How does arrears in contributions from the founders of an LLC arise and what are the consequences?
Within the time limits established by the constituent documents (but no later than 4 months after the registration of the company), all founders of the LLC are required to make their contribution to the authorized capital to the balance sheet of the company (Clause 1, Article 16 of the Law “On LLC” dated 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ ).
Immediately upon completion of registration of the company with the Federal Tax Service, the debt of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital (AC) is recorded in the accounting registers. It exists until all founders make full contributions to the management company.
If any of the founders refuses to contribute their share to the authorized capital, then individual sanctions provided for in the constituent agreement may be applied to him. The release of the founder from the obligation to pay for such shares is, in principle, not allowed (Clause 2 of Article 90 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, such founders must, within the limits of unpaid shares in the management company, bear joint liability for the debts of the company (clause 1 of Article 87 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
All founders bear subsidiary liability for the company’s debts until the debt on the authorized capital is fully repaid (Clause 4, Article 66.2 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Until contributions to the management company are made in full, the founders do not have the right to distribute the company’s profits (Clause 1, Article 29 of Law No. 14-FZ).
But what should the partners of the founder do, who, for one reason or another and despite the sanctions, fundamentally refused to pay for the authorized capital - in whole or in part?
The authorized capital has not been paid: what should the company do?
If payment for the share in the company’s management company is not made within the prescribed period, then this share becomes the property of the company (Clause 3, Article 16 of Law No. 14-FZ). After this, the founders of the company must:
1. Within a month, inform the Federal Tax Service by sending there Form R13014 about the transfer of the share to the LLC (clauses 2, 3, 6 of Article 24 of Law No. 14-FZ).
2. During the year, buy back and redistribute (or sell to third parties) this share. Within a month after the redistribution or sale of the share, also notify the Federal Tax Service about this.
If the founders do not do any of the above actions, then the authorized capital is subject to reduction by the amount of the share that has not been redeemed or redistributed or sold (clause 5 of Article 24 of Law No. 14-FZ). The Federal Tax Service must also be informed about the reduction in the capital within a month.
See also “Procedure for reducing the authorized capital of an LLC.”
If the final amount of the authorized capital is less than the minimum (for an LLC - 10,000 rubles), then the enterprise can be liquidated at the request of the Federal Tax Service as having failed to comply with the requirements of the law on registering a business company (subclause 1, clause 3, article 61 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Next, we will consider a situation where the founder nevertheless agreed to repay the existing debt on time.
Where is the debt of the founders reflected on the balance sheet?
At the time of state registration of the company, a standard entry is generated for the amount of the authorized/share capital. The same entries are made with a further increase in the amount of capital. At the same time, the credit balance of the account. 80 is equal to the amount of the authorized capital reflected in the constituent documentation. Primary documents are decisions, constituent/payment documents, acceptance certificates, cash orders, appraisers’ opinions, etc.
You can contribute start-up capital in several parts. In this case, the first must be at least 50%. The outstanding debt must be repaid within the first year of operation of the firm. If the obligations are not fulfilled, the founder must reduce the size of his share. If the authorized capital is reduced to a level below that established by law, the company will be liquidated.
07 Apr 2022 klasterlaw 225
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Child custody benefit in 2022
- Eviction Housing Code of the Kyrgyz Republic
- How many reasons for traffic police officers to check documents in 2022?
- Demolition of houses in Cheboksary in 2022
How can the founder's debt be repaid?
The debt of the founders on contributions to the authorized capital can be repaid:
- in cash;
- securities;
- property;
- rights of claim on receivables.
Find out in ConsultantPlus how to reflect the contribution of funds to the authorized capital in accounting and what are the nuances of tax accounting for the contribution of property as a contribution to the management company. Get free access to the K+ help system to find out all the details of this procedure.
In this case, the minimum amount of the authorized capital must be represented in cash. An assessment of the value of property that is planned to be added to the balance sheet as a management company is carried out by an independent appraiser (Clause 2 of Article 66.2 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Funds can be contributed to the authorized capital in cash or by transferring them to a current account. In the first case, a PKO is issued according to form No. KO-1.
The procedure for repaying debt under a capital company using the receivables of the company’s founder is also common. Let's study its features.
Accounting for settlements with founders
The creation of an enterprise begins on the initiative of individuals and/or legal entities. To open a business, statutory documents are drawn up, including a constituent agreement. Each participant makes his contribution according to the share determined by the agreement (protocol/decision). According to legislative norms, on the date of registration, the authorized capital must be repaid by at least 50%. In the process of subsequent economic activities, the founders have the right to count on receiving income (dividends) from participation.
Documentation and accounting of settlements with the founders are carried out on the basis of statutory documents, each copy of which should be kept in the organization. In this case, settlements with the founders are reflected in the balance sheet separately, with detailed data on sub-accounts. Analytical accounting is required to be maintained separately for each participant, except for shareholders of a JSC with “bearer” status.
Important! The minimum amount of creditor claims for which the founders are liable is the amount of the authorized capital of the enterprise.
