Types of balance sheet
The balance sheet is classified according to various criteria - the period of its preparation, the nature of the data, purpose, and method of reflecting information.
According to the method of reflection, they are distinguished:
- balance - formed on a specific date;
- circulating – compiled based on turnover for a certain period.
Balance sheets are also distinguished in relation to the moment of compilation:
- the current one is compiled as of the reporting date;
- introductory – at the beginning of activity;
- the person being rehabilitated will be needed at the stage of the so-called recovery of a company that is on the verge of bankruptcy;
- liquidation – upon liquidation;
- dividing or unifying – when dividing or, respectively, merging organizations.
Balances are distinguished by data volume:
- single – reflected for one company;
- the consolidated balance sheet includes the amounts of several organizations;
- consolidated - for several interrelated organizations, between which internal turnover is excluded when preparing reports.
The balance according to its purpose is divided into 4 categories:
- preliminary also known as trial;
- final;
- reporting;
- predictive.
According to the nature of the initial data, the balance sheet can be inventory - compiled according to the results of the inventory, as well as book - only according to accounting data. There is another variation on this basis - the general balance sheet. It is based on accounting data that takes into account inventory results.
The balance in the way information is reflected is:
- gross - including data from regulatory items (reserves, depreciation, markup);
- net - with the exception of these regulatory articles.
Reporting form No. 1 may differ depending on the organizational and legal form of the organization - public, joint, private, as well as the type of activity (main or auxiliary). Balances are also divided according to frequency – quarterly, monthly and annual.
There are several types of balance sheet:
- horizontal – the balance sheet currency is defined as the amount of assets, which in turn is equal to the amount of capital and liabilities;
- in vertical reporting, the balance sheet currency is equal to the amount of net assets, in other words, the amount of capital. Net assets are equal to a business's assets minus its liabilities.
An organization can independently choose the frequency and methods of preparing a balance sheet if it is intended for internal purposes. Reporting to the fiscal service must have a certain form approved by current legislation.
Balance due dates
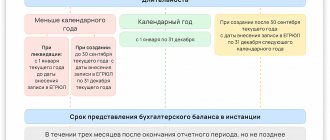
According to the general rules, the balance sheet - Form 1 must be submitted as part of the reporting for the past year no later than March 31 of the following year. This deadline must be observed when submitting balance sheets and other forms to the Federal Tax Service and statistics.
In addition, under certain conditions, an audit report must be sent to Rosstat as an attachment. The deadline is set for ten days, but no later than December 31 of the following year.
Some organizations need to submit financial statements and publish them due to the type of activity they carry out, or according to other criteria defined by law. For example, tour operators must send their reports to Rostrud within three months from the date of their approval.
The legislation provides for separate deadlines for organizations that registered after September 30 of the reporting year. Due to the fact that their calendar year may be determined differently in this case, the due date may be set by such organizations on March 31 of the second year after the current one. For example, Rebus LLC received an extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities on October 25, 2017; the accounting report must be submitted for the first time on March 31, 2022.
Attention! Accounting statements are usually submitted based on the total for the year. However, it is possible to present it quarterly. In this case it is called intermediate. Such documentation is very often needed when applying for loans from banks, company owners, etc.
What is reflected in the assets and liabilities of the balance sheet
The asset states:
- value of property (intangible assets, fixed assets, goods, materials);
- amount of accounts receivable (debt of buyers, customers).
The asset includes two parts - non-current and current assets.
Non-current assets include assets intended to generate profit for a period of more than one year. Current assets are repaid within one year.
The liability reflects the sources of formation of the organization's funds - the amount of its own capital and its accounts payable (debt on loans to counterparties). Liabilities contain three parts - capital and reserves, long-term and short-term liabilities.
Capital and reserves are the profit and authorized capital of an organization, in other words, its funds. Long-term liabilities include the organization's debts that must be repaid within more than one year. Short-term loans are returned within a period of no more than one year.
Balance sheet form 2022 free download
Balance sheet form 1 form 2022 download free in Word format.
Balance sheet form 1 form 2022 download free in Excel format.
Balance sheet with line codes form download in Excel format.
Download a sample of filling out the balance sheet in Form 1 for 2022 in PDF format.
Example of preparing a balance sheet
Let's look at the example of a limited liability company. The Assets section contains several subsections. In the column “Fixed assets” their full cost is indicated if the property is new. If it was used, the depreciation amount is deducted from the amount.
