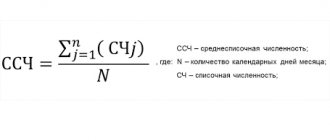How to calculate the required number of employees
Methods for calculating the number of personnel
To make the calculations, you don’t have to contact an accountant or HR officer; you can do everything yourself. For this purpose, there are methods for calculating the number of personnel.
- Regulatory
- calculated according to the standards from the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Calculation of the staffing norm shows how many employees there should be ideally, when no one goes on vacation, gets sick or goes on a business trip. Does not take into account business specifics and force majeure.
Suitable if you are just planning to open a business and roughly estimate how many people will work, how much to pay them and how best to draw up a budget. You won’t get exact results, but you will be able to get your bearings at the start, when you have a minimum of specific numbers on hand.
- Planned
- also calculated according to the standards of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, but already takes into account the specifics of the company: what it produces or sells, how many hours each employee works per week, etc. The results are more accurate than when calculating according to dry standards.
Suitable if you have a revenue goal for the year or season. You need to calculate how many employees will be needed to make this plan a reality.
- List (actual)
- shows how many total employees work at the enterprise under an employment contract.
It will be needed when you need to evaluate the performance of employees, determine the average salary, or calculate the staff turnover rate - how often people quit. You can request this information from your accountant or human resources department.
- Average
- shows how many employees worked in the company per month or year.
The business has already started. It's time to fill out tax reports. To do this, you need to calculate the average number of personnel for a specific period of time. It does not take into account those who are on maternity leave, working remotely or under a contract.
- Attendance
- takes into account only those employees who are at the workplace.
Gives an understanding of how many people should go to work every day so that the work process is not interrupted and the service does not sag
- Regular
- takes into account the specifics of the business: revenue, number of working hours, volume of work per employee. The calculation includes all employees plus people who are needed to replace those who go on sick leave or vacation. To do this, the absenteeism rate is added to the calculations.
You draw up a staffing schedule that will not change during a specific period. There must be enough people in it so that the work plan is fulfilled, no one is underworked or overloaded, and there is enough budget for salaries.
Each type of headcount calculation serves its own purposes. If you want to expand or reduce your staff, then you should calculate the staffing level. How to do it? We'll look at it in the next chapter.
Standards
There are different staffing standards. Among them are production standards, service standards, etc. To find how many people are required to implement a certain labor function, calculations are used based on the number of personnel.
Reliance on standards allows you to plan the number and composition of the company's employees, which practically leads to a level of productivity that corresponds to the technical characteristics of the company.
Here are several calculation options.
Method 1. In accordance with production standards. They are defined as the amount of work (for example, the number of finished products) that a team (or an employee with sufficient qualifications) is required to complete in accordance with existing organizational criteria per unit of working time.
Method 2. In accordance with the size standard. The basis for this calculation is a fixed number of employees with certain qualifications required to solve managerial or industrial problems. The main disadvantage of using this standard is the not very high accuracy of the characteristics. This is due to the fact that only normal volumes are taken into account when determining staffing standards. The more complex the actual work process, the more it deviates from the typical one. Therefore, the accuracy of the calculation decreases.
Method 3. In accordance with time standards. Here you need to take into account the amount of time spent on implementing a unit of an industrial process by an employee or team.
Method 4. In accordance with service standards. In these calculations, the basis is the number of pieces of industrial equipment (for example, machine tools, animal heads) that a group of employees must process within a certain time. This rule is almost the same as for employees who perform service functions. Often, when calculating the number of employees in an organization (both regular and standard), the headcount indicators are fractional and require rounding. The obtained values are used as arguments for making various management decisions in the field of personnel policy.
Calculation of staffing levels
Staffing is the number of people needed to complete the work plan for a specific period. It takes into account the average number of sales per employee. For example, 10 trips to Sochi per week, 5 apartment transactions per month.
Additionally, the error, or the coefficient of fulfillment of the norm, is calculated. It shows how much work in the plan differs from what happened in practice last year or month.
Calculation formula:
- V is the planned amount of work that needs to be completed over a specific period of time: month, year, quarter, shift. For example, earn 1 million rubles by sewing 20 wedding dresses.
- FW - how much time it takes to complete the plan. For example, 10 hours or 1 year to earn 500 thousand rubles.
- IDP - how much each employee must sell or produce during the FW. Here we take only the sales department and those who produce the product or service, we do not take into account the cleaning lady, office manager, etc.
- KVN - coefficient of fulfillment of the norm. It shows the error between how much was actually earned in the past period and how much is planned now. For example, in March we made 10 cakes, in April we are planning 15.
