Let's get acquainted with the balance sheet items for 2022: their codes and explanations
Everyone who has ever held a balance sheet in their hands, much less drawn it up, paid attention to the “Code” column.
Thanks to this column, statistical authorities are able to systematize the information contained in the balance sheets of all companies. Therefore, it is necessary to indicate codes in the balance sheet only when this report is submitted to state statistics bodies and other executive authorities (Article 18 of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ, clause 5 of the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n). Let us remind you that only organizations whose reports contain information classified as state secrets, as well as in cases established by the Government of the Russian Federation, need to submit their balance sheet for 2022 to the statistics. Other companies do not need to submit a balance sheet.
If the balance is not annual and is needed only by owners or other users, it is not necessary to indicate the codes.
ATTENTION! From 2022, financial statements will be submitted exclusively in electronic form. Paper forms will no longer be accepted. Read more about changes to the rules for presenting financial statements here.
From 06/01/2019, the balance sheet form is valid as amended by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated 04/19/2019 No. 61n.
The key changes in it (as well as in other financial statements) are as follows:
- now reporting can only be prepared in thousand rubles, millions can no longer be used as a unit of measurement;
- OKVED in the header has been replaced by OKVED 2;
- The balance sheet must contain information about the audit organization (auditor).
The auditor mark should only be given to those companies that are subject to mandatory audit. Tax authorities will use it both to impose a fine on the organization itself if it ignored the obligation to undergo an audit, and in order to know from which auditor they can request information on the organization in accordance with Art. 93 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
What negative consequences are possible if the auditor’s report is not yet ready at the time of reporting, find out from a typical situation from ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
In the balance sheet, line codes from 2014 must correspond to the codes specified in Appendix 4 to Order No. 66n. At the same time, outdated codes from the expired order No. 67n with the same name, dated July 22, 2003, are no longer applied.
It is not difficult to distinguish previously used codes from modern ones - by the number of digits: modern codes are 4-digit (for example, lines 1230, 1170 of the balance sheet), while outdated ones contained only 3 digits (for example, 700, 140).
For information on what the form of the current balance sheet with line codes looks like, read the article “Filling out Form 1 of the balance sheet (sample)” .
Accounting entries for accounting for the purchase and installation of equipment
In accounting, the acquisition and installation of equipment can be reflected in the following entries (Instruction No. 94n):
| Contents of operations | Debit | Credit | A document base |
| Equipment requiring installation has been taken into account | 07 | 60 | Supplier documents, Certificate of acceptance (receipt) of equipment |
| VAT presented by the seller is reflected | 19 | 60 | Invoice |
| The submitted VAT is accepted for deduction | 68 | 19 | Invoice |
| Payment was transferred to the seller for the equipment | 60 | 51 | Bank account statement |
| The equipment has been handed over for installation | 08 | 07 | Certificate of acceptance and transfer of equipment for installation |
| Equipment installation costs are taken into account when determining its initial cost | 08 | 23, 60 | Certificate of completion of work, Work order, Accounting certificate |
| The installed equipment is accepted for accounting as an OS object | 01 | 08 | Certificate of acceptance and transfer of fixed assets, Inventory card for accounting of fixed assets |
Note! Starting from reporting for 2022, Federal Accounting Standards FSBU 6/2020 “Fixed Assets” and FSBU 26/2020 “Capital Investments” are applied, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 09.17.2020 N 204n (hereinafter referred to as FSBU 6/2020, FSBU 26/ 2020), and therefore PBU 6/01 becomes invalid. At the same time, the organization has the right to decide to apply FAS 6/2020 and FAS 26/2020 before the specified deadline (clauses 2, 3 of Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia N 204n).
Thus, for accounting purposes, capital investments are understood as the organization’s costs for the acquisition, creation, improvement and (or) restoration of fixed assets. These include, in particular, the costs of delivering and bringing the object into a condition and location in which it is suitable for use for the intended purposes, including its installation and installation (clause 5 of FSBU 26/2020).
FAS 26/2020 introduces a number of new rules and features for accounting for capital investments, different from PBU 6/01, among which are: a new accounting procedure for unused material assets when making capital investments, checking capital investments for impairment, recognizing fixed assets as an object during operation parts of the capital investment object until the completion of capital investments (clauses 15, 17, 18 FSBU 26/2020).
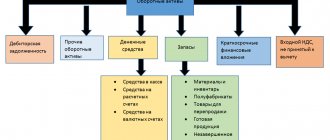
How to decipher balance sheet asset lines
Before deciphering an asset item, let’s consider its code - it carries certain information. So, the first digit shows that this line refers to the balance sheet (and not to another accounting report); 2nd - indicates the section of the asset (for example, 1 - non-current assets, etc.); The 3rd digit reflects assets in increasing order of their liquidity. The last digit of the code (initially it is 0) is intended to help in line-by-line detailing of indicators considered significant - this allows you to fulfill the requirement of PBU 4/99 (clause 11).