“Intangible assets” specifies the costs of purchasing intangible assets and increasing/decreasing their value. As in the previous subsection, if necessary, the amount of depreciation is deducted. “Capital investments” include funds spent on the construction of real estate.
“Equipment” contains information about the price of technical equipment minus depreciation. “Financial Investments” provides information about deposits made/investments in investment projects. “Material assets” indicates the cost of consumed materials, raw materials, spare parts, fuels and lubricants, and so on.
“Work in progress” includes information about the expenses incurred by the company for the acquisition of current assets. “Distribution costs” - used when drawing up a balance sheet by limited liability companies that operate in the catering industry. The cost of unsold products is indicated here. “Deferred expenses” are filled in if the purchase was originally planned, for example, for 2022, but materials were actually purchased in 2022. The line “Finished products” contains information about all products manufactured by the company during the year. “Products” contain information about goods purchased for the company’s own needs.
If the company’s activities are related to trade, contract work, the “Services Rendered” form indicates income from sales. The amount of debt from counterparties is reflected in the “Accounts receivable” cell.
The information entered into the Passive will be as follows. The amount of the authorized capital established by the Charter or its appendices, if there have been changes to it (the founders left or joined), is entered in the column “Authorized capital”. “Reserve capital” shows the residual value of funds after the base capital.
If the organization's funds have not been spent in accordance with the spending plan, they are transferred to the reserve for a future reporting period. The amount is recorded in the column “Reserves to cover payments and expenses.” The line “Deferred income” is filled in if the company, for example, has committed to deliver to a business partner in January, and the contract was drawn up in September. Those. payment is due after actual shipment, but the advance has been paid now. This amount is referred to as deferred income. The “Profit” cell contains data on income received for 12 months. “Accounts payable” indicates the amount of the issued loan from the bank.
When filling out the balance, errors may be made; they are divided into significant and insignificant. The evaluation criteria are set out in the company's accounting policies. Correction methods are fixed in the Accounting Regulation No. 22/2010. Typical violations include incorrect use of calculation methods, inaccuracies in the report - both technical and computational, entering an erroneous code, indicating information in the wrong column. When correcting the balance, a certificate is submitted to the fiscal service in any form or on form No. 2. Amendments must be made in the year in which the error was discovered.
Balance
This solution is indicated exclusively for intraperitoneal use.
The method of therapy, frequency of administration and required duration are determined by the attending physician.
Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis
( CAPD )
Adults:
Unless otherwise prescribed, the patient receives an infusion of 2000 ml of solution in exchanges four times daily. After the solution remains in the cavity between 2 and 10 hours, the solution should be drained.
It is necessary to individually adjust the dose, volume and number of exchanges for some patients.
If pain occurs during peritoneal dialysis treatment, the volume of exchange solution should be temporarily reduced to 500-1500 ml.
For larger patients and if residual renal function is lost, an increased volume of solution will be needed. For such patients, as well as for those who are able to tolerate large volumes, up to 2500 - 3000 ml of solution is prescribed for one exchange.
Pediatric population:
For children, the volume of solution for exchange should be prescribed in accordance with age and body surface area (BSA - body surface area).
When initially prescribed, the volume of exchange solution should be 600-800 ml/m2BSA with 4 (sometimes 3 or 5) exchanges per day. The dosage may be increased to 1000-1200 ml/m2BSA, depending on tolerability, age and residual renal function.
Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPP) method: stay • safe ® system.
The required dose is administered by infusion into the abdominal cavity through a peritoneal catheter over 5-20 minutes. Depending on the doctor's instructions, the solution should be stored in the peritoneal cavity for 2 - 10 hours (equilibrium time), and then drained.
The solution in the bag is first heated to body temperature. For bags up to 3000 ml, this should be done using a suitable heating tray. The heating time for a 2000 ml tank with a starting temperature of 22°C is approximately 120 minutes. The thermostat operates automatically and is set at 39°C ± 1°C. More detailed information can be obtained from the heating instructions. The use of microwave ovens is not recommended due to the risk of localized overheating.
1. Preparation of the solution.
♦ Check the heated bag with the solution (label, expiration date, transparency of the solution, absence of damage to the bag and protective shell, integrity of the connecting seam).
♦ Place the bag on a hard surface.
♦ Remove the protective cover from the bag and the packaging of the disinfection cap.
♦ Disinfect your hands with antimicrobial cleaning lotion.