Calculation of the number of personnel using an example.
The store employs 10 people. The owner decided to cut costs and reduce the number of staff. Before doing this, he calculated using a formula how many people should be on staff for optimal work. The data is as follows: V - 1,180,000 rubles in revenue for 12 months; Federal Reserve Bank - 1,980 hours per year with a 9-hour working day, taking into account holidays and force majeure; IDPs - 118,000 rubles in revenue per person per year and 60 rubles/hour (118,000/1,980); KVN - 1.18, it was obtained as a result of the calculation: 1.18 million rubles divided by 1 million rubles of revenue for the previous year. We count: 1,180,000/(1980 x 60 x 1.18) = 8 people. This means that the staff is slightly overstaffed: 10 people are working, and two employees can be made redundant.
Calculation using this method gives an approximate result: it does not take into account that sometimes employees go on vacation or maternity leave, get sick or quit. To make the results more realistic, you need to calculate the absenteeism rate and include it in the general formula. It will show how many people are needed so that the process does not stop if someone is not at work.
Personnel composition
The structure is understood as the unification of its employees into groups and functioning units according to various criteria. The following groups are distinguished by composition, shown in the table below.
| Groups | Characteristic | Classification stage | Characteristic |
| Non-industrial | Those workers who are not directly involved in the production process. Workers of the social segment | _ | _ |
| Industrial production | Those employees who are involved in the production process | Company managers | -lower level (masters); -medium (managers of structural divisions); - senior (CEO, deputies) |
| _ | _ | Employees | Secretary, cashier, timekeeper, forwarder. All employees involved in documentation, financial and accounting work |
| _ | _ | Specialists | Engineers, economists, lawyers, technologists, personnel officers, accountants, etc. Performing administrative, economic, engineering, economic and legal tasks |
| _ | _ | Workers | Those who directly create the company's products, produce the final product, and provide services. |
The structure and number of personnel may be influenced by the following factors:
- Automation and computerization of production.
- Use of modern technologies.
- Use of the latest materials.
- Organization of production.
How to calculate the number of employees taking into account the human factor
Formula for calculating the absenteeism rate:
- KN—absenteeism rate. Characterizes the number of people who cannot go to work due to illness, take leave or go on maternity leave.
- DN - the share of non-working time in the total amount of time. This is the FRB figure from the previous formula (1,980 hours).
Example of calculating absenteeism rate
After the store owner considered that he could reduce the sales staff by two people, he decided to clarify the result to make sure that in case of dismissal the quality of service would not decrease. To do this, he calculated the employee absenteeism rate over a 12-month period. It turns out that each employee goes on vacation for 28 days, or 252 hours, per year. DN = 252 hours/1,980 hours (FRV indicator) = 0.13. 1 + 0.13 = 1.13 is the absenteeism rate.
Now we will calculate the number of personnel of the enterprise along with the absenteeism rate.
Formula for staffing (SH) taking into account the absenteeism rate (AB):
Let's add an example
In the calculation, it turned out that the staff of 10 people can be reduced to 8. Now let’s calculate the number along with the absenteeism rate (1.13).
8 x 1.13 = 9
This means that the store must have at least 9 employees. Therefore, you can only fire one person
What to do if you don't like the results
Calculation results may differ from reality. For example, you are expanding your business, and, according to the figures, you need to hire 4 more people, but there is no budget for their salaries. Or vice versa: you need to optimize the salary fund, and the numbers say that you can fire 2 people, but in reality there are not enough people, everyone is being sewn up anyway. What to do in such cases?
For example, consider two situations.
Situation 1: Need to hire more people, but no money
In this case, you can optimize your workflows:
- Improve staff qualifications
by sending them to courses or training in a related profession. Before doing this, you need to figure out what will be cheaper: hiring a new employee or paying for training for the old one. Sometimes both options are not suitable at once. - Outsourcing some of the tasks
is suitable if the outsourcing contractor will cost less than a full-time employee with a white salary. - Automate work using a CRM system
- it will remove some of the routine tasks from employees. As a result, staff productivity will increase, and you won’t have to hire more people. - Motivate
- measure productivity and reward achievements. For example, give bonuses, make unusual gifts, offer training courses. All this increases productivity, people will do more than before and may not have to hire anyone.
Try these methods to increase staff productivity and see what happens. If none of these methods help, then you are left with few options: hire a person at least part-time or consult a business analyst so that he can analyze your processes and, possibly, identify the cause of the problem.
