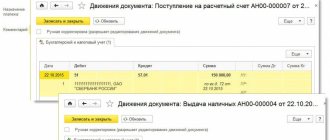
Account correspondence 44
Active account 44: entries are made with an increase in debit and a decrease in credit, subject to closure at the end of the reporting period through a routine operation by allocating costs to the base indicator. Before we figure out how to close account 44, let’s list the main subaccounts:
- Account 44.01 - is intended to formulate the value of distribution costs in trading companies.
- Account 44.02 - is used to collect data on commercial expenses for sales in manufacturing/industrial enterprises.
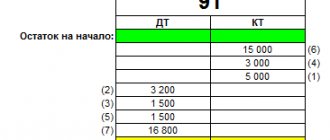
By debit account 44 reflects the organization's expenses for the reporting period in correspondence with accounts - 02, 04, 05, 10, 23, 29, 16, 19, , 68.71, 69, 70, 76, , 97, 96, etc. For the loan account. 44, full or partial closure of account 44 is carried out with postings to the income accounts of the enterprise - , 99.
Commercial expenses in UE
establishing the procedure for accounting for commercial expenses
– what will relate to such costs:
How does accounting take into account the costs of delivering goods to the buyer?
The costs of delivering goods to the buyer are included in distribution costs and are expenses of the current period:
- document Receipt (act, invoice, UPD) type of operation Services – Cost item of the type other expenses
Costs will be fully written off on Dt 90.07 at the end of the month.
The company produces products and delivers them to wholesale buyers. Products are accounted for in several product groups and produced by different divisions. Which document and on which account should be used to correctly reflect the costs of delivering products so that the costs increase the cost of production? Products from different product groups are delivered at the same time.
Delivery of finished products cannot be included in the actual cost of production (clause 26 of FSBU 5/2019). Delivery costs should be charged to account 44 “Sales expenses”.
How to close account 44 - postings
Monthly closure of 44 accounts (entries can be generated manually or through a routine operation) differs depending on the type of activity of the organization. In this case, the zeroing of cost costs occurs for all types of expenses, with the exception of some, distributed as follows:
- In trade and intermediary firms, transport costs are distributed among inventory balances according to the total sales volume and warehouse balances at the end of the period.
- In production and industry, transport costs and packaging costs are subject to distribution between individual product types of sold products, taking into account weight, volume, cost and other factors.
- Agricultural producers use accounts 15 and/or 11 to distribute procurement costs.
Definition
In those companies where production and industrial activities are carried out, this account may include expenses such as:
- Containing, as well as packaging in those warehouses where finished products are stored.
- Costs for delivering products to the point of departure, loading goods into wagons, cars or any other vehicles.
- Commission payments that were made in the sales process or to any other companies that are intermediaries.
- Payment for the maintenance of the premises where the goods are sold.
- Remuneration of workers involved in the sale of goods.
- Expenses incurred in advertising a product.
- Entertainment expenses.
- Other similar costs.
In those organizations that are primarily engaged in trading activities, the following distribution costs may be reflected in the account:
- when transporting cargo;
- for wages;
- if there is a lease;
- maintenance of various premises, buildings, as well as work equipment;
- during storage of products;
- for product advertising;
- other costs of this type.
If the organization’s activities are related to the agricultural industry (for example, poultry, vegetables, cotton, livestock, etc.), then the following data will be reflected in the account:
- other expenses;
- during general procurement work;
- to receiving and procurement points;
- at reception centers for livestock and poultry.
Account 44 accumulates costs associated with the organization’s work, namely the sale of work, goods and services. They must be written off partially or completely. In the event that amounts are partially written off, the following is subject to distribution:
- If we are talking about companies engaged in industrial or other activities, the costs that go towards transportation or packaging.
- When it comes to organizations engaged in trade or other intermediary activities - costs that relate to the transportation of goods.
- If it concerns agricultural activities, the distribution goes according to accounts 11 and 15.
As for all other expenses, one way or another related to the products, they are charged every month to the cost of products that have already been sold.
Analytical accounting for account 44 is carried out by items and types of costs.
Correspondence on this account is carried out with a decrease in credit and an increase in debit, and is closed at the end of the month using a routine operation due to the distribution of salaries to the base indicator. Therefore, before moving on to closing this account, you need to familiarize yourself with the main sub-accounts:
- Subaccount 01 was created specifically so that trading companies can generate the amount of distribution costs.
- Subaccount 02, in turn, is used primarily in industrial and manufacturing enterprises in order to collect the necessary information on business costs.
If we talk about the debit of this account, then along with it in correspondence for the past month such accounts as 02, 04, 10, 29, 19, 60, 70, are reflected. As for loans, partial or complete closure is performed here with postings to such organization accounts as 99 and 90.