NOTE! The requirement for detail may not be fulfilled by small businesses (clause 6 of Order No. 66n).
Read about what distinguishes accounting carried out by small businesses in the material “Features of accounting in small enterprises” .
The asset lines of the balance sheet with codes and explanations are shown in the table:
| Line name | Code | Decoding the string | |
| By order No. 66n | By order No. 67n | ||
| Fixed assets | 1100 | 190 | The total amount of non-current assets is reflected |
| Intangible assets | 1110 | 110 | The information reflected in lines 1110–1170 is explained in the notes to the statements (information on the availability of assets at the reporting dates and changes for the period is disclosed) |
| Fixed assets | 1150 | 120 | |
| Profitable investments in material assets | 1160 | 135 | |
| Financial investments | 1170 | 140 | |
| Deferred tax assets | 1180 | 145 | The debit balance of account 09 is indicated |
| Other noncurrent assets | 1190 | 150 | Filled in if there is information about non-current assets that are not reflected in the previous lines |
| Current assets | 1200 | 290 | The final result of current assets is determined |
| Reserves | 1210 | 210 | The total balance of inventories is given (debit balance of accounts 10, 11, 15, 16, 20, 21, 23, 28, 29, 41, 43, 44, 45, 97 without taking into account the credit balance of accounts 14, 42) |
| Value added tax on purchased assets | 1220 | 220 | Indicate account balance 19 |
| Accounts receivable | 1230 | 240 | The result of adding the debit balances of accounts 60, 62, 68, 69, 70, 71, 73, 75, 76 minus account 63 is reflected |
| Financial investments (excluding cash equivalents) | 1240 | 250 | The debit balance of accounts 55, 58, 73 (minus account 59) is given - information on financial investments with a circulation period of no more than a year |
| Cash and cash equivalents | 1250 | 260 | The line contains the balance of accounts 50, 51, 52, 55, 57, 58 and 76 (in terms of cash equivalents) |
| Other current assets | 1260 | 270 | Filled in if data is available (for the amount of current assets not indicated in other lines of the section) |
| Total assets | 1600 | 300 | Total of all assets |
You can see line-by-line comments on filling out asset lines in the ConsultantPlus system. Get trial access to the K+ system and proceed to the explanations for free.
Transformation of the old form of financial reporting into a new one (after 2011)
After 2011, new forms of financial reporting appeared. It is often necessary to convert old forms of financial (accounting) reporting to new ones. Below is a table of translation (Forms No. 1 and Forms No. 2 into the new forms “Balance Sheet” and “Financial Results”). The old lines (designated by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 66n) are matched with new lines (designated by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 67n).
| Indicator name | Old codes (before 2011) | New codes (after 2011) |
| Intangible assets | 110 | 1110 |
| Fixed assets | 120 | 1130 |
| Construction in progress | 130 | |
| Profitable investments in material assets | 135 | 1140 |
| Long-term financial investments | 140 | 1150 |
| Deferred tax assets | 145 | 1160 |
| Other noncurrent assets | 150 | 1170 |
| FIXED ASSETS | 190 | 1100 |
| Reserves | 210 | 1210 |
| VAT on purchased assets | 220 | 1220 |
| Accounts receivable (more than a year) | 230 | |
| buyers and customers | 231 | |
| Accounts receivable (less than a year) | 240 | 1230 |
| buyers and customers | 241 | |
| Short-term financial investments | 250 | 1240 |
| Cash | 260 | 1250 |
| Other current assets | 270 | 1260 |
| CURRENT ASSETS | 290 | 1200 |
| ASSETS total | 300 | 1600 |
| Authorized capital | 410 | 1310 |
| Extra capital | 420 | 1350+1340 |
| Reserve capital | 430 | 1360 |
| reserves formed in accordance with legislation | 431 | |
| reserves formed in accordance with the establishment. documents | 432 | |
| Retained earnings (uncovered loss) | 470 | 1370 |
| CAPITAL AND RESERVES | 490 | 1300 |
| Loans and credits (long-term) | 510 | 1410 |
| Other long-term liabilities | 520 | 1450 |
| LONG TERM DUTIES | 590 | 1400 |
| Loans and credits (short-term) | 610 | 1510 |
| Accounts payable | 620 | 1520 |
| debt to the government off-budget funds | 625 | |
| Debt to participants (founders) for payment of income | 630 | |
| revenue of the future periods | 640 | 1530 |
| Reserves for upcoming expenses and payments | 650 | 1540+1430 |
| Other current liabilities | 660 | 1550 |
| SHORT-TERM LIABILITIES | 690 | 1500 |
| LIABILITIES total | 700 | 1700 |
| Sales proceeds (excluding VAT, excise taxes...) | 010 | 2110 |
| Cost of goods, products, works, services sold | 020 | 2120 |
| Gross profit | 029 | 2100 |
| Business expenses | 030 | 2210 |
| Administrative expenses | 040 | 2220 |