Formation of authorized capital at the expense of receivables: nuances
This legal relationship assumes that the founder, who has the right to claim on receivables, will pay off his own debt under the authorized capital by placing his receivables in the management company as an asset. To do this, he, together with other founders, needs to hold a meeting at which the value of such a contribution to the management company will be assessed. If the amount of the debt claim is above 20,000 rubles, then an independent appraiser will be required to evaluate the deposit (Clause 2, Article 15 of Law No. 14-FZ).
Supporting documents on the basis of which the receivable will be attributed to the authorized capital may be, in particular:
- agreement on the assignment of rights of claim (if it is required under the agreement between the founder and the debtor);
- loan agreement;
- receipt;
- writ of execution if the debt is already being collected.
A scenario is also possible in which the debt under the charter capital is partially repaid by the founder.
The contribution to the authorized capital has been partially repaid: legal consequences
The founder who partially paid the debt on the authorized capital:
1. Will retain responsibilities:
- to pay the remaining share before the expiration of the established period for the formation of the management company;
- participation in further redistribution of the unpaid share;
- bearing joint and several liability for the debts of the company.
2. At the same time, he will receive the rights:
- for part of the profit after redistribution based on the unpaid share;
- sale of the paid part of the share (its receipt upon liquidation of the company);
- participation in the meeting of founders and decision-making on business issues.
But the founder will not be able to count on profit, since the company will not have the right to distribute it.
Let us now study what is the procedure for accounting for the debts of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital.
Responsibility for unfair actions
The founder and director, as subsidiary debtors, become such not by default, but by violating the principle of reasonable and conscientious behavior in the management of the LLC. At the expense of the guilty person, damages caused by unreasonable and dishonest actions are compensated. This often happens if:
- director and founder are the same person;
- such persons voted at the general meeting for decisions that led to destructive processes in the company;
- the founder owns more than half the share and actually determines the vector of development of the company;
- the founder or participant alone makes all decisions regarding the company.
Subsidiary debtors may be jointly and severally liable for the debts of an LLC if the guilt of several persons is proven simultaneously, including by way of recourse. In order for the director or founder of an LLC to become vicariously liable for the company’s debts, a cause-and-effect relationship between their actions and the resulting negative consequences must be proven.
Responsibility of the former manager
The number of abandoned LLCs is increasing. The tax service forcibly closed about half a million companies on its own. However, the law allows creditors outside the bankruptcy procedure, after the closure of the company, to initiate subsidiary liability of former managers, even if the entry in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities has already been excluded. The procedure is simplified by the fact that there is no need to challenge such a decision of the inspectorate, initiate bankruptcy or restore the LLC to the register. The directors and founders of a defunct company are brought to subsidiary liability directly: creditors only need to submit an application for recovery directly to such persons. This aspect once again emphasizes the importance of legal support during LLC liquidation and bankruptcy. Legal provides professional support to the company and its officials, which helps prevent the onset of subsidiary, administrative, and criminal liability and minimize all kinds of risks.
Nominal and actual director
A fairly common situation is when an LLC is managed by a nominee director, and the actual controlling persons are unknown to creditors. Judicial practice in this matter shows that such a “conditional” status does not relieve liability. If the actual manager can be identified, both entities are held jointly and severally liable. If not, the Supreme Court made it clear that a nominal position does not remove the director’s ability to influence the situation and the direction of development of the company. His actions or inactions in violation of the principles of reasonableness and good faith may be regarded as those that led to the company's debts. That is, the subsidiary liability of the director of an LLC arises according to the general rules. To identify the remaining persons involved who control the debtor, the court requests documents for previous periods of the company’s functioning. If such subjects are identified, they are involved as co-defendants. A nominee director will not be able to avoid liability by arguing only by the presence of actual managers, so the help of a lawyer is required.
Payment of debt on authorized capital: accounting
When maintaining accounting records for transactions related to the formation and repayment of debts of the founders on the authorized capital, the following entries are used:
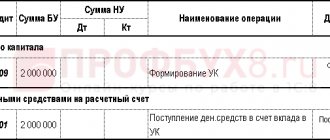
- Dt 75 Kt 80 - to reflect in accounting the fact of debt formation (when registering a company with the Federal Tax Service);
- Dt 50 (or 08, 10, 41, 51, 52 - depending on the method of payment of the authorized capital) Kt 75 - to reflect the fact of debt repayment (in whole or in part);
- Dt 80 Kt 75 - a reflection of the forced reduction of the capital when the debt is not repaid by the founder on time and is not subsequently redistributed.
If the authorized capital is formed at the expense of receivables, then the following sequence of transactions is applied:
- Dt 76 Kt 75 - the company has been transferred the right to claim the debt on account of the management company;
- Dt 51 Kt 76 - the debtor paid the company.
In the balance sheet, the authorized capital is classified as liabilities and is reflected in the amount determined by the constituent documents in line 1310 (even with partial payment). The current debt of the founders is, in turn, an asset, and it is reflected on the balance sheet in line 1230.
Read about the nuances of filling out the balance sheet in the article “Deciphering the lines of the balance sheet (1230, etc.).”
Postings when the founder pays the debt of the enterprise
The debt for dividends accrued to the founders is reflected in the accounting entry (entries are made on the date of adoption of the resolution by the participants):
- Dt 84 Kt 75 – dividend amounts are accrued for members of legal entities and individuals who are not employees of the organization paying the income;
- Dt 84 Kt 70 – dividend amounts are accrued for those who are employees of the income payer.