Account 44 in accounting: closing
The debit accumulates the amounts of expenses incurred by the enterprise in connection with the sale of work, goods, and services. They are subject to full or partial write-off in the DB account. 90. In the latter case, the following are subject to distribution:
- At enterprises that conduct industrial and other production activities, the costs of transportation and packaging. Costs are distributed between individual categories of shipped goods every month in accordance with weight, volume, cost or other indicators.
- For enterprises engaged in trading or intermediary activities, transportation costs. The distribution of expenses is carried out between the goods sold and the remaining goods on the last date of each month.
- At enterprises processing and procuring agricultural products - in DB account. 15, reflecting the amount of costs for the acquisition and procurement of material assets, or account. 11, summarizing information about the costs of procuring poultry and livestock.
Other expenses that are reflected in account 44 in accounting are also subject to write-off. Closing in other, not specified cases, is carried out by transferring amounts to the cost of products, works, and services sold.
Characteristics of account 44 (active or passive, debit/credit, reflected in the balance sheet, etc.)
As you can see, many characteristics of account 44 depend on industry affiliation.
Count 44 - active or passive? Of course, active - it is located in section IV of the Chart of Accounts “Finished products and goods”. This means that the debit account is for the accumulation of expenses related to sales, and the credit account is for the monthly write-off of costs, partially or completely.
The accounting policy must indicate the methods of write-off and indicators for the distribution of commercial expenses.
In case of partial write-off, the following should be distributed monthly:
| Industry | Composition of distribution costs | Distribution indicators |
| Industrial production | Packaging and transportation costs | Between individual types of shipped products based on weight, volume, production cost and other indicators |
| Trade | Transportation costs | Between goods sold and balance at the end of the month |
| Procurement and processing of agricultural products | To the debit of account 15 - expenses for the procurement of agricultural raw materials and/or to the debit of account 11 - expenses for the procurement of livestock and poultry |
All other sales expenses are written off in full on a monthly basis to the cost of sales in Dt 90.
The debit balance on account 44 represents the balance of packaging and transportation costs related to goods/products unsold for the period, and is included as work in progress in line 1210 “Inventories” of the balance sheet.
The amount of business expenses written off for the period is reflected in line 2210 “Business expenses” of the income statement.
Account 44 in accounting: postings
At the end of the month, costs may remain for transport services provided by intermediaries. After they are assigned to account 44, no entries are made in accounting. These expenses remain and are carried forward to the next month. The account in question corresponds with the articles:
By debit:
- Depreciation of fixed assets (account 02).
- Settlements with various creditors/debtors (account 76).
- Intangible assets (account 04).
- Depreciation of intangible assets (account 05).
- Materials (count 10).
- Settlements with accountable persons (account 71).
- Deviations in the standard of material assets (count 16).
- Auxiliary proceedings (account 23).
- Settlements with employees regarding wages (account 70).
- VAT on purchased objects (account 19).
- Service farms and industries (account 29).
- Payments for fees/taxes (account 68).
- Goods (count 41).
- Settlements for social security and insurance (account 69).
- Trade margin (account 42).
- Finished products (account 43).
- Settlements with contractors/suppliers (account 60).
- Shortages and losses from damage to valuables (count 94).
- Reserves for future expenses (account 96).
- On-farm settlements (account 79).
- Future expenses (account 97).
By loan:
- Materials.
- Animals for fattening and growing (count 11).
- Acquisition and procurement of material assets (account 15).
- On-farm settlements.
- Shipped goods (account 45).
- Settlements with different creditors/debtors.
- Sales
- Losses and shortages from damage to valuables.
- Losses and profits (account 99).
As you can see, there are quite a lot of corresponding articles. In general, we can say that account 44 is considered universal in accounting. It has been around for a long time and is used by most businesses.
Account characteristics
In order to correctly make entries, you need to know exactly: is account 44 in accounting active or passive? The account is active, synthetic and collective. The latter means that the balance at the end of the period is written off to another account. For the entire month, the debit of account 44 records the enterprise's expenses for the sale of goods, which are reflected in the financial result accounts.
The debit balance in the balance sheet (item “Work in progress”) is indicated only if goods were not fully sold during the reporting period.
Reflection of expense write-offs
Expenses incurred in trade organizations are divided into indirect and direct. The latter includes the cost of purchased products (which is indicated in 41 invoices) and the costs that go towards transportation (such amounts are indicated in 44 invoices). As for other costs that the company incurred during the current period, they can be classified as indirect.
You can learn how distribution of sales expenses works in this video.
about the author
Grigory Znayko Journalist, entrepreneur. I run my own business and know first-hand the problems and difficulties that individual entrepreneurs and LLCs face.