♦ Fold the package on the outer wrapping foil at one edge until the middle seam is exposed. The solutions in the two chambers will mix automatically.
♦ Now roll the bag from the top edge until the seam of the surface layer of the lower
triangle will not open completely.
♦ Check that all surface seams are completely open.
♦ Check that the solution is clear and that the bag is not leaking.
- Preparing a replacement package.
♦ Attach the bag to the top holder of the infusion stand, unscrew the line of the bag with the solution and place the DISC in the organizer. Then unroll the line into a drainage bag and secure it to the lower holder of the infusion stand. Place the catheter adapter into one of the two slots in the organizer.
♦ Place the new disinfection cap in another empty slot.
♦Disinfect your hands and remove the DISCa safety cap.
♦ Attach the catheter adapter to the DISCy.
- Drain.
♦ Open the catheter clamp. The draining procedure begins.
♦ Position
- Flash.
♦After draining is complete, drain fresh dialysate into the drainage bag (approximately 5 seconds).
♦ Position
- Bay
♦ Start filling by turning to the “○••” position.
- Security step.
♦ Close the catheter adapter by placing the PIN into the adapter connector.
♦ Position “••••”
- Disconnect.
♦ Remove the protective cap from the new disinfection cap and screw it into the old one.
♦ Unscrew the catheter adapter from DISCa and screw the new disinfection cap onto the catheter adapter.
- closure .
♦ Close the DISC with the open end of the protective cap (which fits in the right opening of the organizer).
- Check the drained dialysate
(for clarity and volume)
and,
if the effluent is clear,
discharge.
Automated peritoneal dialysis
( APD )
If a machine is used ( sleep
•
safe
cycler or
PD - NIGHT
cycler) intermittent or continuous cyclic peritoneal dialysis, large-volume packages are used that provide more than one exchange of solutions. The cycler exchanges solutions in accordance with the medical prescription stored in the cycler. Adults:
Typically, patients spend 8-10 hours per night connected to the cycler.
The volume of solution maintained ranges from 1500 to 3000 ml, and the number of cycles is usually from 3 to 10 per night. The amount of liquid used is usually from 10 to 18 liters, but can range from 6 to 30 liters. Therapy performed with a cycler at night is usually combined with 1 or 2 exchanges during the day.
Pediatric population:
The volume per exchange should be 800-1000 ml/m2BSA with 5-10 exchanges overnight. It may be increased to 1400 ml/m2BSA depending on tolerability, age and residual renal function.
Automated peritoneal dialysis method: sleep • safe
(to set up
the sleep
•
safe
system, please refer to the operating instructions of the device).
The prescribed solution connectors in the sleep*safe package are placed into a free sleep
•
safe
on the platform and then automatically connected to the
sleep
•
safe
of the cycler.
The cycler checks the barcodes of the solution packages and generates an alarm if the package does not match the prescription stored in the cycler. After this check, a set of lines can be attached to the patient's catheter and treatment can begin. The solution is automatically warmed to body temperature using the sleep • safe
cycler during infusion into the abdominal cavity.
The time for which the solution is left in the abdominal cavity and the choice of glucose concentration are set in accordance with the medical prescription stored in the cycler (more detailed information can be obtained from the current instructions for the sleep
•
safe
cycler).
1. Preparation of the solution.
♦ Check the solution bag (label, expiration date, solution clarity, bag and packaging bag, release seal for damage).
♦ Place the bag on a hard surface.
♦ Open the outer packaging of the package.
♦ Treat your hands with antimicrobial cleaning lotion.
♦ Unfold the middle seam and the connector of the bag.
♦ Roll the bag on the outer wrapping foil from the diagonal edge towards the bag connector. The midline suture will open. » Continue until the seam of the small chamber is also open.
♦ Check that all seams are completely open.
♦ Check that the solution is clear and that the bag is not leaking.
2. Expand the package trunks.
3. Remove the protective cap.
4. Insert the packet connector into the free sleep
•
safe of the cycler.
5. The package is ready for use in
a sleep safe kit.
Automated Peritoneal Dialysis ( APD)
): Safe•Lock system (to set up the Safe•Lock system, please refer to the operating instructions of the device).
The connectors of the prescribed solution in the Safe•Lock bag are manually attached to the PD- NIGHT
cycler line set.