On the date of payment, a tax is charged, which is withheld upon payment (according to analytics, a division is made by type of tax):
- Dt 75 Kt 68 – for participants who are not employees (personal income tax);
- Dt 70 Kt 68 – for participants who work for the payer (personal income tax).
Dividends were paid on the date of payment, divided by members of the company:
- Dt 75 Kt 51 (50) - for members who do not work at the payer enterprise;
- Dt 70 Kt 51 (50) – for recipients of employees of the payer enterprise.
Taxes paid on the date of payment of dividends (divided by members and type of tax): Dt 68 Kt 51 .
Unclaimed dividends were written off to profit, the deadlines for which had expired: Dt 70 (75) Kt 84.
Tax accounting of debt on authorized capital: nuances
When maintaining tax accounting of deposits in the management company, you should keep in mind that:
1. Cash and property contributed to replenish the authorized capital by the founder-individual or legal entity:
- are not subject to VAT;
- do not form a tax base for personal income tax, income tax or the simplified tax system.
But if the founder-legal entity pays VAT, then if the tax is accepted for deduction (on property transferred to the authorized capital), the VAT must be restored (subclause 1, clause 3, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the amount of recovered and paid VAT cannot be included in profit expenses. The organization for which the authorized capital is formed has the right, in turn, to receive a VAT deduction restored by the founder-legal entity (Clause 11 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When redistributing a share in a business in favor of a specific founder (or when increasing the nominal value of his share in the authorized capital), the founder does not have to calculate personal income tax. However, if the nominal price of the management company is reduced by decision of the founders (not for the purpose of fulfilling the requirements of the law), then the founders will have to pay personal income tax on the difference between the previous and new value of the shares (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 14, 2011 No. 03-04-06/3-88) .
Upon payment of contributions from all founders in full, the authorized capital may be increased:
- through additional contributions from the founders;
- as a backup option - by raising capital from third parties.
Let's consider the specifics of the main option for increasing the capital, when the owners of the company manage on their own.
A practical guide to filling out a balance sheet for a novice accountant (page 4)
Account 71 is credited for amounts spent by accountable persons in correspondence with accounts that record expenses and acquired values, as well as other accounts depending on the nature of the expenses incurred.
Settlements can also be made with the organization’s personnel for other transactions, in particular for loans issued, compensation for material damage, etc.
To summarize information about all types of settlements with employees of the organization, except for settlements for wages and settlements with accountable persons, account 73 “Settlements with personnel for other transactions” is used.
The debit of account 73 includes the amounts of loans provided to employees of the organization or amounts to be recovered from guilty persons.
Until the loan is repaid, damages are compensated, etc., the enterprise has a debit balance of account 73, reflected in line 240 of the balance sheet asset “Accounts receivable (payments for which are expected within 12 months after the reporting date).”
The appearance of a credit balance on account 73 means the enterprise's accounts payable. Accounts payable will be reflected in the liability on line 625 “Other creditors”.
There may also be settlements that are not reflected in the accounting accounts, for example, settlements for property and personal insurance, for claims, for amounts withheld from the wages of the organization’s employees in favor of other organizations and individuals on the basis of executive documents or court decisions, etc.
Such calculations are recorded on account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”.
The debit balance of account 76 indicates the amount of receivables reflected in line 240 of the balance sheet asset “Accounts receivable (payments for which are expected within 12 months after the reporting date).” The balance of account 76 for the loan indicates the amount of accounts payable to be reflected on line 625 “Other creditors”.
If structural divisions in the form of branches or representative offices are allocated to separate balance sheets (intra-balance sheet settlements), account 79 “Intra-business settlements” is used to display information about all types of settlements with them.
Account 79 displays information on the types of calculations performed.
The property allocated to the divisions is written off by the organization from account 01 “Fixed assets” to the debit of account 79 “On-farm settlements”, and the divisions, in turn, take it into account from the credit of account 79 “On-farm settlements” to the debit of account 01 “Fixed assets” and etc.
The property transferred to trust management is written off by the founder of the management from accounts 01 “Fixed Assets”, 04 “Intangible Assets”, 58 “Financial Investments”, etc. to the debit of account 79 “Intra-business settlements” (at the same time, a debit entry is made for the amount of accrued depreciation accounts 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets”, 05 “Depreciation of intangible assets” and the credit of account 79 “Intra-business settlements”). The property accepted by the trustee on a separate balance sheet is reflected in the debit of accounts 01 “Fixed assets”, 04 “Intangible assets”, 58 “Financial investments”, etc. and the credit of account 79 “Intra-business settlements” (at the same time, an entry is made for the amount of accrued depreciation on the credit of the accounts 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets”, 05 “Depreciation of intangible assets” and credit account 79 “Intra-business settlements”).
In the event of termination of the property trust management agreement and the return of the property to the management founder, reverse entries are made. If the property trust management agreement provides for other operations with the property transferred to trust management, then accounting for these operations is carried out in accordance with the general procedure.
