to 5 thousand rubles).
Create a staffing table using a ready-made template Try for free
Who is paid severance pay?
Labor legislation does not provide for mandatory payment of severance pay when an employee leaves the organization by agreement of the parties. Participants must resolve this issue independently.
The basis for terminating a contract in the form of an agreement between the parties has been very popular lately, as it is convenient for management and the worker.
An employer can quickly fire a person if necessary by agreeing with him on the terms of this procedure. For example, this is relevant when reducing staff, liquidating an organization, or dismissing unwanted or inconvenient employees.
In order not to carry out an official layoff, it is much easier to formalize everything with an agreement, promising the employee additional monetary compensation.
For an employee, leaving work by agreement is also convenient, as it frees you from mandatory service. If the procedure is carried out with the payment of additional compensation, then the benefit for the person increases even more.
The payment of severance pay is covered by Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which lists cases of mandatory payment of this type of compensation. Termination of the contract by agreement of the parties is not included in this list, however, it is said that the parties can independently establish additional cases of assigning compensation.
A person dismissed by agreement may receive severance pay:
- if this point is specified in the collective or labor agreement;
- if compensation is specified in an agreement signed by the participants.
How to issue an issue?
You can pay money to an employee only if there is a documentary basis. The amount to be issued and the rules for calculating it are prescribed in a collective or employment contract or agreement of the parties.
Based on these documents, money is credited to the employee. For the calculation, the calculation note T-61 can be used, which includes all accrued amounts to the dismissed person.
.
The fact of dismissal is always formalized by order; this can be a standard T-8 form or a free form.
If the order is formed in free form, then, in addition to the order to dismiss the employee by agreement of the parties, it also indicates the order to assign and pay severance pay in a certain amount and within a specified time frame.
Payment terms
If severance pay is established by a local act, an employment contract or a dismissal agreement, then these documents usually stipulate not only the fact of accrual and the amount of compensation, but also the timing of the payment of funds to the employee. For example, a time period after dismissal may be agreed upon during which the amount will be issued.
The main settlement with the dismissed person is made on the last working day. As for the compensation that the parties agreed upon additionally, it can be assigned along with the full settlement or paid later within additionally established and agreed upon periods.
If deadlines are not established, then severance pay must be paid on the last day of work in the organization.
If the contract is terminated by agreement of the parties, the last working day is established by the signed agreement.
Amount of compensation payment according to law
The law allows the amount of severance pay to be determined at the discretion of the parties. At the same time, it is said that an amount within three average monthly earnings of an employee (six if the employee works in the northern regions) does not require taxation.
In the event of termination of the employment relationship by agreement, no restrictions are established on the minimum and maximum amount of compensation in the form of severance pay.
The amount of compensation in each specific case is determined by the parties in the agreement or established by the employer in a collective or labor agreement. Typically, compensation is calculated based on average earnings over the last year.
Most often, a two-week or monthly average salary is assigned, but in some cases payment may also be provided for the second, third and subsequent months.
Read here what an employee should do if the employer does not pay upon dismissal.
How to calculate compensation?
The basis is the employee’s earnings for a period of one year. The 12 months preceding the month of calculating severance pay are taken.
The received daily earnings are multiplied by the number of working days in the period for which the benefit is assigned.
Formulas for calculation:
Severance pay = Avg.days. earnings * Number of working days of the period for payment.
Average daily earnings = Income for the billing period / Number of working days in the period.
The recorded earnings should include those payments to the employee that are assigned in the billing period and that are related to the employee’s work function. That is, salaries and bonuses should be taken into account; sick leave and maternity benefits, payment for business trips and vacations, and financial assistance should not be taken into account.
To determine daily earnings for the purpose of calculating severance pay, the total income should be divided by working days of the billing period, and not by calendar days. The number of working days is determined in accordance with the production calendar.
What taxes and insurance contributions are subject to?
Severance pay paid in accordance with Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is not subject to personal income tax and contributions only within the limits of:
- six average monthly earnings - for those working in the RKS;
- three average monthly earnings - for other persons.
If the payment amount exceeds the specified amounts, then from the excess amount you need:
- Withhold income tax at 13%.
- Calculate insurance premiums, the total percentage of which is 30%.
That is, only the amount above the legally established limit is subject to taxation.
