What income does Article 249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation classify as income from sales?
Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation classifies income as follows:
- income from sales (Article 249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- non-operating income (Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Income from sales is revenue, namely receipts from (clause 1 of Article 249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- sales of manufactured products;
- resale of purchased goods;
- realization of property rights;
- performance of work;
- provision of services.
It is very important to correctly account for income from sales in tax accounting. Otherwise, disputes with tax authorities are possible. Find out how recent judicial practice is developing on the application of Art. 249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, from an analytical selection from ConsultantPlus. Study the material by getting trial access to the K+ system for free.
To learn how income from sales is reflected in the income statement, read the article.
On changes in the taxation of income from the sale of securities
The conditions for exemption from taxation of income received from the sale of shares have changed. The new rules apply to both personal income tax taxpayers and income tax taxpayers. In addition, for 2022, tax agents will have to submit information about income paid to individuals and the amount of personal income tax withheld using a new form. The changes that have taken place are discussed in an interview with Sergei Razgulin, 3rd Class Actual State Advisor of the Russian Federation.
What conditions must be met by a taxpayer to exempt income from the sale of shares from taxation?
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for exemption from personal income tax and taxation of income tax at a rate of 0% of income from operations on the sale or other disposal (including redemption) of shares in the authorized capital of organizations, as well as shares (clause 17.2 of Article 217, clause 4.1 of Article 284 of the Tax Code RF).
The specified tax exemption was introduced by Federal Law dated December 28, 2010 No. 395-FZ.
There are several conditions for obtaining an exemption. Shares (stakes) must be shares (stakes) of Russian organizations (specifics are established by Article 284.7 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation when selling shares (stakes) by an international holding company).
There are special requirements for shares: they must not be traded on the securities market (subclause 1 of clause 2 of Article 284.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), with the exception of: - shares constituting the authorized capital of organizations, no more than 50% of whose assets consist of real estate located on territory of Russia; — shares classified as shares of the high-tech (innovative) sector of the economy. Moreover, such shares can constitute the authorized capital of organizations, more than 50% of whose assets consist of real estate located in Russia.
As a general rule, shares (shares) must be continuously owned by the taxpayer for more than five years.
Is a five-year period of ownership by the taxpayer required for any shares?
No. Federal Law No. 396-FZ dated December 29, 2015 introduced conditions on January 1, 2016 regarding income received from the sale (redemption) of circulating shares, bonds of Russian organizations, investment shares related to the innovative sector of the economy.
For exemption from personal income tax (paragraph three of clause 17.2 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and the application of a 0% rate (paragraph two of clause 4.1 of article 284, article 284.2.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) it is sufficient if the specified shares, bonds, shares were owned for one year and one day.
The above rules for taxation of income from the sale of such securities are valid from January 1, 2016 until January 1, 2023. After 2022, the provisions of Article 284.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation on a five-year holding period as a basis for obtaining tax exemption, suspended until the specified date, will again begin to apply to them.
The rules for classifying shares and bonds of Russian organizations, as well as investment units traded on the organized securities market, as securities of the high-tech (innovative) sector of the economy were approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated February 22, 2012 No. 156.
Are there any requirements for the period of acquisition of shares?
The limitation on the period of acquisition of shares (stakes) was provided not in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, but in Part 7 of Article 5 of the Federal Law of December 28, 2010 No. 395-FZ. It stated that the provisions of paragraph 17.2 of Article 217, paragraph 4.1 of Article 284 and Article 284.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation apply to securities (shares in the authorized capital) acquired by taxpayers starting from January 1, 2011.
So, part 7 of Article 5 of the Federal Law of December 28, 2010 No. 395-FZ was declared invalid as of November 27, 2022 (Article 3 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 424-FZ).
Therefore, the exemption can now be applied to the sale of shares regardless of when they were acquired?
The abolition of restrictions associated with the moment of acquisition of shares applies to the provisions established by clause 17.2 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 4.1 of Article 284 and Article 284.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended by Federal Law No. 395-FZ of December 28, 2010.
Taking into account the amendments, income from the sale of shares of Russian organizations that are not traded on the organized securities market during the entire period of ownership of such shares by the taxpayer may be exempt from tax regardless of the period of acquisition of such shares. Including in the case of their acquisition before 2011, but provided that they were not sold before November 27, 2022 (Part 11 of Article 9 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 424-FZ).