The transfer of funds at the expense of the profit (income) due to the founder of the management in a separate balance sheet is reflected in the credit of cash accounting accounts and the debit of account 79 “On-farm settlements”. The funds received by the founder of the management on account of this profit (income) are credited to the debit of cash accounts in correspondence with account 79 “On-farm settlements”.
The amount of compensation due by the trustee for losses caused by loss or damage to property transferred to trust management, as well as the amount of lost profits, is reflected in the debit of account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” in correspondence with the credit of account 91 “Other income and expenses” " When the founder receives control of these funds, cash accounting accounts are debited and account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” is credited.
An important feature of the reflection of information on account 79 in accounting is the absence in the reporting of information on balances on account 79 “Intra-business settlements”. When preparing consolidated statements, the balances on the separate balance sheet accounts are added to the balances on the corresponding accounts of the parent organization. And for the parent organization it will be fully covered by the corresponding balances on this account of the separate divisions.
When preparing consolidated statements, equal balances on account 79 will not appear.
If a balance sheet is drawn up only for a separate division or only for the parent organization, then the balance of account 79 in debit will complement the reporting indicators on line 240 of the balance sheet asset “Accounts receivable (payments for which are expected within 12 months after the reporting date)”, and the balance of account 79 for a loan - reporting indicators on line 625 “Other creditors”.
So, the indicator on line 625 “Other creditors” reveals the amount of other accounts payable that was not reflected in the previous lines of the balance sheet.
Special-purpose financing.
In the standard balance sheet form there is no independent line with this name. Targeted financing for non-profit organizations is reflected in the “Capital and Reserves” section. Commercial organizations reflect such amounts in line 640 “Deferred income” or separately in the “Current liabilities” section.
Debt to participants (founders) for payment of income (line 630).
The main type of income received by shareholders (founders) is dividends.
The source of dividend payment is the company's profit after tax (net profit of the company), determined on the basis of financial statements.
In a situation where dividends are accrued but not paid as of the reporting date, their amounts are reflected in line 630 of the balance sheet “Debt to participants (founders) for payment of income.”
Accounting for settlements with founders is carried out on account 75 “Settlements with founders”.
If the founders-shareholders are employees of the organization, then dividends are calculated in correspondence with account 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages”.
The accrual of dividends to shareholders (founders) results in the company's obligations as a tax agent. The personal income tax withholding rate depends on the status of the person to whom the payments are made. It is important to remember that income tax is charged only when dividends are actually paid; if dividends are not paid, then no tax is charged.
So, the indicator on line 630 “Debt to participants (founders) for payment of income” reveals the amount of dividends accrued in favor of shareholders (participants) but not paid as of the reporting date.
Deferred income (line 640).
Income received in the reporting period, but relating to subsequent reporting periods, must be reflected in the balance sheet as a separate item as deferred income. These incomes are included in the financial results of a commercial organization or an increase in income in a non-profit organization upon the onset of the reporting period to which they relate.
It can be:
- rent or rent;
— utility fees;
— revenue for freight transportation, for passenger transportation on monthly and quarterly tickets;
— subscription fee for using communication means;
— assets received by the organization free of charge;
— receipts of debt for shortfalls identified in the reporting period for previous years, etc.
In addition, in the line “Deferred income”, commercial organizations show the budget funds received.
Future income is accounted for on account 98 of the same name. Account 98 also takes into account future receipts of debt for deficiencies identified in the reporting period for previous years, and the difference between the amount to be recovered from the guilty parties and the value of the valuables accepted for accounting when the deficiency was identified and damage.
The occurrence of deferred income is reflected in the credit of account 98, and write-offs are reflected in the debit of this account.
So, the indicator on line 640 “Deferred income” reveals the amount of income received in the reporting period, but relating to the following reporting periods.
Reserves for future expenses (line 650).
Organizations, in order to evenly include upcoming expenses in the costs of production or circulation of the reporting period, have the right to create reserves for the upcoming payment of vacations to employees; payment of annual remuneration for long service; payment of remuneration based on the results of work for the year; repair of fixed assets; production costs for preparatory work due to the seasonal nature of production; upcoming costs for land reclamation and other environmental measures; upcoming costs of repairing items intended for rental under a rental agreement; warranty repairs and warranty service; covering other anticipated costs and other purposes provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation, regulatory legal acts of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
At the end of the reporting year, reserve balances carried over to the next year are reflected in a separate item in the balance sheet.
Reservation of amounts and use of the accrued reserve are reflected in account 96 “Reserves for future expenses.”
Analytical accounting for account 96 is carried out for separate reserves. The construction of analytical accounting can be based on the principle of opening separate sub-accounts to account for each type of reserves. The formation of a reserve for future expenses is carried out in correspondence with the accounts of production costs and sales expenses.
Expenses for which a reserve has been created are written off from the created reserve by making a debit entry to account 96.
Amounts of expenses exceeding the amount of the created reserve are included in the expenses of the enterprise.
If actual costs are less than the reserve, then the balance of the unused reserve increases profit at the end of the reporting year.
The amount of the reserve that is not fully used in the reporting period may be carried forward to the next reporting period. The amount of the reserve newly created in the next reporting period is adjusted to the amount of the reserve balance of the previous reporting period.