With regard to severance pay paid to those dismissed by agreement of the parties, in accordance with the statements of the Ministry of Finance, the same rules apply. Amounts within the normal limits should not be subject to taxes and contributions.
Such rules apply to all categories of employees, regardless of position, salary and other factors.
Calculation example for 2022
Initial data:
Employee Potapov is dismissed by agreement of the parties, which provides for the payment of compensation in the form of severance pay in the amount of average monthly earnings.
The dismissal date is August 29, 2022.
The calculation period for severance pay is from 08/01/2018 to 07/31/2019.
Potapov’s total salary for the specified annual period was 485,000 rubles, in addition, he received vacation pay in the amount of 18,000 rubles. and sick leave benefits in the amount of 4,600 rubles.
Potapov’s work schedule is a 5-day work week with two days off.
In the period from 08/01/2018 to 07/31/2019, with a five-day week, Potapov worked 215 days (days of annual leave and sick leave are excluded).
It is necessary to calculate the amount of compensation to be paid to Potapov.
Calculation:
Average daily earnings = 485,000 / 215 = 2,255.81 rubles. (vacation pay and sick leave are not taken into account).
Compensation is due for one month - from 08/30/2019 to 09/29/2019, in this period there are 21 working days.
Severance pay = 2,255.81 * 21 = 47,372.01 rubles.
Since the amount of compensation does not exceed three times monthly earnings, severance pay is not subject to taxation - there is no need to withhold personal income tax and calculate insurance premiums.
Dismissal of pregnant women
The Labor Code does not contain restrictions on the circle of persons who can be dismissed “by agreement”. This means that a similar method of terminating an employment contract is also permissible in relation to a pregnant woman, regardless of the stage of her pregnancy. Including, the conclusion of an agreement is possible even after the employee goes on maternity leave.
But there is one caveat.
If a woman found out about her pregnancy shortly after signing the agreement and, therefore, changed her mind about quitting, it is better to reinstate the employment contract. Otherwise, the court can do this (rulings of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated 06.20.16 No. 18-KG16-45 and dated 09.05.14 No. 37-KG14-4). Therefore, before concluding an agreement to dismiss an employee, you need to make sure that she has previously submitted documents about her pregnancy. This could be a certificate of registration in the early stages of pregnancy, or an application for leave or time off due to pregnancy, etc. If there are no such papers, and the employer is not ready for the subsequent reinstatement of an employee who has changed her mind about leaving, then it is better not to formalize the dismissal “by agreement” with her. Attention!
There is no need to indicate the fact of pregnancy in the agreement. This may be regarded as dismissal for this reason. And such an action is a crime, liability for which is provided for in Article 145 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation (clause 16 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated December 25, 2018 No. 46). Similar criminal liability will arise if the court finds that a pregnant woman was forced to sign such an agreement. Evidence may include facts of physical impact or psychological pressure; creation of unfavorable working conditions; illegal imposition of disciplinary sanctions; threats of using methods of influence that could lead to adverse consequences not only for the employee, but also for his relatives (appeal rulings of the Supreme Court of the Republic of Dagestan dated 08.16.16 No. 33-2669/2016, Astrakhan Regional Court dated 05.30.12 in case No. 33-1592 /2012).
What the judges say
Many people well remember the Ruling of the RF Armed Forces dated September 23, 2016 No. 305 - KG16-5939 in case No. A40-94960/2015 (included in the Review of Judicial Practice of the RF Armed Forces No. 4 (2016) , approved by the Presidium of the RF Armed Forces on 12/20/2016, sent by Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated December 23, 2016 No. SA-4-7/ [email protected] ).
The panel of judges especially emphasized: in order to recognize a sum of money paid to an employee in connection with the termination of an employment contract by agreement of the parties as an expense for the purpose of calculating corporate income tax, it is necessary that such payment be economically justified. If the amount of this amount is significant and its obvious inconsistency with the circumstances characterizing the employee’s work activity, the taxpayer bears the burden of disclosing evidence justifying the nature of the payment made and its economic justification. In the absence of evidence, the tax authority has the right to assume that payments made to employees in the relevant part are personal security for employees provided for the period after their dismissal and do not reduce taxable profit.