| Profit (loss) from sale | 050 | 2200 |
| Interest receivable | 060 | 2320 |
| Percentage to be paid | 070 | 2330 |
| Income from participation in other organizations | 080 | 2310 |
| Other income | 090 | 2340 |
| Other operating expenses | 100 | 2350 |
| Profit (loss) before tax | 140 | 2300 |
| Current income tax | 150 | 2410 |
| Net profit | 190 | 2400 |
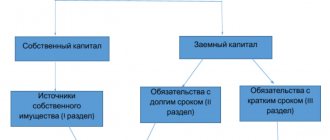
Interpretation of individual balance sheet liability indicators
Liability codes are also 4-digit: the 1st digit is the line’s belonging to the balance sheet, the 2nd is the number of the liability section (for example, 3 is capital and reserves). The next digit of the code reflects obligations in order of increasing urgency of their repayment. The last digit of the code is for detail purposes. Total liabilities in the balance sheet are line 1700 of the balance sheet. In other words, total liabilities in the balance sheet are the sum of lines 1300, 1400, 1500.
Liability items of the balance sheet with codes and explanations are shown in the table:
| Line name | Code | Decoding the string | |
| By order No. 66n | By order No. 67n | ||
| TOTAL capital | 1300 | 490 | The line contains information about the company's capital as of the reporting date |
| Authorized capital (share capital, authorized capital, contributions of partners) | 1310 | 410 | Information on lines 1300–1370 is detailed in the statement of changes in equity and the statement of financial results (in terms of net profit for the reporting period). The company has the right to determine the additional amount of explanations about capital. |
| Revaluation of non-current assets | 1340 | 420 | |
| Additional capital (without revaluation) | 1350 | ||
| Reserve capital | 1360 | 430 | |
| Retained earnings (uncovered loss) | 1370 | 470 | |
| Long-term borrowed funds | 1410 | 510 | The information is deciphered in tabular (Form 5) or text form in the explanations to the balance sheet |
| Deferred tax liabilities | 1420 | — | Indicate the credit balance of account 77 |
| Estimated liabilities | 1430 | — | The credit balance of account 96 is reflected - estimated liabilities, the expected fulfillment period of which exceeds 12 months |
| Other long-term liabilities | 1450 | 520 | Provides information about long-term liabilities not indicated in the previous lines of the section |
| TOTAL long-term liabilities | 1400 | 590 | The final result of long-term liabilities is reflected |
| Short-term debt obligations | 1510 | 610 | Account credit balance 66 |
| Short-term accounts payable | 1520 | 620 | The total credit balance of accounts 60, 62, 68, 69, 70, 71, 73, 75, 76 is reflected. The information is deciphered in the notes to the balance sheet (for example, in Form 5) |
| Other current liabilities | 1550 | 660 | Filled in if not all short-term liabilities are reflected in other lines of the section |
| Total current liabilities | 1500 | 690 | The total total of short-term liabilities is indicated |
| Liabilities of everything | 1700 | 700 | Summary of all liabilities |
ConsultantPlus experts have prepared a line-by-line commentary on filling out the balance sheet, including liability lines. If you don't have access to K+, get it for free.
Read about what characterizes simplified accounting in the article “Simplified reporting for small businesses.”
Where can I find revenue on the balance sheet?
When a company has been operating for a year, everyone is interested in knowing what its revenue is for this period and what part of it is expenses.
It is by these indicators that one can judge the profitability or unprofitability of its activities. According to all accounting laws, the balance sheet is a snapshot of the company’s performance indicators at a certain reporting date. Searching the balance sheet for a line that would show revenue is useless. No such line exists. To reflect revenue, another important accounting report is used - financial results.
Learn how to read a balance sheet using the example in this material.
However, revenue and balance sheet are related, although this connection is not clearly visible. Let's trace it using the example of individual balance sheet lines.
You can find out which receipts are revenue and which are not from the Guide from ConsultantPlus. Get trial access to the system for free and proceed to the material.
Results
Decoding the balance sheet allows users to extract as much useful information as possible from its meager figures. For automated processing of data from accounting reports carried out by statistical authorities, accounting lines are encoded.
Sources:
- Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ “On Accounting”
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 N 66n
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.