So, the indicator on line 650 “Reserves for future expenses” reveals the amount of reserves for the upcoming payment of vacations to employees; payment of annual remuneration for long service; payment of remuneration based on the results of work for the year; repair of fixed assets; production costs for preparatory work due to the seasonal nature of production; upcoming costs for land reclamation and other environmental measures; upcoming costs of repairing items intended for rental under a rental agreement; warranty repairs and warranty service; covering other anticipated costs and other purposes.
Other short-term liabilities (line 660).
This line of the balance sheet shows the amounts of short-term liabilities of the enterprise that are not shown under other items in section. V “Short-term liabilities” of the balance sheet.
Total for section V (line 690).
Line 690 is the final line of the section. V balance sheet “Short-term liabilities”. It reflects the total amount of short-term liabilities of the enterprise, namely the sum of the balance sheet lines:
— Loans and credits (line 610);
— Accounts payable (line 620);
— Debt to participants (founders) for payment of income (line 630);
— Income for future periods (line 640);
— Reserves for future expenses (line 650);
— Other short-term liabilities (line 660).
Let us systematize in the table the progress of the formation of indicators in section. V balance.
Balance (line 700).
Line 700 “Balance” is the total of the balance sheet liability (balance sheet currency). It is defined as the sum of the balance sheet indicators: the total of Sect. III “Capital and reserves” (line 490), the result of section. IV “Long-term liabilities” (line 590) and the total of section. V “Short-term liabilities” (line 690), displaying the sources of formation of the enterprise’s property (own and attracted) indicating the intended purpose (if any) and the repayment period.
Chapter 4. OFF BALANCE ACCOUNTS
After filling out the assets and liabilities of the balance sheet, it is necessary to disclose the indicators taken into account off-balance sheet in off-balance sheet accounts.
And to do this, you need to fill out a certificate confirming the presence of valuables recorded in off-balance sheet accounts.
Off-balance sheet accounts are intended to summarize information about the presence and movement of assets temporarily in use or disposal of the organization (leased fixed assets, material assets in custody, in processing, etc.), contingent rights and obligations, as well as to control individual business transactions.
Leased fixed assets (line 910).
Under a lease (property lease) agreement, the lessor (lessor) undertakes to provide the lessee (tenant) with property for a fee for temporary possession and use or for temporary use.
Land plots and other isolated natural objects, enterprises and other property complexes, buildings, structures, equipment, vehicles and other things that do not lose their natural properties during their use can be leased.
Generalized information on the availability and movement of fixed assets leased by the organization is located on off-balance sheet account 001 “Leased fixed assets”.
Fixed assets accounted for in account 001 are included in the valuation specified in the lease agreements.
Analytical accounting for account 001 is carried out by lessor, for each object of leased fixed assets (according to the lessor's inventory numbers).
In case of disposal of a fixed asset, the amount reflected in the debit of account 001 is written off as a credit.
This line, in addition to information about leased fixed assets, may contain information about fixed assets received by the organization for free use.
So, the indicator on line 910 “Leased fixed assets” reveals the cost of fixed assets leased by the organization in the valuation specified in the lease agreement.
Including leasing (line 911).
The line “Including leasing” of the certificate discloses the value of fixed assets received under a leasing agreement, if the agreement provides for the inclusion of these values on the lessee’s balance sheet.
The indicator on line 911 indicates the amount of fixed assets received by the organization under leasing agreements, in the assessment specified in the agreements.
Inventory assets accepted for safekeeping (line 920).
To account for the presence and movement of inventory items accepted for safekeeping, account 002 “Inventory assets accepted for safekeeping” is used. This account takes into account the assets held by the organization, the ownership rights to which this organization does not have, for example:
- unpaid valuables received under an agreement that stipulates that ownership of them passes only after payment;
— valuables that arrived at the enterprise by mistake or did not meet the terms of the order;
— values for which the organization legally refused to accept invoices of payment requests and their payment;
— valuables that were left in safekeeping with suppliers, documented with safekeeping receipts, but not removed for reasons beyond the control of the organizations;
— valuables accepted for safekeeping for other reasons.
Inventory assets are recorded on account 002 at the prices provided for in acceptance certificates or in payment requests.
Analytical accounting for account 002 is carried out by owner organizations, by type, grade and storage location.
So, the indicator on line 920 “Inventory assets accepted for safekeeping” reveals the cost of inventory assets accepted for safekeeping, the ownership of which does not belong to this organization, in the prices stipulated in the acceptance certificates or in payment requirements.
Goods accepted for commission (line 930).
When concluding a commission agreement, the ownership of the valuables transferred to the commission agent remains with the principal. The commission agent, when accepting valuables for commission, must organize their proper accounting. Goods accepted for commission are recorded in account 004 “Goods accepted for commission” at the prices stipulated in the acceptance certificates.
Analytical accounting for account 004 is carried out by type of goods and organizations (persons) - principals.
Debt of insolvent debtors written off at a loss (line 940).
To account for the debt of insolvent debtors, account 007 “Debt of insolvent debtors written off at a loss” is intended.