Did the condition on the date of acquisition apply to the shares specified in subclause 4 of clause 2 of Article 284.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation?
Let me remind you that the Federal Law of November 24, 2014 No. 376-FZ, paragraph 2 of Article 284.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation was supplemented by subparagraph 4, which concerns shares constituting the authorized capital of Russian organizations, no more than 50% of whose assets directly or indirectly consist of real estate located on territory of the Russian Federation.
Federal Law No. 376-FZ dated November 24, 2014 came into force on January 1, 2015 and did not provide for any transitional provisions regarding the application of the new subclause 4 of clause 2 of Article 284.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Restrictions on the application of the exemption or 0% rate to income from the sale of only those shares (stakes in the authorized capital) that were acquired by taxpayers starting from January 1, 2011 concerned the original wording of Article 284.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (as amended by Federal Law No. 395-FZ).
Therefore, in my opinion, the tax base for transactions of sale or other disposal (including redemption) of shares of Russian organizations constituting the authorized capital of Russian organizations, no more than 50% of the assets of which directly or indirectly consists of real estate located on the territory of the Russian Federation , a 0% tax rate could be applied or, accordingly, income from their sale could be exempt from personal income tax regardless of the date of acquisition of such shares.
At the same time, the Ministry of Finance expressed a different position on this issue. In the letter dated 08/31/2017 No. 03-03-06/1/56062 it was reported that the provisions of the first paragraph of clause 4.1 of Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation apply to securities acquired by the taxpayer starting from 01/01/2011 (by virtue of Part 7 of Article 5 of the Federal Law No. 395-FZ). Consequently, in the opinion of the Ministry of Finance, the norms of Article 284.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (regardless of the expansion of the list of securities specified in this article) should be applied only to securities acquired by the taxpayer starting from 01/01/2011.
But in any case, taking into account the recognition of Part 7 of Article 5 of Federal Law No. 395-FZ as no longer in force, there are currently no restrictions associated with the moment of acquisition of such shares.
Are there still restrictions on the period for purchasing shares in the innovation sector?
You can take advantage of the period of ownership of shares in the innovation sector, reduced to one year, for the purposes of exemption from personal income tax and the application of a 0% rate in relation to shares acquired starting from January 1, 2011, provided that they were not sold before December 29, 2015 (clause 4 Article 4 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2015 No. 396-FZ).
Shares in the innovative sector of the economy are covered in paragraph three of paragraph 17.2 of Article 217, paragraph two of paragraph 4.1 of Article 284 and subparagraphs 1 and 2 of paragraph 1 of Article 284.2.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (as amended by Federal Law No. 396-FZ of December 29, 2015).
Restrictions associated with the time of acquisition of such shares remain in effect. For the purposes of exemption from personal income tax and the application of a 0% income tax rate, the corresponding shares of the high-tech (innovative) sector of the economy had to be acquired starting in 2011.
Separately, we note that if an individual acquired marketable securities after January 1, 2014, and they were owned for more than three years, then the positive financial result from their sale (redemption) may be exempt from taxation. Such exemption is provided in the form of an investment tax deduction (subparagraph 1 of paragraph 1 of Article 219.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Let us assume that the taxpayer received a loss from the sale of shares that were continuously in his ownership for more than five years. Is it permissible in this case to use the general procedure for determining the tax base for corporate income tax using a rate of 20%?
The tax base and tax rate are mandatory elements of taxation. At the same time, Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in a number of cases provides for the right of an organization to apply a tax rate of 0%. For example, an organization carrying out educational, medical activities, social services for citizens (Articles 284.1, 284.5 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Articles 284.2, 284.2.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation do not allow a taxpayer to voluntarily switch to the application of a tax rate of 0% (to abandon the tax rate of 0%) to the tax base for transactions on the sale of participation interests in the authorized capital of Russian organizations, securities continuously owned by the taxpayer by right of ownership or on another property right for more than five years (one year).
By virtue of paragraph 2 of Article 274 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the tax base for profits taxed at a rate different from the rate of 20% is determined by the taxpayer separately. Accounting for income (expenses) for transactions for which, in accordance with Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a different procedure for accounting for profit and loss is provided for, is carried out separately by the taxpayer.
Therefore, the tax base to which the 0% rate applies is determined separately.