In the Determination of December 12, 2016 No. 305 - KG16-16415 in case No. A40-195535/2015, the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation supported the tax department, since it considered that collective and labor agreements did not provide for the payment of severance pay upon termination of employment contracts by agreement of the parties, and also did not were related to the performance by employees of their work duties. As a result, the court found it lawful for the Federal Tax Service to exclude disputed payments from expenses taken into account when determining taxable profit.
In the Ruling of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 28, 2017 No. 305 - KG16-16457 in case No. A40-7941/2015, the following opinion was expressed: in order to recognize as economically justified expenses payments made by a taxpayer to an employee upon termination of an employment contract by agreement of the parties, it is sufficient to establish the achievement of the goal (actual dismissal of a specific employee), as well as maintaining a balance of interests between the employee and the employer, in which payments are aimed at resolving a possible conflict situation during dismissal and do not serve solely the purpose of personal enrichment of the dismissed employee.
The panel of judges noted that only if the amount of such payments is significant, their obvious incomparability with the usual amount of severance pay, for which, in accordance with Art. 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation has the right to calculate the dismissed employee, the length of his work experience and the labor contribution made by him, as well as other circumstances characterizing the employee’s work activity, the taxpayer bears the burden of disclosing evidence justifying the nature of the payments made and their economic justification.
Please note that
the amount of payments upon dismissal by agreement of the parties may not fully coincide with the amount of payments provided for by labor legislation in the event of dismissal due to staff reduction or in connection with the liquidation of an enterprise, since their size may also be influenced by the fact that such payments represent a kind of payment for the employee’s consent to renounce the employment contract. At the same time, the amount of this fee is not determined by law; it is established by agreement of the parties.
At the same time, the tax authority has the right to question the economic justification of such expenses if there is evidence that the taxpayer does not have a business economic goal when dismissing an employee on a basis other than that provided for in Art . 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation , without interfering with the assessment of the appropriateness of the decisions made.
These conclusions correspond to the legal position set out in the rulings of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 27, 2017 No. 305 - KG16-18369 in case No. A40-213762/2014 , dated March 17, 2017 No. 305 - KG16-17247 in case No. A40-186959/2015 .
Tax legislation does not contain provisions allowing the tax authority, when applying Art. 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation to evaluate expenses incurred by taxpayers from the standpoint of their economic feasibility. Expenses are recognized as economically justified if they are necessary for the activities of the taxpayer ( resolutions of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated 03/09/2011 No. 8905/10 , dated 02/25/2010 No. 13640/09 ). In addition, within the meaning of the legal position of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation, expressed in Resolution No. 3 - P , judicial control is not intended to check the economic feasibility of decisions made by business entities that have independence and broad discretion in the business sphere.
In the commented Determination of October 26, 2017 No. 305 - KG17-9814 , the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation also did not agree with the unanimous position of the courts of the first, appellate and cassation instances, pointing out a significant violation of the law, and sent the case for a new trial.
Dismissal of pensioners and pre-retirees
Working pensioners and pre-retirees also have the right to resign by agreement of the parties to the employment contract. But there are nuances here too. The fact is that Article 144.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation provides for criminal liability for the dismissal of pre-retirement employees. It occurs if the reason (motive) for dismissal is the employee’s age. This means that the dismissal agreement should not contain provisions from which it can be concluded that it was concluded in connection with the employee acquiring pre-retirement status. In particular, there is no need to indicate the fact that a person has reached the appropriate age, or whether he has benefits provided to pre-retirees.
As in other cases, the conclusion of the agreement must be voluntary. Otherwise, the pre-retirement person will be reinstated at work, the company will be fined (Part 1 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation), and its manager may be brought to criminal liability (Article 144.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
Fill out and submit the SZV-TD online for free
Dismissal of part-time workers
It is also possible to conclude an agreement to terminate an employment contract by agreement of the parties with an employee who has a part-time job (see “Part-time and part-time work: what is the difference”). The Labor Code does not contain any exceptions in this part.
The only peculiarity is that you do not need to enter information about the dismissal of an external part-time worker in his paper work book. If necessary, this will be done by his main employer on the basis of the agreement presented by the dismissed part-time worker (Article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). However, this does not exclude the need to submit a SZV-TD. This form must be submitted upon dismissal of both external and internal part-time employees. For more details, see “Part-time work: how to properly formalize the hiring of an employee.”