That is, writing off a debt at a loss due to the debtor’s insolvency does not constitute cancellation of the debt. This debt is reflected on the balance sheet for five years from the date of write-off in order to monitor the possibility of its collection in the event of a change in the debtor's property status.
Accounts receivable can be written off off-balance sheet if the debtor company is liquidated.
Analytical accounting for account 007 is maintained for each debtor whose debt is written off at a loss, and for each debt written off at a loss.
Security for obligations and payments received (line 950).
This line reflects information about the amounts of guarantees received by the enterprise to ensure the fulfillment of obligations and payments.
In accounting, information on the availability and movement of guarantees received to secure the fulfillment of obligations and payments, as well as security received for goods transferred to other organizations (individuals), is displayed on account 008 “Securities for obligations and payments received.”
If the guarantee does not specify the amount, then for accounting purposes it is determined based on the terms of the contract.
The amounts of collateral recorded in account 008 are written off as the debt is repaid.
Analytical accounting for account 008 is maintained for each collateral received.
So, the indicator on line 950 “Securities for obligations and payments received” discloses the amount of guarantees received by the enterprise to ensure the fulfillment of obligations and payments.
Security for obligations and payments issued (line 960).
Accounting for guarantees issued to secure the fulfillment of obligations and payments is kept in off-balance sheet account 009 “Securities for obligations and payments issued.”
If the guarantee does not specify the amount, then for accounting purposes it is determined based on the terms of the contract.
The collateral amounts recorded in account 009 are written off as the debt is repaid.
Analytical accounting for account 009 is maintained for each issued collateral.
Depreciation of housing stock (line 970).
Depreciation of external improvement objects and other similar objects (line 980).
For housing facilities (residential buildings, dormitories, apartments, etc.), external improvement facilities and other similar facilities (forestry, road construction, specialized shipping facilities, etc.), as well as for productive livestock, buffaloes, oxen and deer, perennial plantings that have not reached operational age, if these objects are not used to generate income, depreciation is not charged.
For such objects at the end of the reporting year, depreciation is calculated according to established depreciation rates.
Depreciation amounts are accounted for in a separate off-balance sheet account 010 “Depreciation of fixed assets.” It groups information on the movement of depreciation amounts by housing stock objects, external improvement objects and other similar objects (forestry, road management, specialized shipping facilities), and for non-profit organizations - by fixed assets.
It is necessary to distinguish between the depreciation of the housing stock and the depreciation of external improvement objects, information about which is taken into account on one account 010 “Depreciation of fixed assets”. For this purpose, the enterprise organizes analytical accounting, which is maintained for each object.
So, the indicators on line 970 “Depreciation of the housing stock” and on line 980 “Depreciation of external improvement objects and other similar objects” reveal the amount of accumulated depreciation for the enterprise’s housing stock, as well as external improvement objects and other similar objects.
Intangible assets received for use (line 990).
There is no special off-balance sheet account to display such information in the Chart of Accounts.
If an enterprise has such assets, information on them can be reflected in a separate off-balance sheet account.
Analytical accounting on such an account is maintained for each object.
Other assets recorded in off-balance sheet accounts.
There is also no such line in the standard help form. However, if there is information in the company’s accounting about other valuables recorded in off-balance sheet accounts, but not reflected in the certificate, it is necessary to make additions to the certificate and indicate information about the following values:
— materials accepted for processing;
— equipment accepted for installation;
— strict reporting forms;
- fixed assets leased.
Materials accepted for processing (account 003).
Account 003 “Materials accepted for processing” is intended to summarize information on the availability and movement of raw materials and customer materials accepted for processing (raw materials supplied by customers), not paid for by the manufacturer.
Accounting for the costs of such raw materials and materials is carried out in the usual manner in production cost accounts reflecting the costs associated with them. The exception is the cost of raw materials and materials of the customer. The customer's raw materials accepted for processing are accounted for in account 003 “Materials accepted for processing” at the prices stipulated in the contracts.
Analytical accounting for account 003 is carried out by customers, types, grades of raw materials and materials and their locations.
Equipment accepted for installation (account 005).
Information about the availability and movement of equipment received by the organization from the customer for installation is disclosed on account 005 “Equipment accepted for installation” at the prices specified by the customer in the accompanying documents.
Analytical accounting for account 005 is carried out for individual objects or units.
Strict reporting forms (account 006).
Strict records must be kept using strict reporting forms, reflecting their availability and movement. Information about strict reporting forms in accounting is reflected in off-balance sheet account 006 “Strict reporting forms” in a conditional valuation.
Analytical accounting for account 006 is maintained for each type of strict reporting forms and their storage locations.
Fixed assets leased (account 011).
When concluding an agreement under the terms of which fixed assets leased are recorded on the balance sheet of the lessee (tenant), such assets are recorded in off-balance sheet account 011 “Fixed assets leased”.
Fixed assets leased are accounted for on account 011 in the valuation specified in the lease agreements.
Analytical accounting for account 011 “Fixed assets leased” is carried out by tenant, for each object of fixed assets leased. Fixed assets leased out outside the Russian Federation are accounted for separately on account 011 “Fixed assets leased out.”