If the purchase price of the specified shares, shares in the authorized capital, taking into account expenses associated with the sale, exceeds the proceeds from their sale, the difference between these values is recognized as a loss, which is not taken into account for tax purposes. The provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation on the transfer of losses do not apply to losses received by the taxpayer from the sale or other disposal of shares, participation interests in the authorized capital of Russian organizations, bonds, shares specified in Articles 284.2, 284.2.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 1 of Article 283 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) .
The use by the taxpayer in the situation under consideration of the general procedure for calculating the tax base will mean committing a tax offense in the form of non-payment (incomplete payment) of tax (Article 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This circumstance should be taken into account when planning the date of sale.
It turns out that the abolition of the limitation on the period for acquiring shares may not be beneficial for taxpayers selling shares acquired long ago?
Please note that the procedure for taxation of income from the sale of shares and shares specified in subparagraph 1, paragraph 1 of Article 284.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation acquired before 2011 has changed during the tax period of 2022.
Income received during the period 11/28/2018-12/31/2018 from the sale of shares (stakes) acquired before 2011 falls into the tax base, to which a 0% rate is applied. If a loss is received from the sale for tax purposes, it “disappears.” This circumstance changes the tax regime during the tax period not to the better for the taxpayer. This may lead to disputes, the subject of which will be the admissibility of the taxpayer in such a situation applying the general norms of paragraph 1 of Article 5 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation on the procedure for the entry into force of acts of legislation on taxes and fees.
What are the changes regarding the submission by tax agents of personal income tax to the tax authorities of information on paid income?
The tax agent submits to the tax authority at the place of its registration documents containing information about the income of individuals of the expired tax period and the amounts calculated, withheld and transferred to the budget system for this tax period of personal income tax (clause 2 of Article 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Starting with reporting for 2022, such information is presented using a new form approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service dated October 2, 2018 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected]
The main change is that two certificates are provided: one for submission to the tax authorities (form 2 - personal income tax), the second for issuance to individuals upon their applications. Form 2-NDFL consists of a main sheet and an appendix. The application displays information about income and deductions broken down by month.
When drawing up certificates in form 2-NDFL, the codes of types of income and deductions given in the Federal Tax Service order dated September 10, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected]
Certificates are issued for each individual.
There are no longer any lines for indicating the place of residence of an individual. The TIN of an individual is still an optional detail in the certificate.
If there is paid income taxed at different rates (sections 1, 2, 3 of the main sheet), certificates and an application are filled out for each of the rates.
How are income information reported?
The deadline for submission is annually no later than April 1 of the year following the previous one. For 2022, the deadline for submitting information is April 1, 2022.
The procedure for submitting information on the income of individuals to the tax authorities is approved by the same order as the information form.
What to pay attention to when submitting reports to the tax authorities?
If the number of individuals who received taxable income during the tax period is 24 people or less, the tax agent may, in relation to these individuals, submit certificates in Form 2-NDFL on paper in person, through a representative, or send by mail with a list of the contents.
In electronic form, the reporting provided for by Chapter 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (2-NDFL and 6 - NDFL) is submitted by tax agents exclusively according to the TKS. Electronic media (CDs, DVDs, flash memory devices) are not used.
Does successful submission of information indicate its acceptance by the tax authority?
For each method of submitting information (directly, by post, via TKS) its own date is determined, which records the moment of submission.
In this case, information that has passed the filling control (format control) is considered submitted.
The fact of submission of information is confirmed by the Protocol of receipt of certificates.
Within 10 working days from the date of sending the information, the tax authority must send to the tax agent the Register of certificates of income and tax amounts of individuals for the corresponding year in electronic form, a protocol for receiving certificates of income and tax amounts of individuals, which may contain information about errors.
Therefore, when information is not submitted in person, it is advisable to send it in advance, in particular, certificates 2-NDFL before March 17. The time allowance will allow the tax agent to clarify the information if necessary.
In case of clarification, only the information that has been corrected is submitted to the tax authority. If, when submitting information in the reception protocol, information containing errors is identified, then only the corrected (corrected) information is sent again. The entire file is not presented again.
If the tax agent was unable to fully withhold the tax amount for the tax period. What information is provided in this case?
The tax agent informs the taxpayer and the tax authority at the place of his registration in writing about the impossibility of withholding the calculated amount of personal income tax.