Procedure and procedure for dismissal by agreement of the parties in 2022
The types and forms of documents on the basis of which dismissal is carried out by agreement of the parties are not defined by law. Likewise, there is no established procedure for such dismissal.
In practice, employees often take the initiative to terminate the contract by agreement of the parties, submitting a corresponding application to the HR department. However, such a statement is not mandatory - dismissal “by agreement” will be legal without it.
The main document when parting with an employee under an article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is the agreement of the parties to the employment contract. However, the law also did not establish any requirements for the form of this agreement.
Prepare a termination agreement for free using a ready-made template
Agreement between the parties
Usually it is drawn up on the same principle as an employment contract - in the form of a separate document, drawn up in duplicate, and signed by both parties. The agreement must indicate:
- information about the employee (full name, date and place of birth, passport details, position);
- information about the employment contract (date of conclusion and number, if available);
- reason for dismissal (agreement of the parties) and a link to the relevant article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
ImportantAccording to paragraph 17 of the Procedure for maintaining and storing work books (approved by order of the Ministry of Labor dated 05/19/21 No. 320n), an entry on the termination of an employment contract by agreement of the parties is entered into the work book with reference to paragraph 1 of part 1 of the article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This means that this is the norm that needs to be included in the text of the agreement. Additionally, there is no need to provide a link to the article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- date of dismissal (letter of the Ministry of Labor dated April 10, 2014 No. 14-2/OOG-1347). The date is entered without any pretext (i.e. you need to write “December 01” and not “from December 01”). It should be taken into account that the specified date is the employee’s last working day (Article 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). This means that on this day he must appear at his workplace.
All other conditions (including the procedure and deadline for transferring cases; return of the employer’s property held by the employee; as well as severance pay and additional compensation) are optional. Dismissal will be legal without this data. However, if they are included in the text of the document, they become binding on both parties.
Attention!
If the dismissal agreement provides for the payment of severance pay or other “compensation” that is not directly provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, then it is better to draw up the corresponding document as an additional agreement to the terminated employment contract. Simply put, in the “header” you should indicate not “Agreement on termination of the employment contract dated No. _”, but “Additional agreement to the employment contract dated No. _”. And all amounts paid are called “severance pay”.
This approach will significantly reduce the risk of claims from tax authorities regarding the accounting of relevant payments for tax purposes. After all, according to the rules of the Labor Code (Part 14 of Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the payment of severance pay must be provided for precisely by the employment contract. Only in this case can the payment amount be included in labor costs (clause 9 of Article 255 and clause 21 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Calculate all payments for a dismissed employee in the web service Calculate for free
The document terminating the employment contract is signed by both parties to the agreement. One copy is given to the employee, and the other remains with the employer. In this case, a mark must be made on the employer’s copy stating that the employee received his copy (the mark must be certified by the employee’s signature). This is especially true if the document is drawn up as an additional agreement to an employment contract (Article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The dismissal agreement can be dated to any date prior to the date from which the employment contract will be terminated. Including, it is possible to dismiss “one day”, when the day of conclusion of the agreement coincides with the last day of work, that is, the day of dismissal.
Note that if an organization has switched to electronic personnel document management, then this agreement can be drawn up in electronic form. The employee must sign on this document using an enhanced qualified or unqualified electronic signature (for more details, see “Personnel documents are converted into electronic form: read the latest amendments to the Labor Code”).
Document on payment of compensation
In which document should information about the payment of vacation pay be indicated - only in the agreement on termination of the employment contract or in the collective (labor) agreement as well?
Based on Art. 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, we can conclude that it is in the labor or collective agreement. Therefore, it is considered that indicating this point only in the agreement on termination of employment is insufficient.
However, there is another opinion - the termination agreement is an integral part of the employment contract, and therefore information about compensation can only be contained in it.
Judicial practice shows that the courts have not reached a consensus on this issue.
For example, the Appeal ruling of the Sverdlovsk Regional Court dated June 30, 2016 in case No. 33-9473/2016 states that labor legislation does not contain information about the right of the parties to labor relations to establish a condition for the payment of severance pay when concluding an agreement on termination of labor relations. And on the basis of this, the court makes a decision in favor of the employer, who wished to return the amount previously paid to the employee, since information about it was contained only in the termination agreement.