So, the indicators for the line “Other assets recorded in off-balance sheet accounts” reveal the amount of other assets recorded in off-balance sheet accounts, but not reflected in other lines of the Certificate. Such values could be:
— the cost of materials transferred for processing at the prices stipulated in the contracts;
— the cost of equipment accepted for installation, in prices specified by the customer in the accompanying documents;
— conditional cost of strict reporting forms;
— cost of fixed assets leased;
— the cost of other valuables recorded in off-balance sheet accounts.
Chapter 5. CHECKING DATA TO FORM A BALANCE
Before proceeding with the preparation of the balance sheet, it is necessary to check the correctness of the reflection of transactions in the accounting accounts and reconcile the balances in the accounting registers.
Thus, one of the elements of drawing up a balance sheet is an internal audit of data for the formation of a balance sheet and an internal audit of data from an already formed balance sheet.
Intangible assets (line 110).
Fixed assets (line 120).
It is necessary to check the depreciation charge for fixed assets and intangible assets for the reporting period. And one more thing - the balance is formed in a net valuation, that is, without taking into account the amounts of accrued depreciation.
Long-term financial investments (line 140).
Short-term financial investments (line 250).
It is necessary to check whether interest has been accrued on loans provided. It is also necessary to ensure that interest amounts are included in the loan amount.
Value added tax on acquired assets (line 220).
Account 19 “Value added tax on purchased assets” and line 220 of the balance sheet account for the amount of VAT paid to suppliers when purchasing goods, works, and services.
The receipt of goods, works, services, as well as the reflection of “input” VAT is carried out by postings:
Debit 10, 20, 25, 26, 41, 44, etc. Credit 60, 76
— the cost of goods, works, services excluding VAT;
Debit 19 Credit 60, 76
— the amount of VAT on goods, works, and services received.
The entire turnover of account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” or account 76 “Settlements with various creditors and debtors” for the loan reflects the amount of debt to suppliers, including VAT. It is not difficult to derive and calculate the proportion.
By comparing the purchase ledger data with the amounts recorded in the Debit 68 Credit 19 posting, you can determine how well the accounting data corresponds to this tax accounting register. Although during such a check it is necessary to take into account the impact of VAT amounts on advances received.
Discrepancies can arise as a result of an accounting error, as well as as a result of some specific accounting transactions.
Accounts receivable (payments for which are expected more than 12 months after the reporting date) (line 230).
Accounts receivable (payments for which are expected within 12 months after the reporting date) (line 240).
The balance sheet must reflect all significant indicators. That is, it is necessary to assess the materiality of accounts receivable indicators. In the balance sheet form, only information on buyers and customers is indicated as a decoding line. However, this does not relieve the need for a more complete decoding of the composition of accounts receivable in the balance sheet if it is material.
In addition, it is necessary to show the expanded balance of settlement accounts in the balance sheet.
Loans and credits (line 510).
Loans and credits (line 610).
When forming a balance sheet, these lines are influenced by the same factors as in line 140 “Long-term financial investments”, as well as line 250 “Short-term financial investments”.
Debt for taxes and fees (line 624).
To check the correctness of the derivation of data for creating a balance, you must refer to tax returns for taxes, as well as the corresponding tax registers.
If the sales book and VAT return for the corresponding period contain the same numbers, then the General Ledger is filled out correctly and the balance sheet will also be formed correctly.
It is also necessary to check whether the amounts of fines and penalties accrued to the enterprise are reflected in the accounting. These amounts are reflected in accounting separately from the amounts of taxes and fees.
Other creditors (line 625).
Here it is necessary to check the correctness of the reflection in the balance sheet of the balance in account 79 “Intra-economic settlements”.
It is also necessary to ensure that there are no unreconciled balances on account 79 in the balance sheet.
Chapter 6. SUMMARY TABLE
ON COMPLETING THE BALANCE SHEET
I. Non-current assets
| Balance line | Balance line code | How to get data to create a balance |
| Intangible assets | 110 | 1) debit balance of account 04 “Intangible assets” (when calculating depreciation without using account 05 “Amortization of intangible assets”); 2) the difference between the debit balance of account 04 and the credit balance of account 05 |
| Fixed assets | 120 | The difference between the balance of account 01 as a debit and the balance of account 02 as a credit (with the exception of the subaccount “Depreciation on income-generating investments in tangible assets”) |
| Construction in progress | 130 | Balance of accounts 07 “Equipment for installation”, 08 “Investments in non-current assets” by debit plus (minus) debit (credit) balance, subaccounts of account 16 “Deviation in the cost of material assets” in terms of deviations from the estimated cost related to objects under construction |
| Profitable investments in material assets | 135 | The difference between the debit of account 03 “Income-generating investments in tangible assets” and the credit of account 02, subaccount “Depreciation on income-generating investments in tangible assets” |
| Long-term financial investments | 140 | Debit balance of account 58, subaccount “Long-term financial investments”, reduced by the credit of account 59 “Reserves for depreciation of financial investments”, subaccount “Reserves for depreciation of long-term financial investments” |
| Deferred tax assets | 145 | Account balance 09 “Deferred tax assets” by debit |
| Other noncurrent assets | 150 | Indicators not indicated in other lines of the balance sheet section “Non-current assets” |
II. Current assets
| Due to the large volume, this material is placed on several pages: 4 |
Increasing the authorized capital through additional contributions: nuances
The decision on additional investments in the authorized capital is made at a separate meeting of the founders. After its adoption, business owners must replenish the capital for the agreed amount within 2 months, unless they specify a different period (Clause 1, Article 19 of Law No. 14-FZ).