The impossibility of withholding the amount of personal income tax based on the results of 2022 must be reported no later than March 1, 2022 (clause 5 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The letter of the Ministry of Finance dated December 29, 2011 No. 03-04-06/6-363 concluded that fulfilling the obligation to report the impossibility of withholding tax and the amount of tax does not relieve the tax agent from the obligation to provide information on the income of individuals of the expired tax period and the amounts accrued taxes withheld and transferred to the budget. The Federal Tax Service takes a similar position (letter dated March 30, 2016 No. BS-4-11/5443).
Since we are talking about fulfilling two obligations: to report the impossibility of withholding and to report the income of an individual, it is advisable to send the relevant certificates to the tax authority twice in Form 2-NDFL.
Thus, you need to submit to the tax authority: - a certificate for 2018 with the sign “2” before March 2, 2022, - a certificate for 2022 with the sign “1” before April 2, 2022.
The 2-NDFL certificate with sign “1” indicates the amounts including income and the calculated amount of tax, as well as the amounts of tax not withheld by the tax agent, which were previously reflected in the certificate with sign “2” (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated October 27, 2011 No. 03 -04-06/8-290).
At the same time, the liability for failure to submit a certificate under Article 126 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation can be avoided if the submitted 2-NDFL certificate with attribute “2” contained all the necessary information to be indicated in the 2-NDFL certificate with attribute “1” (resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District dated 09.24.2013 No. F09-9209/13).
After sending a message about the impossibility of withholding, the tax agent does not withhold the amount of tax debt from income paid in the next tax period.
If it is impossible for a tax agent to withhold tax on income paid in 2022, an individual pays tax based on a notification from the tax authority no later than December 1, 2019 (clause 6 of Article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
What are the features of presenting information on the income of individuals from transactions with securities?
Persons specified in Article 226.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (brokers, depositories, trustees), when carrying out transactions with securities, transactions with derivative financial instruments, when making payments on securities of Russian issuers (coupons, dividends on shares) provide information on income on form approved by order of the Federal Tax Service dated October 19, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected]
Such information is submitted as Appendix No. 2 to the tax return for corporate income tax only for the tax period. For 2022 - no later than March 28, 2022. 2-NDFL certificates for relevant income are not submitted.
Separate certificates are drawn up for each individual individual. Moreover, in contrast to the certificate in form 2-NDFL, separate certificates are drawn up for an individual’s income from securities and derivative financial instruments, taxed at different rates.
Despite the fact that the information is presented in a form that is an appendix to the tax return, liability associated with its failure to submit arises on the basis of Article 126 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which deals with the document, and not the declaration.
If, at the end of 2022, it turned out to be impossible to withhold personal income tax on transactions with securities, tax agents must report this to the tax authorities by March 1, 2019 using Form 2-Personal Income Tax (clause 14 of Article 226.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 2 of the Federal Tax Service order dated 10/02/2018 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected] ).
Information on dividends paid that are not related to dividends on shares of Russian organizations is presented in Form 2-NDFL in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated January 29, 2015 No. 03-04-07/3263).
When must a tax agent provide the taxpayer with a certificate of income received and personal income tax amounts withheld?
In accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax agents issue certificates of income received and tax amounts withheld to individuals upon their applications.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not establish the deadline for issuing such a certificate, as well as the responsibility of the tax agent for the failure to issue (untimely issue) the certificate.
In accordance with Article 62 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, upon a written application from an employee, the employer is obliged to provide the employee with copies of documents related to work, which may include certificates of income received. In other words, the certificate must be issued no later than three working days from the date the employee submits the application.
According to Article 20 of the Federal Law of July 27, 2006 No. 152-FZ “On Personal Data,” the operator, which is also the organization that organizes and (or) carries out the processing of personal data of an individual, is obliged to provide the opportunity to familiarize himself with personal data when contacting the subject of personal data. data or his representative or within thirty days from the date of receipt of the request of the personal data subject or his representative. If we are talking about issuing a certificate of income received at the request of an individual - a party to a civil contract, then the tax agent as an operator of personal data should proceed from the fact that the period for issuing the certificate should not exceed 30 days.
In what form does a tax agent issue a certificate of income to an individual?
A separate form has been approved for a certificate issued to individuals about income received and tax withheld (Appendix No. 5 to the Federal Tax Service order No. ММВ-7-11 dated October 2, 2018 / [email protected] ).