Situation 2: you need to cut costs and fire someone, but there are already few staff
A crisis occurred and demand for products fell sharply. The easiest way to straighten out the situation and reduce costs as quickly as possible is to fire an employee. We calculate the number of personnel in the organization and it turns out that there is no one to fire. On the contrary, it is advisable to hire at least one more person to the team.
What can be done:
- Compile a time sheet - study the productivity of employees
during the day or week. How efficiently they work, what they are distracted by, perhaps someone is lazy or very late. It happens that the problem is precisely the staff, and not the heavy workload. Dismiss the lazy people, distribute their tasks evenly among those who are not busy all day. - Conduct recertification
- find out whether everyone knows their responsibilities well or whether someone has lost their skills. This way you will separate irreplaceable employees from those who cannot cope: they can be sent to advanced training courses or fired. - Introduce a system of fines and warnings
, set stricter deadlines. These measures will bring staff into good shape and improve performance indicators. Those who fail will deservedly receive a lower salary. - Optimize processes using a CRM system
- it will take over part of the operations. As a result, the volume of work will be reduced, and you will need fewer people to do it than before, which means you can fire someone without sacrificing quality of service.
If it is necessary to fire someone no matter what measures are taken, there is always the opportunity to get by with a little bloodshed. For example, if you have vacancies in other departments, you can try to retrain the employees you are planning to fire and transfer them to another position.
Keep in mind that when optimizing staff, it is easy to lose valuable personnel: fire someone who does their job really well and leave an incompetent employee. To prevent this from happening, re-certification and timing are required.
Be sure to submit information about the number of employees to the tax office
Employers are no longer required to submit average headcount information as a self-report. This is stated in the amendments to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. That is, it is no longer possible to report on the number of employees in any form.
The changes came into force on January 1, 2022. And if previously every employer was required to submit such a report annually, now data on the number of employees in the organization must be included in the calculation of insurance premiums (DAM).
It is necessary for all organizations with hired employees to submit information on the average number of employees (ASN). An exception is individual entrepreneurs without employees.
to fill out the RSV on the Consultant’s website.
filling out the RSV.
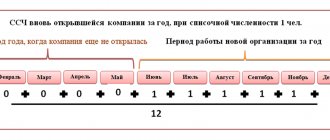
How to calculate the average number of employees
The annual MSS is the sum of the monthly one. To calculate the monthly average, you need to add up the number of employees for each day and divide by the number of days in the month.
The calculation takes into account:
- employees on vacation;
- employees on sick leave.
The calculation does not take into account:
- women on maternity leave;
- employees under GPC agreements;
- employees on unpaid study leave;
- employees on parental leave.
For example, as of 02/01/2021, the company employs 50 people. One employee goes on maternity leave on February 16, and another employee goes on maternity leave on the same day. This means that from the 16th they will not be taken into account in the calculation. From February 1 to February 15 (15 days) - 50 people. From February 16 to February 28 (13 days) - 48 people. We count: (50 x 15) + (48 x 13) = 1374 Then we divide this amount by the number of days in February: 1374:28 = 49
To calculate the annual NHI, such a calculation must be made for each month. Then add up the resulting numbers for each month and divide by 12 - the number of months in a year.
Why do you need staffing and structure?
The staffing table is a document that reflects the structure of the company and the number of employees in it. Scheduling is not a mandatory procedure for companies. The law does not require this.
The number of staff and the structure of the company are prescribed in the statutory documents. This is especially important when the organization is developing dynamically.
You should not refuse to draw up these documents; this allows you to avoid too much burden on the company, both new and existing. In addition, the schedule contains a list of all divisions of the organization with a management hierarchy.
The need for staffing is also clear. It reflects not only how many people work in the company, but also their official salaries.
The schedule is approved by order of the organization.
Cheat sheet for calculating headcount
In order not to get lost among formulas and numbers, let’s put everything into a checklist:
1. If you need to balance the work of the company’s personnel, consider the number of employees.
2. To calculate, use the formula H = V / (FRV x VPL x KVN).
3. To calculate the number taking into account those who may get sick or go on vacation, calculate the absenteeism rate using the formula KN = 1 + DN.
4. Supplement the formula for calculating staffing levels with the absenteeism rate. The formula looks like: ШЧ = H x KN.
5. When you need to submit information to the tax office, consider the average number of employees.
6. If the numbers are not clear and you still need to fire someone, or there is no money to hire new employees, optimize work processes, identify lazy people, tighten deadlines, motivate, connect CRM.
Author: Anna Naumkina, Daria Milakova