If the agreed amount could not be added to the authorized capital within the prescribed period, then all funds and property contributed by that time in order to increase the capital are returned to investors within a reasonable time. If it is missed, then the funds and property are returned with an additional payment, the amount of which is determined in accordance with Art. 395 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
The legislation does not contain unambiguous criteria for determining a reasonable period. As a rule, it is established by the court. It is possible that the court will order additional payment under Art. 395 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation immediately after the expiration of the deadline for increasing the authorized capital by law (or in accordance with the decision of the founders).
No one has the right to oblige the founder to pay an additional contribution to the authorized capital (Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated May 25, 2010 No. 446/10). Accordingly, even if it is known that it was not possible to increase the authorized capital due to the refusal of a particular founder to make an additional contribution, this founder will not be held liable for possible losses of the company.
Reflection of transactions with dividends in accounting
The basis for accrual of these incomes in the accounting of the organization are the minutes of the meeting of participants with the decision made on payment within the established time frame and an accounting certificate calculating the amounts due to each of the owners.
To combine information on accrued and paid dividends, use account 75/2 “Settlements with founders” and the subaccount “Settlements for payment of income”. If this type of income is received by a company employee, then account 70 “Payments with personnel for salaries” is used. The corresponding account is account 84 “Retained earnings”.
Accounting entries are made separately for each participant. The main wiring is as follows:
| Operation | D/t | K/t | |
| At the end of the year | |||
| Retained earnings have been generated | 99 | 84 | |
| On the date of the decision on payment | |||
| Income accrued to each owner | 84 | 75/2 (70) | |
| On the dividend payment date | |||
| Paid from the cash register or from a current account | 75/2 (70) | 50, 51 | |
| Taxes withheld from accrued amounts (NDFL) | 75/2 (70) | 68 | |
| On the date of transfer of taxes to the budget | |||
| Taxes transferred | 68 | 51 | |
Results
Within 4 months after registration of the LLC (or an earlier period determined by the constituent documents of the business company), the founders of the company must repay the debt on contributions to the authorized capital. This can be done at the expense of cash, property, securities, receivables. Until the debt is repaid, the founders have no right to distribute profits. If it is not repaid on time, then the authorized capital is reduced by the amount of the unpaid share (if it is not purchased by someone).
You can learn more about the features of forming the authorized capital of an enterprise from the articles:
- “Accounting entries for contributions to the authorized capital”;
- “Why is the authorized capital of an LLC needed and can it be spent?”
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Line 1230 of the balance sheet, what it includes
- Balance on the debit side of the account. 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”, takes into account the debt on products, goods, work, services sold to the buyer;
- Account debit balance 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees,” speaks of the debt of budgetary authorities to the organization. Accounts receivable on this account may arise due to amounts transferred during the year, advance payments for taxes from budget funds. The amount of transferred advance payments exceeds the amount of calculated tax for a certain period of time;
- Debit balance by account 69 “Calculations for social insurance and security” tells us about the debt of the social insurance authorities to your company. It may arise, for example, due to the amount of excess expenses calculated by the organization on certificates of incapacity for work before accrued insurance premiums;
- Balance on the debit side of the account. 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages”. A debit balance is very rare. It may arise, for example, due to transfers of amounts to an employee (employee) for accrued leave (labour or pre- and post-natal leave). This happens when, at the beginning of the month, the organization’s employees are paid arrears of wages accrued on the last day of the month, and payment is also made for accrued maternity and postpartum leave. The accrual amount will be reflected in the accounting accounts only on the last day of the month, and payment will be made on the current date;
- Debit balance of the account. 71 “Settlements with accountable persons.” Payments to persons to account for funds, non-cash and cash are accounted for on the debit side of the account. 71. After payment, submits a report on expenses incurred to the company’s accounting department. This may include payment for business expenses, payment for purchased materials, expenses for staying in a hotel during a business trip, expenses for moving to and from the place of business trip, and others;
- Debit balance of the account. 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations.” All relationships between employees of the organization are reflected in this active-passive account, except for payroll calculations and payments of funds to the account. The debit of the account reflects the employee's debt to the organization. An employee may be provided with borrowed funds for construction, rent, and other business needs. Also, the employee may have a relationship to compensate for material damage to the company. These are the situations that are reflected in the score 73;
- Balance on the debit side of the account. 75 “Settlements with founders.” The formation of the authorized capital is taken into account according to the D account. 75 and K-tu account. 80 “Authorized capital”. Until the founder deposits personal funds in the amount of the authorized capital, the debit balance will remain on account 75;
- Debit balance of the account. 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors.” Account 76 is active - passive, it reflects debts not reflected in account 60, 62 and other accounts. The account may reflect arrears of payment to the insurance company; claims settlements; withholding funds from employee salaries for third-party companies and persons under executive documents (acts).
We recommend reading: Children of Chernobolets 18 benefits Krasnodar