The same conclusion was made in the Appeal ruling of the St. Petersburg City Court dated February 24, 2016 No. 33-2415/2016 in case No. 2-6251/2015. In this case, it was stated that the termination agreement is not an additional agreement to the employment contract and it does not change the terms of the main document. The agreement is only the basis for terminating the employment relationship and terminating the contract.
But at the same time, other judicial authorities take a different position, believing that the termination agreement is an integral part of the employment contract (Appeal ruling of the Moscow City Court dated December 14, 2020 No. 2-2613/2020).
You also need to focus on what specific circumstances exist in a particular case. For example, a former employee lost a legal dispute because the employment contract specified one basis for payment of compensation, and the termination agreement specified another basis.
Accordingly, it is possible to specify the payment of compensation only in the agreement on termination of the employment contract, and then the company does not bear some risks. But at the same time, other types of risks arise for the employer - in terms of accounting and taxes.
Attention!
To ensure mobile interaction between employees and accounting departments on personnel issues, the 1C:Employee Account service was launched.
In their personal account via the Internet, employees will be able to receive payslips, a 2-NDFL certificate and other documents, and in turn, employees can send a vacation application, notice of absence, advance report, sick leave in electronic form.
Order to dismiss an employee
Based on the agreement, a dismissal order is issued (you can use the unified form No. T-8, approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee dated 01/05/04 No. 1). In this case, in the line (column) “Grounds for termination (termination) of the employment contract (dismissal)” you must indicate: “Agreement of the parties, paragraph 1 of part one of article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.” And in the line (column) “Base (document, number, date)” you should write: “Agreement dated_ No. on termination of the employment contract dated_ No_”, or “Additional agreement dated_ No_ to the employment contract dated_ No_”, depending on how the agreement was concluded.
Next, you need to familiarize the employee with the dismissal order. Compliance with this requirement is confirmed by the employee’s personal signature on the document. Familiarization with the order by affixing an electronic signature is impossible (Article 22.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Compose and print an order for free using form No. T‑8
What is included in severance pay?
According to Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, depending on the reasons for dismissal, the amount paid at the time of dismissal may vary. The employee will receive a monthly average income as severance pay if the employment contract was terminated for the following reasons:
Liquidation of the organization.- Reduction of staff.
- Violation through no fault of the employee of the rules established by law for concluding an employment contract, if this excludes the possibility of him continuing to work and there is no possibility of transferring him to another job.
Also, the payment amount will be two weeks’ average income for the following reasons for termination of the employment contract:
- refusal to transfer to another position for medical reasons;
- conscription for military service;
- reinstatement at work by decision of the court or labor inspectorate of an employee who previously held this position;
- refusal to transfer to another location together with the employer;
- the employee is unable to perform his or her job duties due to health conditions;
- changes to the employment contract associated with changes in technological or organizational working conditions, entailing the impossibility of subsequent performance of job duties.
Two weeks' average earnings as compensation for dismissal are always paid by a seasonal employee.
The amount of severance pay always includes compensation for unused vacations, if any.
For the period of employment after dismissal, the employee continues to receive a salary, but no more than for two months from the date of dismissal. In some cases, payments may last 3 months. The entire amount paid as a result is the amount of severance pay.
The amount of compensation for employees hired for a period of no more than two months must be specified in a local regulation, or a collective or labor agreement. If this point is not regulated in any way, then the payment of severance pay will not be made.
Termination of an employment contract by agreement of the parties retains the employee’s all rights to compensation payments and severance pay. Also, in this case, the employee can apply to retain his average earnings for the next two months after dismissal (and in some cases for 3 months) or until employment.
How to dismiss by agreement of the parties: entry in the work book
In a paper work book, an entry about the dismissal of an employee “by agreement” is made according to the same rules as other entries about dismissal. In particular, the serial number of the record, the date and reason for dismissal, as well as the details of the dismissal order are indicated.
As the basis for dismissal, in column 3 you need to write: “The employment contract is terminated by agreement of the parties, paragraph 1 of part one of article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.” For more details, see the article “Filling out a work book: rules and sample.”
Reflection of dismissal in a personal card
If the organization has not refused to maintain personal cards (unified form No. T-2), then in this document it is necessary to duplicate the record of dismissal by agreement of the parties (in Section XI). In this case, you should use the same wording that is indicated in the work book. Next, the date of dismissal and details of the dismissal order are indicated.