One Safe•Lock bag is placed on the warming platform of the cycler to warm the solution that will enter the patient's abdominal cavity during the procedure. The time for which the solution is left in the abdominal cavity and the choice of glucose concentration are set in accordance with the medical prescription stored in the cycler (more detailed information can be obtained from the current instructions for the PO - NIGHT
cycler).
- Preparation of the solution:
see the description for the
sleep • safe .
♦Remove the protective cap of the connector from the connecting line.
- Connect the lines to the package.
- Break the internal lock by bending the line and pin more than 90° in both directions.
- The package is ready for use on the system.
There are no specific dosing recommendations for elderly patients.
Peritoneal dialysis solutions with high glucose concentrations (2.3% or 4.25%) are used when body weight is above the desired dry weight. The removal of fluid from the body increases relative to the glucose concentration of the PD solution. These solutions should be used with caution to be gentle on the peritoneal membrane, to prevent dehydration, and to keep the glucose load as low as possible.
Peritoneal dialysis is a long-term therapy that involves repeated prescriptions of separate solutions.
Balance 15% glucose, 1.25/175 mmol/l calcium
contains 15 g of glucose per 1000 ml of solution.
Balance 2.3°/o glucose, 1.25/1.75 mmol/l calcium
contains 22.73 g of glucose per 1000 ml of solution.
Balance 4.25%> glucose, 1.25/1.75 mmol/l calcium
contains 42.5 g of glucose per 1000 ml of solution.
Patients must be properly trained to perform PD before performing it at home. The training must be carried out by qualified personnel. The treating physician must be confident that the patient has sufficient mastery of the technique before the patient performs PD at home. If you have any problems or uncertainties, you should contact your doctor.
Dialysis in the prescribed doses must be carried out daily and treatment must be continued for as long as the use of renal replacement therapy.
Balance 1.5% glucose, 1.25/1.75 mmol/l calcium:
depending on the required osmotic pressure, can be used sequentially with other dialysis solutions with a higher glucose content (i.e. higher osmolarity).
Balance 2.3% glucose, 1.25/1.75 mmol/l calcium:
depending on the required osmotic pressure, can be used sequentially with other dialysis solutions with lower or higher glucose content (i.e. lower or higher osmolarity).
Balance 4.25°/o glucose, 1.25/1.75 mmol/l calcium: depending
on the required osmotic pressure, can be used sequentially with other dialysis solutions with a lower glucose content (i.e. lower osmolarity).
The ready-to-use solution should be used immediately, but if this is not possible, then within a maximum of 24 hours after mixing. Plastic containers can sometimes become damaged during transportation or storage. This can lead to contamination with the growth of microorganisms in the dialysis solution. Therefore, all containers should be carefully inspected for damage before connecting and using peritoneal dialysis solution. Any damage, even minor, to the connectors, during packaging, or when welding seams and corners, must be noted due to possible contamination of the solution. Packages that are damaged or have clouded contents should never be used.
This solution can only be used if the solution is clear and the packaging is not damaged.
The wrapping should only be removed immediately before administration.
Do not use solutions from two reservoirs without mixing.
Aseptic conditions must be maintained during dialysate exchange in order to reduce the risk of infection.
Adding drugs to the peritoneal dialysis solution. Medicines can be added under aseptic conditions and only if prescribed by a doctor. Due to the risk of incompatibility between the peritoneal dialysis solution and the drug, only the following drugs and in the indicated dosages may be added if prescribed by a physician: heparin 1000 IU/L, insulin 20 IU/L, vancomycin 1000 mg /l, teicoplanin 400 mg/l, cefazolin 500 mg/l, ceftazidime 250 mg/l, gentamicin 8 mg/l. Once completely mixed and verified that there is no cloudiness or particles, the PD solution should be used immediately (no storage).
1C: Accounting 8
“1C: Accounting 8” is the most popular accounting program that can take accounting automation to a whole new level. A convenient product and services connected to it will allow you to effectively solve the problems of the accounting department of any business!
- Support of different tax systems, maintaining accounting and tax records, submitting reports;
- Inventory accounting, batch accounting, settlements with counterparties, extracting primary documents;
- Payroll calculation, accounting of cash transactions;
- Integration with other 1C programs and websites;
- Working with electronic certificates of incapacity for work (ELS).
Try 30 days free Order
Did you like the article?
Want to receive articles like this every Thursday? Keep abreast of changes in legislation? Subscribe to our newsletter
Common mistakes when filling out a balance
When filling out a balance sheet, novice accountants often make the following mistakes:
- Accounts receivable and payable are shown as a collapsed indicator. This is a mistake - in the balance sheet you need to show separately the debt to debtors or creditors and separately - received or paid advances. Profits and losses should be reflected using the same principle.