A certificate in form 2-NDFL, submitted to the tax authority, and a certificate of income and tax amounts of an individual, issued to an individual, are different certificates.
In this regard, the tax agent is recommended to include in the income certificate issued to an individual, including information on income received by the individual from transactions with securities (if any).
The liability of a tax agent for failure to comply with the form of a certificate of income received and withheld tax amounts issued to individuals is not established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
But if a certificate is necessary for an individual to submit to the tax authorities, then it is better to use the certificate form approved by the Federal Tax Service.
reporting
Send
Stammer
Tweet
Share
Share
What methods exist for accounting for sales income?
The method of accounting for income (and expenses) is the first thing an income tax payer needs to decide on. There are 2 such methods:
- accrual method - in this case, income is taken into account when calculating tax in the period in which it actually occurred (the taxpayer received the right to it), regardless of the payment period (Article 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
Read about the application of this method in accounting in the material “What is the essence and features of the accrual method in accounting .
- The cash method is the so-called “on payment” method, when income increases the base at the time of receipt of money or repayment of debt in another way (Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Read more about it in the article “What is the procedure (conditions) for recognizing income and expenses using the cash method?” .
When choosing a method, keep in mind that the first can be used by all taxpayers, and the scope of the second is limited.
Read more about this in the material “Accrual method and cash method: main differences” .
Please note: income should be assessed from all receipts associated with sales, including income received in non-monetary (in kind) form (clause 2 of Article 249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
ConsultantPlus experts have prepared step-by-step instructions for determining the amount of income from sales in tax accounting:
If you do not have access to the system, get a trial online access to K+ for free.
What is sales income
Reflection of income from sales in accounting and tax accounting is carried out according to similar principles.
From the point of view of Chapter 25 of the Tax Code, sales income is recognized as proceeds from the sale of goods, works, and services, both self-produced and previously purchased. Revenue from the sale of property rights is taken into account in a similar way (Article 249 of the Tax Code).
In turn, proceeds from the sale of goods, works or services are receipts in payment for these goods, works or services, and these calculations can be expressed both in cash and in kind. The latter is relevant for cases when a company closes a transaction with a barter transaction, that is, in payment, for example, for the sale of its own goods, it accepts the provision of reciprocal services from the same counterparty. In this situation, despite the absence of actual monetary payment for goods, their value, “covered” by the buyer’s services, will be recognized as income from their sale.
The date of receipt of income from sales from the point of view of income tax can be determined in two ways: by the accrual method and by the cash method. In the first case, the dominant role is given to the moment of transfer of goods to the client, the execution of work or the fact of provision of services. There may still be no payment from the buyer, but the company is already required to take into account income from sales for the purposes of calculating income tax. With the cash method, income is determined, just the opposite, by the date of receipt of funds from the counterparty.
When applying the simplified tax system, income from sales is included in the tax base also on a cash basis, that is, on the date of receipt of actual payment from the client (Article 346.17 of the Tax Code).
What is not included in sales income?
First of all, these are incomes that are not taken into account for taxation due to the direct instructions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Among the most common:
- the amount of prepayment received for goods and services, property rights (for taxpayers recognizing income and expenses using the accrual method);
- amount of the deposit or deposit (also using the accrual method);
- contributions to the authorized capital;
- receipts under intermediary agreements (commission, agency agreement, etc.), except for the amounts of the intermediary’s remuneration, which, as a rule, is revenue, i.e. basic income;
- borrowed funds received (credits, loans), etc.
For more information about non-accounted income and issues related to them, read the article “List of income not taken into account when establishing the profit base in accordance with Art. 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation."
Also, non-operating income is not included in revenue. These are side incomes that accompany the main activity. Their list is contained in Art. 250 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. At the same time, when classifying income in accounting, it is necessary to keep in mind the type and specifics of the business. For example, income from leasing property can be both non-operating income (clause 4 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and revenue from sales (if leasing is the direct business of the company).
Read more about non-operating income in the material “How to take into account non-operating income when calculating income tax?” .