In this case, the employer has the right to decide for himself whether employees will be familiar with the records in the T-2 form. Also see “Rostrud clarified whether it is possible to maintain a personal T-2 card electronically.”
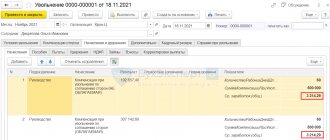
Drawing up a note-calculation in form T-61
A settlement note in the unified form No. T-61 is not a document that must be drawn up and given to an employee upon dismissal by agreement of the parties. However, if a corresponding written statement has been received from the dismissed person, the employer must prepare a note-calculation and give it to the employee. Also, this document will have to be issued to the employee if this is provided for in the dismissal agreement itself.
Let us remind you that form No. T-61 contains information about vacations used and unused during work, as well as the calculation of payments upon dismissal.
Insurance and contributions to the Pension Fund
According to Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, upon dismissal by agreement of the parties, insurance contributions from the severance pay payment are not charged if the amount of compensation does not exceed three times the average monthly income (six times for the northern regions).
Otherwise, the insurance premium is collected from the non-taxable part of the severance pay (the difference between the actual amount of severance pay and the average salary for 3 months).
According to Article 425 and Article 426 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the total amount of strass contributions consists of:
pension insurance - 22%;- health insurance - 5.1%;
- social insurance - 2.9%.
Thus, returning to the example above, the cost of insurance premiums will be:
56,000 rubles (taxable part of compensation)*(22 + 5.1 + 2.9)% = 16,800 rubles.
This is the amount you will have to pay as an insurance premium.
In total, the amount of severance pay minus personal income tax and insurance contributions will be:
224,000 rubles - 7,280 rubles - 16,800 rubles = 199,920 rubles.
It is important to note that at the legislative level, these contributions upon dismissal are not provided for by agreement of the parties, but in this case, the grounds for their collection (just like for personal income tax) are the economic unreasonability of the employer’s expenses and their inconsistency with the employee’s work qualities.
Full settlement with the employee
With regard to the amounts that are transferred to all dismissed employees (wages for time worked, compensation for unused vacation, bonuses), the general rules of Article 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation apply. Such amounts must be transferred on the last day of work.
But additional amounts provided for in the dismissal agreement (including severance pay) can be paid at other times, if this is expressly provided for in this document. Such conclusions are contained in the report approved by Rostrud.
Important
Do not forget to give the employee a pay slip (the employer must develop and approve the form of this document himself). If payments are made in several stages, then in each case a new payslip is issued.
Calculate your salary and benefits taking into account the increase in the minimum wage in 2022 Calculate for free
Delivery of documents
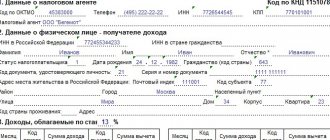
All work-related documents (work book or information in the STD-R form, extracts from SZV-M, RSV and SZV-STAZH, salary certificate, etc.) are issued to the employee directly on the day of dismissal, that is, on the last working day. For more details, see “Documents when dismissing an employee.”
If the provision for the issuance of such documents is included in the text of the dismissal agreement, it is advisable to obtain a signature from the employee on the copy of the agreement that remains with the employer. This will confirm the timely transfer of the relevant papers to the dismissed employee.
Taxation of compensation for unused time off
Since the issue of payment for unused “labor” time off has not yet been clearly resolved, there are no uniform recommendations on how to calculate them.
Opinion of an Atypical Accountant
If you pay a dismissed employee for unused time off, then you need to classify them as wages. After all, the occurrence of such time off is associated with the employee’s performance of work duties.
Therefore, additional payments made for unused time off upon dismissal must be fully subject to insurance premiums and withholding personal income tax.
Likewise, with this approach, the amount of compensation paid and contributions calculated from it can be included in the reduction of the income tax base.
Notification of the military registration and enlistment office
When dismissing an employee subject to military registration, the employer must notify the military registration and enlistment office. The message is sent in the form given in Appendix No. 9 to the Methodological Recommendations for maintaining military records in organizations (approved by the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation on July 11, 2017). This must be done within two weeks from the date of dismissal (subparagraph “a”, paragraph 32 of the Regulations on Military Registration, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 27, 2006 No. 719).