- The amount of the advance received should not be reflected in pure form, but together with the VAT received with this payment.
- Fixed and intangible assets are reflected at historical cost. This is not true. These values must be adjusted to the amount of accrued depreciation for each type of property.
- Interest-free loans are shown as part of financial investments. This is incorrect; they should be shown as part of accounts receivable by maturity.
- Negative indicators are written with a minus sign. According to the instructions for filling out the form, negative values must be shown in parentheses without a minus.
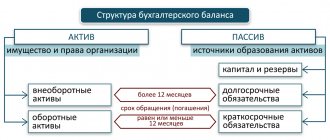
Balance sheet structure
The balance sheet of an enterprise characterizes the financial position of an economic entity as of a specific reporting date and is a table with certain columns. Since it reflects assets and liabilities, the table is divided into two large sections:
- Asset – to reflect the property and assets of the organization,
- Liability – to reflect the obligations of the organization.
Each section of the balance sheet is divided into groups that have individual lines with a specific name. The current form of the balance sheet can be taken from the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation “On the forms of financial statements of organizations” dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n. Note that you cannot delete any lines from it, but you can add columns if necessary.
Line-by-line information is collected from synthetic accounting accounts or taken from the balance sheet for a specific period.
Basic approaches to filling out a balance
The rules according to which the balance sheet of an enterprise is compiled is a single regulatory document regulating accounting. Currently, the rules of PBU 1/2008 are in effect.
The main requirements for preparing financial statements are:
- in order to avoid mixing of the company's assets and liabilities, it is necessary to account for them separately
- when preparing financial statements, we assume that the company will not cease its activities
- The accounting policies adopted by the enterprise will presumably be applied in the future
- Transactions in accounting must be reflected at the time of actual completion, regardless of payments associated with them
Rules for evaluating accounting items
The document regulating the rules for evaluating accounting items is PBU 4/99.
Here are the basic conditions necessary for mandatory compliance:
- the assessment of balance sheet items does not contradict the rules of PBU 1/2008 “Accounting policies of the organization”
- reporting indicators of articles are confirmed by inventory results
- data at the beginning of the reporting and previous periods are comparable
- numerical indicators that are included in the accounting report are reflected in the net estimate
- Offsetting is not allowed between asset and liability items, but there are exceptions
- some balance sheet items are subject to separate valuation rules
Next, we propose to consider examples of evaluating frequently filled out balance sheet items.
Methods for valuing balance sheet asset items
Fixed assets
To evaluate the fixed assets of an enterprise, you must follow the rules of PBU 6/01 “Accounting for fixed assets”. At the same time, they are reflected in the balance sheet according to the residual value principle. Also, it is worth considering that fixed assets costing less than 40,000 rubles may be reflected in the balance sheet as inventories.
For your information. In 2022, PBU 6/01 will lose force. They will be replaced by FSBU 6/2020 “Fixed Assets” and FSBU 26/2020 “Capital Investments”. The use of the newly introduced standards is permitted from the beginning of 2022, having made the necessary amendments to the accounting policies of the enterprise.
Accounts receivable
When forming a balance sheet, the debt of counterparties is indicated in full. To reflect overdue and unsecured debt amounts, you must be guided by PBU 21/2008 “Change in estimated values.”
Cash and cash equivalents
This line of financial statements must reflect the full amount of cash balances and balances on current accounts, including foreign currency and special accounts.
Methods for assessing balance sheet liability items
Authorized capital
The information for this accounting line is taken from the constituent documents. At the same time, the founder’s debt for the contribution of the authorized capital is reflected in the balance sheet separately.
Retained earnings (uncovered loss)
Here it is worth considering the following point: if the company started operations in the reporting period, then retained earnings will be the actual profit for the reporting year. In this case, the amount of profit is reflected minus all taxes and payments.
Accounts payable
Information under this article reflects the actual debts of the enterprise to counterparties, the budget or other representative as of the reporting date. The amount of debt is confirmed by executed reconciliation acts.
Conclusion
Drawing up a balance sheet requires knowledge of certain rules, methods and careful reflection of all items. Accounting rules reflect complete information on requirements related to reporting, evaluation of items and indicators of economic activity. If difficulties arise, seek advice from specialists who provide accounting services in this area.