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Income from sales in accounting
In accounting, sales income is income from ordinary activities. The definition of such income is given in PBU 9/99: income from ordinary activities is revenue from the sale of products and goods, income related to the performance of work and the provision of services. This concept is inextricably linked with the type of business that the company carries out, and is often associated with the OKVED codes declared in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. Additional income that does not relate to ordinary activities is identified from an accounting point of view as other income. Therefore, income from sales in tax and accounting may still vary slightly. For example, if the transfer for temporary use of a company’s own property is its officially registered type of activity, then income from the sale of such services will be income from ordinary activities in accounting. If this type of activity is not declared, then such income will fall into other income, but from the point of view of tax accounting, it will still remain income from sales.
It should also be noted that in accounting, income from ordinary types of activities, as well as other types of income, are determined using the conditional accrual method, that is, they are taken into account on the date of issuing primary accounting documents to the client for the transfer of goods, provision of services or performance of work.
Accordingly, advances received from counterparties on account of upcoming deliveries are not considered income in accounting and when using the accrual method to determine income tax. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
REVENUE PLANNING METHODS
The total amount of revenue from core activities includes revenue from the sale of products, works and services of an industrial and non-industrial nature.
To determine revenue from product sales, you need to know the volume of product sales in current prices without VAT, excise taxes, trade and sales discounts and export tariffs for exported products.
There are two methods for determining planned revenue:
- direct counting method;
- calculation method.
Direct counting method
This method is based on guaranteed demand . It is based on the fact that the entire volume of manufactured products is calculated on a pre-issued package of orders for the coming financial year (based on contracts and requests from customers).
This method of revenue planning is the most reliable , since the production plan and sales volume are linked in advance to consumer demand, the required assortment and production structure are known, and appropriate prices are set. Here, the level of development of the product range by type, brand, grade, coordination with customers of their volume and prices for the planned period is of great importance.
The essence of the method : for each type of product, the volume of sales is calculated in selling prices, and then the results are added up. In this case, sales revenue ( B ) can be determined using the following formula:
B = P × C,
where P is the volume of comparable products sold;
P is the price of a unit of products sold.
Calculation method
The calculation method is used in conditions of uncertainty of demand for the products produced by the enterprise. The basis of the method is the volume of products sold, adjusted for input and output balances.
When using the calculation method, the planned amount of sales revenue is determined based on the amount of expected balances of unsold products at the beginning and end of the planning period, as well as from the amount of the forecasted output of marketable products in the planning period.
Since in a given period the produced marketable products are not fully sold, when planning sales revenue, the volumes of carryover balances at the beginning and end of the planning period are taken into account, as a result of which the planned sales volume is determined using the following formula:
Vpl = He + TP – Ok,
where Vpl is the planned revenue from product sales;
It is the carryover balance at the beginning of the period;
TP - commercial products;
Ok - carryover balances at the end of the period.
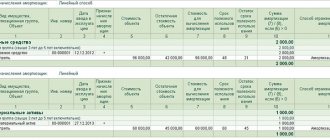
Let's calculate the revenue from product sales (Table 1).
An important point: the calculation of the planned revenue depends on the method of its accounting.
Determining the planned amount of revenue using the shipping method and the cash method
When planning shipment revenue, only finished products in the warehouse at the beginning and end of the planned period are considered unsold. The amount of revenue from sales of products using the shipment method in planned financial calculations can be determined using the following formula:
Vpl = Tpl + O1 + O2,
where Vpl is the planned value of sales revenue;
Tpl - the value of the forecasted output of marketable products in the planning period;
O1 - change in the balances of finished products in the warehouse at the end of the planning period compared to the beginning in selling prices;
O2 - change in the balances of goods shipped at the end of the planning period compared to the beginning in selling prices.
If we consider the cash method of revenue planning, the expected balances of unsold products at the beginning of the planning period consist of:
- finished products in warehouse;
- goods shipped for which payment was not due;
- goods shipped but not paid for on time by buyers;
- goods held in safe custody by buyers.
The balance of unsold products at the end of the planning period takes into account:
- finished products in warehouse;
- shipped goods for which payment is not due.
When planning balances of finished products at the beginning of the planning period, the enterprise does not have comprehensive data on the actual amount of balances, therefore, the expected balances of unsold products are taken into account.
The cost of balances is calculated using a conversion factor, which is the quotient of dividing the volume of production in prices of the reporting period by the production cost of production for this period.
NOTE
Sales prices in the planning period are determined based on the prices of the base period, which are adjusted for expected changes in the planning period, including taking into account supply and demand.