Prepare personnel reports for the military registration and enlistment office and other regulatory authorities Try for free
Severance pay upon dismissal by agreement of the parties
The dismissal agreement may stipulate the employer’s obligation to pay the dismissed employee severance pay. For commercial organizations, the amount of such benefits is not limited by law (Article 349.3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In other words, the employer and employee can agree on absolutely any amount of compensation (severance pay).
But it is still better not to set too large amounts of “compensation”. Such behavior may be regarded as an abuse of law, which will undoubtedly give the tax authorities grounds for excluding the corresponding amounts from expenses (see the appeal ruling of the St. Petersburg City Court dated March 27, 2018 No. 33-6196/2018).
Payment of insurance premiums
If the policies of different authorities regarding the payment of personal income tax differ, then they adhere to the same position regarding the payment of insurance. Starting this year, this type of payment began to be regulated exclusively by the Tax Code. All cases where there is no need to pay an insurance premium are provided for in Article No. 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This list also includes compensation, but its amount should not exceed three average salaries of an employee (for those who live on the Extreme Server, the maximum amount of severance pay does not exceed six salaries).
Taxation of payments upon dismissal by agreement of the parties
There is no need to withhold personal income tax on the amount of severance pay that does not exceed three times the average monthly salary of the employee (six times if the organization is located in the Far North and equivalent areas) (clause 1 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Also, insurance premiums do not need to be charged for this amount (subclause 2, clause 1, article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Accordingly, it is necessary to transfer “salary” taxes on the excess amount on a general basis.
If the dismissal by agreement of the parties in 2022 was formalized in accordance with the rules described above, and the amount of “compensation” is reasonable, then the employer should not have problems taking into account the severance pay. This amount can be written off as part of labor costs both under OSNO and under the simplified tax system (clause 9 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, subclause 6 of clause 1 and clause 2 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Attention!
After the dismissal of an employee, by agreement of the parties, the employer must submit a report in the SZV-TD form. This must be done no later than one working day following the day the dismissal order is issued. When maintaining personnel records in the web service, you will receive timely reminders about the need to submit the SZV-TD. If you hire or fire an employee, the program will remind you to submit a report by a certain date. After this, you will be able to fill out the SZV-TD in the program interface and submit the report via the Internet.
Compensation is attributed to company expenses
According to paragraph 9 of Art. 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the company can attribute these payments to labor costs as accruals to dismissed employees. For example, these include severance pay paid upon termination of an employment relationship, if they are provided for in a collective agreement or employment contract, or a separate agreement thereto, incl. agreement to terminate the employment contract.
Thus, severance benefits provided for in termination agreements can also be included as expenses. But sometimes tax authorities do not agree with this position and make claims to the business entity in terms of accounting for these payments. The problem, according to the Federal Tax Service, is that the compensation clause is indicated only in the agreement, but not in a collective or employment contract.
However, the taxpayer may well challenge this position of the tax authorities, using precisely the wording of clause 9 of Art. 255 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It is spelled out clearly, without ambiguity. And the Ministry of Finance also thinks so, indicating this in Letters dated 07/18/2019 No. 03-04-06/53226, dated 03/12/2021 No. 03-03-06/1/17367.
And the courts currently support the companies’ side during the proceedings, although the cases mainly concerned the period in which the earlier version of clause 9 of Art. 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (without mentioning the agreement on termination of the employment contract). And now, with the new edition of the article, companies are in an even more advantageous position.
However, you need to pay attention to another nuance - the size of these compensations. The employer has the right to set the amount himself, but if the amount is large, tax officials often find fault with it, believing that it is seriously overestimated.
One or three salaries is not such a big amount, and the tax authorities will not find fault with it. In addition, the employer will be able to defend his case in court. But if the employer paid seven or ten salaries to the dismissed person, his risks increase significantly. And it is not a fact that the court will take the employer’s side.
Sometimes the courts supported the tax authorities, because the employer could not provide evidence of the economic justification of this amount of payments. The obligation to disclose this evidence arises if the payment is in a significant amount, clearly not comparable to normal severance pay upon dismissal, taking into account the characteristics of the work activity of a particular employee (length of service, labor contribution to the company's activities).
Companies are advised not to set compensation in a significant amount or to select evidence to justify such a large amount of payment.